Pathologies of the sigmoid colon have different symptoms; they are always determined by the severity and neglect of a particular disease diagnosed by a doctor. Diseases of the sigmoid colon almost always reduce the patient’s quality of life and often require its removal. Therefore, resection of the sigmoid colon is a fairly common procedure in modern medicine. It is believed that diseases of any part of the intestine with certain disorders can even lead to death. Thus, resection of the sigmoid colon is performed with the same frequency as removal of other parts of the intestine.
Location of the sigmoid colon
If we turn to anatomy, this part of the large intestine is a bending area, usually on the left side. In front of it is the descending colon, and after it the rectum. This section of the large intestine is actively involved in digestion. It is here that a significant amount of liquid is absorbed and feces harden at a certain stage of digestion. Currently, various intestinal diseases are known.
Causes of inflammation
Externally, the sigmoid colon is very similar to the Latin letter sigma, its length depends on the person’s physique, sometimes it can reach 60 centimeters. This section of the intestine helps digest food, absorbs water and saturates the body with it, and the final formation of feces occurs in it. The peculiar shape of the section delays the movement of processed food through it, as a result it becomes denser and enters the rectum.
Hemorrhoids are one of the main factors that can cause the disease.
The causes of sigmoiditis can be very different. Inflammation can develop due to stagnation of feces in it, which is facilitated by its curvature, as a result of infection, damage to the mucous membrane by hard feces or indigestible food particles, etc. The main factors that can cause the disease include the following:
- circulatory disorders in the pelvic area, varicose veins, thrombosis, hemorrhoids;
- diseases of the rectum - anal fissures, proctitis, paraproctitis, Crohn's disease;
- colibacillary infection, dysentery, dysbacteriosis;
- nutritional disorders, lack of fiber-rich foods in the diet;
- a sedentary lifestyle, sitting for a long time (this provokes congestion in the pelvis);
- regular constipation, deterioration of intestinal motility, which developed against the background of other diseases of the digestive system (duodenitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, enzyme deficiency, cholelithiasis, food allergies, pancreatitis);
- pathologies of the prostate gland, chronic gynecological diseases;
- increased pressure on the intestine of the uterus during pregnancy;
- some surgeries and abdominal injuries.
Complications and prognosis
Usually, with appropriate treatment and proper nutrition, the prognosis is favorable and the patient recovers completely.
In case of incorrect or untimely therapy, the following complications may develop:
- peritonitis (inflammatory process occurring in the abdominal cavity);
- proctitis (inflammation of the rectum);
- polyarthritis;
- eye diseases;
- erythema;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, kidneys, liver, gall bladder.
The inflammatory process can spread to other intestinal parts, as well as provoke adhesive disease.
Due to stagnation of feces, diverticulitis is considered a dangerous consequence..
If untimely treatment of diseases that complicate sigmoiditis can even result in death.
Types of sigmoiditis
As mentioned earlier, inflammation of the sigmoid colon can be acute or chronic.
- The acute form is accompanied by pronounced clinical manifestations. It develops soon after exposure to a traumatic factor, for example, an intestinal infection.
- The chronic form has less pronounced symptoms and often occurs due to dysbacteriosis.
The disease is also divided depending on the nature of the damage. Sigmoiditis happens:
- catarrhal - the mildest form of the disease, in which inflammation covers only the upper layer of epithelial tissue;
- erosive - usually develops as a result of untreated catarrhal sigmoiditis, when it forms erosions on the mucous membrane that can bleed;
- ulcerative is the most severe form of the disease, which is characterized by the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane; either one ulcer or several foci of different depths and localization can occur. Often develops with ineffective treatment of erosive sigmoiditis.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
The clinical manifestations of the disease largely depend on the exact form in which the disease occurs.
Symptoms of sigmoiditis, which occurs in acute form, are as follows:
- intense pain localized to the left in the iliac region;
- spasmodic pain radiating to the left leg and lower back;
- bloating;
- frequent loose stools that have an unpleasant odor, and in some types of disease may be mixed with blood and pus;
- signs of intoxication (pale skin, weakness), fever;
- nausea, vomiting.
The chronic form of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- feeling of rubbing in the abdominal area;
- pain that occurs during bowel movements;
An inflammatory process of this nature leads to deterioration in the digestion and absorption of food. Because of this, with a long course of the disease, a person may begin to lose weight and experience a lack of certain substances. Long-term presence of feces in the sigmoid region can cause allergic reactions on the skin and poisoning of the body. Chronic sigmoiditis, as a rule, occurs with periods of remission, during which unpleasant symptoms subside. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the disease usually worsens. This can lead to:
- diet violation;
- physical stress;
- stress;
- acute infectious diseases;
- injuries.
Is there always a need for hemorrhoid surgery?
What is a colonoscopy and how is it performed? Read more in this article.
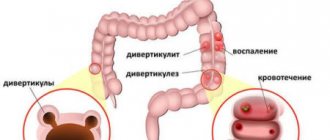
Organ diverticulosis
The disease is more common in old age. Sac-like protrusions (diverticula) form on the walls of the intestine. Alarming symptoms do not appear for a long time. In the later stages, pain in the iliac region and stool disturbances appear. The occurrence of diverticulosis is promoted by:
- weakening of the muscles of the intestinal wall, which is typical for elderly patients;
- cavities on the surface of the intestine, in which increased intraintestinal pressure can be created;
- underdeveloped connective tissue;
- insufficient consumption of fiber, which promotes the elimination of food;
- disturbance of microcirculation as a result of compression of blood vessels;
- genetic predisposition.
As a result of stagnation of feces, diverticula become inflamed (diverticulitis). Complications are indicated by constant pain and fever. If the inflammatory process spreads to the tissue surrounding the diverticulum, peritonitis may occur.
For diagnosis, X-ray examination with a contrast agent, ultrasound, and irrigoscopy are used.
In cases where patients do not experience significant clinical manifestations, a special diet that includes foods containing fiber is recommended. For severe symptoms, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Antibiotics are used to treat diverticulitis. The patient should be prepared for long-term drug therapy. Usually it gives a lasting effect. With frequent exacerbations of diverticulosis and the formation of fistulas, surgical intervention is recommended. Perforation of the diverticulum threatens the patient's life, so the affected area of the sigmoid colon is urgently removed.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosing sigmoiditis is not always easy. The disease is often confused with acute appendicitis. After collecting anamnesis, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the abdomen and palpates it. An experienced specialist will be able to determine the localization of the source of inflammation and thereby determine which part of the colon is affected.
To establish the nature and severity of the disease, a stool and blood test is required. In addition, instrumental studies are provided:
Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity may be recommended.
An abdominal ultrasound may be recommended for diagnosis.
It is very important during diagnosis to determine the cause of the disease, since the success of future treatment may depend on this. If there is an erroneous diagnosis or untimely contact with a doctor, the sigmoid colon will not be able to work properly. The inflammatory process will begin to increase, which can lead to serious consequences - fusion of the intestine with neighboring organs, perforation with the occurrence of peritonitis.
Preventive actions
The sigmoid colon is a vulnerable organ, as food and lifestyle have a significant impact on it. But you can prevent the appearance or worsening of the pathology. To do this, it is important to know what precautions will help avoid serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. First of all, it should be borne in mind that if you have bad habits, it is extremely difficult to avoid diseases, so it is better to get rid of bad habits. It is also recommended to start playing sports, this will not only help avoid the development of a pathological process, but will also strengthen the entire body.
It is worth reviewing your diet, stopping snacking on the go, as well as eating unhealthy foods. It is better to avoid overeating and replace unhealthy foods with fruits and vegetables. An important factor is to drink as much water as possible, since with sufficient fluid intake, the likelihood of constipation, which has a detrimental effect on the sigmoid colon, is significantly lower.
You should not neglect going to the doctor if you have seemingly minor symptoms or pain, as they are sometimes the first warning signs. Even with minor signs, action will be required, so it is important to know how pathology can manifest itself. If there are no symptoms of disease development, you should visit a gastroenterologist at least once a year for prevention. This will not only avoid serious illnesses, but will also help keep the body in great shape.
Despite the fact that the development of diseases in the sigmoid colon is a complex and dangerous process for the body, you can try to avoid inflammation. If the disease is already in the development stage, then with proper therapy you will be able to recover and live a full life. The main principle of treatment is the desire to be cured. The main thing is not to try to recover without the help of a doctor. Without knowing the true cause of the disease, without an accurate treatment plan, you risk harming the body even more. And with careful attention to your health, almost every case, regardless of the degree of development of the disease, has a positive outcome.
Features of treatment
Treatment of sigmoiditis is a difficult, lengthy process that requires the patient to strictly follow the recommendations. Treatment of inflammation of the sigmoid colon is carried out using a special diet and medications.
Nutrition and diet
In case of acute inflammation of the sigmoid colon, gentle nutrition is prescribed, which eliminates irritation of the mucous membrane, helps eliminate inflammatory processes and allows for normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The diet for sigmoiditis significantly limits the consumption of carbohydrates and fats. Thanks to this, processes that cause fermentation and putrefactive phenomena are inhibited, peristalsis is improved, and a sufficient amount of gastric juice is released for good digestion of food. It is recommended to adhere to it for at least a week, during which time the functioning of the digestive tract, as a rule, normalizes. During the diet, foods should be consumed in small quantities, but often. It is advisable to increase the number of meals to 6 per day, and you should try to eat at the same time. All dishes are served pureed, pureed and liquid.
Excluded from the menu:
- fresh bread and flour products;
- fatty, stringy meat, sausages;
- milk soups, strong meat broths;
- fish, fatty varieties, canned food;
- fresh fruits, herbs, berries, vegetables;
- whole milk, fresh and fatty fermented milk products;
- all sweets;
- coffee, kvass, alcohol, carbonated drinks;
- smoked meats, pickles, marinades, seasonings, spices, fried.
During treatment you must stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
The diet is recommended to consist of the following products:
- lean poultry, fish and meat, only pureed, steamed cutlets, meatballs, meat soufflés, purees;
- stale white bread;
- slimy pureed soups cooked in weak broth;
- soft-boiled eggs, steam omelettes;
- pureed porridges from oatmeal, rice, buckwheat, cooked in water;
- low-fat non-acidic cottage cheese, curd soufflé;
- green tea, infusions of bird cherry, blueberry, currant, rose hip, pear jelly, quince, blueberry, currant;
- pureed apples in limited quantities.
In case of severe exacerbation, accompanied by intense pain and diarrhea, you should completely stop eating for a couple of days. During this period, you need to drink more water, infusions, and weak black tea. After finishing the diet, it is contraindicated to immediately switch to your usual diet or eat fatty, poorly digestible and high-calorie foods. Introduce foods to the menu gradually and at the same time monitor the body’s reaction to them.
Drug treatment
During the acute period, the patient is advised to remain in bed. The main therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes of sigmoiditis, inflammatory processes and symptoms of the disease. Drug treatment of inflammation of the sigmoid colon is usually carried out using the following means:
Nutrition for illness and menu
With sigmoiditis, it is important to maintain proper nutrition. Diet No. 4 is usually used.
It consists of excluding the following foods from the diet:
- herbs and spices;
- smoked meats;
- alcoholic drinks;
- fried food;
- carbonated drinks.
It is necessary to reduce salt intake. The amount of carbohydrates and fats consumed should also be kept to a minimum.
After some time, you can include fermented milk products in the menu.
If a patient has constipation, then it is necessary to consume foods containing fiber in large quantities:
- beets;
- dried apricots;
- pumpkin;
- carrot;
- bran.
It is better to establish fractional nutrition - take food in small portions, but increase the frequency of intake to eight times.
It is advisable to eat steamed, oven-baked or boiled food. The patient is recommended to eat pureed dishes.
In case of acute sigmoiditis, it is recommended to fast for several days.
Forecast
With proper treatment, inflammation of the sigmoid colon usually goes away and leaves no consequences. But in order to achieve such a result, the patient should be prepared for the fact that the therapeutic course will take a lot of time (usually 1-2 months) and will be accompanied by significant dietary restrictions.
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon is a disease that rarely occurs on its own and in most cases has concomitant diseases. This inflammation is also called sigmoiditis, from the Latin words “sigma” - a letter of the alphabet (this part of the intestine is similar to it) and the suffix “itis”, which means inflammation.
Where is the sigmoid colon located?
Sigmoiditis occurs more often in women, as well as in older people. We will now figure out where the inflamed area of the intestine is located and how it hurts.
Polyps
Polyps are formed from glandular epithelium. Their formation is promoted by inflammation of the mucous membrane, hereditary factors, chronic inflammatory diseases, and viral infections. Typically, neoplasms do not manifest themselves. With large growths, patients complain of pain in the left lower abdomen and upset stool. In rare cases, polyps provoke bleeding and intestinal obstruction.
Villous polyps are considered the most dangerous. In approximately 40% of cases, malignant tumors form from them.
Pathological growths can be detected by colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. During the examination, polyps are removed. Small formations are cauterized with a coagulating instrument. If cancer cells are detected, the growth is removed along with a section of the intestine. Relapses of the disease are rare. But, strictly follow your doctor's recommendations. After a polypectomy, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations. It is recommended to limit the consumption of fatty and fried foods, as they contribute to the formation of polyps. It is advisable to eat more seafood, fresh fruits and vegetables.
Types of sigmoiditis
The sigmoid colon is the terminal part of the colon, followed by the rectum. It is located on the left in the iliac region.
Inflammation can occur in different ways and depending on this, the following types of sigmoiditis are distinguished:
- Catarrhal sigmoiditis is the mildest, since in this case only the upper mucous layer of the intestine is affected.
- Erosive is more severe, because in this case the lesion covers the deep layers of the intestine and leads to bleeding.
- The ulcerative form or purulent-hemorrhagic is characterized by the presence of ulcerations of the sigmoid colon (there may be one ulcer, or there may be several of them). It is often a consequence of untreated erosive sigmoiditis.
- Perisigmoiditis is characterized by inflammation of the mesentery, as well as the serous membrane of the intestine, which leads to the appearance of adhesions between the intestinal loops.
Depending on how long the disease lasts, chronic and acute sigmoiditis are distinguished.
They will differ from each other in the symptoms of the disease, as well as the factor that provoked them.
One of the main causes of constipation and diarrhea is the use of various medications.
.
To improve bowel function after taking medications, you need to drink a simple remedy
.
Causes of inflammation of the sigmoid colon
Most often, the sigmoid region becomes inflamed simultaneously with another section of the intestine (large intestine, rectum). So with colitis, proctitis or enterocolitis, the sigmoid colon is also affected by the disease. Less commonly, the sigmoid colon becomes inflamed on its own.
This happens in the following cases:
- irritation of the intestine with feces, when they become very hard and difficult to pass through the intestines;
- constipation, including during pregnancy, when the fetus grows and compresses the intestines, preventing feces from moving forward;
- insufficient blood supply to the intestinal walls due to atherosclerosis or thrombosis;
- Crohn's disease, diverticulitis, inflammation of the colon, paraproctitis;
- intestinal dysbiosis, may be due to long-term use of antibiotics;
- low physical activity, especially in a person who has a sedentary job;
- intestinal infections, as well as viral diseases;
- carrying out radiation therapy;
- formation of adhesions after intestinal surgery;
- abdominal injuries.
If you are having problems with your gut and you are not sure what is causing it, it is best to consult a doctor for advice. He will want to not only check the sigmoid colon, but also examine nearby parts of the intestine to get a more complete picture. Having established the causes of sigmoiditis, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
There is no need to do this yourself, because good modern drugs from advertising can only do harm if the diagnosis is incorrectly established.
Sigmoid colon: what is it and where is it located?
This part of the intestine is S-shaped (the name comes from the Latin letter sigma). It is located in the lower part of the intestine, connecting the descending colon (part of the large intestine) and the rectum. The length of this section is different for each person, ranging from 10 to 65-65 cm. The average is 40 cm. The mesenteric ligament ensures the mobility of the sigmoid colon, so it can change location.
Active digestion of food no longer occurs in the sigmoid. Here, the consumed liquid and electrolytes dissolved in it are absorbed, and feces are formed.
The anatomy of the sigmoid colon is designed in such a way that if the digestive system malfunctions, feces do not move in the opposite direction. In the presence of certain factors (decreased peristalsis, sedentary lifestyle), feces can stagnate in this section, causing inflammation of the sigmoid colon.
Sigmoid colon hurts: what are the causes?
It is extremely rare that diseases of this part of the intestine occur independently. More often they develop against the background of existing acute or chronic inflammation of the digestive system, especially the large intestine.
Other causes of sigmoid colon diseases include:
- Congenital features. The human intestine has a convoluted shape, but the number of curves varies. The more there are, the more difficult it is for food and feces to move through it. Stagnant processes occur more often; long stay of feces in the intestines leads to inflammation and general intoxication.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, duodenal ulcer or any other part.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Chronic constipation of various etiologies.
- In women, inflammation of the sigmoid colon occurs during pregnancy due to increased pressure of the uterus on the intestines. Sigmoiditis also occurs against the background of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. It is in this section that adhesions most often occur.
- Impaired blood supply to the intestines, decreased vascular tone, increased blood density, high blood cholesterol levels.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Abdominal surgery, which could result in damage to the intestines.
- Ionizing radiation, which causes cell degeneration.
Another article on this topic: Preparations for restoring microflora: probiotics and prebiotics for the intestines
Symptoms of sigmoiditis
Symptoms of inflammation of the sigmoid colon will depend on what type and form of the disease the person has.
| Form of sigmoiditis | Symptoms |
| Acute sigmoiditis | lower left abdominal pain; |
| nausea; | |
| vomiting that does not bring relief; | |
| pain in the intestine may radiate to the left leg or lower back; | |
| increased body temperature; | |
| bloating; | |
| diarrhea that has an unpleasant odor; | |
| impurities of mucus, pus or even blood in the stool; | |
| dehydration; | |
| weakness and drowsiness. | |
| Chronic sigmoiditis | constipation and diarrhea alternate with each other; |
| the pain subsides and then returns; | |
| distension in the abdominal cavity; | |
| painful act of defecation; | |
| nervousness. |
Signs of inflammation of the sigmoid colon can, in a chronic course, be caused by an external or internal factor, which will manifest the presence of the disease, but will not be its root cause, as many people think.
Video:
These factors include:
- getting abdominal injuries;
- stressful and conflict situations;
- violation of diet and non-compliance with the principles of rational nutrition;
- sudden changes in taste preferences in food;
- hypothermia;
- the presence of infectious diseases, especially those that affect the intestines.
Treatment of peritonitis
If inflammation of the sigmoid colon is missed in the acute period (healed or not treated, treated without making a diagnosis), then sigmoiditis can become chronic. It is characterized by periods of remission, that is, the symptoms either subside or return again.
Such inflammation of the sigmoid colon can be treated only at the time of exacerbation and only after consultation with a doctor. If the disease is neglected, complications such as peritonitis may occur due to perforation of the intestine, as well as fusion of the intestine with nearby organs.
One of the main causes of constipation or diarrhea is poor diet.
.
Therefore, to improve bowel function, you need to drink a simple drink
.
Cancer
Insufficient peristalsis leads to fecal retention. It puts pressure on the walls of the colon sigmoideum, and blood circulation is disrupted. This promotes the proliferation of the epithelium and the formation of adenomatous polyps, which develop into a precancerous state and later into adenocarcinoma.
Sigmoid colon cancer occurs unnoticed in the initial stages. Pain appears at a later stage. Abnormal bowel movements, fatigue, and loss of appetite are inherent in many diseases and do not immediately alarm anyone. Be careful! Such symptoms are a reason to undergo examination.
Later, nausea, belching, pain, bloating, and red blood in the stool appear. If the tumor grows into the intestinal lumen, the passage of feces and gases is disrupted, and severe abdominal pain begins to bother you. The main cause of sigmoid colon cancer is prolonged contact of feces with the mucous membrane as a result of a sedentary lifestyle or weakened peristalsis. A large amount of toxins are absorbed from the feces into the colon sigmoideum. Additional risk factors include:
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- polyps and papillomas;
- atrophy of the intestinal mucosa;
- genetic predisposition.
If close relatives are diagnosed with sigmoid colon cancer, undergo regular examination. This will help diagnose the disease at an early stage. Elderly people are also at risk. Treatment of adenocarcinoma depends on its size, depth of germination, and the presence of metastases. To determine the treatment method, colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy is prescribed. During the study, a piece of tissue is taken for histological examination.
MRI allows you to determine the shape, size, localization of the tumor and detect metastases. Experts believe that the most optimal treatment method is tumor removal.
For small adenocarcinoma, minimally invasive surgery is possible. Access to the tumor is provided using a sigmoidoscope. The classical method involves resection of part of the colon. In severe cases, the sigmoid and rectum have to be removed. Radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed in combination with surgical treatment. Adenocarcinoma rarely metastasizes to adjacent organs. In the first and second stages of the disease, the survival rate is about 95% over five years. The survival rate for stages 3 and 4 is 40%.
Treatment
Therapy for inflammation of the sigmoid colon should be comprehensive. It includes treatment with medications, diet and folk remedies.
Medicines
Medicines will be used for infectious intestinal diseases (antiviral drugs and antibiotics). For dysbacteriosis, medications are prescribed that restore normal intestinal microflora.
To relieve pain , analgesics and antispasmodics are prescribed. Prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs will be mandatory.
Suppositories are also sometimes used for local administration of medication, as well as for alleviating the symptoms of sigmoiditis. In case of intoxication, water balance is restored with electrolytes and saline solutions.
Diet food
The diet for intestinal sigmoiditis should be followed by the patient in full. The diet lasts about a week, since it contains practically no vitamins, and also because a week is enough to restore the functions and functioning of the intestines.
Table No. 4 is assigned, which includes the following products:
- dry day-old bread and homemade crackers;
- chicken, rabbit, turkey meat;
- lean types of fish;
- soups with low-fat broth, preferably vegetable broth;
- eggs are cooked soft-boiled;
- steam omelette;
- buckwheat, rice, oatmeal;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- you can eat green apples, quince, currants, bird cherry, blueberries, pears;
- green tea, rosehip decoction, compotes and jelly from permitted berries.
In case of inflammation of the sigmoid colon, the following must be excluded from food:
- fatty meats and fish;
- dairy products;
- milk broths, as well as fatty and rich broths;
- all smoked meats, pickles, preserves, marinades;
- coffee, cocoa, kvass, carbonated drinks, alcohol;
- sauces, spices and seasonings;
- everything sweet and floury;
- fried and hard-boiled eggs;
- pasta and products made from it;
- all legumes.
If in the first days the patient’s health is poor, then a hunger strike with the consumption of large amounts of liquid would be appropriate.
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies must be agreed with a doctor and should not replace diet and medications.
With a timely diagnosis, the disease is easily treated and has a favorable outcome. However, to maintain his well-being, the patient will still need 1-2 months of dieting and taking medications to consolidate the achieved effect. The main thing is not to self-medicate, but to seek qualified medical help.
Prevention
Lack of fluid in the diet is one of the main causes of constipation. To get rid of it in 3 days, you need to drink a simple remedy every day.
A patient with sigmoiditis needs bed rest and sound sleep. When the first period of illness passes, you can prescribe light exercises so that the abdominal muscles are developed and there is no stagnation of feces.
Practicing gastroenterologist. Work experience: 9 years in a private clinic. If you haven't found the answer to your question, ask the author!
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of one or another part of the intestine is called colitis. However, such processes rarely cover the multiple surfaces of this entire section of the gastrointestinal tract.
Most often it is localized in one of its departments, depending on the causes of its occurrence. Such conditions have their own names, determined in most cases precisely by their location.
Sigmoiditis is a pathology characterized by the development of inflammation in the sigmoid region of the large intestine.
What are the features of inflammation of the sigmoid colon, symptoms and treatment of this disease?
Causes
The name of this section of the large intestine is due to its resemblance to the letter of the Latin alphabet “sigma”. The length of the sigmoid colon depends on the size of the person, reaching 60 cm in some cases.
The main task of the sigmoid region is to help digest food, separate moisture from the digested masses and saturate the rest of the body with it.
In this section of the intestine, fecal masses are formed and compacted, and the already formed feces pass from it into the rectum.
The causes of the development of inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon include various conditions.
The main ones are listed as follows:
- stagnation of fecal matter due to natural curvature or other reasons;
- infectious intestinal infection;
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane due to the consumption of indigestible food or hard feces with systematic constipation.
In addition, a number of factors predisposing to the onset of the disease can be identified:
- impaired blood flow in the pelvic area and, as a consequence, varicose veins (hemorrhoids), the formation of blood clots in weak blood vessels;
- various pathologies of the rectum (paraproctitis, fissures in the anal area, Crohn's disease);
- persistent or chronic dysbacteriosis;
- malnutrition - lack of plant fiber in the diet;
- passive lifestyle;
- decreased gastrointestinal motility due to various diseases, as well as systematic constipation;
- diseases of the genitourinary system - diseases of the prostate gland in men, gynecological pathologies in women, characterized by a chronic course;
- increased load on the pelvic area during pregnancy;
- consequences of surgery in the abdominal cavity, or a number of injuries to this area.
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon is extremely rarely an independent pathology. That is, in most situations this is a consequence of the development of other intestinal diseases.
Those rare cases in which inflammation of the sigmoid colon develops independently are caused by physiological abnormalities in the development of this part of the gastrointestinal tract - its elongation and/or the presence of extra bends and loops.
Classification
The course of the disease allows us to distinguish two forms: acute and chronic. The first (acute sigmoiditis) is characterized by pronounced symptoms, most often preceded by an infectious infection of the gastrointestinal tract.
The second - chronic sigmoiditis - is expressed by less intense manifestations, which tend to alternate with periods of remission. It mainly occurs with persistent dysbacteriosis.
The severity of symptoms and the nature of the damage caused by the pathology make it possible to distinguish several stages of the disease.
Stages of the disease include:
- Catarrhal. It is considered the least traumatic stage of the disease. Damage affects exclusively the upper layers of the epithelium. Treatment of sigmoiditis at this stage is not difficult; the main problem is diagnosis.
- Erosive. Progression of the previous stage leads to the development of erosive. It is characterized by damage to the deeper layers of the epithelium, so erosive sigmoiditis is often accompanied by bleeding, albeit of low intensity.
- Ulcerative. This stage refers to the severe form of the disease. As the name implies, ulcers (either one or several) form on the mucous membrane of the sigmoid portion of the intestine. The onset of a stage such as ulcerative sigmoiditis is possible when the disease is neglected or the previous one is treated incorrectly.
- Perisigmoiditis (paralytic or spastic sigmoiditis). This stage of the disease is considered the most dangerous. In addition to the symptoms of the above stages of the disease, there is a decrease in the motor function of this part of the intestine and the appearance of so-called adhesions (fusion of bends or loops of the sigmoid intestine with each other). This type of sigmoiditis requires treatment that is different from the usual (most often surgical).
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of sigmoiditis, you must follow the following recommendations from specialists:
- Treat chronic diseases and diseases of the digestive organs in a timely manner.
- Have routine medical examinations once a year.
- Eat a balanced and rational diet.
- Give up bad habits, in particular alcohol.
- Lead a healthy and active lifestyle.
- Establish a drinking regime.
- Use medications only according to medical recommendations.
- Observe hygiene rules.
If you follow these tips, the likelihood of developing the disease can be reduced several times.
Treatment of sigmoiditis is a long-term process. However, if the correct diagnosis is established and appropriate therapy is carried out, the prognosis is favorable.
Symptoms
The manifestations of the disease directly depend on the form of its course.
Thus, the acute form of inflammation of the sigmoid intestine has the following characteristic features:
- intense pain in the left side of the abdominal cavity (in some cases, the pain tends to radiate to the left leg);
- increased gas formation with all the ensuing consequences (flatulence, bloating);
- systematic diarrhea, accompanied by a strong unpleasant odor of feces, as well as the presence of mucous, blood or purulent fragments in them (in some cases);
- feverish state, symptoms of intoxication (pallor of the skin, general weakness);
- nausea, sometimes with bouts of vomiting.
Diagnostics
The problems in identifying pathology are that in most cases it acts as a secondary disease. Its symptoms are confused either with signs of a primary disease or something completely different.
Thus, attacks of acute sigmoiditis are often mistaken for inflammation of appendicitis, also in acute form.
At the first suspicion of inflammatory processes in the lower intestine, you need to contact a specialized specialist to undergo a full examination.
It begins with an initial examination, during which the doctor collects an anamnesis, visually and using fingers (palpation) assesses the condition of the abdomen. A competent specialist, based on the results of these procedures, will be able to determine, with a high degree of probability, the localization of inflammation.
After this, the type of pathology and the degree of damage resulting from its course are determined. At this stage, information is obtained from the results of blood tests and, naturally, stool.
In addition, to clarify the diagnosis or in case of doubt regarding the preliminary diagnosis, the following studies are prescribed:
In some cases, it is advisable to use an ultrasound examination.
The importance and value of diagnostics is difficult to overestimate. Establishing the cause of the ailment in the early stages is an opportunity to begin treatment of sigmoiditis earlier, which will naturally affect its prognosis and timing.
Otherwise, the decrease in the performance and functionality of the sigmoid intestine will only increase. The consequence of this may be the appearance of adhesions (fusion of loops with each other or with other organs) or perforation of the intestine (perforation), followed by peritonitis.
Considering such negative dynamics, it is necessary to choose a medical institution and a specialist for diagnostic procedures with special care.
Diagnosis of sigmoiditis
The disease is diagnosed by a proctologist based on clinical symptoms, physical examination, rectal examination, endoscopy and laboratory tests. When palpating the abdomen of a patient with sigmoiditis, tenderness is detected in the left iliac region. Rectal examination reveals a full, edematous lower part of the sigmoid colon. When proctitis and sigmoiditis are combined, swelling is noted not only in the sigmoid colon, but also in the rectum. After removing the finger from the rectum, traces of blood and mucus are visible on the glove.
The most informative method for diagnosing sigmoiditis is sigmoidoscopy, which allows one to assess the severity and prevalence of changes in the intestinal mucosa. A general blood test indicates the presence of leukocytosis. A coprogram of patients with sigmoiditis and a stool culture test make it possible to confirm inflammation in the large intestine and identify the pathogen in infectious lesions of the intestine. In difficult cases (with atypical localization of pain), laparoscopy is performed to differentiate sigmoiditis from acute appendicitis and peritiphlitis.
Treatment
Relief of inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon takes quite a long time. And the success of treatment directly depends on the patient’s ability to strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
How to treat sigmoiditis? The main points of treatment are drug therapy and strict adherence to diet.
Drug therapy
In the presence of an acute course of the pathology, the patient is prescribed bed rest. The effect of medications prescribed for diagnosed sigmoiditis is aimed at relieving the causes of the disease, inflammation of the mucous membrane, as well as symptomatic manifestations of the disease.
Thus, the drugs that form the basis of treatment include:
- painkillers (depending on the individual characteristics of the patient and the tolerability of certain components);
- antispasmodics;
- absorbent drugs - Neosmectin, Smecta (if there are contraindications - activated carbon);
- antibiotics - Doxycycline, Tetracycline (for more serious or extensive infections - Ampiox, Fthalazol);
- antacids - Almagel and others;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Salofalk and others;
- probiotics - Linex, Hilak-Forte (mandatory use after a course of antibiotics or after relief of symptoms);
- rectal suppositories (suppositories) - suppositories for sigmoiditis are prescribed as an additional measure. Depending on the goals pursued, medications with mityluracil, sea buckthorn oil, and others may be prescribed.
In some cases, in particular, if catarrhal sigmoiditis is diagnosed (that is, the least dangerous and unexpressed), microenemas with medications are prescribed.
Diet
The main objectives of the diet compiled in the treatment of sigmoiditis are:
- avoiding irritation of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon;
- helping to relieve inflammation in this area;
- restoration of normal functioning of the digestive tract.
A diet for sigmoiditis, or rather with antisigmoiditis therapy, implies a serious reduction in consumed fats and carbohydrates.
The result is an almost complete absence of fermentation and putrefaction of the intestinal contents. There is an improvement in peristalsis, as well as the production of only the digestive juice necessary for normal digestion.
The minimum period for following this type of diet is 7 days. It also provides for the principle of fractional nutrition, that is, eating food often, but in small portions (the average number of snacks per day should be 6-7 times).
One of the recommendations would be to accustom the digestive system to a regular diet - eating food every day at the same time, this helps improve peristalsis and normal digestion of consumed foods.
Another feature is the type of food served - it should be grated, liquid or pureed. Hard large pieces are strictly not recommended.
The main thing is a diet for inflammation of the sigmoid colon, which involves excluding from the diet:
- freshly baked bread and pastries;
- fatty meats and fish;
- smoking and canning products (especially industrial);
- rich broths and soups made from milk;
- whole milk and its derivatives;
- fermented milk products with a high fat content;
- fresh vegetables, berries, fruits and herbs;
- hot spices and herbs, marinades;
- carbonated drinks (including homemade ones, for example, kvass), coffee, strong tea;
- alcoholic products.
Conversely, the basis of nutrition should be products from the following list:
- lean meat, fish and poultry (passed through a grater or blender);
- meat soufflé, steamed cutlets;
- vegetable puree;
- dried bread (white);
- steamed omelettes and soft-boiled eggs;
- porridge (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat), exclusively cooked in water and passed through a blender;
- fermented milk products with reduced fat content;
- weak green tea and fruit and berry compotes;
- apples (grated in small quantities).
In the acute form of the pathology, accompanied by pain of increased intensity, you need to generally limit food intake for 1-2 days, that is, fast.
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon is dangerous not only because of its consequences, but also because its symptoms are often confused with manifestations of other diseases.
Therefore, at the first suspicion or presence of symptoms, you need to urgently contact a competent specialist. Timely diagnosis is half the success of treatment.
After prescribing the necessary therapy, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations. In this case, treatment of inflammation of the sigmoid colon will take the shortest possible time, and the disease will not bother you in the future.
Otherwise, serious complications may occur, including such dangerous conditions as peritonitis and the appearance of intestinal adhesions with other abdominal organs.
Dolichosigma
The normal length of the colon sigmoideum is 24-46 cm. A pathological increase in the length of the sigmoid colon leads to impaired intestinal evacuation. The thickness of the walls and the diameter of the lumen of the organ do not change with this anomaly. Congenital deformation of the organ is caused by the adverse effects of environmental factors on the fetus, the use of certain medications by the expectant mother, and heredity. The cause of acquired dolichosigma is the processes of fermentation and putrefaction that occur due to the prolonged presence of feces in the intestinal lumen. This condition leads to stretching of the organ. The main symptoms of the disease are frequent constipation, bloating, and pain during bowel movements. In some cases, pain radiates to the spine and chest. With this pathology, dangerous complications arise. Fecal stones, volvulus, and kinks of the colon sigmoideum can cause intestinal obstruction. From rotting dense formations, toxic substances are absorbed into the intestines and poison the entire body. Therefore, with dolichosigma, symptoms of chronic intoxication and dysbacteriosis are often observed. The disease is diagnosed using irrigography. In most cases, conservative treatment and diet are sufficient to regulate the functioning of the organ. The diet includes foods high in fiber. Probiotics, B vitamins, and herbal laxatives are prescribed. Electrical stimulation of the intestines and colon hydrotherapy give good results. In case of intestinal obstruction or kinks, excess loops are excised. As you can see, any colon sigmoideum disease is easier to cure at the initial stage. Try to consult a doctor even with minor symptoms and get examined.