Number of views: 343 620
Last updated date: 08/28/2020
What discharge is considered normal Why does lingering discharge appear Signs of pathology The importance of maintaining good intimate hygiene during lingering discharge
Stretching vaginal discharge often frightens women and makes them think about the presence of inflammatory processes. In fact, viscous mucus from the genital tract does not always indicate any pathological conditions if there are no additional complaints. Sticky vaginal discharge serves a protective function and cleanses the genital tract. Mucous discharge maintains an optimal level of hydration, as well as comfort during intimate contacts. Depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the hormonal background of a woman, vaginal discharge can have different volumes and consistency.
Why do stretchy discharge appear?
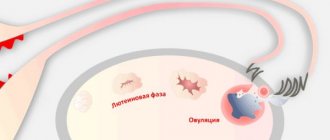
Stretchy discharge of increased viscosity appears as a result of changes in the body associated with preparation for conception. An increase in the amount of cervical mucus allows sperm to reach the egg faster and complete fertilization. The nature of vaginal discharge is influenced by the amount of estrogen and progesterone - female sex hormones. Immediately after menstruation, the discharge is slight and sticky. Shortly before ovulation, the mucus thins out, becomes viscous and elastic. Similar discharge also appears within 1–2 days after unprotected sexual intercourse. This is also considered the norm. If a woman is very bothered by viscous vaginal discharge, it is better to consult a gynecologist and undergo an examination. Some diseases, especially those of an inflammatory nature, can lead to increased production of vaginal secretions, but other health complaints are usually present.
Most often, the nature of vaginal discharge changes due to urogenital infections. They can appear not only due to unprotected intimate contacts, but also as a result of changes in the vaginal microflora under the influence of unfavorable external and internal factors. Hormonal imbalances, long-term use of antibiotics and a general weakening of the immune system contribute to changes in microbial balance.
Possible diseases
Orange discharge in women is characteristic of both infectious (STDs, thrush) and non-infectious diseases:
- erosion;
- vaginosis;
- endometriosis;
- oncology;
- adnexitis.
With the development of sexually transmitted diseases, women's discharge acquires a rich orange or yellow hue.
They are always accompanied by unpleasant symptoms:
- itching;
- burning;
- swelling of the labia;
- redness;
- rash;
- pain when urinating.
| Name of the disease | Nature of the discharge | Additional symptoms |
| Chlamydia | When examining the vagina, increased production of cervical secretions is noted, flowing down the walls of the vagina. | Additional signs are enlarged Bartholin glands, pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. |
| Trichomoniasis | Vaginal mucus is produced abundantly, has a foamy structure, and a pungent putrid odor. | The fall of mucous secretion onto the skin provokes severe irritation, accompanied by redness, swelling, and tingling. |
| Gonorrhea | Cervical secretion is released in moderate quantities, eliminating the smell of rot. A distinctive feature of the disease is the opening of bleeding without matching the cycle. In the initial stages of the disease, vaginal mucus has a grayish tint. A change in its color to orange indicates the transition of gonorrhea from the acute to the chronic stage. | It is accompanied by a pain syndrome of the “lowered belt” type - it covers the lumbar region, lower abdomen, and inner thighs. |
Thrush
The second name of the pathology is vaginal candidiasis. This is an infectious disease of a fungal nature.
The provocateurs of its development are:
- promiscuous sex life;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- stress;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- violation of vaginal microflora;
- decreased immunity;
- alcohol abuse.
Characteristic symptoms (intensify after sexual intercourse):
- copious white or yellowish discharge with a cheesy consistency;
- sour smell;
- itching and burning;
- discomfort during urination.
Orange discharge in women with thrush indicates advanced disease. The fungus has the ability to multiply quickly and affect deep tissues, forming small bleeding ulcers on the mucous membranes of the vagina. Blood entering the cervical mucus causes it to turn orange.
Erosion
The disease is characterized by the formation of an ulcer (wound) on the cervical canal (cervix). The cause of development is injury to the mucous membranes.
This can happen during:
- childbirth;
- abortion;
- rough sexual intercourse.
Erosion is rarely accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. Sometimes it can provoke the appearance of aching pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies during and after sexual intercourse.
Vaginal discharge is moderate, without a strong odor, white or clear. But under the influence of certain factors, the wound on the cervix may bleed, which causes the cervical mucus to turn orange.
Vaginosis
The cause of vaginosis is an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina.
Such violations can be caused by:
- frequent change of partner;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- taking antibiotics;
- weakened immunity;
- bad habits.
The first sign of the development of vaginosis is the appearance of grayish-white vaginal discharge, which gives off the smell of missing fish. If they take on an orange tint and become sticky, this indicates an advanced form of the disease.
Endometriosis
It is characterized by the growth of the internal epithelium of the uterus beyond its boundaries.
Provoking factors are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- surgical interventions (including mechanical abortions);
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- negative impact of the environment on the body.
Symptoms:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies during sexual intercourse, menstruation, urination, defecation;
- violation of the MC;
- increase in the abundance and duration of menstruation;
- infertility.
Discharge from endometriosis is moderate and white. Their coloring in a yellow or orange tint indicates bleeding of the walls of the uterus. And the appearance of an unpleasant odor indicates the addition of an infection. In this case, fever, weakness, and malaise may occur.
Oncology
Orange discharge in women can also appear with malignant neoplasms in the pelvis. Coloring in this color occurs due to the presence of pus and blood in the cervical secretion.
Additional symptoms are girdle pain in the lower abdomen and sacrum. Fluctuations in body temperature, weakness, and malaise are possible. As the disease progresses, the vaginal mucus darkens. First it turns dark red, then brown, and then black.
Adnexit
Characterized by inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Most often it is a secondary disease that develops against the background of sexually transmitted infections or inflammation of the internal genitalia.
Adnexitis manifests itself as moderate orange or yellow discharge. An additional symptom is abdominal pain. In the acute period, the pain syndrome is strong and cramping. Upon transition to the chronic stage, it becomes of medium intensity, drawing, dull.
If pathological vaginal discharge is not treated in time, it can lead to serious complications:
- infertility;
- recurrent miscarriages;
- cancer;
- violation of the MC;
- Reiter's syndrome;
- abscess;
- sepsis.
Even if the appearance of orange discharge in women is not accompanied by additional symptoms, do not put off visiting a doctor. Some diseases can occur in a latent form and their only manifestation is a change in the nature of vaginal mucus.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Signs of pathology
When vaginal discharge is associated with gynecological diseases, additional pathological signs appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- copious yellow-green discharge with an unpleasant odor or a cheesy consistency;
- discomfort during urination and intimate contacts;
- redness of the vulva, swelling of the external genitalia;
- menstrual irregularities, etc.
If the above signs are present, a woman should be wary. It is recommended to make an appointment with a gynecologist, tell the specialist about your problems and undergo a comprehensive examination. Based on the results of the examination and tests, the doctor can make a diagnosis and, if necessary, select appropriate treatment.
What to do if you have yellow vaginal discharge?
Although changes in odor, color, consistency, and vaginal mucus are symptoms of early pregnancy, you should still see a doctor immediately. To determine the cause, your doctor will likely ask you:
- When did the yellow mucus start?
- what color is the discharge?
- does it have any smell?
- Do you experience itching, burning or swelling around your vagina?
- Did you have sexual intercourse with another partner before the abnormal discharge began?
- did you take a shower?
- Have you used scented soaps for personal care?
- Have you taken antibiotics recently?
Your doctor may also take samples of the discharge to determine exactly what is causing it. In some cases, your doctor may also do a Pap test to collect cells from your cervix to see if cervical cancer may be causing the abnormal discharge.
The type of treatment usually depends on the underlying cause. If you have yellow mucus discharge during pregnancy, no treatment is required.
The importance of maintaining high-quality intimate hygiene during lingering discharge
Stretching vaginal discharge should not cause significant discomfort. But mucus often stains laundry. In addition, sticky vaginal discharge is a breeding ground for many bacteria and fungi. To prevent the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases, it is necessary to monitor the quality of personal hygiene, wash regularly and use special protective equipment. This will allow you to maintain maximum comfort in the intimate area throughout the day. When choosing personal hygiene products, give preference to products with natural and safe compositions that do not irritate the skin and support healthy vaginal microflora.
Carefree® panty liners help solve the problem of non-menstrual discharge, which can be quite heavy, especially in the middle of a woman's cycle. The delicate surface immediately absorbs mucus, allowing you to feel comfortable.
Yellow leucorrhoea during pregnancy
After conception, a powerful hormonal change occurs in the body, many habitual processes change, and leucorrhoea may acquire a yellow tint of varying degrees of intensity.
Causes of yellow leucorrhoea in pregnant women:
- In the early stages, a mucous plug forms, which protects the baby from the negative effects of external factors, the body takes care of the safety of pregnancy. Along with the discharge, excess plug comes out, which is colored pale yellow.
- In the second trimester, against the background of active growth of the fetus, many processes in the female body change, and the immune system weakens. Against this background, sensitivity to allergens increases - reactions to panty liners and intimate hygiene products may occur. Often in the second half of pregnancy, inflammatory processes occur in the ovaries and fallopian tubes, which are accompanied by yellowish discharge.
- 2-3 weeks before birth, yellow mucous discharge appears as the mucus plug comes out.
- Yellow sticky discharge from the mammary glands - colostrum, most often appears immediately before childbirth, sometimes at 5-6 months.
- After childbirth, yellow discharge normally appears at the final stage of lochia release.
Cystitis often occurs in pregnant women; it occurs against the background of hormonal changes and weakened immunity. Normally, the disease is accompanied by clear discharge. If during cystitis the discharge changes color or smell or consistency, this may indicate vaginosis, sexually transmitted infections, or colpitis.
The nature of leucorrhoea, its structure and quantity depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Why does yellow discharge appear in teenage girls? Leucorrhoea without a particular odor appears approximately 10–12 months before the first menstruation, which indicates the beginning of preparation for reproductive activity.
What does white-yellow discharge indicate during ovulation? Moderate leucorrhoea indicates the maturation of the cells; as the date of menstruation approaches, their quantity increases, but at the same time they become more liquid.
The week before menstruation, the amount of leucorrhoea becomes maximum, and if a woman is depressed or stressed, the volume of dark yellow discharge increases noticeably.
Important! Yellow leucorrhoea often occurs as a result of allergies to pads, tampons, underwear, and contraceptives.
Normally, yellow leucorrhoea before menstruation should be uniform, without clots, and their amount should not exceed 4–6 ml. If yellow discharge is accompanied by pain and burning, or its volume significantly exceeds the norm, you should consult a specialist.
Discharge like yellowish snot is often the first sign of pathologies of the genitourinary organs.
In what cases does mucus appear constantly:
- With vulvovaginitis, leucorrhoea can become bright yellow; with this pathology, pain occurs during emptying the bladder and sexual intercourse.
- Cervical erosion is characterized by inflammatory processes in the tissues of the vaginal mucosa and cervix. This weakens the protective barrier, and the organs of the reproductive system are affected by pathogenic microorganisms. Against the background of erosion, concomitant diseases often appear - vaginitis, cervicitis. In this case, after sexual intercourse, yellow discharge with blood appears.
- Adnexitis, salpingitis - inflammatory processes are accompanied by yellow-brown discharge with purulent inclusions. Additional signs are nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, the process of urination causes discomfort.
- Yellow, curd-like discharge is a sign of candidiasis, and it often has a sour odor. The pathology develops against the background of frequent stress, hormonal imbalance, and weak immunity.
Important! Yellow discharge and itching, pain in the groin area are the main signs of many diseases that are sexually transmitted.
With chlamydia and trichomoniasis, yellow-green discharge appears, which acquires a rotten smell as the disease progresses. The labia and nearby tissues constantly itch, emptying the bladder and sexual intercourse is accompanied by pain and burning. The mucous membrane of the labia minora becomes swollen and acquires a bright red color.
Composition and physiological characteristics of female secretions
Sticky discharge is individual, its nature and volume depend on several factors, including:
- age;
- hormonal balance;
- allergic reactions to contraceptives;
- pregnancy;
- phase of the menstrual cycle.
Lifestyle and poor hygiene can also affect the nature of leucorrhoea and the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
Compound
Stretching discharge is heterogeneous. They contain:
- secretion of the cervical canal, Bartholin's and other sex glands;
- exfoliated particles of the mucous membrane;
- microflora of the vagina, and both beneficial and a small part of pathogenic bacteria are represented there.
If the discharge does not smell, there is no pain or other signs of the development of diseases of the genital area, it is enough for a woman to undergo a regular regular examination by a gynecologist.
Consistency
Transparent discharge appears in girls about a year before the arrival of the first menstruation. During reproductive age, its character is constantly changing, and viscous discharge in women is considered a variant of the norm. Sticky leucorrhoea can be:
- thin and watery;
- thick and jelly-like.
The color range also varies from transparent, white, yellowish and greenish. Unpleasant symptoms in the form of pain, itching and irritation, spasms or increased urge to urinate indicate diseases of the genitourinary system.
Factors contributing to changes in discharge
The nature of the discharge can vary slightly depending on the general health of the woman and the medications she is taking. Moreover, such changed discharge will not always indicate problems with the genitals and reproductive area. You just need to eliminate the factor that provokes the changes.
So, allocations may change if:
- a woman is being treated with antibiotics or cytostatics;
- takes hormonal medications or oral contraceptives;
- there is an endocrine pathology, in particular diabetes.
In any case, if you have any concerns, you should once again be examined by a gynecologist. Not to mention that regular preventive examinations should become a habit.
Why does the discharge darken?
There is a situation when a woman does not complain about the state of her body, absolutely nothing bothers her, there are no unpleasant sensations, but the discharge changes its color - at the end of the day, not transparent discharge appears on her panties, but a little dark.
Experts say that there is no pathology here. It’s just that natural mucous secretions can change color due to exposure to air and fabric. So, the longer the discharge remains on the laundry, the darker it can become. Therefore, the factor of how often underwear is changed plays a role.
If you want to find out whether this is normal discharge, insert a fairly clean finger into the vagina, and then run your finger along the glass. If a woman’s mucous discharge is light, there is no cause for concern. If there is a burning sensation, itching, or any suspicious color, then you should be examined by a specialist.
White discharge
In normal conditions, a woman may have a white sticky discharge in a minimal amount. They are colored white because there are epithelial cells in the vagina that begin to turn white during the day.
Before your period begins, vaginal discharge may become stronger, and after your period it may remain white for several days.
Physiological reasons for changes in secretion
The first vaginal discharge appears in girls between the ages of 11 and 14, when the ovaries begin to actively function.
As a result, the secretion of secretions by the cervical and Bartholin glands increases. The main function of transparent, odorless discharge, like snot:
- the formation of a mucus plug during pregnancy;
- creating a suitable environment for faster movement of sperm to the egg;
- protection of the uterus and other organs of the reproductive system from pathogens from the outside;
- protection of the vaginal membranes from mechanical injury during sexual intercourse.
The secretion of a healthy woman has a slightly sour odor.
The vaginal environment is capable of destroying not only bacteria, but also sperm that enter the reproductive system before the egg matures. For this reason, the possibility of conceiving a child during the absence of ovulation is difficult.
Copious discharge like snot is the norm only for sexually mature women. In young girls who have not established a menstrual cycle, this symptom cannot be considered natural. This is due to the fact that their egg is still in the stage of formation, and the hormone estrogen (under the influence of which the mucus becomes thicker and more abundant) is released in insufficient quantities.
The external volume of secretion will depend on the predominance of a particular hormone in the body.
Let's consider the main situations when discharge, transparent and stretchy, like mucus, can be considered physiologically determined:
- After monthly blood loss. Women may observe yellowish, transparent or pinkish clots on the pad. The mucus changes color due to incomplete cleansing of the genital tract from endometrial particles. The thick consistency is associated with the predominance of the hormone estrogen in the female body in the first days of the menstrual cycle.
- Mid cycle. Before ovulation, the hormone progesterone begins to be actively released into the blood. It provokes the appearance of more transparent mucous discharge with a watery consistency. In such an environment, it will be easier for sperm to move to a mature egg. At the same time, a woman may notice sudden mood swings and minor pain in the lower abdomen.
- Before menstruation. At the end of the menstrual cycle, the mucus acquires the consistency of jellied meat and contains white impurities.
Signs of mucous membranes that do not require seeing a doctor:
- absence of a sharp unpleasant aroma;
- absence of foreign impurities and foam inclusions;
- whitish, beige or transparent color;
- leaving yellowish marks on underwear after drying;
- increased production during sexual arousal or intercourse.
Thick and viscous discharge or jelly-like discharge also appears as a result of abnormal factors. These include:
- Allergic reactions to intimate hygiene products and lubricants used. Copious mucous discharge that appears as a result of allergies is usually odorless, but is accompanied by itching and burning of the genital tract. In severe cases, women may experience swollen eyes, watery eyes, and sneezing. In this case, allergy symptoms must be eliminated with the help of antihistamines: Zodak, Zyrtek, Tavegil. Allergy discharge is usually liquid rather than viscous.
- Bacterial infections. When infected, the secretion acquires yellow, greenish or marshy shades and has an unpleasant (putrefactive) odor. Pathological symptoms are caused by chlamydia, staphylococcus, gardnerella. Such violations can only be eliminated with the help of antibacterial agents. On average, therapy for a bacterial infection lasts 7-10 days (depending on the stage of advanced disease and its symptoms)
- Fungal infections. Discharge of white mucus in women indicates the development of a dangerous fungal disease - thrush. In appearance, this secretion resembles cottage cheese with white lumps. With vaginosis, the secretion takes on a sour odor. The patient notes severe itching, swelling and irritation of the genitals. Thrush is treated with antimycotic drugs in tablets or suppositories. The duration of therapy will depend on the type of medication prescribed.
- Inflammation of the appendages. The problem appears when fungal or bacterial pathology is not treated in a timely manner. Pathogenic microorganisms from the vagina enter the uterine cavity and spread to the appendages, provoking an inflammatory process. With inflammation of the appendages, brown, pink or bloody discharge may be observed when the walls of the vessels of the reproductive system are damaged. Purulent viscous discharge, accompanied by high temperature, appears during an acute course of a bacterial infection. Another symptom characteristic of inflammation of the appendages is snot-like leucorrhoea with a yellowish tint.
- Endometriosis. Accompanied by bloody or glassy discharge. The same secretion is characteristic of a sharp change in hormonal levels, polycystic ovary syndrome and uterine fibroids. An ultrasound examination and a blood test for hormones will help determine why the problem occurred.
- Polyps are growths from glandular tissues of the mucous membranes. They are benign neoplasms, but with constant trauma they can degenerate into a malignant tumor. When polyps are injured, a large amount of tugging, bloody mucus is released from the vagina, and when infected, it is yellowish or green.
- Cervical erosion. The disease is usually detected accidentally during a visit to the gynecologist. Erosion provokes intense mucous discharge, which turns brown or pink during inaccurate sex.
- The most dangerous reason for the appearance of discharge that stretches like snot is cervical cancer. The disease is often diagnosed in women over 50 years of age and, if not treated in a timely manner, is complicated by death. The first signs that may indicate oncology: weight loss, periodic pain in the lower abdomen, unpleasant odor of discharge, irregular periods. More pronounced symptoms of oncology appear in the later stages of its development, when treatment is ineffective in most cases.
- A similar symptom is often provoked by pathogens of a viral nature. With genital herpes, reddish itchy blisters appear on the mucous membranes of the vulva and labia, which burst and leave behind small wounds. As a result of a viral infection, a woman may develop genital warts or condylomas. They are not dangerous to health, but their very occurrence indicates that the immune system is weakened and vulnerable to bacteria and fungi.