Home Pneumonia Treatment of pneumonia What symptoms can be used to recognize pneumonia without fever in adults?
Pneumonia, which is better known as pneumonia, occurs due to damage to these organs by pathogenic microorganisms .
This disease develops quickly and can be fatal if left untreated.
Diagnosing this pathology is not difficult, since in most cases it is characterized by obvious symptoms.
is much worse if the disease occurs without fever - in such situations, other signs of the disease may be mild, which makes it difficult to make a diagnosis.
- 1 What is pneumonia?
- 2 When can pneumonia in adults occur without fever?
- 3 Symptoms of the disease
- 4 Reasons for the development of pathology
- 5 First actions in case of illness
- 6 Treatment
- 7 Prevention measures
- 8 Useful video
How dangerous is pneumonia without fever?
The most obvious problem with pneumonia is the severity of the patient's condition. It can occur along with symptoms of influenza or ARVI, so it is extremely difficult to identify. This cannot be done at home.
Often the disease develops as a complication after untreated bronchitis. And of all the series, it is pneumonia without fever that is dangerous, since threatening signs are usually noticed too late.
Complications and risk factors
Pneumonia is a direct threat to life and causes a number of irreversible health consequences. Complications after pneumonia:
difficulty breathing or even lung failure, which may require connection to a ventilator;
provoking chronic diseases - for example, COPD;
accumulation of fluid in the lungs (surgery and installation of drainage are often required);
lung abscess (formation of pus in the pulmonary pocket and sepsis);
bacteremia (spread of a pathogen into the bloodstream), which can lead to septic shock;
alveolitis – fibrosis of the interstitial tissue of the lungs.
Those most susceptible to these risks are:
elderly people over 65 years of age;
people with weakened immune systems;
people with chronic diseases (COPD, asthma, cardiovascular diseases).
Consequences and complications of the disease
The likelihood of developing complications with latent pneumonia is quite high, since the diagnosis is confirmed late in the course of the disease.
In most cases, advanced forms of the disease lead to damage to the bronchopulmonary and cardiac systems:
- decreased lung volume;
- the formation of sclerotic areas in the lung tissues;
- development of pleurisy;
- the formation of voids in the lungs;
- accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity.
Against the background of AIDS, tuberculosis and other severe pathologies, latent pneumonia is complicated by the development of sepsis and multiple organ failure. In 35% of cases, patients with such complications cannot be saved.
A favorable prognosis for the disease is possible only with intensive treatment with appropriate antibacterial drugs followed by preventive support for the body.
Atypical pneumonia without fever
In general, in the classification of pneumonia there are many varieties of atypical pneumonia - this is the name for a whole group of diseases that occur with uncharacteristic symptoms (lack of cough, croup, fever, etc.)
However, now atypical pneumonia is more of an everyday term from the media. It is more important for doctors to determine the causative agent of the disease. Therefore, other types of the disease are distinguished:
Bacterial pneumonia
Typical pathogens in this case are streptococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) and Haemophilus influenzae.
Atypical pathogens are:
Chlamydia (Chlamydophila pneumoniae).
For example, infection of the lungs with chlamydia is characterized by asymptomatic inflammation - in other words, this is a classic example of atypical pneumonia without fever, sometimes with headache, weakness and cough. This disease is often carried on the legs and easily becomes chronic.
Viral pneumonia
As the name implies, viruses become pathogens:
Influenza A and B viruses;
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV);
With viral pneumonia of any nature, cough, temperature and fever always occur.
Fungal pneumonia
Fungal infections most often affect the lungs of people with weakened immune systems. However, in some cases, completely healthy patients can become infected with them.
Fungi are often found in soil or bird droppings. Among them:
How to recognize the symptoms of pneumonia without fever?
Well, now the main thing: are there ways to detect the disease at an early stage? Of course. But to do this, we strongly advise you not to ignore any symptoms and suspicious signs. The disease may start with little things like a cold cough, but it will only get worse.
To recognize the first symptoms of pneumonia without fever, answer a few questions:
Have you been in contact with someone with pneumonia recently?
Do you experience unexplained fatigue (malaise) or loss of appetite?
Do you have a persistent cough with phlegm (productive)?
Do you experience chest discomfort when you cough or take deep breaths?
Do you feel shortness of breath during walking or normal activities?
Did these symptoms appear after a viral infection (ARVI, influenza, bronchitis)?
If the answer to most questions is “Yes,” then immediately make an appointment with a doctor. You can't hesitate!
How is pneumonia without fever diagnosed in adults?
Of course, a person, even with careful attention to his health, can only suspect signs of illness. An accurate diagnosis is made only during a hospital examination, especially if the disease is accompanied only by a cough (in which case it is often confused with bronchitis), and is otherwise asymptomatic.
There are a number of tests that routinely diagnose pneumonia in adults:
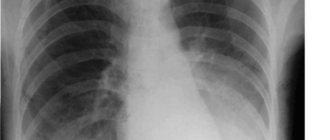
Fluorography of the chest. In the image, foci of pneumonia will appear as a dense darkening. This method is often sufficient to make an initial diagnosis;
General blood analysis. The doctor is interested in the level of leukocytes, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), leukogram (leukocyte formula), the state of neutrophils;
Sputum analysis. Helps identify the causative agent of the disease;
Pulse oximetry (oximetry). Needed to determine the amount of oxygen in the blood.
In advanced cases or suspected complications, the doctor may prescribe:
Pleural fluid culture analysis;
Computed tomography (CT) of the chest for better visualization;
Bronchoscopy (insertion of a special camera into the bronchi to examine the respiratory tract).
How does coronavirus proceed without pneumonia?
According to the latest data, in 80% of patients the disease is quite mild - symptoms are similar to those that appear with the flu. Pneumonia associated with the new coronavirus has an unusual course. This is because patients with COVID-19 experience a wide range of degrees of lung damage with vastly different clinical presentations.
There is no fever, no cough, no shortness of breath. At the same time, when performing a computed tomography, patients show signs of pneumonia. This indicates that humanity is faced with the possibility of developing absolutely asymptomatic forms of pneumonia.
Candidate of Medical Sciences and infectious disease doctor Ilya Akinfieva talk about the asymptomatic course of coronavirus
There are two variants of the coronavirus disease. There may be asymptomatic viral shedding - this is when a person has no symptoms, feels great, but there is a virus in his body that is actively spreading into the environment.
According to the latest data, in 80% of patients the coronavirus disease is quite mild.
And the so-called “mild course” of coronavirus. A person may have mild rhinitis, body aches, a subjective feeling that he is starting to get sick, but his temperature and frequency of respirations do not increase. This is the most common option.
As soon as the slightest symptoms appear, immediately call the clinic and have a doctor come to your home. Usually they immediately take a coronavirus test. Unlike bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia is not felt by a person at the very beginning of the disease. There may be a slight cough without sputum production, fatigue, and sweating. But no classic symptoms - no chest pain, no difficulty breathing. But very quickly 25-30% of the lungs can be affected - and this is already very serious.
To quickly detect such cases, all doctors who come to the home now have pulse oximeters with them - special devices that can non-invasively, using a beam of light, determine the oxygen saturation of the blood. With viral pneumonia, a person may not feel a lack of oxygen in the blood for quite a long time, and when it starts, it will be too late. Therefore, do not be afraid to call a doctor for any symptoms - in a situation like now, it is better to be safe.
How to treat pneumonia
Your doctor will provide you with the necessary list of medications to treat pneumonia. These may be antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs.
If pneumonia occurs without fever and is recognized in time, the patient is allowed to go home for treatment. Here's what you can do to get rid of the disease:
Rest. Do not strain under any circumstances and minimize physical activity;
Lots of liquid. It not only helps you avoid dehydration, but also helps thin mucus;
What causes the disease
The most common source of viral pneumonia is parainfluenza and complications of ARVI. We must not forget that the disease can be a consequence of improper treatment of chickenpox, rubella or measles. Infants, elderly people, and patients of oncology clinics are at risk. In such patients, the pathology often occurs without fever or other manifestations.
Symptoms of pneumonia are often detected in heart patients and asthmatics. Experts have noticed that bronchitis and other respiratory infections provoke disturbances in the functioning of the epithelial cilia. As a result, the body cannot get rid of phlegm and pathogenic microorganisms - viral pneumonia occurs.
Causes
The most common cause of asymptomatic pneumonia without fever is a particularly weakened immune system that has not had time to recover after suffering serious illnesses. Pneumonia without fever can progress when the body is affected by other inflammations or infections. Also, the reasons for the manifestation of asymptomatic inflammation include taking antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription. At the same time, addiction to these drugs almost always develops, so their effectiveness decreases. The medicine stops working correctly for the body and does not eliminate pathogenic bacteria.
With prolonged uncontrolled use of antitussive drugs for pneumonia without fever, but with a cough, microorganisms begin to accumulate, causing pneumonia. The risk of inflammation increases with the unreasonable use of drugs that block the discharge of mucus from the respiratory tract.
Some people are at risk for developing asymptomatic pneumonia without fever:
- alcohol dependent people;
- smokers;
- people diagnosed with HIV;
- people in the age group over 50 years old.
Sometimes symptoms of pneumonia without fever appear in newborns, since their respiratory system has not yet fully adapted to the conditions of the surrounding world.
Symptoms in adults and children
The disease can occur without fever or cough. Typically, this development of a pathological condition is typical for people with weakened immune systems (HIV, tuberculosis, chronic diseases of the respiratory system).
What you need to pay attention to:
- attacks of arrhythmia;
- weight loss, loss of appetite;
- abnormal sweating;
- headache;
- unmotivated fatigue.
Many patients in specialized clinics note that viral pneumonia causes dizziness and fainting. This condition occurs against the background of a sharp narrowing of blood vessels.
Fortunately, in most cases, the pathology causes obvious signs of an inflammatory process. Infection of the lungs can be suspected by a persistent increase in body temperature (usually about 37.5°), painful shortness of breath, dry non-productive cough, pain in the back (between the shoulder blades) and chest.
In children, viral pneumonia is usually quite severe. Symptoms of the disease in young patients:
- dry or wet breast cramps;
- constant retraction of the intercostal spaces during inhalation and exhalation;
- arrhythmia, shortness of breath.
In a child, pneumonia rarely occurs without a persistent increase in body temperature (more than 3 days up to 38°). Associated symptoms include runny nose, conjunctivitis, and pale skin.
Features of asymptomatic disease
The inflammatory process in the lungs, which occurs without signs characteristic of this condition, still makes itself felt. The patient may experience:
- Weakness, sweating;
- Sickly pallor with characteristic bright spots of blush;
- Breathing problems, wheezing;
- Increased heart rate or heart rhythm disturbances with minor physical effort;
- Pain in the back and even throughout the entire body, especially when turning the body;
- Constant thirst.
In children, you may notice loss of appetite, drowsiness and lethargy, and a “bluish” tint of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
Diagnostic techniques
The doctor determines viral pneumonia in adults and children by classic symptoms. Usually, to make a preliminary diagnosis, collect anamnesis, examine the oral cavity and listen to breathing.
To confirm or refute concerns, the therapist (pulmonologist, infectious disease specialist) refers the patient for additional laboratory and instrumental tests. If viral pneumonia occurs without obvious signs of inflammation or fever, but wheezing is heard in the chest, then you must do the following:
- X-ray, computed tomography (studying the condition of the lungs and bronchi);
- pulse oximetry (measuring the quality of breathing and oxygen saturation of tissues);
- blood and sputum tests (search for antibodies to viruses, exclusion of tuberculosis).
It is important to start treatment as early as possible. If respiratory failure or pleurisy occurs, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Viral pneumonia can cause alveolitis, which is difficult to treat with antibiotics.
The symptoms of such a disease can only be eliminated with the help of intravenous infusions of dangerous solutions.
Therapy for atypical inflammation
Since in almost all cases the diagnosis of pathology occurs in a medical institution, treatment is prescribed only by a doctor. It is impossible to get rid of pneumonia on your own, because therapy (especially for a one-year-old child) must take place under medical supervision. Antibacterial medications are necessarily used in the course of treatment.
When choosing the right trade name, the specialist is guided by the results of blood and sputum tests. It is important to correctly identify the pathogen and select the necessary remedy for it with a sufficient level of sensitivity. Possible drug options:
- Acetylcysteine. At the same time, it is a mucolytic, which helps get rid of sputum, thin it and facilitate elimination. Children under 2 years of age are prohibited from taking a dosage of 100 mg, and this drug is not prescribed to pregnant women.
Acetylcysteine removes mucus from the respiratory tract
- Mukobene. Like the previous medicine, it is produced in the form of granules for dissolution in liquid, but this drug can be prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly. It is used for inhalation. It is effective against purulent sputum and does not negatively affect human immunity.
- Ambrobene. It is also a mucolytic, which is used in the presence of a cough reflex and colds. The drug can reduce the viscosity of sputum and facilitate the process of mucus discharge. The effect is noticeable within half an hour, and it lasts up to 12 hours. There is a decrease in redness of the throat and pain when swallowing.
- Mukodin. This medication belongs to the group of stimulants of the motor function of the respiratory systems and is a secretolytic. Helps in the process of removing mucus, making its viscosity the desired consistency, while the active substances regenerate the mucous membrane.
Lazolvan is prescribed for wet cough
- Lazolvan. A mucolytic drug prescribed for cough. After use, an improvement in mucus removal is observed. The use of the product has a positive effect on the healing process due to a better concentration of the antibiotic in sputum and bronchial secretions.
After an intensive course of medications, the patient may be sent home if positive dynamics are observed. You need to make yourself nutritious meals, but you shouldn’t eat fatty and heavy foods. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, which will prevent the body from suffering from dehydration and will not allow the temperature to rise.
For the lungs, the patient undergoes physical therapy. Bedridden persons are prohibited from staying on one side for a long time.
Physical therapy can help improve your health
How to treat pneumonia
Viral pneumonia develops quickly and “invades” lung tissue, so treatment of the disease should be carried out only in a hospital hospital. General recommendations include bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and alleviating the patient’s condition with antipyretic (if necessary) and expectorant medications. If the pathology occurs without fever, then there is no need for Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
The use of antiviral injections and tablets is beneficial only if you seek help in a timely manner (the first 2-3 days). Nomitex and Oseltamivir are used. Therapy with acyclovir inhibitors and inhalation powders shows good results. Subsequently, pharmacotherapy with antibiotics is necessary to eliminate complications and destroy pathogenic microflora in the respiratory tract.
You can avoid infection with viral pneumonia by following simple recommendations from doctors - proper nutrition (vitamins, microelements), hardening, exercise, avoiding contact with carriers of influenza and other viruses. Preventive vaccination will not be superfluous. Injections can save you from fever and other symptoms of ARVI.
Symptoms of pneumonia (pneumonia) without fever
It is very difficult to notice the symptoms of pneumonia without fever. Many people do not realize that they are faced with this serious disease. Poor health is attributed to fatigue. However, the disease progresses and, in the absence of adequate therapy, leads to serious health problems. There are frequent cases where death occurs.
More and more people want to know the exact answer whether an adult or child can have pneumonia without coughing and without fever. Let's look at this issue in this article.
A weakened immune system is the main cause of this pathology. When human immune cells are suppressed by infections, they do not respond properly to pathogenic microorganisms. In such patients with pneumonia, the body temperature often remains normal, there is no cough, and there are no fighting sensations.
Diagnostics
If pneumonia is observed without fever and there is no cough, you need to pay attention to the following signs:
- weakness and fatigue;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing when walking, physical activity;
- increased sweating;
- frequent headaches;
- lack of appetite, increased thirst;
- pain with slight turns of the body.
According to experts, pneumonia without fever leads to a deterioration in the patient’s general condition and causes severe complications. The diagnosis is confirmed by the doctor by auscultation of the lungs, in which dry or, conversely, moist rales are heard. When performing percussion, the sound of dullness in the area of inflammation is clearly audible. For diagnosis, X-ray examination is used in several projections, where areas of damage to the lung tissue are clearly visible in the form of darkening. In addition, vital lung capacity is measured. The local doctor can refer the patient for a consultation with a phthisiatrician, because a latent form of pneumonia in adults sometimes masks the process of decay of lung tissue against the background of advanced tuberculosis.
General and specific symptoms of pneumonia without fever and cough
In most cases, pneumonia is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees. But latent pneumonia does not have such a symptom. Here are the symptoms of early and advanced pneumonia without fever:
- chest pain;
- malaise;
- drowsiness;
- dyspnea;
- severe pain in the head;
- nasal congestion, runny nose;
- heavy sweating.
Pneumonia without fever is often diagnosed in people who have not completely cured a cold. At first there may be a slight cough, which gets worse over time. The volume of sputum increases. Sometimes additional symptoms occur:
- difficulty breathing;
- constant feeling of thirst;
- pain occurs when moving;
- sweating increases during any physical activity;
- a blush appears on the face on the side of the affected lung.
Attention! Do not self-medicate. Contact your doctor as soon as possible. This will increase your chances of recovery.
Signs of latent pneumonia in children
Pneumonia without symptoms is usually diagnosed in newborns and children under one year of age. The respiratory activity of the lungs in a child who is not yet walking is insufficient. Parents may think that teething has begun. It is important to know the signs of pneumonia without cough and fever in children:
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent crying;
- refusal of food;
- low activity;
- frequent regurgitation;
- bloating.
In older children, pneumonia without cough may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pale complexion;
- spots on the cheeks;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia;
- fatigue;
- a whistling sound when inhaling or exhaling.
Pneumonia without fever can develop in children of different ages due to a violation of the daily routine. Poor diet and lack of physical activity can also lead to the disease.
Attention! Even a doctor may not recognize the disease in a child during the initial examination. This is why it is important to observe over time.
How to detect pneumonia without fever?
Pneumonia without fever in adults and children is diagnosed based on information obtained during a blood test. The presence of the disease is indicated by an increased number of leukocytes and accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation. In order to clarify the diagnosis, such studies can be carried out.
- MRI or CT. The whole picture of the developing disease is established.
- X-ray. Usually prescribed for suspected pneumonia. The localization of the process is determined.
- Bronchoscopy. It is carried out to determine the cause of the disease and select a treatment method.
Attention! If the cough does not go away within two weeks, then there is a very high probability that pneumonia has developed.
What to do if latent pneumonia is detected?
The main therapy is medication. The process must proceed in several directions.
- Taking medications aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the disease.
- Taking medications that enhance immunity and medications that eliminate cough and fever (if necessary).
Attention! It is important to strictly follow the recommendations of your doctor.
The patient is prescribed antibiotics. First of all, these are drugs from the penicillin group: aminopenicillin, benzylpenicillin. If there is no improvement within two days, higher-order medications are prescribed: clamithromycin, azithromycin, ceftriaxone.
Medicines must be taken for three days. Then the patient's condition is analyzed. In the absence of positive dynamics, other drugs are prescribed or antibacterial medications are prescribed.
If the disease is caused by viruses, antiviral drugs are prescribed: bronchomunal, oseltamivir, etc. If pneumonia is caused by a fungus or parasite, fluconazole or Diflucan is prescribed. In some cases, agents that dilute sputum are indicated: lazolvan, bromhexine. Fenoterol or salbutamol helps get rid of shortness of breath.
Attention! In case of a complex course of the disease, immunomodulators are prescribed: thymalin, prodigiosan, etc.
For latent pneumonia, complete rest and bed rest are indicated. It is important to drink a lot of clean water. You can also drink tea with rose hips, viburnum, and raspberries. You must adhere to a special diet. Moderate breathing exercises are useful. The room where the patient is located must be wet cleaned daily.
Attention! People with hypertension should not drink a lot of water.
To prevent pneumonia without fever in adults or children, it is recommended to resort to the following preventive measures:
- strengthen immunity;
- harden the body;
- eat right, consume enough minerals and vitamins;
- get vaccinated;
- monitor the condition of your teeth;
- try not to be in places with large crowds of people.
Please share this material on social networks. This way, even more people will find out whether pneumonia can occur without high body temperature.
Pneumonia without fever, but with cough
Pneumonia can be suspected by its characteristic symptoms - high body temperature combined with a severe cough. However, this is not always the case. In some cases, the temperature does not rise, but the person continues to cough. This can confuse the patient and he puts off visiting the doctor. As a result, valuable time is lost. When contacting the Yusupov Hospital, the patient is immediately prescribed an examination, thanks to which it is possible to accurately diagnose and begin treatment on time.
Treatment
The features of the therapeutic effect for latent pneumonia are determined by the degree of development of the disease and the presence of complications. Therapy is based on drug treatment with antibiotics and physiotherapeutic procedures. However, surgery may be necessary to improve the patient's condition.
Drug therapy
The choice of drugs for drug treatment is made on an individual basis, taking into account the specifics of the patient’s body and provides for the achievement of the following tasks:
- complex effect on the causative agent of the disease;
- elimination of inflammatory processes - anti-inflammatory drugs (fluoroquinolones, penicillins, macrolides, carbopenems);
- restoration of respiratory functions, cleansing of the bronchi and removal of sputum - expectorants (Lazolvan, Ambroxol, Eufillin), rubbing ointments;
- increasing immunity - immunomodulators, vitamin complexes;
- Elimination of symptoms - taking antipyretic and painkillers.
Physical activity and physical activity are contraindicated for patients with pneumonia.
The minimum treatment course for SARS, according to the WHO protocol, is 14 days.
Surgery
The use of surgical intervention for pneumonia is indicated in cases of the development of such severe complications as abscess, gangrene of the lungs, pleurisy, and empyema.
The surgical intervention involves installing drainage systems for patients to ensure the outflow of purulent contents from the lungs, as well as the removal of necrotic tissue.
Folk remedies for pneumonia
When used skillfully, traditional medicine can provide effective assistance in the treatment of pneumonia. According to pulmonologists, the use of folk remedies is only relevant in combination with traditional therapeutic measures.
Among the most effective traditional medicines:
- thyme infusion - two tablespoons of herb per glass of boiling water. Leave for four hours. Take half a cup three times a day;
- fig drink. Boil two fruits in a glass of milk for several minutes. Take a serving after meals;
- decoction of fireweed tea. Brew a teaspoon of herbs in a glass of water and leave for about an hour. Take two large sips three times a day before meals. Course 10 days;
- pine bud syrup. Young pine buds are sprinkled with sugar in a glass container, covered with gauze, and kept in the sun for several days, shaking occasionally. Take a tablespoon three times a day. Store in a dark place. Shelf life: one year;
- compress of cottage cheese or potatoes. A small portion of warmed cottage cheese or hot boiled potatoes is mixed with honey and placed on the chest before bed. Then they wrap themselves up thoroughly and drink a cup of diaphoretic tea (with linden or raspberry). In the morning, remove the compress, take a shower and change clothes. If yellow or green spots appear on the cottage cheese after the compress, this is a sign of a severe form of pneumonia;
- aloe with honey. Grind a few aloe leaves and mix with an equal amount of honey. Take a spoon before meals;
- nuts with honey. The ground nuts are mixed with an equal amount of honey. Take a spoon before meals.
Despite the general effectiveness of folk remedies, it is impossible to completely cure pneumonia with their help. Recommendations from traditional healers should be considered as additional measures to improve the patient’s condition.
Causes of pneumonia
Pneumonia begins as a result of damage to the respiratory system by a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. Most often, pneumonia is bacterial in nature. Among the causative agents of pneumonia, the following main bacteria are distinguished:
Pneumonia can develop against the background of colds, flu, bronchitis; or begins as an independent disease. People with weak immune systems are most at risk for pneumonia. The disease is more common in childhood and old age. The presence of immunodeficiency states and chronic diseases contributes to the development of pneumonia. In smokers and people who abuse alcohol, the disease is more severe and complications are more likely to develop. This is also associated with a decrease in the body's protective functions due to the toxic effects of alcohol and cigarettes.
Methods for diagnosing latent pneumonia
It is not always possible to establish a latent form of pneumonia through visual examination, due to the absence of visible symptoms of the disease. Therefore, pulmonologists use a set of diagnostic measures, both basic and additional.
The main diagnostic measures include:
- blood tests - general to determine the quality of blood composition, and biochemical, to assess the functioning of internal organs;
- sputum culture - to determine the type of pathogen;
- examination of sputum using the Gram method helps to establish or exclude the bacterial nature of the pathology;
- Chest radiography is the most informative method for diagnosing all types of pneumonia. Allows you to detect inflammatory foci in the lung tissues and assess the degree of their changes;
- computed tomography is a method of detailed visualization of the respiratory organs.
As additional diagnostic procedures, doctors use electrocardiography, urinalysis, bronchoscopy and biopsy of the lung, pleural cavity and pleura.
Final diagnostic conclusions about the type and nature of pneumonia can be made only after a careful study of the data obtained through the study.
Main symptoms of pneumonia
The clinical picture, which is most often observed in patients with pneumonia, includes the following components:
- increase in body temperature above 38C,
- severe cough with sputum production,
- chest pain when coughing or taking a deep breath,
- pale skin,
- weakness,
- drowsiness.
Some types of pneumonia cause joint pain, headaches, and red spots on the neck and face. During the examination of the patient, wheezing in the lungs is clearly audible during auscultation. Based on this factor, the doctor has grounds to prescribe additional examination methods, which include radiography.
The first signs of pneumonia in children and adults
Pneumonia is a disease that is of infectious origin and is characterized by inflammation of the lung tissue when provoking physical or chemical factors occur, such as:
- Complications after viral diseases (influenza, ARVI), atypical bacteria (chlamydia, mycoplasma, legionella)
- Exposure to the respiratory system of various chemical agents - toxic vapors and gases (see chlorine in household chemicals is hazardous to health)
- Radioactive radiation, which is associated with infection
- Allergic processes in the lungs - allergic cough, COPD, bronchial asthma
- Thermal factors - hypothermia or burns of the respiratory tract
- Inhalation of liquids, food, or foreign bodies can cause aspiration pneumonia.
The cause of the development of pneumonia is the emergence of favorable conditions for the proliferation of various pathogenic bacteria in the lower respiratory tract. The original causative agent of pneumonia is the Aspergillus fungus, which was the culprit in the sudden and mysterious deaths of researchers of the Egyptian pyramids. Owners of poultry or fanciers of urban pigeons may become ill with chlamydial pneumonia.
Today all pneumonias are divided into:
- community-acquired, arising under the influence of various infectious and non-infectious agents outside the walls of hospitals
- hospital infections, which cause nosocomial microbes that are often very resistant to traditional antibacterial treatment.
The frequency of detection of various infectious pathogens in community-acquired pneumonia is presented in the table.
| Pathogen | Average % detection |
| Streptococcus is the most common pathogen. Pneumonia caused by this pathogen is the leader in the incidence of mortality from pneumonia. | 30,4% |
| Mycoplasma - most often affects children and young people. | 12,6% |
| Chlamydia – chlamydial pneumonia is typical for young and middle-aged people. | 12,6% |
| Legionella is a rare pathogen that affects weakened people and is the leader after streptococcus in the frequency of deaths (infection in rooms with artificial ventilation - shopping centers, airports) | 4,7% |
| Haemophilus influenzae - causes pneumonia in patients with chronic diseases of the bronchi and lungs, as well as in smokers. | 4,4% |
| Enterobacteriaceae are rare pathogens that mainly affect patients with renal/liver failure, heart failure, and diabetes mellitus. | 3,1% |
| Staphylococcus is a common causative agent of pneumonia in the elderly population and complications in patients after influenza. | 0,5% |
| Other pathogens | 2,0% |
| The causative agent has not been identified | 39,5% |
When the diagnosis is confirmed, depending on the type of pathogen, the age of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, appropriate therapy is carried out; in severe cases, treatment must be carried out in a hospital setting; in mild forms of inflammation, hospitalization of the patient is not necessary.
The characteristic first signs of pneumonia, the extent of the inflammatory process, acute development and the danger of serious complications if not treated in a timely manner are the main reasons for the population to urgently seek medical help. Currently, a fairly high level of development of medicine, improved diagnostic methods, as well as a huge list of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs have significantly reduced the mortality rate from pneumonia (see antibiotics for bronchitis).
Typical first signs of pneumonia in adults
The main symptom of the development of pneumonia is a cough, usually at first it is dry, obsessive and persistent (see antitussives, expectorants for dry cough), but in rare cases, the cough at the onset of the disease may be rare and not severe. Then, as inflammation develops, the cough during pneumonia becomes wet with the release of mucopurulent sputum (yellow-green).
Any cold viral disease should not last more than 7 days, and a sharp deterioration in condition 4-7 days after the onset of acute respiratory viral infection or flu indicates the onset of an inflammatory process in the lower respiratory tract.
Body temperature can be very high up to 39-40C, or it can remain subfebrile 37.1-37.5C (with atypical pneumonia). Therefore, even with low body temperature, cough, weakness and other signs of malaise, you should definitely consult a doctor. A repeated jump in temperature after a light interval during the course of a viral infection should be alarming.
If a patient has a very high temperature, then one of the signs of inflammation in the lungs is the ineffectiveness of antipyretic drugs.
Pain when taking a deep breath and coughing. The lung itself does not hurt, since it is devoid of pain receptors, but the involvement of the pleura in the process gives a pronounced pain syndrome.
In addition to cold symptoms, the patient experiences shortness of breath and pale skin. General weakness, increased sweating, chills, and decreased appetite are also characteristic of intoxication and the onset of an inflammatory process in the lungs.
If such symptoms appear either in the midst of a cold, or several days after improvement, these may be the first signs of pneumonia. The patient should immediately consult a doctor to undergo a full examination:
- Take blood tests - general and biochemical
- Take a chest x-ray and, if necessary, a computed tomography scan
- Submit sputum for culture and determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics
- Submit sputum for culture and microscopic determination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
The main first signs of pneumonia in children
Symptoms of pneumonia in children have several features. Attentive parents may suspect the development of pneumonia if the child has the following ailments:
- Temperature
Body temperature above 38C, lasting more than three days, not brought down by antipyretic drugs; there may also be a low temperature of up to 37.5, especially in young children. In this case, all the signs of intoxication appear - weakness, increased sweating, lack of appetite. Young children (as well as older people) may not experience high temperature surges with pneumonia. This is due to imperfect thermoregulation and immaturity of the immune system.
- Breath
Rapid shallow breathing is observed: in babies up to 2 months of age, 60 breaths per minute, up to 1 year, 50 breaths, after a year, 40 breaths per minute. Often the child spontaneously tries to lie on one side. Parents may notice another sign of pneumonia in a child; if you undress the baby, then when breathing from the side of the diseased lung, you can notice retraction of the skin in the spaces between the ribs and a lag in the breathing process of one side of the chest. Breathing rhythm disturbances may appear, with periodic pauses in breathing, changes in the depth and frequency of breathing. In infants, shortness of breath is characterized by the fact that the child begins to nod his head in rhythm with breathing, the baby may stretch out his lips and puff out his cheeks, and foamy discharge may appear from the nose and mouth.
- Atypical pneumonia
Inflammation of the lungs caused by mycoplasma and chlamydia differ in that at first the disease goes away like a cold, a dry cough, runny nose, and sore throat appear, but the presence of shortness of breath and a persistently high temperature should alert parents to the development of pneumonia.
- Character of the cough
Due to a sore throat, at first only a cough may appear, then the cough becomes dry and painful, which intensifies when the baby cries or feeds. Later the cough becomes wet.
- Child behavior
Children with pneumonia become capricious, whiny, lethargic, their sleep is disturbed, sometimes they may completely refuse to eat, as well as diarrhea and vomiting, and in infants - regurgitation and refusal to breastfeed.
- Blood analysis
A general blood test reveals changes indicating an acute inflammatory process - increased ESR, leukocytosis, neutrophilia. Shift of the leukoformula to the left with an increase in band and segmented leukocytes. With viral pneumonia, along with a high ESR, an increase in leukocytes is observed at the expense of lymphocytes.
With timely consultation with a doctor, adequate therapy and proper care for a sick child or adult, pneumonia does not lead to serious complications. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of pneumonia, you should provide medical assistance to the patient as soon as possible.
zdravotvet.ru>
Is there pneumonia without fever?
The symptoms described above are typical for pneumonia. However, in some cases, pneumonia develops without an increase in body temperature. This may be an individual reaction to an infectious irritant. In situations where there is no fever or cough, they speak of an atypical reaction and call pneumonia “asymptomatic.”
Pneumonia without fever is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness,
- increased sweating,
- dyspnea,
- cough (dry or wet).
There may also be no cough in asymptomatic pneumonia. This reaction is observed with the abuse of antitussive drugs. They suppress the cough reflex. Thus, phlegm accumulates in the lungs and does not come out, aggravating the condition.
Pneumonia without fever develops in people with reduced immunity. Children and the elderly are more susceptible to this type of disease. In older people, immune activity is reduced, which is reflected in the imaginary ease of pneumonia. In children, a similar reaction to the inflammatory process occurs due to the immaturity of the immune system. Children cannot describe in detail their feelings during illness, and even the most attentive parents may miss the development of a serious illness that does not have classical manifestations.
This is the danger of pneumonia without fever. The inflammatory process progresses without visible symptoms, which makes treatment difficult and can cause life-threatening consequences.