Millions of women around the world experience menstrual irregularities. Ovarian dysfunction is a consequence of hormonal imbalance; it can be a complication after infectious diseases, and if left untreated, leads to adverse consequences for women's health.
Ovarian dysfunction is a pathology of female reproductive function, accompanied by hormonal disorders, menstrual cycle disruptions, inability to get pregnant, as well as many other symptom complexes and possible complications.
Risk factors
Ovarian dysfunction during the reproductive period can occur due to various reasons. In medicine, a complex of reasons is identified that lead to disturbances in the hormonal regulation of the ovaries:
- salpingoophoritis, adnexitis, oophoritis, endometritis, cervicitis. Inflammation can provoke anovulatory ovarian dysfunction;
- endometriosis, fibroids, cervical cancer, ovarian cysts;
- endocrine diseases: hyperthyroidism, autoimmune thyroiditis, diabetes mellitus, adrenal gland pathologies;
- a psychogenic factor also cannot be excluded: exposure to stress, depression, and nervous disorders contributes to the development of dysfunction;
- history of abortions and spontaneous miscarriages. Particularly dangerous are so-called medical abortions, which become a serious stress for the female body in the first months of pregnancy;
- an intrauterine device installed without a doctor’s indication;
- inappropriate hormonal contraception;
- the use of medications that suppress ovarian function can cause ovarian amenorrhea;
- age-related changes (menopausal ovarian dysfunction);
- an incompletely formed genitourinary system, which causes menstrual irregularities in adolescents.
What it is
Ovarian dysfunction is a disruption of the hormonal functioning of the ovaries, which occurs due to a woman having an infection, inflammation of the pelvic organs or diseases of the endocrine system.
Normally, the menstrual cycle lasts from 21 to 35 days. The rate of blood loss during critical days varies from 100 to 150 ml. When both ovaries are dysfunctional, cycle disruption occurs. It can be extended to 35 days or last less than 21 days. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is present.
Why does pathology develop?
The proper functioning of organs depends on the functioning of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The following causes of ovarian dysfunction are distinguished:
- Endocrine disorders.
- Extragenetic pathologies.
- Ovarian diseases.
- Pathologies of other organs of the reproductive system.
Psychosomatics is of great importance.
Ovarian dysfunction often develops when a woman is unable to realize her potential. The psychosomatics of menstrual cycle disorders is interesting. His “jumping” may mean denial of his nature. Ovarian dysfunction is diagnosed in emotionally unstable women who are in a stressful situation. The psychosomatics of the pathology also lies in the fact that a person eats poorly, abuses physical activity, and is addicted to ultraviolet baths.
External factors include an incorrectly installed intrauterine device. The disease can be provoked by surgical intervention or artificial termination of the first pregnancy.
How dysfunction manifests itself
Symptoms of ovarian dysfunction are divided into 3 large groups:
- ovulatory;
- menstrual;
- hormonal.
The regularity of anovulatory cycles increases. This is due to insufficient production of LH and FSH. The resulting pregnancy may be terminated. The main hormonal sign of pathology is “jumps” in pressure. The hair becomes dull, brittle, and the nail plates become very peeling. The skin on the face becomes oily and acne appears. The woman becomes irritable, aggressive, and often complains of causeless weakness. Even if she tries to eat right, there is a sharp jump in weight.
Hormonal dysfunction of the ovaries is characterized by a violation of the cycle. 7 days before the arrival of menstruation, a nagging pain syndrome appears in the lower abdomen. Blood is released very abundantly or sparingly. The discharge is often present for more than a week. Between cycles a “daub” appears.
With ovarian dysfunction, a delay in menstruation is observed. If menstruation does not come for six months, amenorrhea develops.
Anovulatory ovarian dysfunction is characterized by the absence of ovulation. If prolonged bleeding is combined with breast tenderness, this may mean an increase in estradiol levels.
Possible complications
It is important to know that if left untreated, ovarian dysfunction is characterized by dangerous complications. Acyclic bleeding can mask the oncological process occurring in the cervix or dysplasia. An ectopic pregnancy is often hidden behind a single cycle disorder.
Heavy bleeding provokes the development of anemia. Hormonal imbalance contributes to a malfunction in the body's absorption of calcium. This leads to bone osteoporosis. Impaired ovarian function in women under 40-46 years of age provokes the development of fibrocystic mastopathy.
How to recognize a violation of the hormonal function of the ovaries?
The onset of ovulation is a process that is regulated by special hormones. These hormones are produced by the pituitary gland. As a rule, a violation of their synthesis leads to anovulation.
With amenorrhea, the level of progesterone in the female body decreases, the so-called corpus luteum phase does not occur, and pregnancy becomes impossible.
Signs of ovarian dysfunction:
- irregular and “floating” cycle, scanty or excessive bleeding;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- infertility, miscarriage, history of miscarriages, difficulty conceiving;
- severe premenstrual syndrome;
- irritability, apathy, emotional lability;
- amenorrhea (disappearance of menstruation for a period of 5 months or more).
Any of these symptoms is an alarming signal that reminds you that it’s time to take care of your own health. At the slightest suspicion of anovulatory dysfunction, you should visit a gynecologist-endocrinologist. The doctor will prescribe a comprehensive examination to exclude the presence of concomitant diseases and prescribe the optimal course of treatment.
Fallopian tube HSG: is the procedure painful? The consequences and complications of fallopian tube HSG are discussed in our article. You will learn about how chlamydia manifests itself in women from this article.
Causes of ovarian dysfunction
Ovarian dysfunction is primarily a consequence of the fact that the hormones prolactin and estrogen are not normal. The first thing a woman needs to do is get tested to determine her hormonal levels, and after that we can talk about the causes of the pathology that has arisen.
As a rule, ovarian dysfunction is caused by processes such as:
- Inflammation of the ovaries, appendages or uterus. Similar inflammatory processes occur in a woman’s body when the hygiene of the genital organs is impaired, as well as infection of the vagina through sexual contact with a partner. The infection can also enter the uterus through the blood through the intestines;
- Tumor of the ovaries and uterus - endometriosis, fibroma, malignant tumors;
- Disturbances of the endocrine system;
- Excessive body weight;
- Diabetes;
- Nervous exhaustion, constant stress, depression;
- Abortion during the first pregnancy;
- Violation of the location of the intrauterine device;
- Drug therapy;
- A fundamental change in environmental conditions is a change in climate.
What examination is needed?
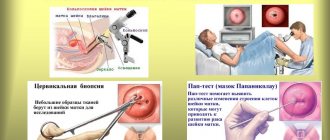
First of all, the specialist must find out whether the patient has cancer or surgical intrauterine pathologies. To recognize a disease in medicine, the following procedures are used:
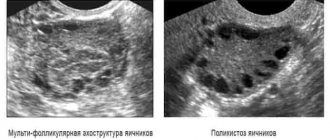
- Ultrasound of the uterus, mammary glands and thyroid gland;
- PCR tests to determine STDs, vaginal smear to determine the composition of bacterial microflora;
- blood test for prolactin, progesterone, estrogen, luteinizing hormone;
- blood test for thyroid hormones;
- in some cases, brain tomography is prescribed if there is a suspicion of a pituitary tumor;
- hysteroscopy with curettage of the uterus, as well as further histological examination of tissues taken for analysis.
The diagnostic scheme for each patient will be strictly individual, as it depends on the personal history.
If you have diagnosed dysfunction and ovarian amenorrhea, you should regularly visit a gynecologist. Control examinations will help monitor the condition of the patient’s reproductive system and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment measures.
Diagnostics
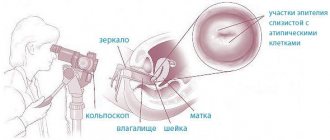
The patient is examined and treated for ovarian dysfunction by a gynecologist-endocrinologist. If ovarian dysfunction is suspected, first of all, surgical pathology – ectopic pregnancy and tumor processes – is excluded. The menstrual calendar is analyzed, complaints are listened to, a gynecological examination is performed and a diagnostic plan is drawn up.
The set of diagnostic procedures may include:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, pelvic organs and adrenal glands;
- microscopy and culture of vaginal secretion flora;
- PCR diagnostics to exclude sexually transmitted infections (ureaplasmosis, candidiasis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.);
- determination of the level of sex hormones (follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, prolactin, progesterone and estrogens) in the blood and urine;
- blood test for the level of hormones secreted by the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- X-ray examination of the skull, CT scan of the brain and MRI of the brain to exclude lesions of the pituitary gland;
- EEG of the brain in order to exclude the possibility of pathological processes occurring in it;
- hysteroscopy with targeted biopsy of the cervix or diagnostic curettage of the cervical canal and uterine cavity for histological examination of endometrial areas.
The examination plan is drawn up individually based on the patient’s complaints and examination. How to treat ovarian dysfunction is determined by the doctor taking into account the clinical picture and characteristics of the patient’s body.
The success of disease correction is largely determined by the severity of the disorder, therefore any irregularities in the menstrual cycle should cause alertness and prompt a woman to undergo examination, regardless of her age. Ovarian dysfunction in the premenopausal period is no less dangerous than in reproductive age. When diagnosing the disease, in order to avoid complications, regular monitoring by a gynecologist-endocrinologist is recommended. Even if there are no changes in the patient’s condition, it is recommended to undergo examinations 2-4 times a year. Menopausal ovarian dysfunction, if uncontrolled by a doctor, increases the risk of developing cancer.
Ovarian dysfunction and pregnancy
Ovulatory dysfunction significantly complicates pregnancy planning.
Due to impaired ovarian function, pregnancy may not occur for a long time, making it much more difficult for a married couple to conceive a child. The resulting pregnancy should also be monitored by a doctor who assesses the dynamics of the patient’s condition, regularly conducts ultrasound monitoring, and also monitors the results of blood tests for the content of sex hormones, on the basis of which hormonal drugs are prescribed.
Modern treatment methods allow a woman with ovulatory dysfunction to successfully become pregnant, carry the pregnancy to term without complications and give birth to a healthy child. All this is possible subject to careful and attentive monitoring of pregnancy from the first month.
Treatment
When ovarian dysfunction is diagnosed, not only a gynecologist, but also an endocrinologist needs to get involved in treatment.
As a rule, if the indications are urgent, then the fight against pathology initially takes place in the hospital.
They are admitted to the hospital when there is heavy bleeding.
It is then customary to begin the treatment process with alleviation of the patient’s general condition.
There are two types of hemostasis: surgical and symptomatic. The latter includes taking various hormonal medications.
Important! The surgical method is used only in cases of heavy bleeding that threatens the patient’s life.
After the operation, the following stages of treatment are carried out:
- histological scraping is studied,
- Until the bleeding stops completely, doctors prescribe symptomatic therapy, including hormones. All this is combined with OK and physiotherapy to achieve a more significant effect,
- Next, you should move on to the prevention of bleeding. Typically, from 16 to 25 DC, drugs are used whose main active ingredient is progesterone,
- Along with this, anemia is prevented,
- The final phase of treatment is characterized by taking various drugs and OK.
When the bleeding stops, doctors begin to treat the underlying cause of ovarian dysfunction. In particular, if inflammatory diseases or genital infections are diagnosed, antibiotics are prescribed. After them, ovulation is restored on its own.
Extragenital pathology requires correction of found diseases, such as thyroid problems and diabetes. If ovarian dysfunction is influenced by external factors, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- proper nutrition,
- providing emotional peace,
- compliance with the work and rest schedule,
- taking vitamins according to the phases of the cycle,
- moderate physical activity.
Pathology caused by a tumor, fibroid, cyst or endometriosis is treated depending on each individual case.
Important! It is prohibited to install an intrauterine device in women who have undergone treatment for ovarian dysfunction.
Folk remedies
In the fight against such problems, an effective remedy is tincture of boron uterus.
During the period of lack of medicine, it was she who helped women get rid of many pathologies, and even get pregnant.
For treatment, you can use exclusively the components of the above-ground part of the corresponding herb.
Popular recipes:
- Over the course of a month, 50 grams of the dry component are infused in 500 ml of alcohol. This tincture is subsequently filtered and the juice is squeezed out. It is taken 30 drops diluted in a small amount of drinking water,
- the second type of decoction is used for douching. A tablespoon of crushed boron uterus is infused for 30 minutes in a glass of boiling water. Then the product is available for use.
You can improve the functioning of the ovaries with the following folk remedies:
- infusion of sweet clover and coltsfoot herb. The components are crushed and combined in a ratio of 10:1. You need to infuse a tablespoon in a glass of boiling water. Take 150 ml three times a day,
- wintergreen. Leaves are poured into a half-liter jar and filled with vodka. All this is settled for two weeks. Then the tincture is taken three times a day, 50 grams,
- Potentilla goose. 2 tablespoons of the component are infused in 0.5 liters of boiling water. One glass is taken three times a day.
It is worth remembering that the use of folk remedies must be combined with elements of traditional medicine. Otherwise, the patient will not be able to restore ovarian function.
How to treat ovarian dysfunction?
Only a doctor can prescribe drugs for the treatment of ovarian dysfunction, since the treatment regimen directly depends on the initial reasons that caused the disruption of the ovulatory cycle.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, accompanied by the prescription of hormone-containing drugs and regular ultrasound examinations. If a woman has chronic infections, they also require urgent treatment.
Treatment of ovarian dysfunction with duphaston and utrozhestan is widespread. With the help of these drugs, millions of women successfully restore the ovulatory cycle and wait until pregnancy occurs.
To generally strengthen the immune system, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes to patients, designed specifically for women suffering from cycle disorders (Cyclodinone, Lady's Formula).
How effective is herbal treatment for breast cysts? Main symptoms and signs. Pregnancy after removal of an endometrial polyp. Read more
Modern methods for diagnosing cervical ectopia. Removal of cervical erosion with laser /prizhiganie-erozii-sheyki-matki
Symptoms of dysfunction
A number of characteristic symptoms indicate that a woman has ovarian dysfunction. First of all, this is a violation of the regularity and duration of the cycle.
With normal ovarian function, the level of estrogen in a woman of childbearing age gradually decreases towards the middle of the cycle, and the level of progesterone increases. Thanks to this, the endometrium develops normally in the uterus and a healthy egg is formed, ready for fertilization. If conception does not occur, then menstruation occurs in a timely manner, lasting 3-5 days and volume 40-80 ml. Dysfunction leads to a sharp change in hormone levels, which can lead to uterine bleeding between menstruation. It can be so intense that a woman needs emergency medical attention to stop it. Large blood loss is life-threatening.
Lack of estrogen leads to a shortening of the first phase of the cycle and a reduction in its length. Menstruation begins to come randomly and more often than after 21 days. Excess estrogen leads to a lack of ovulation and significant delays in menstruation. One of the possible consequences of ovarian dysfunction is amenorrhea - the complete cessation of menstruation in a woman of reproductive age (for six months or more).
Insufficient production of progesterone makes it impossible to maintain pregnancy and carry the fetus to term. At the same time, the woman’s periods become longer and more abundant. Blood loss leads to symptoms of iron deficiency in the body (dizziness, weakness, nausea, headache).
An excess of the hormone causes a prolongation of the second phase of the cycle and indicates abnormal development of the corpus luteum that produces it. This condition is characterized by the appearance of migraines, swelling and tenderness of the mammary glands, depressive mood, and decreased sexual activity.
Both an excess and a deficiency of female sex hormones may cause symptoms such as a feeling of constant fatigue, allergic skin reactions in the form of itching and rashes, blurred vision, and a drop in blood pressure. With ovarian dysfunction, neurological disorders occur: insomnia, pain in the heart, causeless mood swings. There is excessive growth of body hair, deterioration in the condition of the skin, hair, and nails.
Complications of ovarian dysfunction
Menstrual irregularities and scanty periods are a pathology that does not pose an immediate danger to human life. However, in the absence of timely treatment, impaired ovarian function can lead to serious consequences and complications, including complete impairment of reproductive function.
If dysfunction is not treated on time, the risk of the following pathologies increases:
- infertility;
- mastopathy;
- fibroids;
- breast and cervical cancer;
- autoimmune thyroiditis.
What are the chances of getting pregnant?
If the diagnosis of ovarian dysfunction was timely, and the specialist immediately prescribed the correct treatment, then the chances of complete restoration of the menstrual cycle reach 80%, and in this case, pregnancy may well occur. In case of serious disorders, positive results are temporary, but if, after stabilizing the condition, you immediately begin trying to conceive, you can soon become parents.
If restoring the functions of the appendages is impossible, then in this case one should not despair. It is worth seeking advice from a reproductive specialist and considering the advisability of using assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization.
With ovarian dysfunction, a woman can not only completely forget about the symptoms of the disorder, but also solve the problem and become a mother. To get pregnant and live a full life, consult a doctor on time and start treatment.
(votes: 2, rating: 5.00 out of 5)
Share the news on social networks
Ask a Question! You have questions? Feel free to ask any questions! And our staff specialist will help you. Go>>
- Recommended Articles
- Vaginal acidity: when to sound the alarm
- How to treat acute and chronic cervicitis?
- Inflammation of the uterus
« Previous entry
Prevention
In order to avoid such problems, doctors recommend that women avoid stress and nervous strain, maintain a healthy diet, observe sanitary and hygienic standards, and avoid promiscuity.
Moderate physical activity and proper nutrition are important factors that contribute to the normalization of metabolic processes, and therefore the normalization of hormonal levels. Any hormonal medications should be taken only after consulting a doctor.