Features of the problem
This type of epidermophytosis is characterized by the formation of large spots that have clearly defined boundaries with an almost clean center. Along the edges of the spot there are a large number of vesicles and pustules, which may have a purulent or mucous filling. There may be little or no tenderness in these areas.
Athlete's foot in the groin area is considered a fairly contagious dermatological lesion that can be transmitted through close bodily contact.
As the pathology worsens in the absence or insufficiency of treatment, pronounced peeling of the affected area is noted, which is explained by the activation of a fungal infection. At the same time, the area of the lesion also increases; the treatment process may be delayed due to the larger area of the lesion and worsening of the symptoms of the disease.
Inguinal athlete's foot and its causes - the topic of the video below:
Treatment of Epidermophyton floccosum
Getting rid of the manifestations of athlete's foot inguinal is quite difficult. Only an experienced dermatologist can choose the best treatment for each specific situation. Therapy must be comprehensive and include:
- Carrying out hygiene procedures.
- Taking and applying medications.
Additionally, it is extremely important for patients to eliminate pathogens from the environment - objects and things that have been in use. At the initial stage of treatment, it is necessary to spend time and effort on complete disinfection and cleaning of the room:
- Treat all objects and surfaces using a vinegar solution (take 1 tablespoon of vinegar essence for 1 liter of water). It is necessary to rinse hard-to-reach areas with special care.
- Throw away those items that simply cannot be disinfected - pumice stones, washcloths, etc.
- Wash clothes, as well as linen and towels at high temperature (about 90 ° C) or boil.
In the absence of adequate disinfection, it will not be possible to get rid of the disease. Even with proper treatment, re-infection will occur.
Hygiene procedures
Patients diagnosed with athlete's foot need to:
- Pay special attention to personal hygiene, in particular in affected areas.
- Carry out water procedures every day and carefully treat skin folds. It is important to prevent the accumulation of moisture residues in the affected areas. The skin should be blotted dry, but not rubbed.
- Carry out baths with the addition of infusions of medicinal herbs, for example, chamomile, oak bark or string. Such procedures have a good drying effect and help to subside the inflammatory process.
When performing hygiene procedures, you need to remember the risk of infection to other family members. You should take special care to protect your loved ones and remove towels and clean the bathroom on time.
Medicines
To stop the inflammatory process and get rid of the symptoms of weeping, you need to:
- Treat the affected areas with resorcinol (in the form of a 1–2% solution), chlorhexidine (0.1%) or silver solution (0.25%). Sometimes doctors recommend the use of the drug Mycozolon with antifungal effectiveness. Such products are suitable for preparing lotions.
- Lubricate the affected areas with hormonal medications selected by the doctor individually. The need for such treatment arises when inflammation is particularly severe. Hormonal medications can only be used short-term, since long-term use can cause various undesirable effects.
After neutralizing the acute inflammatory process, the main treatment begins (if the inflammation is not too severe, such therapy is started immediately after diagnosis). Patients are usually prescribed only topical medications:
- Ointments or creams with clotrimazole, terbinafine or ketoconazole. Sometimes medications containing oxiconazole or bifonazole become the drugs of choice. Such products should be used twice a day, lubricating the affected areas with them.
- Fukortsin solution.
- Sulfur-tar or sulfur-salicylic ointment.
- Drying zinc ointment.
- Iodine tincture (2%). She needs to lubricate the areas on the skin where the lesions were located, even after successful recovery - for three weeks.
Treatment of epidermophytosis lasts on average from 3 to 6 weeks. In the chronic course of the disease, the treatment regimen can be adjusted, and the process itself can be delayed for a longer period.
When spots on the skin cause particularly severe discomfort to the patient, antihistamines can be used to relieve unpleasant symptoms. They do a good job of relieving itching and excessive swelling. The drugs of choice most often are those drugs that need to be taken only once a day - Loratadine or Cetrin, etc.
How to treat at home?
Coping with the disease on your own is quite difficult. Therefore, all home treatment measures should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. Traditional medicines are usually recommended to be used in parallel with medications for more effective therapy. In particular, at home you can use:
- Tea tree oil. This medicine has powerful antifungal properties, and to achieve a therapeutic effect you just need to lubricate your skin with it twice a day.
- Soda solution. Regular baking soda will help eliminate fungus and restore skin. You need to dilute 1 tbsp. l. soda in 1 liter of warm water and mix well. Use to prepare lotions and baths.
- Infusion of celandine. To prepare this medicine you need to take 4 tbsp. l. dry herbs and brew 1 liter of boiling water. Strain the cooled infusion and use to wipe the affected areas.
- Collection of herbs. Combine an equal share of chamomile, as well as string herbs and sage. 1 tbsp. l. collection, brew 1 liter of boiling water, boil for a quarter of an hour, cool and strain. Use to wipe the skin and prepare lotions.
- Another collection. To create such a medicine, you need to combine equal shares of birch leaves, as well as willow with St. John's wort. 3 tbsp. l. The mixture must be brewed with 1 liter of water and put on fire. The medicine should be boiled within 15 m after boiling over low heat. Use the resulting product strained to treat the skin 1-2 times a day.
It is worth considering that traditional medicine can provoke individual hypersensitivity reactions (allergies). Therefore, they must be used carefully, preferably after a preliminary allergy test on a small area of skin.
Classification and localization
There is a fungus that causes the development of athlete's foot, mainly in the deep folds of the skin, especially in the groin area. However, when visiting public places where high temperature and high humidity are constantly maintained (for example, a swimming pool, public bath), there is a possibility that this disease will be localized in the area of the feet and nail plates on the toes. Therefore, to prevent the fungus that causes the development of the disease in question from getting on your feet, you should always have individual rubber shoes with you when visiting such public places.
Depending on the stage of neglect, there are two options for the development of this skin lesion, each of which has a number of characteristic symptoms and manifestations:
- The initial stage of inguinal epidermophytosis is characterized by the appearance of small pink spots on the skin, mainly in deep skin folds, which have blurred outlines and a clear middle. At the initial stage of development of the pathological process on the skin, minor changes are likely to appear inside the spot, the color is weak, itching bothers the patient only when walking and when the spot comes into contact with clothing, as well as in case of insufficient personal hygiene.
- Advanced stage - in this case, spots characteristic of the disease are formed in a significant number, and as their number increases, they merge with each other. In this case, the inflammatory process inside the spot spontaneously disappears, resulting in the formation of characteristic rings of inflamed areas on the skin. In advanced stages of athlete's foot, there is a high probability of spots appearing on large areas of the skin, as well as on the feet and nail plates (in the most advanced cases). The patient is bothered by severe itching and burning of the skin in the affected area.
The process of treating pathology associated with the active proliferation of the fungus that causes athlete's foot depends on the degree of neglect of the pathological process, the presence of other concurrent diseases that weaken the body, as well as the quality of the patient's immune system.
Photos of inguinal athlete's foot in women
Symptoms in men and women
Inguinal athlete's foot begins gradually, but in the absence of timely treatment progresses rapidly:
- At first, small spots of pink or red color (no more than a centimeter in diameter) form on the skin. They are characterized by a flaky surface.
- The spots grow in size, reaching up to 10 cm.
- The inflammatory process is localized at the edges, the central part almost seems normal.
- Large spots can merge with each other, forming rather large oval lesions with jagged edges. They are red in color and look swollen.
- The central part of the lesions may be covered with small pustules, crusts and scales, while the border is formed by a ridge of swollen and reddened epidermis covered with blisters. Basically, all skin defects are located near the border of the lesions.
- The central part of the spots may become pale and sunken.
- The rollers may begin to get wet.
- The spots cause discomfort - they itch and sometimes burn. The severity of discomfort increases when walking, especially when there is noticeable friction of the affected skin with clothing.
After a clear clinical picture, the symptoms of the disease may subside. As a result, pale lesions with a noticeable ridge form on the skin. This development of events does not indicate an approaching recovery, but the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Over time, the disease may worsen or subside. Sometimes periods of remission last up to several years.
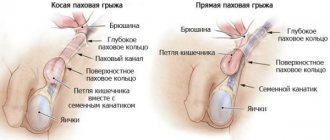
Inguinal athlete's foot is localized in different areas of the skin of the groin. Most often, spots appear in the folds of the skin, but they can occur on:
- Femoral surface (inner part).
- Intergluteal fold.
- Anal areas.
- Male scrotum.
The disease may spread to the armpits and skin under the mammary glands. With significant body weight, spots may appear on the stomach. Rarely, the symptoms of athlete's foot spread to the spaces between the toes.
Causes
Manifestations of the disease are most often observed when the functions of the immune system are weakened, since activation of the fungus is observed when the body is weakened, in the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and in the absence of adequate treatment. Also, reasons that can provoke the appearance of characteristic symptoms of the skin disease in question include:
- lack of personal hygiene - the fungus begins to actively multiply at high temperatures and humidity, therefore, with sweating and lack of regular washing of the skin, there is a high probability of developing this skin pathology;
- when visiting public places with high humidity and ambient temperature - baths, saunas, swimming pools without personal protective equipment: personal rubber shoes, towels;
- with obesity and frequent and profuse sweating caused by it, when the process of maintaining personal hygiene becomes difficult;
- when sharing washcloths, towels, and household products.
Inguinal epidermophytosis develops with insufficient individual skin care and insufficient attention to personal hygiene. Therefore, the main means of preventing this skin lesion should be considered regular showering and eliminating the causes of active sweating.
Causes
As already mentioned, athlete's foot is a fungal disease (dermatomycosis). The causative agent is the fungi Epidermophyton floccosum, Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Fungi are transmitted by touch, as well as by ordinary household methods, for example, through a towel, bed linen, or washcloth. If hygiene is not observed, you can pick up a fungus in the bathhouse, in the common locker room, and even on the beach.
The development of the disease is facilitated by obesity (which makes it difficult to carefully care for skin folds), increased sweating (creating favorable microflora for the fungus), and scratches on the skin (an opportunity for the fungus to get caught in a certain area of the skin). Also, the fungus thrives in high humidity and high air temperatures (again, a bathhouse and the beach are ideal for it, it’s just waiting for an opportunity to catch on).
Diagnostics
If the above signs of the disease occur, you should consult a dermatologist. The doctor will examine the body, ask about symptoms, and prescribe additional tests to confirm the diagnosis. Usually, a skin scraping is taken from the affected areas, which makes it possible to identify the pathogen. Men may need to consult a urologist.
In differential diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude psoriasis, erythrasma, candidiasis, and rubromycosis from possible diagnoses.
Symptoms of inguinal athlete's foot
The manifestations of the disease in question are similar in both children and adults. However, according to the intensity of the development of symptoms and the speed of spread of the lesion, there is a likelihood that symptoms of the lesion will manifest in childhood to a greater extent due to the increased sensitivity and tenderness of children's skin.
The manifestations of the disease are characteristic, allowing timely diagnosis of even the early stages of the pathological process caused by the development of the fungus:
- inflammation of the skin in limited areas, accompanied by the formation of light pink spots with a clearly defined shape in the form of rings - the clean middle of the spot creates a very clear outline of the spot;
- manifestation of spots characteristic of the disease in the area of large skin folds, in which personal hygiene is difficult;
- As the disease progresses, the spots increase in size and their surface begins to peel off;
- the patient is bothered by severe itching and burning of the skin in the affected areas.
The listed manifestations of epidermophytosis inguinalis increase as the pathological process in the skin progresses; in the absence of adequate treatment, spots are noted on an increasingly larger surface of the skin, in some cases they even begin to cover the skin of the feet. If there is no treatment for the disease, it can last up to several years.
Development of athlete's foot
- Metabolic disease.
- Decreased immunity due to past illnesses or as a result of an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Increased sweating.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
- Fungal infections of the nails and feet (onychomycosis and mycosis).
- Diaper rash or skin damage.
Diagnostics
Identification of inguinal athlete's foot is carried out on the basis of a preliminary external examination of the skin, after analysis of the patient's subjective complaints. Characteristic spots on the skin, their peeling and severe itching of the skin allow a preliminary diagnosis to be made by an experienced dermatologist.
However, before starting to draw up a treatment regimen, the diagnosis should be clarified. To do this, it is recommended to analyze and study a skin particle from the damaged area, which will make it possible to exclude the presence of dermatitis and eczema, as well as psoriasis, which require a slightly different approach to treatment. The use of the luminescent glow of a Wood's lamp makes it possible to determine the presence of fungi in the upper layer of the epidermis that cause manifestations of this disease.
How to recognize the disease
A doctor can make a diagnosis based on the outline of wet spots on the patient’s clothing, which can also be used to determine the stage of the disease. Gravimetry is a method of measuring the amount of sweat produced using filter paper, and this method is quite effective. The dry sheet is weighed, after which the process is repeated, only now after applying the sheet to the problem area. Thanks to this, the doctor determines the exact amount of fluid that is secreted by a particular part of the body over a certain time.
Having determined, based on the tests performed, how much the groin area sweats, the specialist makes a definite diagnosis.
Untreated hyperhidrosis can lead to more severe complications, for example, erythrasmus, which is often a consequence of this particular disease. The main cause of the terrible smell is not sweat (it itself does not smell), but bacteria that actively multiply in a humid and warm environment.
Treatment
The process of treating the disease includes therapeutic effects on the skin, the use of certain medications to relieve severe itching of the affected areas, as well as maintenance therapy to avoid relapses of the disease. It is an integrated approach that makes it possible to most quickly eliminate the characteristic symptoms of the disease and eliminate the likelihood of its further spread.
Treatment of inguinal athlete's foot is discussed in the video below:
Therapeutic method
To stabilize the overall condition of the skin, you should actively maintain personal hygiene, using mild cleansers followed by the use of moisturizers, which will maintain the elasticity of the skin and prevent flaking. Baths for affected skin with a decoction of medicinal herbs and plants are very helpful: for example, a decoction of celandine herb, oak bark and chamomile relieves inflammation, eliminates severe itching, and restores the normal condition of the skin.
You can also apply compresses to the affected areas with decoctions and infusions of such herbs, which reduces swelling of the skin, which can be observed during a long-term pathological process.
Physiotherapy
- To speed up the relief of the symptoms of the disease, it is recommended to use ultraviolet rays to treat the skin in areas affected by it, which stops the damage, relieves swelling, and stimulates the body's defenses. The use of magnetic therapy may be used.
- Skin baths and ozone therapy also stimulate the immune system, ensuring a speedy recovery.
By medicinal method
To eliminate itching and burning of the skin, antihistamines are used (Suprastin, which is prescribed to adults and children to relieve swelling and burning of the skin), as well as drugs that stimulate skin regeneration, have proven themselves. Local application can be used ointments and gels with a cooling and anti-inflammatory effect, which help eliminate itching of the skin in areas where it is affected.
- To treat damaged areas of the skin, it is recommended to use disinfectant solutions (0.25% solution of silver chloride, resorcinol), which stop the active proliferation of the fungus, as well as ointments with resorcinol. This therapy allows the inflammation to be eliminated more quickly.
- Almost all drugs against fungal infections are effective, they stop the active reproduction of the fungus and stimulate skin restoration.
How to treat at home
Folk remedies help improve the condition of the skin.
Home treatment with medicinal herbal lotions and treating the affected area with antiseptic solutions will only improve the condition of the skin with athlete's foot. The use of such treatment will not aggravate the patient’s condition in any way, but, on the contrary, will contribute to a speedy recovery: it will reduce ulcers and weeping blisters, relieve itching and burning, and soothe painful skin.
Folk remedies with antimicrobial effect
In case of inguinal skin disease, it is necessary to take water procedures daily, 2 times a day , change underwear, use individual bath accessories, when visiting public places for washing, lay oilcloth on the bench, and do not wear someone else’s slippers.
A solution of iodine, white vinegar, and Burov's liquid have an antimicrobial and antimycotic effect. The finished products are diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10, 1:20 and the resulting solution is used as a lotion on the affected area of the skin. The products block sweat glands, dry weeping wounds, relieve uncomfortable skin conditions, and have a healing effect. It is better to do such lotions at night, and during morning procedures use other medications with a similar effect, but less problematic to use (ointment, cream).
For example, birch tar is well suited for treatment. It can be found in ready-made medicines: tar water, ointment based on the component. Tar has an antiseptic effect, kills bacteria, restores cells and improves blood supply to the skin.
Disease prevention
To prevent the occurrence of inguinal athlete's foot, one should mention personal hygiene using mild detergents (special attention is paid to large skin folds, which is especially important in hot climates, with high humidity and active sweating). You should also use personal protective equipment when visiting public places: in the bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna, use only personal towels, slippers, and washcloths.
Supportive therapy of the immune system in the form of taking vitamin preparations will help to avoid a sharp decrease in the level of functioning of the immune system and the addition of parallel diseases. When living together with a person infected with athlete's foot, you should use common items with extreme caution and boil the patient's bed linen, towels, and personal belongings.
Prevention of hyperhidrosis
To avoid excessive sweating in the groin area, you must follow these simple rules:
The main weapon against bacteria and viruses that cause unpleasant odors is personal hygiene of the genitals. Showering should be done daily at any time of the year to ensure the area is dry and clean.
- Protection will be provided by means of combating excessive sweating, such as flavored talc, special antiperspirant sprays intended for this area (all kinds of aerosols, roll-on deodorants, as well as gel-based antiperspirants). They will help get rid of unpleasant odor, make the skin dry, and prevent the appearance of a red rash. Excess hair should be removed from the perineal area before applying these products.
- Underwear should be changed daily and washed thoroughly. It is recommended to iron it with a hot iron in order to destroy any microorganisms remaining on it. Moreover, it is important to have individual bedding and keep it clean. It is strictly forbidden to use other people's personal hygiene products (washcloths, towels, etc.).
Athlete's foot: types, treatment, symptoms
Athlete's foot is a dermatomycosis caused by infection of the skin with the fungus Epidermophyton floccosum. The causative agent of the disease primarily affects large folds of skin, feet, and toenails.
Types of athlete's foot
Microscopic fungi from the genus Epidermophyton mainly affect the inguinal-femoral skin fold, the skin of the feet, hands, and rarely the nails. Epidermophyton fungi, when examining affected tissues, are found in the form of thin, branching mycelium threads; spores are practically absent in the samples.
Athlete's foot is caused by the anthropophilic fungus Epidermophyton floccosum.
Another name for this causative agent of inguinal dermatomycosis is epidermophilus flocculus; the fungus is localized superficially and destroys the skin, as shown in the photo, due to the utilization of collagen.
Athlete's foot and single nails are caused by Epidermophyton Kaufmann-Wolf. Athlete's disease of smooth skin, folds, feet, hands, face, and nails occurs when infected with the fungus Epidermophyton rubrum.
In the modern classification, fungi Ep. Kaufmann-Wolf and Ep. rubrum are classified in the class Trichophyton. The fungi are called Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Trichophyton rubrum, respectively.
Athlete's inguinal
Men are more likely to suffer from this contagious fungal disease; the inguinal and intergluteal folds are more often affected. In men with inguinal epidermophytosis, the fungus spreads to the scrotum, anus, intergluteal fold, thigh, as in the photo, the penis is rarely affected and requires treatment.
In women, inguinal athlete's foot sometimes spreads to the skin fold under the mammary glands, the armpit, as shown in the photo.
The cause of inguinal epidermophytosis is direct infection with the fungus Epidermophyton floccosum, and predisposing factors are excessive sweating, tight clothing, and poor personal hygiene.
Excess weight, diabetes, and hormonal disorders contribute to the spread of inguinal fungus in women and men; in the photo you can see that areas of diaper rash, deep folds of fat, where sweat is released profusely, are affected.
Infection with athlete's foot occurs through contact with a patient, as well as through bath accessories in the shower, bath, or bath.
It is enough to use a washcloth or towel shared with an infected person so that the epidermophyton fungus gets on the skin.
When the protective properties of the skin are weakened, a lesion appears at the site of introduction of the fungus, gradually growing along the periphery, spreading to areas of healthy skin.
You can become infected with athlete's foot by walking barefoot on the floor of a gym locker room, someone else's apartment, or even in your own home. Flakes of desquamated skin from the foot of a sick person fall first onto the floor, and from there onto the skin of the feet of a healthy person.
In conditions of high humidity, fungi remain viable for a long time, and once on the skin of a new host, they vigorously colonize it.
Symptoms of athlete's foot
A characteristic sign of infection with the fungus epidermophyton is itching, burning in the affected area, the hair follicles are not affected, which is a distinctive feature of the disease.
With inguinal athlete's foot, the patient experiences discomfort when walking. Athlete's disease occurs chronically, recurring in the summer, and also when the immune system is weakened.
Symptoms of inguinal athlete's foot
First, scaly, inflamed spots appear in the inguinal folds; they are usually located symmetrically. The inflamed area of skin has a rounded outline and a red-brown color.
Gradually, with inguinal epidermophytosis, several foci are formed, outlined by ridges of inflamed skin along the edge, measuring up to 10 cm2, as can be seen in the photo.
The roller consists of individual small bubbles, scales, and crusts. The inflamed border is constantly shifting and growing away from the center. In the center of the lesion, all inflammatory phenomena gradually subside, a red-brown ring seems to emanate from the fold.
Growing and merging with other lesions, individual rings merge, separated from healthy skin by a scalloped border of inflamed epidermis.
A symptom of athlete's foot inguinal in men and women is increased sensitivity of the skin in the affected area: the skin is painful to touch, even the touch of clothing causes discomfort.
A peculiarity of the course of epidermophytosis is the appearance of allergic rashes on the skin - epidermophytids. The rashes are located symmetrically, do not contain fungi and go away on their own as the parasitic fungus gets rid of.
Symptoms of athlete's foot
The clinical picture of athlete's foot and hands is similar to the manifestations of the skin disease dyshidrosis. The commonality of symptoms is manifested in the formation of bubbles with liquid deep in the skin, causing severe itching.
In the case of dyshidrosis of the feet and/or hands, the presence of parasitic fungi is not detected in the liquid, and the very appearance of the disease indicates trouble in the digestive system, nervous exhaustion, and allergies.
With athlete's foot and hands, a culture test reveals the presence of the fungus Epidermophyton floccosum in the liquid.
When these blisters open, they leave areas of damaged skin (erosion) on the skin, surrounded by a scalloped ridge of inflamed epidermis.
With athlete's foot, as with other tinea pedis, the skin between the toes is first damaged, as can be seen in the photo.
Interdigital epidermophytosis at the beginning of infection looks like diaper rash. Then bubbles appear in this area, weeping occurs, hyperkeratosis (keratinization) and inflammation occur.
The spread of the fungus on the skin of the foot is accompanied by penetration into the nail bed, leading to epidermophytosis of the nails. This type of onychomycosis, a nail fungus, is called superficial white onychomycosis.
Our next article, How to identify nail fungus from a photo, will help you learn more about the disease onychomycosis, as well as look at photos of nail fungus.
Diagnostics
The effectiveness of treatment for athlete's foot in men and women depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. To do this, a laboratory examination of skin scrapings from the source of infection is carried out, microscopy of the sample taken, and the fungus is inoculated on Sabouraud's medium - a special nutrient mixture.
Forecast
The prognosis is favorable, athlete's foot can be treated in both the acute and chronic stages. Modern antifungal agents can prevent relapses and re-infection with the epidermophyton fungus.
We also suggest that you familiarize yourself with other types of dermatomycosis in the following articles:
Trichophytosis;
Symptoms, treatment, prevention of microsporia;
Fungal disease rubrophytia: symptoms, treatment;
Favus.
Advice from Elena Malysheva: how to cure foot and nail fungus in a month
Source: https://skincenter.ru/mikozyi/dermatomikozyi/epidermofitii.html
Prognosis and possible complications, prevention
Experts assure that the prognosis of the disease is positive - treatment carried out under the guidance of a doctor allows you to completely get rid of the disease. However, even if inguinal epidermophytosis is eliminated, the risk of relapse cannot be excluded.
If treatment therapy is not started in time, pathogenic spots unite, forming a large affected area. Gradually, the central part of the spot clears up, the skin acquires a normal color and a relatively healthy condition.
A pronounced dark edging remains, which is a sign of active fungal activity and the development of the disease. If there is no quality therapy, the pathology can progress for many years, affecting an increasingly larger area of the patient’s skin.
The danger of epidermophytosis is that it can become chronic. The patient will begin to experience exacerbations in the spring-summer season, as well as with climate changes.
As you know, it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat its consequences. Prevention of fungus DPS-1067 will significantly reduce the risk of infection. If you already have the disease, preventive measures will speed up the recovery process and protect loved ones from possible infection.
Basic preventive measures:
- Take a hot shower every day. Perform water procedures after exercise or fitness classes. Increase the number of water procedures in the summer, when particularly increased body sweating is noted.
Store hygiene products and personal belongings of the infected person separately. This primarily applies to a washcloth and towel.
- After each shower, the patient must carefully treat the skin affected by the fungus. All items used for treatment procedures must be stored in a separate place, inaccessible to other family members. Also, after completing water procedures, it is necessary to disinfect the bathroom.
- Do not scratch the skin affected by the fungus, even if it is severely itchy. Try to avoid any touching of the affected area; if you come into contact with the infected area, wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- In case of excessive sweating, as well as in the hot summer, it is necessary to use antiperspirants. Moreover, it is necessary to treat not only the armpit area, but also the groin area.
- After removing clothing, it must be processed.
Particularly thorough disinfection should be carried out regarding those wardrobe items that were in direct contact with infected skin.
- If you have a disease, you must carefully choose clothing. It is recommended to avoid synthetics and give preference to cotton fabrics.