What is transvaginal pelvic ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is a non-invasive diagnostic method. It is built on the principle of an echolocator sensor. The main element of the device generates an acoustic pulse. Its frequency is not detected by the human ear. The pulse, reaching the surface of the organ under study, is reflected from it. A sensitive sensor located on the handle detects it. The signals are recorded, processed by a computer and visualized on the screen as an image. The outlines of the organs are clearly visible on it. By studying them, the doctor can identify healthy and inflamed tissues, natural structures and tumors, and developmental abnormalities.
Advantages of the method
The described diagnostic examination allows monitoring the condition of the pelvic organs in real time. The emitted waves pass through tissues without disturbing the natural processes that occur inside them. The doctor receives accurate visualization. This is achieved by bringing the sensor as close as possible to the area of study.
The image is produced in 3D format; it can be used to study the blood flow and structure of OMT tissues.
Until recently, it was not possible to perform an ultrasound scan on women with urinary incontinence or other disorders of the genitourinary system. With the invention of transvaginal diagnostics, this problem was solved. The procedure is safe, painless, and has a small list of restrictions.
Transvaginal ultrasound procedure during pregnancy
Transvaginal ultrasound is performed exclusively in the early stages of pregnancy, in the first trimester.
This ultrasound diagnostic method allows you to determine an ectopic pregnancy, as well as check whether the fertilized egg has attached correctly, whether placental abruption is observed, or whether there is a threat of miscarriage.
This is the first ultrasound performed on pregnant women. In subsequent times, the abdominal method of examination is used.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is performed to diagnose the condition of the pelvic organs in women. The study is prescribed to identify urological and gynecological diseases, monitor their course and treatment results, as well as to determine the duration of pregnancy and exclude pathologies in the first trimester. TVUS today is the most accurate and informative method for examining the pelvic organs in women.
Indications and contraindications
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs with a vaginal sensor is used in cases where the abdominal method of studying the pelvic organs using ultrasound turns out to be ineffective. There are symptoms for which the doctor must prescribe a referral for the described type of diagnosis:
- pain in the lower abdomen, the appearance of which is not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- absence of menstrual bleeding;
- too long or too short a period between two periods;
- impossibility of pregnancy;
- bleeding not related to the cycle;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- the occurrence of severe weakness, nausea and vomiting with the onset of menstruation.
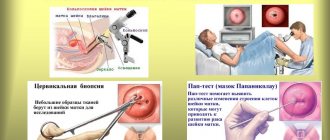
This type of diagnosis helps to identify the presence of tumor formations in the early stages, perform a biopsy and determine the etiology of diseases. Today it is actively used to diagnose infertility, to measure the size of the organs of the reproductive system, and to monitor the course of pregnancy in the first trimester. Using intravaginal pelvic ultrasound, you can monitor the condition of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
A method is actively practiced when the patient undergoes an abdominal and transvaginal ultrasound examination with two sensors. This diagnosis makes it possible to identify disturbances in the functioning of organs located high in the pelvis.
The described type of ultrasound is not used in the second and third trimester of pregnancy: a sensor in the vagina can provoke uterine contractions and early delivery. It is not suitable for women who are allergic to latex. Direct contraindications are virginity and epilepsy.
Indications for TVUS
Transvaginal ultrasound examination is prescribed for suspected diseases of the pelvic organs, emergency conditions, and also to assess the results of treatment. Indications for this diagnostic technique are:
- Severe pain during menstruation.
- Lack of menstruation or irregularity.
- Suspicion of hormonal imbalance in the body.
- The appearance of bleeding outside the menstrual cycle.
- Presence of symptoms of inflammation of the uterus or ovaries.
- Pathological changes in the endometrium: hyperplasia, polyps, chronic endometritis, submucosal nodes.
- Diagnosis of endometriosis of the uterus or adjacent organs.
- Determination of the presence of pathological fluids in the fallopian tubes.
- Suspicions of underdevelopment of the pelvic organs.
- Identification of neoplasms suspected during a gynecological examination.
- Diagnosis of neoplasms and tumor processes of the uterus and bladder.
- Detection of ovarian tumors and cysts.
- Suspicion of ruptured ovarian cysts.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract.
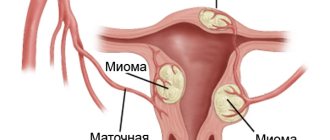
- Suspicion of uterine fibroids.
- Diagnosis of the causes of urological diseases, urinary incontinence and other urinary disorders.
- Determining the location of the intrauterine device.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
- Monitoring the condition of the endometrium with an intrauterine device installed or taking hormonal drugs.
- Inability to conceive for six months.
- Preparation for IVF and support of the procedure.
Transvaginal ultrasound allows a woman to know when she is ready to conceive a child. To do this, during a TVUS, a special substance is injected into the fallopian tubes, which, as a contrast, shows the patency of the tubes on the day of the study.
No other method, except TVUS, is capable of recording the baby’s heartbeat as early as the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy. Therefore, transvaginal ultrasound in early pregnancy can confirm the fact of successful conception.
Preparation for the procedure
To obtain objective results, the following requirements must be met:
- Before the procedure, you need to empty your bladder.
- For three days, experts recommend applying a diet and excluding from the diet foods whose absorption contributes to gas formation.
- With increased flatulence, it is important to take a drug in advance that will normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. You should consult your doctor about choosing a remedy.
The timing of the ultrasound is of great importance. If the procedure is prescribed for preventive purposes, it is better to do it immediately after the end of menstruation. To diagnose endometriosis, the second half of the cycle is selected. When it is necessary to track the dynamics of the development of a disease or the effectiveness of the treatment taken, examinations are carried out several times during one cycle: at the beginning, middle and end. There are no restrictions to determine the cause of bleeding not related to menstruation. When going for the procedure, it is important to remember to maintain personal hygiene.
When is a transvaginal ultrasound prescribed?
Transvaginal ultrasound is used to examine the pelvic organs in women
Transvaginal ultrasound diagnostics can be prescribed to women who have become sexually active. Main indications for transvaginal ultrasound:
- Bloody discharge between periods.
- Diagnosis of pregnancy.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Infertility.
- Abdominal pain.
If during a gynecological examination a woman experienced an enlargement of the uterus and appendages, as well as mass formations in the genital area, the gynecologist will prescribe a transvaginal ultrasound.
This study allows you to diagnose early ectopic pregnancy. Vaginal ultrasound is indicated before placing intrauterine devices, before performing in vitro fertilization. Transvaginal ultrasound should be performed annually as a preventive examination.
Often, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed to examine the bladder. This is an alternative method to catheterization or palpation. The study is prescribed for frequent urination, lower back pain, bladder injury, and the presence of blood in the urine. In some cases, this diagnosis will help determine the cause of urological diseases, urinary incontinence, and urethral pathologies.
In women with severe obesity, transabdominal ultrasound is difficult to perform, so transvaginal diagnosis is the best option.
In late pregnancy, ultrasound is prohibited, but there are a number of cases when diagnosis is necessary. Such cases are:
- Diagnosis of the location of the placenta and their anomalies.
- Assessment of the condition of the cervix.
- The condition of the uterine scar if there has been a history of childbirth or a cesarean section.
To prescribe ultrasound diagnostics in the later stages, there must be serious reasons for this.
Is preparation necessary?
For a reliable result, ultrasound should be done after the end of menstruation.
There is no special preparation for examining the reproductive organs using the transvaginal method. It is important to follow some recommendations to ensure that the results are reliable.
The examination is performed on an empty bladder, in contrast to transabdominal diagnosis, when the examination is performed through the abdominal wall. A few days before the ultrasound, you should stop eating foods that increase gas formation.
If you have increased gas formation, you should take Espumisan or Smecta. These medications will help reduce flatulence. You should remember what day is best to undergo the examination. Accurate data will be available after ovulation. For every woman, this happens in the middle of the cycle, around day 12-14. During this period, the woman’s body undergoes some changes and prepares for pregnancy.
It is best to conduct the study after the end of menstruation on days 5-8 of the cycle, but it can be done later.
For example, with endometriosis, it is better to conduct research in the second phase of the cycle. The timing of the study is discussed with the doctor. If spotting is observed regardless of menstruation, then the study is still carried out. During pregnancy, diagnosis is carried out only in the first trimester. In the future, transabdominal ultrasound is indicated due to the risk of miscarriage.
How is the examination carried out?
Transvaginal ultrasound is prohibited in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy
The process of examining the female genital organs using a vaginal sensor lasts about 20 minutes:
- The woman comes to the doctor at the specified time. Next, he undresses from the waist down and lies down on the couch.
- Legs are bent at the knees and slightly spread to the sides.
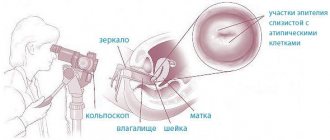
- The doctor places a condom on a special vaginal sensor and lubricates the tip.
- Then he inserts it into the vagina and begins to examine the reproductive organs. The transducer looks like a rod with a length of 12 cm and a diameter of 3 cm.
- An image is displayed on the screen and the doctor determines the necessary parameters and writes them down on a special form. The sensor can be rotated at different angles to obtain a clearer image.
- To evaluate the condition of the fallopian tubes, the doctor injects a contrast agent into the fallopian tubes. This procedure will allow you to examine the patency of the fallopian tubes. If necessary, during the examination the doctor takes pictures.
Transvaginal diagnostics are carried out absolutely painlessly; only unpleasant sensations arise, which quickly pass. At the end of the examination of the genital organs, the doctor makes a conclusion.
There are no absolute contraindications to the study, except that the girl is a virgin. Then ultrasound diagnostics is carried out through the abdominal wall. Vaginal ultrasound during menstruation is not prohibited if there are indirect reasons for this. In another case, it is recommended to wait until the critical days have passed and go for research.
Execution technique
Transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs proceeds as follows:
- The patient undresses from the waist down, lies on the couch, with her head towards the apparatus, and takes the position as for a regular gynecological examination.
- The doctor prepares the drug: puts an individual protective device on the handle - a condom for pelvic ultrasound, and generously lubricates it with a special gel.
- The sensor is inserted shallowly directly into the vagina.
- To get a complete picture, during an ultrasound, the doctor can move the handle from side to side and press on the abdominal area.
The examination lasts ten minutes. The woman does not feel any discomfort. The gel facilitates penetration of the sensor and reduces the likelihood of discomfort. When transvaginal ultrasound is performed correctly, there are no complications.
How is transvaginal ultrasound performed?
The patient should undress below the waist and lie with her back on a gynecological chair or couch, her legs should be bent at the knees and spread apart.
A clean condom is put on the sensor and lubricated with a conductor gel, which performs two functions: it eliminates the air space between the sensor and the organs, and serves as a lubricant for better penetration.
The vaginal sensor, or transducer as it is also called, is carefully and slowly inserted into the vagina. Due to the absence of sudden movements and the shallow depth of penetration, the procedure should not cause unpleasant or painful sensations in the woman; if a woman feels pain, she should tell the uzist about it. The organs being examined are displayed on the screen, and the doctor records the necessary data. The doctor can move the sensor in different directions, this will allow him to better see the size and structure of the organs being examined. The procedure lasts no more than 5 minutes.
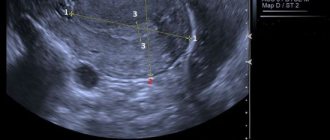
The information transmitted by the vaginal sensor is displayed on the monitor of the ultrasound machine in different projections, and scaling allows you to enlarge the image and examine the tissue fragment of interest in detail.
Decoding the results
Evaluation of the data obtained allows us to determine the following parameters:
- Dimensions of the reproductive organ. In a healthy woman, the length of the uterus is 6 cm, width 4.2 cm. Significant deviations from the norm indicate the presence of pathology.
- Echogenicity. Healthy organs have a homogeneous structure, clear boundaries, smooth edges. The uterus and ovary are clearly visible.
- The big picture. When performing a transvaginal ultrasound, the sensor helps to see the uterus, slightly tilted forward, a piece of the fallopian tube. Without the use of a contrast agent, they should not be clearly visible.
- The presence of fluid and pus in the uterus and fallopian tubes, caused by an infectious process.
- Mechanical damage: ligament ruptures, bruises.
- Excessive growth of the epithelium of the uterine walls (endometriosis), determine its volume, area of distribution.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Cysts and polycystic ovaries, tumors filled with fluid.
- Various polyps.
- Inflammatory processes leading to swelling.
- Bubble drift.
- Fetal development disorders.
- Defects of the reproductive system.
- Ectopic pregnancies.
- Cancer of the uterus, cervix and ovaries.
Using transvaginal ultrasound, it is possible to detect and diagnose chorionepithelioma, a malignant neoplasm that forms during or after pregnancy from the cells of the membrane of the embryo.
Types of ultrasound diagnostics in gynecology
At the MMC ON CLINIC, the following types of ultrasound can be performed any day of the week:
- Transabdominal. It is carried out using a sensor, which the doctor moves along the abdominal wall during the procedure. This study is most often used to monitor the condition of pregnant women and girls who are not sexually active. Before the procedure, the doctor applies a viscous gel to the skin, which ensures contact of the sensor with the skin and creates conditions for optimal visualization of the organ being examined.
- Transvaginal. During an ultrasound, a sensor is inserted into the vagina. This examination method is suitable for women who are sexually active, as well as for pregnant women in the first trimester. This study also uses a special gel.