What it is?
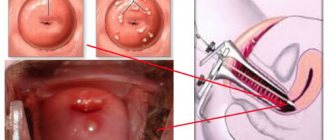
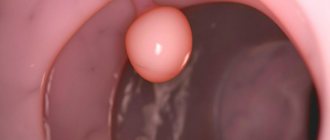
Photo of cervical leukoplakia
Cervical leukoplakia is an atypical change in the epithelium covering the cervix. Another name for the disease is cervical hyperkeratosis.
When visually examining the cervix, the doctor sees a white, dense spot or multiple spots. This explains the name of the disease, which comes from the Greek phrase “white plaque.”
The disease belongs to the group of background precancerous ones - if leukoplakia is not treated and observed, then gray and white plaques degenerate into malignant tissue.
How common is it?
Statistics vary depending on the country - the disease occurs from 1.1% to 12.5% of cases of all identified gynecological pathologies.
REFERENCE The reasons for the degeneration of plaques into a tumor and the reason for the appearance of the tumor itself are difficult to diagnose, and for this reason treatment is complicated.
ICD-10 code: other non-inflammatory diseases of the cervix (N88), the code excludes any inflammatory diseases, including polyps.
Main causes of the disease
The main causes of cervical leukoplakia include:
- malfunctions of the immune system (decreased ability of the body to resist the negative effects of environmental factors);
- mechanical and chemical injuries as a result of the birth process and medical procedures;
- changes in the functions of the endocrine glands;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- dysfunction of the uterine appendages, accompanied by disruption of the monthly cycle and lack of ovulation;
- damage to the epithelial layer of the cervix.
As a rule, the disease develops against the background of several causes that aggravate each other.
Based on the form, cervical leukoplakia is divided into simple and proliferative. Simple is characterized by an increase in the thickness of the epithelium. In this case, the changes do not affect the basal and parabasal layers.
With the development of the proliferative form, compactions are found in all layers of the cervix. Such changes are regarded as a precancerous condition.
Classification
Gynecologists distinguish the following forms of focal leukoplakia:
- Simple or flat - this is the initial stage of the disease; plaques in this form are small, smooth, light or grayish, and do not protrude above the surface of the mucosa. They are easy to miss during visual inspection.
- Verrucous, or warty, is considered the second stage of the disease, in which gray or white plaques and growths are layered on top of each other. Upon visual examination, the pathological lesions rise above the mucous membrane, the neck looks uneven, covered with tubercles.
- Erosive - cracks and damage appear on the altered tissues.
After the disease is detected, pieces of tissue must be submitted for histological examination. Histological examination makes it possible to understand whether the patient has a simple form of leukoplakia or with atypia, that is, with cells prone to transformation into cancer.
Reasons for the development of leukoplakia
The causes leading to the onset and progression of the disease are divided into exogenous and endogenous.
Doctors consider hormonal disorders to be endogenous - in particular, a sharp lack of progesterone, due to which anovulation is constantly observed.
Due to such pathological conditions, hyperplastic processes begin in the female genital organs.
Exogenous factors are divided into:
- chemical;
- infectious;
- traumatic.
Signs of hyperkeratosis
Symptoms of pathology depend on the stage of development:
- with primary, poorly visible leukoplakia, there are most often no symptoms at all;
- with the warty form, the patient may experience periodic burning, itching and discomfort;
- with erosive discharge outside the cycle, small bloody or purulent discharge may appear on the underwear.
IMPORTANT If you have even mild symptoms, you should see a gynecologist as soon as possible - in addition to leukoplakia, such symptoms may indicate other unpleasant diseases of the female genital area.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia directly depend on its type. With focal or simple leukoplakia, signs of pathology may not be observed. Discomfort and burning are observed with the warty form.
The symptoms manifest themselves most clearly with erosive leukoplakia. Ich oozes from the affected area. It is released more abundantly after sexual intercourse. If the plaques spread to the vulva area, then the patient begins to feel burning and itching.
This leads to scratches, cracks and abrasions. But the appearance of such symptoms can also be observed with other diseases of the internal and external genital organs. Therefore, if they occur, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnostics and an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis begins with a basic examination using speculum by a gynecologist. It is during the examination that the doctor most often discovers white or grayish plaques and plaque. After detecting the disease, the doctor prescribes the following tests:
- colposcopy, which allows you to identify the size, shape and extent of tissue damage;
- tests for hidden infections: human papillomavirus and herpes;
- cytological examination of a smear, in which a scraping is taken from the affected tissue;
- hormone tests showing progesterone levels;
- in cases of suspected cancer, a biopsy is performed to 100% exclude or confirm the presence of cells that have degenerated into malignant cells.
PAY ATTENTION It is necessary to find out that the detected pathological process is leukoplakia, and not thrush or specific erosion of the cervix. For this purpose, additional research is being carried out.
Diagnosis and treatment of leukoplakia
Diagnostics
A doctor usually diagnoses leukoplakia by ruling out all other potential causes. This often includes a physical examination and review of your medical history. If leukoplakia is suspected, a biopsy will likely be done to rule out cancer.
The following types of biopsy are usually performed:
- Oral biopsy
: A small rotating brush collects cells from the mouth for examination. - Excisional biopsy
: Plaques are surgically removed for examination. An ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist is often involved in treatment and monitoring.
Treatment
If no cancer is found, the treatment recommended in most cases is to eliminate the factors contributing to the irritation. Good oral hygiene is also recommended. If the plaques do not improve with treatment, they can be removed by a doctor using a scalpel.
Follow-up appointments with your doctor are often recommended for monitoring, as recurrences of leukoplakia occur.
If diseases such as HIV are present, antiviral drugs may be prescribed.
If precancerous or cancerous cells are found, additional monitoring measures are needed to determine the extent of the condition. Treatment is based on the type of cells present. Although difficult to estimate accurately, about 5 percent of oral leukoplakia cases are thought to lead to oral cancer.
Leukoplakia and pregnancy
In some cases, hormonal imbalances and primary infections during pregnancy can lead to the initial form of the disease.
In this case, the doctor will prescribe additional tests to exclude the progression of the pathology, and will carefully monitor the patient throughout the entire period of gestation.
The risks for the baby include the possible development of an infectious disease, which can lead to congenital malformations and even fetal death.
To reduce the likelihood of disease progression and the development of infections, the gynecologist will prescribe regular vaginal sanitation and medications that will reduce the inflammatory process. Also during pregnancy, expectant mothers with a similar pathology are recommended:
- refuse salty and spicy foods;
- to walk alot;
- drink freshly squeezed juices, take vitamins;
- wear cotton panties, synthetics are excluded;
- carefully monitor hygiene;
- avoid hypothermia;
- try not to expose the body to additional stress.
In this case, the risk of cell malignancy will decrease, the disease will be under control and it can be treated after childbirth.
Does the disease prevent conception?
Primary and warty forms of leukoplakia in most cases do not interfere with conception. But, since during the period of hormonal changes in the body the disease can progress sharply, including creating a risk of cell malignancy, it is advisable to cure leukoplakia before planning pregnancy.
Leukoplakia of the cervix
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia
Removal of cervical leukoplakia involves the use of a whole arsenal of techniques, the most used of which are:
- cryogenic exposure;
- diathermocoagulation;
- high-intensity laser radiation;
- medicinal methods.
FSM often develops against the background of inflammatory processes in the vagina or vulva.
Therefore, before starting treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammation. For this purpose, antibacterial, antifungal, antichlamydial and antiviral drugs are used. During treatment, the patient must abstain from sexual activity for 4-6 weeks. The exact period depends on how quickly all damaged cervical tissue is restored.
If you are interested in how to treat cervical leukoplakia, then please note that this pathology is often considered as a benign process. However, it is worth noting here that the appearance of atypical cells during the study may still indicate a precancerous process. The doctor can give a final conclusion only after a biopsy. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you choose a clinic on our website and sign up for a diagnostic examination so that you can decide on a treatment regimen.
Chemical coagulants
In this group of drugs for the treatment of pathology, Solkovagin, consisting of a mixture of inorganic and organic acids, is primarily isolated. This drug has a coagulating effect on the epithelium. Moreover, the depth of its penetration into tissue can reach 2.5 millimeters. Treatment with this drug is completely painless, and its effectiveness is about 73%.
Diathermocoagulation
This is the most common and most frequently used method of getting rid of pathology. However, clinical studies show that, unfortunately, the method does not always give positive results. Moreover, it can cause a number of side effects:
- endometriosis;
- exacerbation of inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- pain syndrome;
- menstrual irregularities;
- relapse of the disease.
Cryotherapy
This treatment method is considered one of the most effective today, which is not at all surprising. It involves exposing pathological areas of tissue to an intense laser, which leads to their necrosis. The procedure is carried out contact-wise, in one go and quite quickly - in just 2-5 minutes. The advantages of cryotherapy are undeniable: the procedure is painless and carried out on an outpatient basis. However, this technique also has its drawbacks - a relapse of the disease is possible, especially if the menstrual cycle is disrupted.
Laser coagulation
A highly effective technique that allows painless, contactless, bloodless and aseptic coagulation of pathological tissue areas. At the same time, a thin film is formed on the surface of the tissue, which prevents the penetration of infections. This technique can even be used to treat extensive tissue damage to the uterus and vagina. In this case, laser coagulation of the cervix is first performed, followed by the removal of the epithelium itself.
It is also worth noting that in some cases it is not possible to do without surgical intervention. Namely, surgery will be needed if there is deformation of the cervix. To treat the pathology in this case, knife and laser conization, reconstructive plastic surgery, cone-shaped or wedge-shaped amputation of the cervix are used.
Of course, today medicine offers a large selection of methods for treating cervical leukoplakia. However, the choice of a specific method that is suitable in a given situation must be approached very carefully. In addition, you should know that none of the methods for treating pathology is perfect, so in many cases it is necessary to use combined treatment.
Complications
The main and most serious consequence of the disease is its probable degeneration into cervical cancer. If the pathology progresses, it enters the precancerous stage - a condition that is most likely to develop into cancer.
Therefore, patients with leukoplakia require constant medical supervision. If the lesions grow, doctors recommend removing sections of the changed tissue surgically.
Prognosis for recovery
In the case of proper treatment of leukoplakia, the disease can be completely cured in almost 100% of cases. If all concomitant diseases are treated, then relapse is excluded.
IMPORTANT There is a small probability of exacerbation of the disease and its transition to cervical dysplasia, which, in turn, often degenerates into cancer. Therefore, even small primary plaques need to be treated as quickly as possible, paying serious attention to the diagnosis and treatment of infectious and other concomitant diseases.
Etiology
The etiology of Leukoplakia is unknown. Its occurrence on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is facilitated by factors that have irritating properties and cause local inflammatory processes (for example, poor-quality dentures, damaged and protruding teeth, smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol, spices, etc.) - L. usually occurs in the vulva area due to involutional atrophy of the mucous membrane. L. can manifest itself as a kind of protective reaction to various, mainly exogenous, influences; of the endogenous etiological factors, dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract play a certain role. tract, vitamin deficiencies A and B (the whole complex). A hereditary predisposition to the development of L. cannot be ruled out. The influence of infectious and thermal factors should also be taken into account. L. can be a symptom of various chronic inflammatory processes, such as syphilis, tuberculosis, mycoses, etc.