Oligomenorrhea can occur for various reasons and is manifested by scanty menstruation, between which there is a time interval of 40 or more days. Contrary to popular belief, this process cannot be considered a variant of the norm and requires a high-quality approach to diagnosis and treatment.
- 2 Classification of the disease
- 3 Reasons for the development of pathology and provoking factors
3.1 Video: why women lose their periods
- 5.1 Photo gallery: diagnostic methods used to determine oligomenorrhea
- 6.1 Folk remedies
What is oligomenorrhea
A pathological condition such as oligomenorrhea is one of the types of menstrual cycle disorders. Otherwise, the disease is often called hypomenorrhea, when it manifests itself with very scanty bleeding during menstruation, or spaniomenorrhea, if menstruation becomes rare. Oligomenorrhea can be characterized by a complex of disorders or the presence of one of them. With this type of disease, menstruation may occur once every few months. Their duration is reduced to two days and can lead to a complete absence of menstruation.
The regular menstrual cycle changes every month
Treatment of oligomenorrhea
With oligomenorrhea, it is necessary to treat not the menstrual disorder itself, but the disease that led to it.
For infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the reproductive system, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy , drugs that enhance local immunity in the genitals, vitamin complexes, homeopathic remedies, and physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated. After such a course of treatment, the menstrual cycle, as a rule, is immediately restored.
For abnormalities and injuries of the genitals, surgical treatment is performed. If the cause of oligomenorrhea is problems with the hypothalamic-pituitary system, it is necessary to treat these diseases - in case of pituitary adenoma, surgical intervention is carried out; in case of insufficient production of hormones, regulators of the functioning of the gonads, hormone replacement therapy is prescribed.
In addition, patients with oligomenorrhea should follow the recommendations of doctors regarding lifestyle, nutrition and physical activity:
- Get enough sleep.
- Have a full rest.
- Control your weight (if you are overweight, you need to lose weight, but if a girl or woman is too thin, you should increase the calorie content of your daily diet).
- Eat foods rich in vitamins.
- Do not smoke or abuse alcohol.
- Be a physically active person.
If the cause of oligomenorrhea cannot be identified and eliminated and if recommendations for lifestyle changes also do not produce positive results, women are shown hormonal therapy aimed at stabilizing the menstrual cycle. For those who do not plan to give birth in the near future, a combined oral contraceptive is selected or a course of progesterone is prescribed. Well, patients who want to get pregnant undergo drug stimulation of ovulation and preparation of the endometrium for implantation of the fertilized egg. If a woman suffering from oligomenorrhea approaches the issue of pregnancy responsibly and follows all the gynecologist’s prescriptions, natural conception and the birth of an absolutely healthy child are quite possible.
Important: trying to independently normalize the duration of menstruation with drugs that were once prescribed by a doctor to someone you know is extremely thoughtless and even dangerous, since such actions can provoke the appearance of heavy uterine bleeding and other serious complications.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical observer, epidemiologist
11 total today
( 58 votes, average: 4.66 out of 5)
Atrophic vaginitis: symptoms and treatment
Ovarian wasting syndrome: causes, diagnosis, symptoms and treatment
Related Posts
Classification of the disease
There are several types of oligomenorrhea:
- The primary form is more common in teenage girls during the formation of the menstrual cycle. If treatment is not carried out during this period, the pathology persists into reproductive age.
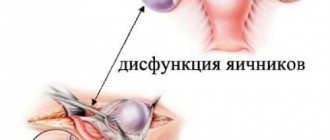
- The secondary form occurs after a normal menstrual cycle has been established. Its development is based on various disorders in the chain of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries.
Disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamus often lead to various disruptions in the normal production of hormones
When, after the necessary research methods, it is difficult to identify the form of pathology, a diagnosis of unspecified oligomenorrhea is often made, which complicates treatment.
Forms of the disease
The diagnosis in the medical history necessarily contains an additional definition: primary or secondary oligomenorrhea. They are caused by various reasons. Primary oligomenorrhea is detected in teenage girls at the onset of menarche (first menstruation). Signals about the occurrence of this pathology are both the establishment of regular menstruation for too long, and their absence at the appropriate age.
Often this reveals infantilism (underdevelopment) of the uterus; in most cases, a hereditary predisposition to it is determined. Conception during infantilism is almost impossible. It is necessary to begin treatment with a specialist immediately after identifying the cause.
The secondary form develops in adult women for the reasons mentioned above and is called pathological oligomenorrhea. And those disorders that precede natural age-related menopause and are associated with the decline of ovarian function are usually called functional, physiological.
With primary oligomenorrhea in adolescents there is no regularity of the menstrual cycle
Causes of pathology development and provoking factors
One of the main factors in the occurrence of the primary form of the disease is the abnormal intrauterine development of the girl. Congenital anomalies occur due to underformation of the uterus. The development of secondary pathology, in particular due to a disorder in the main circuit of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries, occurs for the following reasons:
- acute infections;
- inflammatory diseases;
- tumors of various etiologies;
- abortions;
- severe weight loss;
- poor environmental conditions;
- change in climatic conditions;
- a lot of stress.
Oligomenorrhea is rarely an independent disease and is often combined with:
- with endometriosis;
- with polycystic ovary syndrome.
One of the provoking factors of such menstrual cycle disorders is endometrial curettage, as well as the period before menopause.
Poor estrogen production as a result of many disorders leads to oligomenorrhea
Video: why women lose their periods
Diagnostics
The doctor makes a diagnosis after asking the patient about the regularity of the menstrual cycle and complaints, and conducting a general and gynecological examination - functional, instrumental and laboratory. As additional measures, basal temperature is measured and a graph is created. The patient undergoes a transvaginal pelvic ultrasound. It is also necessary to donate blood for sex hormones and study the patency of the fallopian tubes. It is also recommended to consult a psychotherapist or psychologist, because mental state also plays a serious role in the functioning of the reproductive system.
Symptoms of oligomenorrhea
This pathology is often accompanied by a whole range of symptoms:
- short and scanty menstruation;
- rapid weight gain;
- presence of acne;
- excessive hair growth;
- the presence of developed muscles;
- decreased libido;
- frequent lack of ovulation.
Oligomenorrhea is also characterized by the appearance of a woman, who often becomes similar to a man in physique.
Scanty and infrequent menstruation may be accompanied by a decrease in libido
Types and causes of oligomenorrhea
Taking into account the period and causes of hypomenstrual syndrome, primary and secondary oligomenorrhea are distinguished.
Primary oligomenorrhea occurs during the first menstruation (menarche), when the menstrual cycle is just beginning to form in teenage girls. The following factors can cause primary oligomenorrhea in a teenager:
- pathologies of development of the reproductive organs (infantilism, genital anomalies, etc.);
- ovarian dysfunction resulting from malfunction of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- low body weight. The genital organs can function fully only if there is a sufficient amount of fatty tissue. The lack of fat leads to disturbances in the reproductive system and disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Secondary oligomenorrhea develops in women with an individually formed menstrual cycle. The following factors can provoke the occurrence of this type of hypomenstrual syndrome:
- chronic infectious, inflammatory pathologies of the genital organs;
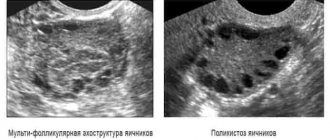
- ovarian dysfunction arising from polycystic disease;
- tumor neoplasms of the pituitary gland;
- hormonal imbalance;
- injuries of the appendages, uterus;
- hypovitaminosis (deficiency of vitamins and nutrients in the body);
- sudden weight loss (dystrophy) or excessive weight gain (obesity);
- complications of previous gynecological procedures (therapeutic endometrial curettage, abortion, etc.).
The cause of short and rare menstruation at any age can be frequent stress and psycho-emotional stress, physical fatigue, the negative impact of occupational factors, taking hormonal medications and oral contraceptives.
In some cases, oligomenorrhea is considered a physiological condition, occurring against the background of certain processes. Short-term and scanty menstruation is considered the norm in women of premenopausal age (after 40 years) and teenage girls (in the absence of pathologies contributing to the development of primary oligomenorrhea). In adolescence, manifestations of hypomenstrual syndrome can last more than a year - this is exactly how long it takes to stabilize the cycle. Also, the appearance of oligomenorrhea is typical for women during lactation.
Diagnostic tests
Diagnosis of oligomenorrhea involves an integrated approach to research. First of all, if you discover such disorders in yourself, you should contact a gynecologist, who, as a rule, defines the pathology as follows:
- Patient interview. An anamnesis is collected, factors that could provoke pathological changes are taken into account. The lifestyle and the presence of concomitant diseases are determined.
- Gynecological examination. Allows you to visually determine the condition of the cervix and palpate the ovaries.
- Blood sampling to study the degree of deviation from the norm of hormones affecting the menstrual cycle:
- estrogen;
- progesterone;
- follicle-stimulating;
- testosterone;
- luteinizing;
- prolactin.
- Ultrasound of the reproductive organs. It is carried out to detect abnormal areas and various gynecological diseases that could provoke menstrual irregularities.
Photo gallery: diagnostic methods used to determine oligomenorrhea
Questioning the patient plays a decisive role in identifying negative factors
A gynecological examination using a colposcope allows you to see a detailed picture of the condition of the cervix
A blood test determines the deviation of hormone levels from the norm in a certain phase of the cycle
Ultrasound examination reveals diseases of the reproductive system
Symptoms of the disease
Deviation from the norm is not accompanied by a pronounced deterioration in health, intoxication, or loss of ability to work. And yet, carriers of this pathology have many problems that set them apart from their environment, create difficulties in society, and bring grief:
- 80% of women suffering from oligomenorrhea are overweight, which is difficult to adjust due to hormonal imbalances;
- if the pathology formed in adolescence, then it is likely that the body type is male - with a developed torso, narrow hips and strong muscles;
- in a quarter of women with this diagnosis, hirsutism is also possible - increased hair growth on the face and chest;
- characterized by the presence of acne on the skin of the head, back and chest, due to the increased function of the sweat and sebaceous glands;
Women with oligomenorrhea are overweight
- decreased libido;
- the voice deepens;
- emotional instability is expressed;
- Fluctuations in blood pressure provoke headaches and dizziness.
These symptoms reduce the likelihood that if you want to have a child, you will conceive without treatment. Spontaneous pregnancy occurs in only 20% of women with such symptoms.
How to treat the disease
The treatment of oligomenorrhea is always approached in a comprehensive manner. Main methods of therapeutic intervention:
- Use of medications. Most often, hormonal drugs containing synthetic estrogens are prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle. Such drugs promote the growth of the endometrium and cause regular bleeding. Oral hormonal contraceptives are often prescribed, which improve the course of the menstrual cycle. When taken, periods become regular. Most often prescribed: Regulon, Lindinet, Novinet, Silhouette and others.
- Physiotherapeutic approach. Thanks to a set of stimulating procedures, it is often possible to stabilize hormonal levels. However, this method is good in combination with medications. Electrophoresis is often prescribed, with the help of which medicinal components penetrate into the tissue under the influence of alternating current. For the same purposes, ultrasound and laser are often used as conductors. Thanks to copper and zinc ions, in some cases it is possible to awaken the ovaries and regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Surgical intervention. Indicated for polycystic ovaries and other benign pathologies of endometrial tissue: polyps and cysts. Using a laparoscope, the doctor gets to the pathological area and removes it. A healthy zone is formed in its place. For accessible areas, the radio wave method, laser beam and cauterization using electric current are more often used.
Hormonal contraceptives help compensate for the lack of estrogen
General recommendations for additional treatment are as follows:
- Review of diet. It is recommended to eat foods that can stimulate the production of estrogen: lentils, beans, peas. Introduce more fresh vegetables and fruits into your diet. Reduce the amount of foods that increase testosterone production: fatty and fried foods, as well as fast food.
- Gynecological massage and acupuncture. A good combination in the treatment of oligomenorrhea is massage and acupuncture. These two methods help improve blood circulation. Massage helps remove congestion and stimulates the ovaries. Using various massage manipulations, the doctor carefully influences the reproductive organs. Acupuncture has a positive effect on all body systems and normalizes hormonal levels.
- Gymnastics. In addition to this, it is very beneficial to exercise and lead an active lifestyle. Light gymnastics or yoga will do. You should not engage in strength training during the period of illness.
Acupuncture regulates the production of all hormones in the right quantities, excluding their pathological excess or deficiency
Treatment of teenage girls is most often carried out with the use of vitamins that help correct the menstrual cycle. Most often, Aevit, Magnesium B6, Cyclovit, etc. are prescribed. At an early stage, oligomenorrhea can be corrected much more easily than with the development of a secondary form of the disease.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes for the treatment of oligomenorrhea are used only as an auxiliary therapy. It is recommended to consult a doctor before using these products.
One of the effective recipes is considered to be a decoction based on chamomile, grated acorns and shepherd's purse. For preparation you will need the listed raw materials in equal quantities, 1 tsp each. The finished mixture should be poured into 1 liter of hot water and placed on the stove. Bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 10 minutes. After this, the broth should be cooled and taken 3 tbsp. l. 3 times a day for 10 days.
In order to prepare the following remedy, you will need 100 g of Rhodiola rosea roots. They must first be crushed and poured into a glass jar. Then pour one bottle of vodka and leave to infuse in a dark place for 14 days. Then the finished product needs to be filtered. The tincture should be taken 3 times a day, 25 drops for two weeks.
The next recipe will require cherry and raspberry leaves. There are 10 sheets in total. They should be filled with 0.5 liters of boiling water and allowed to stand for about 30 minutes. Then take a quarter glass 3 times a day for 10 days.
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs are an excellent way of adjuvant therapy
Causes
- the main reason for the progression of primary oligomenorrhea is congenital defects of the woman’s reproductive system, which began to develop in the embryonic period;
- The causes of secondary oligomenorrhea are disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary structures, ovaries or uterus, which began to progress as a result of previously suffered inflammatory diseases, tumor diseases. This can also occur as a result of injuries to the female genital organs, anorexia, exhaustion, changes in climatic conditions, etc.;
- decreased secretion of sex hormones;
- a common cause of progression of oligomenorrhea is endocrine disorders in the thyroid, pancreas and adrenal glands;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- endometriosis;
- uterine hypoplasia;
- abortions and mini-abortions;
- operations on the uterus;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- oligomenorrhea can develop against the background of diabetes mellitus or thyroid diseases;
- The development of oligomenorrhea is also caused by the use of antiepileptics and antipsychotic drugs.
Risk group:
- girls in adolescence;
- young women actively involved in sports;
- women who have eating disorders such as bulimia and anorexia.
Treatment prognosis, complications and consequences
The prognosis of treatment depends on the severity of the pathology. With an integrated approach to therapy, it is possible to obtain good results and restore the menstrual cycle. Complications of oligomenorrhea are:
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- osteoporosis;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- endometrial cancer.
Prolonged oligomenorrhea can lead to persistent infertility, which is difficult to correct.
A woman's inability to bear children is a common cause of discord between spouses.
Clinic and diagnostics
Oligomenorrhea itself, as a pathological condition, does not bring any inconvenience to the patient; on the contrary, women see a lot of advantages in this. In fact, menstruation, which lasts 1-2 days and is accompanied by a small amount of blood, indicates that the endometrium is not growing well in the uterus. And if it does not gain the required thickness from cycle to cycle, there is a high probability that the fertilized egg will not be able to firmly establish itself in the uterus, that is, the desired pregnancy will not occur.
In addition, hypomenstrual syndrome, and oligomenorrhea in particular, is quite often accompanied by a violation of the ovulatory function of the ovaries (ovulation occurs extremely rarely or does not occur at all) and a decrease in the synthesis of estrogen in the body. That is, in fact, patients develop changes characteristic of the premenopausal period. For young women, the described reproductive dysfunctions are fraught with serious problems:
- Premature aging.
- The occurrence of cardiovascular diseases.
- The development of osteoporosis, pathologies of the joints and spine.
- Emotional lability.
- Decreased libido.
- Increased body weight.
Thus, oligomenorrhea and hypomenstrual syndrome without qualified medical care can transform into difficult to treat infertility and premature menopause - conditions that are extremely undesirable for women of childbearing age. Therefore, if menstrual irregularities such as oligomenorrhea appear, you should definitely undergo a comprehensive examination, including:
- Consultation with a gynecologist.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Hormonal profile study.
- Tests for sexually transmitted infections.
- If indicated , hysteroscopy, diagnostic endometrial curettage, detailed study of the condition of the hypothalamic-pituitary system and other studies.