Causes of the disease in children
Factors that provoke gastroenteritis in a child
This disease most often affects children under 3 years of age. This disease is a rapid inflammatory process in the intestines and stomach, which is provoked by the following factors:
- Infections of a bacterial nature.
- Various viruses.
- Parasites and unicellular microorganisms.
- Products unfamiliar to the child.
- Periodic consumption of cold food.
- Ingestion of a foreign body that can injure the delicate mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
- Eating “harmful” foods.
- Irregular meal schedule.
According to statistics, most cases of disease occur precisely due to infections and viruses. And this is not at all surprising, because children love to come into contact with household items that cannot always be called sterile. In addition, little patients love to try everything by heart. Even some newborns may be diagnosed with this disease. Most cases of infection occur precisely because of failure to comply with basic hygiene rules. A poorly sterilized nipple, bottle, or even the mother's breast can pose potential dangers.
It is worth noting that the disease poses a great danger to young children. That is why it is strongly recommended that young patients be hospitalized in order to continue treatment in a hospital setting.
Treatment of acute gastroenteritis in children
Compensation for fluid and salt losses orally or parenterally (intravenously), depending on the degree of dehydration and clinical condition.
Orally: rehydration solution.
Intravenously: isotonic sodium chloride solution, then - solutions of glucose and electrolytes.
Antibacterial therapy for typhus, cholera, diseases caused by pathogenic protozoa, and septic complications. Treatment with antibiotics for salmonellosis is only in exceptional cases (danger of the formation of bacilli carriage).
Monitoring the patient
- Monitoring vital functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure).
- Assessing the level of consciousness.
- Feces: quantity, consistency, impurities.
- Observation of urine output, water balance.
- Body weight control.
Care
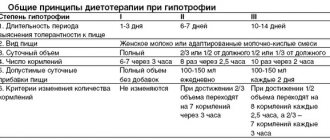
Rapid restoration of nutrition with diluted milk formulas (for example, rice water) or breast milk; young children and older children - a low-fat diet with the exception of carbohydrates (polysaccharides); goal: normal nutrition after a few days to quickly restore the intestinal mucosa.
Loose stools (in the absence of other symptoms) should not be considered as a reason for delayed natural nutrition.
Antipyretic measures - if necessary, do not use suppositories.
Careful care of the skin of the perineum; infants change diapers more often.
Oral care.
Prevention of bedsores - if necessary.
Symptoms and manifestations of acute gastroenteritis
Children aged three years and older with gastroenteritis of non-infectious origin complain of pain in the navel area both before and after meals. If a child speaks, then he can describe in more detail all the unpleasant symptoms, which cannot be said about infants. Infants with illness will behave capriciously after each meal, while tucking their legs towards their stomach. Massage movements will not help to calm the child, but rather, on the contrary, will bring unnecessary discomfort.
As the disease progresses, the patient will experience symptoms such as vomiting and nausea. It is worth noting that a single vomiting may indicate a mild form of the disease. In severe cases of the disease, prolonged and frequent vomiting is characteristic, mainly after eating. In addition to the previous symptom, diarrhea is added. The number of watery bowel movements can be a couple of times a day, or up to 15 times. Of course, with such severe symptoms, the child is immediately hospitalized.
In case of an infectious disease, in addition to diarrhea and vomiting, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Strong unusual odor from stool.
- Increased body temperature (37-38 degrees Celsius).
Feces are liquid with mucus and cheesy inclusions. The same symptoms in infants are manifested by a significant increase in body temperature (over 38.5 degrees).
The next manifestation of the disease is symptoms of intoxication:
- Lethargy.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Loss of appetite.
- Sunken eyes.
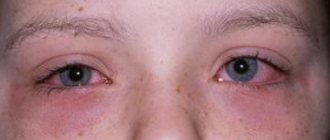
Responsible parents need to know that if a child’s fontanel and eyeballs “sink”, dry mucous membranes and pallor are observed, then it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance for further treatment in the hospital. This condition is extremely dangerous for the child’s life.
Classification of the disease: forms and stages
If we classify a disease by time, then in medicine it is customary to distinguish acute and chronic stages. The acute form of the disease begins quickly and violently with pronounced symptoms. Moreover, the disease bothers the child for 7-10 days. And the chronic form is characterized by periods of relapse and remission.
If we classify the disease by pathogen, we distinguish the following types:
- Viral. Transmitted through nutritional routes. The asymptomatic period is about 2-3 days. This type of disease mainly occurs in the off-season.
- Bacterial. The asymptomatic period is no more than a day. Outbreaks of the disease occur precisely during hot periods of time.
- Toxic. This type manifests itself when toxic substances are ingested - heavy metals, salts, alcohol and household chemicals.
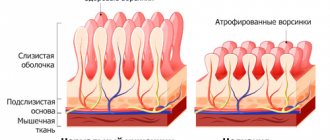
- Helminthic. They are provoked by parasites that provoke inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes. The symptoms of the disease resemble a chronic form, since the manifestations are not pronounced and periodic.
- Allergic. It may occur when consuming new foods to which the child may be allergic.
- Nutritional. This type occurs when a child consumes foods that are not appropriate for his age. The duration of inflammation is short: 1-2 days.
In addition, the disease is classified according to the following criteria:
- Light form. This form is characterized by normal body temperature, single vomiting, and diarrhea no more than 2-3 times a day.
- Medium shape. Complaints of abdominal pain. Body temperature fluctuates between 38 and 39 degrees. Repeated vomiting and diarrhea can reach up to 10 times a day. Due to the large loss of fluid, the child may experience the first symptoms of dehydration: dry mouth, decreased urination, tachycardia.
- Severe form. Body temperature can reach 40 degrees. Frequent vomiting mixed with bile. Defecation can occur up to 20 times per day. Severe dehydration – dry mucous membranes, impaired consciousness, small amount of urination, dark urine, convulsions.
What is gastroenteritis
Infection of the digestive tract with vomiting and diarrhea caused by viruses, bacteria and protozoa.
Life-threatening loss of electrolytes and fluids may occur within a short period of time. Fever is not noted in all cases. There are enterotoxic infections (the leading symptom is watery diarrhea; a typical example is salmonella) and enteroinvasive infections (the leading symptom is bloody-mucous diarrhea; a typical example is shigella, enterohemorrhagic strains of E. coCh).
Vomiting and diarrhea can also occur as concomitant symptoms of extraintestinal diseases, for example, pyelonephritis.
Typhoid fever (Salmonella typhi) is also transmitted by the fecal-oral route through contaminated food (for example, raw eggs). The incubation period is 1-3 weeks. The patient's general condition is serious, without typical gastroenteritis.
In addition to bacterial gastroenteritis, which occurs in the form of infections or toxic infections, there are food poisoning caused by bacteria, most often Staphylococcus aureus. The pathogen present in contaminated food releases a toxin that causes the disease.
Acute gastroenteritis due to helminthic infestations is atypical, but possible.
Consequences and possible complications of the disease
Acute gastroenteritis in a child can cause the following consequences:
- Dehydration.
- Hypovolemic shock.
- Kidney failure.
- Infectious-toxic shock.
- Multiple organ failure syndrome.
It is worth noting that the disease poses a threat to life in children of the first year of life. This is due to the fact that in infants dehydration occurs much more quickly than in older children.
Prevention
Prevention of gastroenteritis in children consists of following the recommendations below:
- Compliance with personal hygiene standards (mandatory hand washing before eating);
- Thorough washing of dishes and food. When eating food in public places, it is advisable to use disposable utensils;
- Safe culinary processing of products (steaming, stewing, baking at the correct temperature);
- Drink only boiled or bottled water;
- Compliance with the terms and conditions of storage of products;
- Limiting the consumption of unhealthy foods (convenience foods, fast food, carbonated drinks).
How to diagnose the disease
Examination of the child
To diagnose the disease, the doctor, in addition to examining and complaining to the parents and the child, prescribes the following mandatory tests:
- Blood sampling for general analysis.
- Antigen-antibody reactions.
- Diagnosis and examination of the digestive organs.
- General urine analysis.
- Examination of stool for bacteria.
In addition to laboratory tests, other methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs.
- Measuring acidity in the gastrointestinal tract.
Methods for treating gastroenteritis
After making a diagnosis, the attending physician determines the scheme, methods and intensity of treatment for the child. They depend on the severity of the disease and the level of dehydration of the body. In mild and moderate stages, the patient can be treated at home under the supervision of the attending physician. In case of severe dehydration (significant weight loss and symptoms appearing more than 10 times), the child is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department, where he receives medical care.
Therapy consists of the following methods:
- Prescription of antibiotics to combat the causative agent of infection.
- Antiviral drugs for suspected gastroenteritis of viral origin.
- Reception of sorbents. They will help relieve intoxication in the body.
- Probiotics and prebiotics to restore microflora in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Therapy with enzyme preparations for better breakdown of food during the recovery stage of the stomach after illness.
- The patient is prescribed a diet that is gentle on the gastrointestinal tract.
- Compliance with drinking regime. Frequently drinking liquid in small portions will help eliminate dehydration and cope with the removal of toxins.
With timely consultation with a doctor, correct diagnosis and individual medication regimen, the disease is highly treatable.
Treatment with medications
Treatment of this disease begins with large amounts of fluid intake. You can find an oral rehydration product at any pharmacy. The most popular is Regidron. This product is sold individually (in sachets) and in packaging. One sachet must be diluted in 1 liter of clean water - this solution is an ideal remedy for restoring the water-salt balance. But it happens that the child refuses to drink this mixture. In this case, any drink is perfect - weak tea, dried fruit compote, still mineral water. If the patient has severe vomiting, which does not allow him to drink a large amount of water, then feed the child with a small spoon, but every 5-10 minutes.
Along with drinking plenty of fluids, treatment with medications is advisable. The disease is treated symptomatically. For example, to normalize digestion, it is possible to prescribe Linex or Motilium, as well as regular activated carbon or Smecta. In order to stop uncontrolled vomiting, Cerucal is prescribed.
For spastic abdominal pain, it is advisable to prescribe no-shpa and paracetamol (as a pain reliever). At high temperatures, antipyretic drugs based on paracetamol and ibuprofen are prescribed.
To maintain intestinal microflora, Hilak Forte, Bifidumbacterin or Bifiform are prescribed.
If there are indications, then I wash the child’s stomach and give him an enema. This is possible in case of poisoning with household chemicals or heavy metals.
In addition to symptomatic treatment, it is necessary to identify the causative agent of the disease and then prescribe appropriate treatment. For bacterial diseases, antibiotics are prescribed. In the fight against a viral pathogen, some doctors may prescribe antiviral drugs, but it is worth remembering that the effect of such drugs has not been proven.
If the disease was caused by the presence of parasites in the child’s body, then the treatment must be supplemented with anthelmintic drugs prescribed by the doctor.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of gastroenteritis have pronounced symptoms, which indicate a deterioration in the general condition:
- The appearance of a white or yellow coating on the tongue;
- Stool disorder (diarrhea);
- Frequent nausea, vomiting;
- The excreted feces are green in color with an unpleasant odor;
- Abdominal pain;
- Increased gas formation;
- General weakness, apathy;
- Increased temperature and chills.
Gastroenteritis has similar symptoms to poisoning and is also dangerous for the body. In a sick child, the symptoms of intoxication worsen, and symptoms of dehydration appear (dry eyes, constant thirst, fainting). This condition is very dangerous, so you need to call an ambulance and go to the hospital.
In the medical institution, the child will be provided with the necessary assistance, all tests will be taken and the cause of the inflammation will be identified. In emergency cases, therapy is carried out to restore the disturbed electrolyte-water balance. Such symptoms should alert parents, since independent treatment is fraught with serious consequences.
Alternative medicine
To begin with, it should be noted that traditional medicine for this disease is an additional method of treatment, but not the main one. Moreover, before you try the recipes on your child, you need to make sure that the baby does not have any allergic reactions to the components of the product. And, of course, a preliminary consultation with a pediatrician is the responsibility of every parent. The most popular and effective recipes include the following:
- Dill water. At any pharmacy you can buy ready-made water or tea bags for brewing. Herbal tea improves digestion and relieves pain.
- Chamomile. To prepare a decoction, you can purchase tea bags or dried chamomile. A tablespoon of medicinal herb must be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and covered for 30 minutes. Give to the child in small portions if there is no vomiting during the day.
- Green tea with lemon balm. It is worth noting that all teas should be made weak so as not to provoke vomiting.
- Decoction with linden and rose hips. You need to take 1 tablespoon of each product and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for half an hour. Consume warm in small portions throughout the day.
As you may have noticed, the actions of alternative medicine are aimed at restoring the water and electrolyte balance in the child’s body, and some of the remedies have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of gastroenteritis in children are effective in combination with the main therapy and must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Decoctions and tinctures can be used as effective remedies:
- A decoction of rosehip or cranberry has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect. With constant intake, the body receives useful substances, and the liquid prevents the development of dehydration. The cooking recipe is based on the fact that the berries are poured with boiling water, infused, and then drunk throughout the day;
- Cooking oatmeal in water, as the cereal has an enveloping effect, which helps remove toxins and bacteria from the body. It is best to boil the grains well until they form a slimy consistency;
- Mint decoction calms the nervous system and saturates the body with essential microelements. The leaves are brewed in boiling water and infused for 30–40 minutes. The finished product is consumed warmly instead of tea throughout the day.
Nutrition during illness
Special diet for children with inflammatory processes in the stomach and intestines
In case of inflammatory processes of the digestive tract, a special diet is strongly recommended, the effect of which is aimed at preserving all functions of the digestive system. In this case, all products that can act aggressively are excluded.
Due to inflammation, food remains in the gastrointestinal tract much longer than it should. Because of this, food rotting processes begin. This provokes the appearance of bacteria, and the child becomes worse. That is why pediatricians recommend adhering to a special diet that excludes the following foods:
- Fresh confectionery.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Legumes.
- Hot, sour, spicy and fiery foods.
- Conservation.
- Fresh dairy products.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Sweets: bee products, preserves, jam.
The listed products can cause additional irritation and inflammation of the mucous membranes. That is why it is better to put sweets aside. But this does not mean that the cooked food will be tasteless. Authorized products include:
- Soups without overcooking and with low-fat meat broth (it is best to choose chicken for making broth).
- Steamed meat dishes.
- Homemade cottage cheese without additives.
- Porridge on the water.
- Butter in small quantities.
- Low-fat fish, steamed or baked.
- Compote of dried fruits or fresh berries.
- Fresh currant jelly.
If a child refuses to eat, then you should not force-feed him, but rather offer him some compote or jelly. Put aside full meals for now. It is worth noting that following a diet is a must in the treatment of acute gastroenteritis in children.
Compliance with a therapeutic diet
To fully restore the body during the treatment of gastroenteritis, it is recommended to follow a diet excluding certain foods from the diet:
- Spicy, fried, pickled salty dishes;
- Flour and confectionery products;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Chocolate, cakes, ice cream;
- Products containing artificial additives and substitutes.
The diet should be dominated by vegetable soups, cereal porridges without adding butter, and lean meats, steamed. Rosehip decoctions, still alkaline mineral water, and mint tea are recommended.
After 7–10 days of treatment, you can introduce a normal diet, but be sure to follow preventive measures to prevent the development of the disease.
Vaccination
Fortunately, a special vaccine has been developed that prevents viral gastroenteritis, it is called Rotarix. The vaccine is administered orally to children in the first six months of life. This remedy contains weakened viruses that provoke the onset of the disease. When they enter a child’s body, they provoke the production of antibodies, which will henceforth “recognize” the virus if it enters the body.
Vaccination is carried out in two stages. The first is oral administration of the drug at the age of 3 months. Then reintroduction at 6 months of age. This is ideal if the child is not sick with anything at the time of vaccination. Otherwise, the pediatrician postpones vaccination until the child has completely recovered.
It is worth noting that if a child was vaccinated during the first year of life, then the body’s protection is 90%. If up to 2 years, then the effectiveness is 85%. This method is designed to protect children from developing the disease for two years. In older children, the disease is mild and does not require hospital treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
When examining a child, the doctor should notice signs of gastroenteritis. In case of illness, pay attention to:
- Muscle weakness in the baby.
- Noise of intestinal peristalsis.
- Swelling of the pharynx.
- There is a white coating on the tongue.
- There are muted tones in the heart.
The doctor detects acute gastroenteritis in severe form by noting the baby’s high fever up to 40˚ C and severe dehydration. The most dangerous degree of the disease is characterized by circulatory failure and anuria, when the child does not produce urine.
Typical manifestations according to which the doctor diagnoses the rotavirus form of gastroenteritis are the development of pharyngitis and rhinitis. To confirm the diagnosis, stool is taken for laboratory analysis, which allows the virus to be isolated.
Prevention and advice to parents
It is possible to protect your baby from such a serious disease if you follow the following preventive measures:
- Wash and disinfect all household items daily: dishes, pacifiers, pacifiers, bottles, potty and toys.
- Baby food should be warm, not hot or cold.
- Do not feed your child “adult” food, even if we are talking about vegetables that have been generously seasoned. Not to mention allowing the child to live on chips, crackers and soda.
- Introduce complementary foods gradually, in small portions, while monitoring the body’s reaction to a particular product.
- Wash your hands before eating and after going outside.
- Try not to contact sick people.
- Visit your pediatrician regularly and get vaccinated.
In conclusion, I would like to note that it is impossible to completely protect a child from viral diseases, but you can reduce the risk of infection if you follow simple preventive measures.
Intestinal infections in children - School of Dr. Komarovsky:
♦ Category: Children's diseases.