09.02.2017
Any mother will think if her child yesterday had fun, played and was active, but today he whines and does not want to play or eat. It immediately becomes clear that something is bothering him. If there are no changes in appearance, look into the child's mouth.
If a white coating is detected on the tongue and cheeks, we can conclude that the baby has thrush. This disease often occurs in newborns, so mothers do not need to worry.
By contacting a specialist for help, treatment will begin that will help quickly get rid of the problem.
Thrush in children in the mouth is a frequently diagnosed disease. It is caused by a fungal infection that develops on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. It causes discomfort and unpleasant sensations. If the disease is detected at the initial stage of development, then treatment will take place quickly.
Causes of thrush
There are many reasons why thrush appears in children, so it is best to consider them depending on the age of the child.
Newborns. Factors influencing the occurrence of the disease in babies are as follows:
- The baby can become infected from the mother during childbirth or breastfeeding. However, this disease can also be picked up from other family members who already have it or simply do not maintain hygiene. Moreover, if they live in the same apartment with a newborn.
- If the disease spreads quickly throughout the entire oral mucosa, this means that the baby has a weak immune system or there have been changes in the composition of saliva, or maybe the mucous membrane is simply drying out for some reason. And the reason may be dry and hot air in the children's room.
- The disease can occur due to poor washing or sterilization of bottles and nipples.
- The cause may be regular regurgitation of the newborn.
- Thrush in female newborns may indicate somatic diseases.
Statistics show that the problem occurs in premature babies.
Infants. During breastfeeding, slightly different reasons may become factors, namely:
- Most often, thrush appears before the age of one year due to poorly washed bottles, nipples or poor oral hygiene.
- The disease is transmitted from child to child, since at this age children learn all objects through the mouth.
- Low immunity of the child.
- Taking antibiotics or treatment with other medications.
The fungus can rapidly multiply, covering more and more new areas of the mucous membrane. The cause is diabetes, dysbacteriosis, bronchitis, chronic tonsillitis and other diseases.
- Also, the cause of thrush will be dental problems in the form of gingivitis or caries.
- In some cases, the cause is microtrauma of the oral mucosa.
- Low-quality mixtures that contain a lot of sugar or very sweet drinks.
Causes and pathogenesis
Thrush can develop in a baby not only with a weakened immune system or during passage through an infected birth canal, but also:
- with poor oral hygiene;
- while taking antibiotics, hormones, immunosuppressants;
- with insufficient or unbalanced nutrition;
- The thrush fungus actively multiplies in the air, and easily survives freezing and drying.
You can become infected:
- by airborne droplets;
- contact and household;
- intrauterine.
Infection occurs at a rapid pace, affecting new areas of the skin and mucous membranes and leading to generalization of the disease. The disease is especially severe in bottle-fed babies.
In children of preschool and primary school age, the problem rarely occurs, but they can be carriers of the spores.
The sensitizing ability of the fungus plays a major role in the pathogenesis of the disease, which affects the reactivity of the body to varying degrees and leads to allergenic reactions that aggravate the situation and determine the course of the disease.
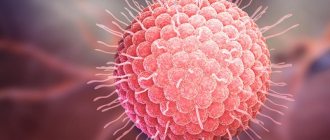
The photo shows a scraping showing Candida fungus under a microscope
Stages of the disease
In babies, it is very difficult to determine the onset of the disease, because they may have residues of milk or porridge in their mouths, which are very similar to the curdled discharge of thrush.
It is for this reason that it is necessary to regularly examine the child’s mouth so that if any pathology appears, a decision on treatment can be made immediately.
This disease has several stages of development.
- Easy stage
The first sign of a mild stage will be the appearance of small red spots in the mouth. Subsequently, they will be covered with a white cheesy coating. If the mother notices such changes, it is very good, because treatment started at this stage goes quickly and can be started at home. In this case, the child will not experience any discomfort.
The signs of this stage are: cheesy plaque, bleeding when trying to remove it, swelling of the mucous membrane.
- Middle stage
Distribution of white spots with plaque throughout the oral mucosa. The main symptom that indicates this stage will be bleeding from the spots, accompanied by pain. At this time, the baby refuses to eat because it hurts him to swallow and suck.
The main symptoms are: cracks in the corners of the mouth, loss of taste in the child, a dense white coating on the tongue.
- Severe stage
During this period, heavy bleeding begins. White plaque completely covers the entire mouth: tongue, gums, pharynx, cheeks, palate. In this case, the baby experiences severe, constant pain and discomfort. This stage is characterized by a sharp deterioration in the baby’s health and an increase in body temperature, up to forty degrees.
How is oral candidiasis classified?
This disease affects different places in the baby’s mouth and, accordingly, looks different. Let's look at the existing types of stomatitis.
- How can you recognize angular candidiasis? It is noticeable in the corners of the baby's mouth. The type of candidiasis in question appears as specks of rich red color. Also, the bottom of these spots may become covered with a whitish coating.
- In what places can you notice the manifestation of pseudomembranous candidiasis? The most affected areas are the mucous membranes of the cheeks, gums, tongue and upper palate. Formations in these areas have the appearance of a coating of cheesy consistency, colored white. It can be removed quite easily with a spatula.
- The next type of candidiasis is quite similar to pseudomembranous. It is called hyperplastic. But, unlike the first, it cannot be separated from the mucous membrane of either the tongue or the oral cavity. Treatment methods and diagnostic methods for these types of stomatitis are the same, which cannot be said about the forms of their manifestation.
- If you find round spots of a reddish hue that are located on the tongue or on top of the palate, it means that your baby has erythematous candidiasis.
Forms of the disease
There are two main forms of thrush:
- Acute
The acute form of thrush is determined by damage to the mucous tissues of the oral cavity, the formation of white plaque on them and the appearance of dryness. The plaque will consist not only of a fungal infection, but also of food debris and dead cells.
Then the plaque will cover the entire mouth and its corners, and cracks will appear there. The lymph nodes in the neck become enlarged; when examining them, the baby feels pain.
The baby's mouth experiences itching, burning and pain when eating.
Symptoms of the acute form are similar to signs of other diseases (diphtheria, stomatitis, tonsillitis), so during diagnosis the main thing is not to make a mistake.
- Chronic
In the chronic form, the plaque changes color and becomes brown or yellow. When you try to remove the plaque, bleeding and pain occur. The oral mucosa swells, and the lymph nodes in the neck enlarge.
The chronic form of the disease appears when treatment for the acute form has not been started. That is, in other words, if the mother did not pay attention to the child’s whims and started the disease. Treating thrush in children in this form is very difficult and takes a long time.
Where can the fungus “settle”?
Candidiasis can appear in a child on almost any part of the body.
Infection of mucous membranes
The fungus may appear in the mouth or genitals:
- Damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks, lips, gums, palate . White inclusions appear in islands, and then merge; if left untreated for a long time, they become dense and grayish, and it is almost impossible to remove them.
- Candida sore throat is a consequence of problems in the mouth; fungal spores spread to the tonsils and throat. If aerosols are not used, Candida spreads to the trachea and bronchi, changing the timbre of the voice. The main difference from other types of infection is the absence of fever.
- Damage to the corners of the lips appears in both corners with a mild halo of inflammation, in contrast to streptococcal infection.
- Damage to the red border of the lips appears in combination with infection of the mucous membrane, manifested in swelling and swelling of the lip contour.
- Vulvovaginitis is accompanied by white discharge from the genital organs; when examined by a gynecologist, white deposits are found on the cervix, in the vagina, and on the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
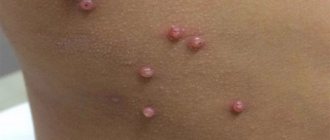
Thrush of the skin
There are two types:
- the intertriginous type appears in infants in large folds of skin, which becomes hyperemic, the process is accompanied by erosions;
- candidiasis of smooth skin is also a problem in infants due to the development of thrush in the folds; rarely in children the scalp is also affected.
Examination and diagnosis
The course of candidiasis in infants is specific, so it cannot be confused with anything else. When examining the oral cavity of an infant, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- You can remove the plaque with your finger, but it itself has a sour smell.
- Body temperature does not rise above 37.5 C.
If parents notice characteristic changes in their baby's mouth, they should show the child to the doctor. This could be a dentist or pediatrician.
Almost always, the diagnosis is made after a visual examination. If necessary, the doctor may refer the child to take a scraping from the mucous membrane. Using microscopic and bacteriological studies, the type of fungus and its sensitivity to drugs will be accurately determined.
Traditional methods
We must not forget that the use of any drugs is permissible only with the permission of the treating doctor.
- Soda solution. You will need to dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water. This solution is used to rinse the mouth.
- Infusion of calendula, St. John's wort, eucalyptus and sage. Add a glass of boiling water to a tablespoon of herb (pre-dried) and leave to steep for half an hour. This decoction will help heal the affected areas, relieve swelling and inflammation. For infants, the oral cavity is treated with this decoction using a cotton swab. It relieves itching well and has antiseptic properties.
- Aloe juice. It is used to treat affected areas; you can also rinse the mouth with the prepared solution.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Herpes on the lips treatment
Treatment of candidiasis
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to balance the baby’s diet and bring the microclimate of the children’s room back to normal.
In some cases, after this, the disease goes away completely. Try to spend more time with your child outside, give him less sweet water, especially before bed, and try to humidify the air in the room.
Treatment with medications involves taking topical medications. However, the medications themselves and how they are used will differ depending on the age of the child. If treatment is needed for a newborn, then some antifungal drugs are prescribed only in extreme cases.
During the consultation, the doctor will tell you how to treat oral thrush in a newborn baby. He will also tell you which products should not be used at all and clarify about allergies to medications.
Treatment of fungus in the mouth
If you have fungus in your mouth, you need to see a dentist. The diagnosis is made based on characteristic external signs, the patient’s sensations and tests. For examination, a scraping of fungal plaque is taken. It is important to make sure that the disease is caused by the Candida microorganism, excluding stomatitis, lichen ruber, glossitis, and herpes.
If black or green is found in the yellow plaque, this indicates the presence of other fungal pathogens.
A blood test will show your sugar levels and help rule out diabetes.
Medicines to treat candidiasis
Systemic drugs
Systemic drugs are divided into two groups: mycotics and polyene antibiotics. The first group includes miconazole and clotrimazole. They are taken from 1 to 3 weeks. The second group is nystatin, Levoril. Course – 2 weeks.
Vitamins B, C, PP, calcium gluconate, iron supplements
Treatment of thrush in infants
You can use a folk remedy that our parents used, this is a soda solution. He is the one who can save the baby from this problem.
So, let's consider two ways:
- Dissolve ten grams of baking soda in two hundred milligrams of warm water. Roll up a swab from gauze, dip it in the solution, and lubricate the child’s mouth. Cover the entire area of the oral mucosa. This must be done several times a day. If treatment was started at an early stage of the disease, then it can be cured in one week.
Due to the fact that after treating the mouth, alkali remains on the mucous membrane, the infection dies, because such an environment is destructive for it.
- Just like soda, you can use potassium permanganate.
Almost always, after such procedures, the disease in infants disappears, so medications at this age are prescribed very rarely.
How does thrush develop?
A person is surrounded by the external environment around the clock. It serves as a kind of conductor for various microorganisms, viruses and fungi, which, choosing a favorable environment for living, settle on the skin, on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose and throat, intestines, and organs of the reproductive system. The immune system of a healthy person successfully inhibits the growth of opportunistic microflora, which includes Candida.
But if the immune barrier is weakened, then fungi begin to penetrate the cells of the mucous membranes and produce dangerous enzymes. White lumps form on the surface of the epithelium - pseudomycelium, consisting of pathogens, destroyed cells of the oral mucosa and food debris. If you remove the plaque, the mucous membrane underneath will look red and inflamed. This is how oral candidiasis develops.
Treatment methods starting from six months
Almost all antifungal drugs are prescribed to children after six months.
In an advanced state, when the disease has already become severe, medications that contain iron are prescribed.
All medications are prescribed only by the attending physician after receiving the results of laboratory tests. If the symptoms go away after a couple of days, do not stop treatment and complete the entire course. After all, without completing the matter, the disease may reappear, only in a more severe form.
When the entire course has been completed, repeat the tests to confirm that the treatment helped.
General symptoms
Oral fungus is common not only in children and the elderly, which is associated with weak immunity, but can also affect healthy adults.
Fungus can be classified into the following types:
- pseudomembranous candidiasis;
- atrophic (in this case the chronic form can be considered);
- chronic hyperplastic.
If you do not consult a doctor on time, each type develops into a more serious stage, which can lead to a lot of unpleasant consequences.
Disease prevention
To keep your child healthy and not contract thrush, you must follow the following rules:
- Sterilize bottles, pacifiers and pacifiers regularly.
- Before breastfeeding, you should wash your breasts with soap.
- Monitor your baby's bowel movements.
- Carry out timely treatment of candidiasis before pregnancy and during it, so as not to infect the child during childbirth.
- Treat viral diseases in a timely manner.
- Boost your baby's immunity.
- Carry out oral hygiene for your baby regularly.
Possible complications
Most often, Candida fungi affect only the superficial layers of the mucous membrane. But without proper and timely treatment, pathogens penetrate other organs and severe complications develop.
Consequences of oral thrush:
- inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes;
- disruptions in the functioning of the heart, kidneys, liver, and digestive system;
- meningitis, sepsis, severe forms of tonsillitis;
- infectious pathologies of the respiratory tract;
- severe exhaustion and dehydration.
Long-term or chronic oral candidiasis leads to severe weakening of the immune system. The child begins to get sick often, even a simple cold often leads to the development of complications.
In girls and boys, thrush in the mouth can cause the development of vaginal candidiasis. The disease negatively affects the functioning of the genitourinary system and the development of the genital organs. For treatment, ointments and suppositories with antifungal action are prescribed.