In modern medicine, couple infertility refers to the inability of sexually active partners to conceive a child within a year. There is a stereotype according to which the absence of a child in the family is associated, first of all, with problems in the functioning of the reproductive system of the female body. However, domestic and international experience of specialists in the field of gynecology and urology shows that men become the “culprits” of a couple’s infertility no less often than their partners. In particular, male infertility accounts, according to various sources, from 45 to 55% of infertile marriages.
Identification of pathologies in the functioning of the male reproductive system often causes severe psychological trauma, not only to the man himself, but also to his partner. That is why today the treatment of infertility is receiving increased attention from scientists and doctors from various parts of our planet.
Types of infertility
According to the Russian Clinical Guidelines for Urology of 2019, depending on the causes of occurrence, male infertility is classified as follows (pathogenetic classification):
- Secretory – testicular dysfunction in terms of sperm production, provoked by congenital or acquired pathologies;
- Excretory – disruption of the transport of sperm from the testicles through the urethra, deterioration of the patency of the seminal ducts;
- Immunological - the body reacts to sperm as foreign agents and produces antisperm antibodies against them;
- Combined – infertility caused by several factors;
- Idiopathic (relative) - the reasons that caused the decrease in sperm fertility cannot be identified: sperm are normal, erectile function is also normal.
Excretory infertility due to blockage of the vas deferens.
Secretory infertility, in turn, is divided into three types:
- Testicular - the reason for poor sperm quality lies directly in the functioning of the testicles and their appendages (impaired spermatogenesis).
- Pretesticular – abnormalities in the functioning of the testicles are caused by hormonal reasons.
- Posttesticular - spermatogenesis is normal, but sperm fertility is reduced due to pathologies of the vas deferens or disorders of the secretion of other glands (prostate, seminal vesicles). The viability of sperm depends on the quality of their secretion.
Depending on the time of occurrence, infertility can be primary (no woman has become pregnant) or secondary (partners have become pregnant). The primary form usually cannot be corrected. Infertility may be accompanied by a number of additional symptoms, the severity of which depends on the cause of the pathology.
Modern scientific discoveries that will help in the future in the treatment of infertility in men:
- cell technologies and gene therapy will open up great opportunities for reproductive medicine in the future, especially for patients with genetic disorders;
- Scientists are close to growing sperm from patient somatic cells. This will help patients with non-obstructive azoospermia, Sertoli cell syndrome, and spermatogenesis block to become fathers of healthy children.
- Expert
- Latest articles
- Feedback
Causes of infertility
All causes of male infertility are divided into several types depending on the affected organ. Testicular pathologies related directly to the functioning of the testicles include the following pathologies:
- Cryptorchidism - in infancy, the testicle does not descend into the scrotum, sperm are not synthesized in it due to unfavorable temperature conditions. Theoretically, reduction to the scrotum is possible by increasing the supply vessel, but in this case doctors do not give guarantees of the organ’s functionality.
- Torsion of the spermatic cord is an acute condition requiring emergency care. Otherwise, the testicle is deprived of nutrition, ischemia of its tissue develops, followed by death.
- Viral orchitis caused by mumps (“mumps”). Due to severe inflammation, testicular tissue begins to melt, deform and be replaced by connective tissue (spermatozoa are not formed in them). It should be noted that not all men who suffered from mumps in childhood are infertile. The problem is relevant only for those who had untimely management of a testicular complication.
Urologist-andrologist, candidate of medical sciences Alexey Viktorovich Zhivov talks about the causes of male infertility
- Chemo- and radiation therapy. Treatment used for cancer often leads to irreversible infertility due to toxic damage to spermatogenic cells. If a man plans to have children in the future, then before starting therapy, doctors recommend cryopreservation of sperm and storing them in a special bank.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic area. The number of leukocytes increases, due to the activity of which sperm are exposed to oxidative stress (reactive oxygen species destroy their shell, damage the DNA chain (fragmentation)).
- Among the testicular causes of male infertility, varicocele is distinguished separately. The pathology occurs quite often (in 40% of cases of male infertility). Blood stagnates in the dilated veins, as a result of which the nutrition of the testicles deteriorates and defective sperm are produced in small quantities.
- Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism is an increased level of gonadotropins (stimulants of the synthesis of male sex hormones) and low testosterone levels due to testicular dysfunction. The pituitary gland and hypothalamus try to trigger the synthesis of androgens, increasing the rate of production of gonadotropins.
- Resistance (stability, immunity) to androgens is a congenital mutation due to which the receptors become insensitive to the effects of male sex hormones; testosterone cannot stimulate the testes to synthesize sperm.
- STD. Some infections penetrate the testicles, attack sperm, and poison spermatogenic cells with the products of their metabolism.
- Reduced hemoglobin. Anemia provokes circulatory failure, including in the testicles.
- Genetic abnormalities (Klinefelter syndrome - karyotype 47XXY, extra female chromosome), deletion (loss of one sector of the Y chromosome). There are two options: absolute infertility (genetic, congenital infertility) due to complete dysfunction of the testicles or the possibility of in vitro fertilization with sperm extracted from the testicle by biopsy.
Endocrinologist-andrologist Daria Aleksandrovna Gusakova talks about how the male disease Klinefelter syndrome manifests itself, is diagnosed and treated.
Posttesticular infertility is usually provoked by a violation of the patency of the seminal ducts. The reason may be inflammatory tissue deformation, the presence of cysts and neoplasms. Posttesticular infertility is also caused by infectious inflammation of the accessory sex glands, the secretion of which is also included in the ejaculate: vesiculitis, prostatitis.
The causes of pretesticular infertility are pathologies of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (glands in the brain):
- Adenoma.
- Infectious inflammations.
- Secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
- Hyperprolactinemia (excess of the hormone prolactin).
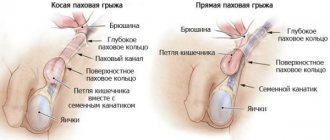
The cause of immunological (autoimmune) infertility is a violation of the structure of the blood-testis barrier - a layer of cells that protect sperm in the seminiferous tubules from the immune system. Provoking factors: perineal trauma, infections of the reproductive system, genetic pathologies, tumors, varicocele, inguinal hernia.
Low sperm fertility is not always the cause of male infertility. In some cases, sperm simply do not enter the woman’s reproductive tract:
- Erectile disfunction.
- Anejaculatory syndrome.
- Retrograde ejaculation (sperm flows into the bladder).
The mechanism of retrograde ejaculation
The functioning of the testicles can be disrupted by smoking (more than 10 cigarettes per day), alcohol (more than 60 g per day), caffeine (more than 300 g per day), and taking certain medications, including:
- Ketoconazole;
- Sulfasalazine;
- Aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Cytostatics.
If, subject to regular sexual activity without the use of contraception, a couple is unable to have a child, then the man should contact an andrologist, urologist or reproductive specialist.
Diagnostics
The task of diagnosis is to confirm the fact of infertility and find out its causes. At the first consultation, the doctor talks with the patient, collects anamnesis, and conducts a physical examination (external examination, palpation of the testicles). On the same day, you can donate sperm for general and biochemical analysis (preliminary preparation is required).
Read about the rules for taking a spermogram.
Spermogram
The doctor's further actions depend on the results of the spermogram. The absence of deviations is designated by the term “normospermia”; in the presence of pathologies, various types of pathospermia are diagnosed:
- Akinozoospermia is the absence of motile sperm.
- Cryptozoospermia - sperm are found only in the semen sediment after centrifugation.
- Teratozoospermia – many sperm with disturbed structure (morphology). To identify pathology, it is necessary to take an extended spermogram with Kruger morphology assessment. There should be more than 4% normal sperm. The analysis costs about 2000 rubles.
- Oligospermia – little seminal fluid (less than 2 ml).
- Azoospermia is the absence of sperm in the seminal fluid. It can be secretory (testes do not produce sperm) or obstructive (sperm cannot pass through the vas deferens).
- Oligozoospermia is a reduced concentration of sperm in 1 ml of ejaculate (the norm is more than 15 million).
- Oligoasthenozoospermia is an insufficient number of sperm and their progressively motile forms.
- Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia – three indicators are below the standard: the total number of sperm, their progressively mobile and morphologically normal forms.
- Necrozoospermia - few living and many immobile sperm.
- Leukospermia is an increased number of leukocytes in semen (a sign of inflammation).
Spermogram with deviations (normozoospermia with aggregation)
If deviations are detected, the spermogram is taken again . This is necessary for an objective assessment, since indicators are constantly changing and depend on a large number of external and internal factors (food, stress, physical activity, overheating).
To identify the cause of pathospermia, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, culture of sperm and prostate juice are prescribed. To exclude retrograde ejaculation, post-ejaculatory urine analysis is prescribed. To determine endocrine infertility, blood is examined for hormones (hormonal profile): LH, FSH, testosterone. The patency of the seminal ducts and the condition of the seminal vesicles are checked using genitography (a series of x-rays after the administration of a contrast agent).
Additional tests for idiopathic infertility
Often, infertility (this also includes miscarriages and missed pregnancies) is diagnosed with a completely normal spermogram. To find out the reason, additional studies are prescribed:
- MAR test - analysis of spermatozoa for the presence of antisperm antibodies (price from 1200 rubles).
- Analysis for sperm DNA fragmentation (TUNEL method from RUB 8,300).
- Karyotype study (especially relevant for azoospermia, oligozoospermia) - cytogenetic analysis to identify the risks of Down syndrome, Kleiefelter syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. The norm is 46XY, price from 4900 rubles.
Urologist Kamaletdinov Rinaz Enesovich clearly talks about the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility
- Study of the body's antioxidant activity - antioxidant status (are there enough antioxidants in the blood, is sperm able to resist reactive oxygen species that damage sperm). Price from 2450 rub. Assessment of sperm oxidative stress (ROS). Price from 2000 rub.
- Acrosin test (assessment of acrosomal reaction) - tests sperm for the ability to penetrate an egg. In the head of the male gamete there is a special vial with enzymes (acrosome), which dissolve the membrane of the female cell upon contact. Price from 3000 rub.
- EMIS is a microscopic examination of the internal structure of sperm. Price from 9000 rub.
- NVA – determination of the degree of sperm maturity. Price from 5000 rub.
Some clinics offer a comprehensive examination that includes the above types of tests. It's called, the price starts from 18,000 rubles. During promotions you can save up to 25-30%.
The general diagram of diagnostic measures is presented below:
Diagnosis of male infertility
A testicular biopsy is performed if there are no sperm in the ejaculate. If they are present in the seminiferous tubules, then the causes of infertility are obstruction of the spermatic ducts; if they are absent, then you can either try to stimulate spermatogenesis or use donor sperm.
Extreme measures
If it is useless to try methods of treating male infertility, since we are talking about an incurable loss of fertility, then a method of artificial insemination of the woman is selected. The following methods are used:
- Artificial insemination is a method in which seminal fluid is medically introduced into a woman’s vagina, without sexual contact. This method allows the entire volume of sperm to enter the cervix and, therefore, increase the likelihood of conception several times. Sperm from different men can be used - both the woman’s sexual partner and a donor (both fresh sperm and frozen sperm are taken).
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) – fertilization is carried out not in the woman’s body, but in a special Petri dish, after which the zygote is placed in the uterus of the expectant mother. This method is most often used in cases of infertility, since the presence of at least one motile sperm is sufficient to fertilize an egg.
Treatment
In case of infertility, before choosing a method of artificial insemination, doctors try to maximize the quality of sperm (if any). The patient is recommended to adjust their lifestyle: move more, eat rationally, eliminate bad habits, lose excess weight (waist circumference should be no more than 94 cm). To improve sperm quality, antioxidant therapy is especially effective:
- Vitamins C, E, A, D;
- L-carnitine, L-arginine;
- Coenzyme Q10;
- Folic acid;
- Zinc, selenium.
Preparations for antioxidant therapy
For the treatment of mild forms of infertility, as well as to restore the functions of the glands after surgical operations on the reproductive organs, complex drugs are prescribed: Speman, Spermaktin, Tribestan, Profertil, Gerimaks Premium. The course of treatment lasts at least three months - the period for the renewal of a full set of sperm. Only after three months does it make sense to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of therapy.
Doctors are positive about some traditional methods of treating idiopathic infertility:
- Beekeeping products (death, beebread, drone homogenate). They take first place in efficiency due to a rich set of biostimulating substances, hormones, vitamins and microelements.
- Herbs (hogweed, sage, St. John's wort).
- Mumiyo, beaver stream.
For many patients with various forms of infertility, doctors recommend treatment in sanatoriums:
- “Beshtau”, “Mashuk Aqua-therm” (Zheleznovodsk);
- "Talaya" (Magadan region);
- All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions (Nizhny Novgorod);
- “Staraya Russa” (V. Novgorod);
- Sanatoriums in Saki (Crimea).
Programs include drinking mineral water, baths, mud treatments, climate therapy (walks through coniferous forests and mountains), microenemas with mineral water, prostate drainage, and physiotherapy.
Treatment methods for certain types of infertility:
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: human chorionic gonadotropin (stimulator of testosterone production), menotropins. Testosterone replacement therapy is not recommended (they suppress the synthesis of LH and FSH).
- Varicocele, obstruction of the seminal ducts. In the first case, the Marmara operation is performed (price from 55 thousand rubles). Impaired patency is corrected by surgical methods (vasovasostomy, tubulovasostomy, transurethral resection). If the operation is successful, sperm production is restored within 3-18 months.
Urologist-andrologist Nikolai Konstantinovich Solovyov talks about the technique of performing the Marmara operation for varicocele
- Infectious lesions of the reproductive organs: broad-spectrum antibiotics. For the treatment of chronic prostatitis, Longidaza, Vitaprost, and Prostatilen are used (more information about the treatment of prostatitis).
- Severe forms of pathospermia: assisted reproductive technologies.
- Lack of sperm: donor sperm.
For erectile dysfunction, PDE-5 inhibitors and alprostadil injections are prescribed.
ART – assisted reproductive technologies
If the sperm have a normal structure, but are inactive or there are few of them, then insemination is used - the introduction of pre-selected male gametes directly into the uterus. If a man has been diagnosed with uncorrectable infertility, the doctor gives a referral for IVF - artificial insemination. The simplest option is to inject sperm into a test tube that already contains pre-extracted eggs. After fertilization, the embryos are placed in the uterus. The full cycle of manipulations from hormonal stimulation to embryo transfer is called a protocol. The price starts from 130 thousand rubles. A repeated protocol if the first one fails will cost less – from 99 thousand rubles.
Theoretically, a woman can become pregnant even with severe forms of male infertility. Even if he has only a few units of suitable sperm, modern technologies make it possible to find them directly in the testicle (TESE, TESA, MESA methods), extract them and use them for fertilization. The sperm is artificially implanted through the membrane of the egg (ICSI, PIXI method), then all that remains is to wait for the process of cell division and the formation of an embryo. ICSI price from 83 thousand rubles.
Assisted reproductive technologies
However, in practice everything is not so optimistic. Many protocols end in failure (IVF efficiency is only 40%), and the clinic does not return the money. Doctors who give a referral for IVF under compulsory medical insurance more objectively assess a couple’s chances of success with male factor infertility. On a paid basis, private clinics accept everyone on the principle of “any whim for your money.”
There are many positive reviews on thematic forums about the following medical institutions:
- Clinic “Mama” (Moscow) is the most popular, the best embryologists;
- Institute "Remedy" (Moscow);
- Clinic “Mother and Child” (various cities);
- ICLINIC (various cities);
- (St. Petersburg).
Criteria that you should focus on when choosing: the presence of your own cryogenic storage facility, the professionalism of embryologists, the percentage of successful pregnancies.
Prevention
Methods for preventing male infertility:
- Healthy lifestyle: moderate regular physical activity, balanced diet (nuts, berries, fruits, greens are required).
- Regular sex so that sperm do not have time to oxidize.
- Timely treatment of STDs.
Do not overheat the groin area often and wear tight underwear. To avoid infertility, you should give up bad habits, of which smoking and drug use are the most destructive for sperm.
Is it always about illness?
It is worth noting that the inability to conceive a child does not indicate the presence of female and male infertility. In fact, such a diagnosis should not be made, even if the couple cannot conceive a child within 1-2 years. Sometimes the initial examination shows that the man and woman are in good health and we are talking about incompatibility of sexual partners. Only clinical studies can determine more precisely what is causing the difficulty in conceiving:
- Lab tests.
- Modern instrumental diagnostic studies.
Only with the data of such studies in hand will the doctor be able to make an accurate diagnosis and draw up a plan for further action that will help eliminate the cause of the disorder and give the couple a healthy child.