With the normal functioning of the female body, from two to seven follicles are formed in the ovaries every month. As they develop, one (less often two) of them subsequently becomes dominant, overtaking the others in growth and oppressing them. If eight or more follicles mature at the same time, this phenomenon is called multifollicular ovaries (MFO). In fact, in most cases, this condition is not a serious illness and does not threaten the health and life of a woman, unlike polycystic disease, which an inexperienced doctor can easily confuse with a normal variant.
Symptoms of multifollicular ovaries
In the vast majority of cases, MFNs are discovered accidentally during a routine ultrasound examination based on the altered echostructure of the ovary. And yet, in some cases a woman may be bothered by:
- Disruptions of the menstrual cycle. Sometimes, due to pathology, amenorrhea (complete absence of menstruation for several cycles) may occur. A delay in menstruation occurs due to the fact that among many follicles, none becomes dominant, which means ovulation does not occur.
- Inability to become pregnant for a long period of time. It is worth considering that the diagnosis of “infertility” is made only after one year of continuous (2-3 times a week) open sexual activity.
- Increased amount of hair on the body.
- Acne.
- Decreased voice tone.
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, usually on one side.
Pashkova Alla Valerievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences.
Ask a Question
Fortunately, the above signs are recorded only in 5-7% of women with pathology.
Causes and signs of multifollicular ovaries
The causes of multifollicular ovaries most often do not pose a danger to the patient. The most common include:
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives as a means of preventing unwanted pregnancy. Any hormonal contraceptive helps suppress ovulation. The egg remains immature because the follicles do not have the opportunity to fully develop. Long-term suppression of the production of the luteal phase hormone causes the presence of a large number of follicles in the female reproductive glands. MFJ is diagnosed within 2-3 menstrual cycles after stopping taking contraceptives.
- Puberty.
- Disruption of the pituitary gland, expressed in a decrease or complete cessation of the production of luteinizing hormone.
- Significant psycho-emotional overload.
- Sudden weight loss or gain.
- Endocrine disorders, in particular diabetes mellitus, obesity, abnormalities in the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
- Breastfeeding period.
Important! ECHO signs of multifollicular ovaries are always determined during the first week of the cycle, which makes the study to confirm the diagnosis uninformative.
The multifollicular structure of the ovaries may be a genetic feature. In this case, there is no disruption of the processes of ovulation, conception and subsequent pregnancy.
If the reason for the simultaneous ripening of a large number of follicles is a low level of luteinizing hormone, then a sign of the condition becomes a menstrual irregularity. Menstruation does not begin for 6 months or more, which is explained by the lack of ovulation.
Quite often, MFN is diagnosed accidentally during a routine ultrasound examination.
Diagnosis of multifollicular ovaries
Of the diagnostic methods for MFJ, the most informative are:
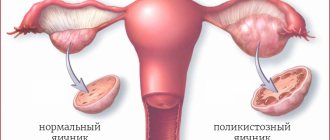
- Ultrasound examination. Ultrasound signs are very important to differentiate from polycystic disease, so the doctor performing the examination must have sufficient experience and knowledge. The difference between echo signs in MFN and polycystic disease looks something like this:
| Manifestations | Polycystic ovaries | Multifollicular ovaries |
| Ovarian size | Not enlarged | Increased |
| Number of follicles | 7-8 | 8 or more |
| Follicle size | 4-8 mm. | More than 9-10 mm. |
| Follicular membrane thickness | Normal | Thickened |
- Blood test for hormone levels. To accurately identify the cause of the failure, it is necessary to undergo a standard blood test for: FSH, LH, insulin, Thyroxine (T4), testosterone, 17-OH-progesterone, cortisol, triiodothyronine (T3), DHEA sulfate, progesterone, thyrotropin (TSH). Hormones never give up all at once, in one day. Each hormone is more pronounced at one time or another during the menstrual cycle, and therefore each one needs to be tested at its own time.
- Tomography of the brain. Since the main hormone responsible for the formation of a larger number of follicles (LH) is produced in the pituitary gland, it is necessary to exclude diseases of this organ.
Diagnostics
Multifollicular ovarian syndrome is easily identified during an ultrasound examination. The glands appear slightly enlarged and contain at least 8-10 follicles - sometimes more - measuring 4-8 mm.
A woman is given a blood test to check hormone levels. MFN syndrome is accompanied by a decrease in the level of luteinizing hormone against the background of an increase in follicle-stimulating hormone.
If a malfunction of the pituitary gland is suspected, a CT or MRI is recommended. The study allows you to identify tumors, injuries, and blood supply disorders.
Ultrasound
To confirm the diagnosis, the woman is prescribed an ultrasound examination (ultrasound). The signs become:
- slight enlargement of glands,
- the presence of numerous antral follicles, the size of which does not exceed 9 mm,
- thickening of the capsule of the dominant follicle is not observed,
- follicles are distinguished by a diffuse arrangement.
Adhesions in the pelvic organs - symptoms and diagnosis Therapy of a functional ovarian cyst - symptoms of pathology Intramural uterine leiomyoma - what is it Accumulation of fluid in the uterine cavity in old age
Multifollicular ovaries and pregnancy
Fortunately, with MFN there is rarely an anovulatory cycle, and the leading egg can be fertilized. But, at the same time, “extra” follicles are considered by obstetricians as a factor that can provoke miscarriage or premature birth (up to 36 weeks). This means that doctors treat women with a similar pathology more carefully and more often prescribe ultrasound diagnostics and certain tests.
To avoid worries during pregnancy, before deciding to conceive, you must undergo a full examination by a gynecologist. Agree, it is much more pleasant to carry a baby, knowing that everything is in order with your health, and the risk of losing it is minimal.
About the structure and function of the ovaries
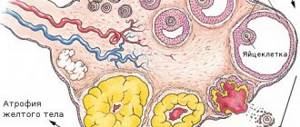
The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system that produces hormones for conception. 4-7 follicles, which contain eggs, mature in them during each menstrual cycle. 1-2 of all follicles mature faster, therefore they are called dominant, and the rest do not develop as expected. When the egg matures, the dominant follicle bursts and a corpus luteum appears in its place. This is a gland that does not last long. The egg is sent into the abdominal cavity, and then into the fallopian tube.
Women and girls should treat their health very carefully, because the consequences of untreated dysplasia, erosion, fibroids, endometritis, endometriosis, metroendometritis, chlamydia, thrush can affect not only her health, but also the health of the unborn child.
We will also answer the question of what follicles are in the ovaries. This is their part surrounded by layers of epithelium and connective tissue.
Did you know? The ovaries are the paired sex glands in the woman's pelvic cavity.
Stimulation of multifollicular ovaries during IVF
IVF (in vitro fertilization) is a modern and effective method of treating infertility. The first stage of preparing the female body for artificial conception is that superovulation is stimulated (an artificial increase in the number of dominant follicles), which significantly increases the chances of the desired pregnancy.
Experienced doctors will answer that it is possible to perform stimulation for MFN if the individual stimulation protocol and medication are selected correctly, and all the characteristics of the patient are taken into account: her age, weight, ovarian structure, etc.
If ovulation stimulation was carried out incorrectly (the risk of medical error is greater with altered ovaries), the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is possible, which is expressed in: an increase in the size of the glands, pain in the lower abdomen, the presence of fluid formations in the abdominal cavity, changes in blood viscosity.
After going through all the stages of preparation for the operation, the doctor transfers the embryos directly into the uterine cavity using a thin catheter. According to IVF rules, no more than 3 embryos can be transferred at a time, otherwise a multiple pregnancy may develop. With MFN, it is not worth carrying twins or triplets at all - the risks of self-abortion increase.
Women who become pregnant using IVF against the background of multifollicular ovaries are subject to more serious medical monitoring. They take progesterone medications for a long time, do ultrasounds more often and visit a fertility specialist.
Treatment
Treatment of multifollicular ovaries is most often medicinal. The selected drugs simultaneously relieve pathological symptoms and help restore the ability to conceive. Only means that can influence the activity of sex hormones can provide such an effect.
The treatment protocol is as follows:
- At the beginning of therapy, medications with antiestrogenic activity are recommended.
- The next stage is therapy with drugs that stimulate ovulatory abilities. A new menstrual cycle (MC) is formed.
- The final step is treatment with oral contraceptives over a long period, which maintains the newly created MS. Duphaston is often prescribed for the treatment of multifollicular ovaries.
- The patient is recommended to take long-term antiandrogens to stop hair growth.
Multifollicular ovaries can be treated surgically. Surgical intervention is practiced exclusively in the absence of effectiveness of conservative therapy or persistent changes in the structure of the glands.
Specialists perform two types of operations:
- Wedge resection. It involves removing the enlarged part of the gland, which reduces the level of male hormones. The remaining share begins to function normally. After some time, ovulation occurs.
- Dissection of the capsule of the dominant follicle, which ensures the onset of ovulation.
In rare cases, cauterization is practiced. Pinpoint burns help reduce the volume of the gland.
Important! The operations are performed laparoscopically, which shortens the recovery period.
In some cases, treatment with traditional methods brings results. Soothing teas are recommended, as women react painfully to the inability to conceive a child.
The use of herbal infusions gives good results. A mixture of seeds and roots of parsley, rose hips, and wormwood gives a good therapeutic effect. But drinking sage with multifollicular ovaries is allowed only after consultation with your doctor, since the herb has the ability to increase tarragon levels.
With proper diagnosis and the right medications, the condition can be cured completely.
Treatment of multifollicular ovaries
In most cases, MFJ syndrome does not require active therapy. It will not be possible to completely get rid of the diagnosis, but the modified ovary often does not affect the quality of life and reproductive function.
A doctor's intervention is only necessary if a woman's normal menstrual cycle is disrupted and she cannot become pregnant. Also, a deviation from the norm is considered to be a situation in which folliculometry (monitoring ovarian activity) does not confirm the presence of ovulation within 5 cycles.
Since the main culprit in the formation of MFN is hormones, this means that treatment involves their correction. To normalize hormonal levels, doctors often prescribe artificial progesterone. Duphaston can be considered the drug of choice in this case, according to medical protocols, because it does not interfere with conception (unlike Yarina), and is suitable for those who are planning to conceive a baby.
Question to the expert
My daughter was diagnosed with Multifollicular Ovaries. She is only 21 years old. Is it dangerous? She hasn't gotten pregnant yet.
No need to worry. If your daughter has a normal period, then most likely nothing bad will happen. Still, I recommend that you see a doctor for an in-person consultation.
Manifestation of symptoms
The problem is almost always diagnosed during an ultrasound. It is not uncommon for there to be no menstruation for six months or more. This disease is called amenorrhea and is the cause of a multifollicular condition. Oligomenorrhea occurs when menstruation is rare: the follicles do not mature at all to dominant signs, which means that ovulation does not occur. This may be the initial stage of polycystic disease.
Symptoms of multifollicular ovarian structure may be similar to those of other gynecological problems.
- The woman's voice lowers in tone.
- The amount of hair on the body increases.
- There is aching pain in the lower abdomen.
- The scalp becomes oilier.
- Menstruation does not appear for a long time, and pregnancy also does not appear.
- Acne.
- Acne on the body and face.
- Infertility.
- Weight increases.
Did you know? The ovaries produce three types of hormones: gestagens, estrogens and androgens. Each species has three subspecies. All of them affect the menstrual cycle.
Is it possible to cure multifollicular ovaries with folk remedies?
Currently, there are many methods for treating MFN at home. However, it is still better to take medicinal herbs after consulting a doctor. It should also be taken into account that adolescents have not yet formed a stable hormonal background, and it is better to avoid grandmother’s methods during this period. You can help balance hormones with MFN by:
- nettle and yarrow;
- red brush;
- boron uterus. The well-known herb is used to treat many gynecological diseases, including infertility;
- ripe viburnum mixed with liquid honey;
- a collection of birch leaves, buckthorn bark, yarrow herb, peppermint leaves, valerian root;
- evading peony;
- sage;
- ginger root;
- propolis;
- celandine.
The above plants are the main, but only a small part of the huge list of folk remedies that help the female body cope with diseases of the reproductive system. Many of the herbs listed need to be steamed in water or made into tinctures with alcohol. Although the Internet is replete with all kinds of recipes, you should not resort to making tinctures yourself. If you are sure that folk remedies are the best treatment for you, contact a specialist who will help you choose the right combination of plants and prepare them correctly. Otherwise, you risk worsening your condition.
In addition to herbs, hormonal changes can be treated with:
- gray or blue clay. Clay compresses are placed on the navel to pubic area several times a day;
- leeches. It is better not to use small parasites on your own, but to contact a specialist who knows how and where, as well as for how long they should be applied.
Prevention
A two-time examination by a gynecologist allows for timely monitoring and prevention of a multifollicular condition. Exercise and weight control are also important factors: sudden changes in weight are not acceptable. Taking hormonal drugs in unreasonable quantities without consulting a doctor can also have an effect, this also applies to contraceptives.
Even after a successful course of treatment, it is worth re-examining and monitoring the condition, especially when planning a pregnancy.
Suspicions of multifollicular ovaries are a reason to visit a gynecologist. Get diagnosed and treated in consultation with your doctor, and be healthy!
Health Deviations and pathologies