How to treat pneumonia (pneumonia), which is poorly resolved under the influence of antibacterial drugs - this question interests not only patients, but also doctors.
According to studies conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO), in the 21st century, most bacteria have developed resistance to existing antibiotics. New groups of antimicrobial agents have not been developed, so it is becoming increasingly difficult to treat. Against this background, the search for alternative methods and medications to get rid of pneumonia is relevant.
Pneumonia is provoked by a wide range of pathogens, ranging from bacteria (pneumococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus) to viruses (influenza, parainfluenza, RS virus). The most dangerous prognostic changes are inflammatory changes in the lungs caused by parasitism in the respiratory tract of mycoplasmas, chlamydia, herpes and parainfluenza. For them, combined treatment regimens should be selected, which do not bring the desired effect in people with weak immunity.
In such a situation, no matter what medicine you use, microorganisms quickly develop resistance to it. The recommendations of American doctors have been aimed at preventing the global use of antibiotics for several years. They are “sounding the alarm”, fearing the end of the era of antibacterial drugs, which are losing their effectiveness in treating pneumonia.
Principles of proper therapy
Correct treatment of pneumonia should be based on:
- Eliminating the cause;
- Elimination of the inflammatory focus;
- Symptomatic therapy.
Etiological therapy is based on the use of antibiotics or antiviral drugs, but this approach is not always rational.
Inflammation is eliminated by using drugs to reduce fever, anti-inflammatory drugs, and consuming large amounts of fluid.
Symptomatic treatment of the disease involves the use of expectorants (to improve sputum discharge, normalize mucociliary clearance, restore the functionality of the bronchi, and relieve allergic complications).
To properly treat pneumonia, a preliminary diagnosis of the patient’s condition is necessary using x-rays, a general blood test and an assessment of respiratory capacity.
In order for the treatment procedure to be of the highest quality, therapy should be started as early as possible, after identifying the symptoms of the disease.
Diagnosis of pneumonia in adults
Only a doctor can detect pneumonia. The first suspicions arise already during the examination and interview of the patient. How to detect pneumonia in an adult? Fluoroscopy will help to accurately answer this question. The specialist will see the affected lesions in the pictures and assess how extensive they are.
A laboratory analysis of sputum gives a correct idea of the course of pneumonia. As a result, the nature of the inflammatory process will be established. Typically, a patient with suspected pneumonia is referred for a blood test. The presence of an increased number of white bodies in it is evidence of the presence of bacteria and viruses.
If the doctor suspects severe disturbances in the functioning of the pulmonary system, he recommends bronchoscopy. In this case, a thorough analysis of the contents taken from the source of inflammation is performed. If too much fluid has accumulated, it must be drained by puncture. Sometimes they resort to surgery.
Early symptoms of the disease
Symptoms such as cough, runny nose and sputum production indicate not only acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI). They may be a manifestation of bacterial pneumonia. For an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to pay attention to other manifestations of pathology:
- Shortness of breath with damage to the lung tissue indicates extensive inflammatory damage;
- An increase in body temperature for more than 2 days most likely indicates bacterial pneumonia;
- Chest pain occurs due to a decrease in the respiratory capacity of the lungs, which leads to increased workload on the heart.
Based on the above signs, you can suspect pathology on your own and immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will supplement the diagnosis with percussion (study of sound permeability of the chest), auscultation (listening to breathing using a phonendoscope) and prescribe the necessary clinical diagnostic methods.
Hospitalization for pneumonia
Hospitalization may be required if:
- Patient over 65 years old
- Decreased kidney function (little urine)
- Systolic blood pressure below 90
- Diastolic blood pressure 60 mm or lower
- Rapid breathing (30 or more breaths per minute)
- There are signs of impaired consciousness
- Body temperature is below normal
- resting heart rate below 50 or above 100
Hospitalization is carried out either in therapeutic departments or in intensive care units if correction of vital functions is necessary.
Children may be hospitalized if:
- They are younger than 2 months
- They are lethargic or excessively sleepy
- They have trouble breathing
- They have low blood oxygen levels
- They appear dehydrated
Effective pathogenetic treatment
Pathogenetic treatment is aimed at eliminating changes in the respiratory tract that pneumonia provokes. There are several forms of the disease, classified according to the size of the pathological foci:
- Focal - the process is localized in one or more alveoli;
- Segmental – an entire segment consisting of many alveolar lobes is affected;
- Lobar - inflammation of the entire lobe of the lung;
- Croupous - total damage to the pulmonary fields on both sides.
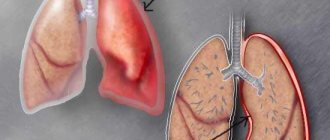
Each form is characterized by specific changes in lung tissue. In the classification list they are arranged according to severity. Focal pneumonia on an X-ray image is represented by small foci (about 1 cm), and therefore does not cause serious disturbances in the human body. However, if it is not treated in a timely manner, it can progress to the segmental form, in which a larger area of the lungs is affected.
Pathogenetic treatment of pneumonia that simultaneously affects the right and left lungs (lobar form) requires placement of the patient in a pulmonology hospital or intensive care unit, since the disease is severe.
Symptomatic drugs used in the treatment of pneumonia:
- Antipyretics – aspirin, paracetamol, ibuprofen;
- Mucolytic (thinning phlegm) - ambroxol, bromhexine, licorice root, ACC.
Other means are selected individually in each specific case after examining the patient by a doctor. Read below about what kind of hikes are used.
Help for children
Antibiotics also form the basis of antipneumatic therapy for children. Folk remedies should be used only in accordance with the recommendations of the pediatrician. The antibiotic drug for children must correspond to the severity of the disease and its nature. A doctor can provide significant assistance in choosing a medicine for children.
Basic Rules
Taking antibiotics for children should only be done on a timely basis. So, when taking a medicine for children is prescribed twice a day, the break should be twelve hours. If the doctor decides to prescribe an antibiotic for children three times a day, then the break lasts no more than eight hours.
The most commonly prescribed medications for children are:
- cephalosporins (take within a week);
- penicillins (take for seven days);
- macrolides (take for five days).
If the medicine was chosen correctly, an improvement is observed within three days. The temperature decreases, shortness of breath decreases, appetite improves.
Note to parents
In addition to taking medications prescribed by the pediatrician, it is necessary to use an integrated approach in the treatment of pneumonia.
Thus, it is extremely important to give the child drugs that provoke painless and rapid release of pathological sputum. In accordance with the doctor’s recommendations, antipyretic and anti-edematous medications are taken
Massage procedures have an excellent effect on a child’s weakened body. It is recommended to start them on the fourth or fifth day, when the inflammation process is completed.
You can also use mustard plasters at home, place jars and bathe your baby in warm baths with medicinal herbs.
Antibiotics against bacterial infection
For bacterial pneumonia, doctors often recommend treatment with antibiotics using a combination regimen. The effectiveness of therapy increases after a bacteriological test for the antibiotic sensitivity of the causative agent.
It involves taking sputum for culture. After bacterial colonies grow, discs with different antibiotics are placed next to them. Near those microorganisms that are sensitive to the drug, colony growth stops. Thus, effective drugs are selected for bacterial inflammation of the respiratory tract. Unfortunately, this method is not applicable for viral etiology of pneumonia.
The method seems to be ideal, but it has not become widespread. This comes with a significant drawback: colonies require about 2 weeks to grow. If treatment is not carried out during this period, microorganisms will destroy the lung tissue.
Without early treatment, it is difficult not only to get rid of pneumonia, but also to save the patient’s life. As a result, etiotropic treatment is prescribed immediately after identifying a pneumonic focus on an x-ray and involves the use of broad-spectrum antibacterial agents (cephalosporins). This is exactly the approach to treating the disease in our country, but WHO recommendations indicate the importance of antibiotic sensitivity testing in prolonged forms of pneumonia.
Features of etiotropic treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics:
- Stepped therapy – two-stage prescription of drugs;
- For a short period of time, switch from intramuscular or intravenous administration of the drug to oral administration (by mouth);
- For patients under 60 years of age with no concomitant pathology, the WHO recommendation is macrolide or penicillin antibiotics;
- Patients with focal or segmental pneumonia after 60 years of age with concomitant pathology should be treated with cephalosporins or aminopenicillins (protected, b-lactam). Treatment is carried out in a hospital to avoid re-infection;
- For complicated or severe lobar pneumonia, it is necessary to use fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin). An antibiotic sensitivity test is performed immediately after admission to the hospital.
Community-acquired pneumonia: causes and antibiotics that help
If a patient is brought in from the street, he has a cough with sputum, chest pain, wheezing in the lungs, the doctor first decides under what conditions the patient will be treated. Not always and not every patient needs to be hospitalized.
If he does not have a high temperature, if the respiratory rate, pulse, pressure are within certain limits, if the blood count is kept within acceptable limits, then he needs to be prescribed antibiotics and sent home.
This raises the question of which antibiotic should be prescribed. Today, almost any antibiotic is available, and doctors usually prescribe quite serious, strong and expensive antibiotics. The patient is happy that he is being treated with a cool antibiotic that costs $50 per bottle, and the doctor is happy that he did everything right. In fact, these expensive antibiotics most likely won't work! Why?
For example, community acquired pneumonia (translation from English - community acquired pneumonia - sounds somewhat clumsy, but this is the official modern name), as a rule, is caused by atypical microorganisms. This is not pneumococcus, which everyone has heard of, but chlamydia, mycoplasma, and a host of other microorganisms that, in fact, are not exactly bacteria, since in some ways they differ from classical bacteria.
They are only affected by a certain class of antibiotics. Therefore, such patients should be prescribed antibiotics of the group, the ancestor of which was erythromycin; older people should remember it. Erythromycin has now been discontinued because it caused severe arrhythmias. Its modern “descendants” are completely safe, can be used even during pregnancy and are quite effective.
Drugs derived from good old tetracycline are very effective in cases of community-acquired pneumonia. Drugs like tavanika and its classmates are very effective.
What to do in case of complicated pneumonia
Recommendations regarding treatment regimens for complicated forms of pneumonia from international medical institutes require detoxification therapy. Against the background of pathogenetic changes in the lungs, toxic substances appear in the blood, so other tissues are affected. By cleaning the bloodstream, it is possible to prevent damage to internal organs.
Detoxification can be carried out either using specialized equipment (“artificial kidney”) or intravenous infusion of solutions.
To get rid of complications, the following drugs and procedures are recommended:
- Hemodesis – purification of blood from toxins using special equipment;
- Antihistamines - tavegil, diphenhydramine, ketotifen;
- General restoratives - tincture of ginseng, eleutherococcus, viferon, groprinosin;
- Cardiac glycosides are necessary in the presence of pathological changes in the heart.
Physiotherapeutic procedures help restore the ventilation capacity of the lung tissue and reduce inflammatory changes in it.
Antibiotics by pathogen
To eradicate the pathogen (suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms that provoked inflammatory processes in the lungs), direct-acting antibiotics are selected.
It is important to establish the type of infectious agents so that the treatment benefits the patient, then the sputum is examined. During microbiological analysis, the sensitivity of the flora to the active ingredients of medications is determined.
Laboratory test results are prepared within 5-7 days. Until this time, the patient is treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
The effect of empirical drugs can be assessed after 48 hours (for inflammation without complications) or after 3 days (in other cases).
In the absence of a therapeutic effect (lowering temperature, eliminating shortness of breath, improving the general condition and clinical picture), the prescribed antibiotics are replaced by another group.
After 5-7 days, when microbiological tests are ready, the doctor adjusts the treatment regimen, depending on the test results.
Current WHO recommendations
There are current recommendations from the World Health Organization regarding the correct treatment of pneumonia at home and in hospital settings. It is especially important to observe them in case of lobar lesions of the lung tissue, which can cause the death of a person within a short time.
WHO recommendations to quickly get rid of pneumonia:
- If staying in a hospital is not possible for the patient, you can get rid of the disease at home. It is carried out under the constant supervision of a doctor and regular blood tests;
- A gentle regimen is an important principle for effective treatment of the disease. It helps speed up recovery by activating the body's own powers. The advisability of a gentle regimen is also due to the presence of side effects of antibacterial agents;
- The use of antibiotics for pneumonia requires caution and long courses of treatment. Otherwise, microorganisms will develop resistance, and it will be more difficult to get rid of them;
- Recovery does not occur after the patient's condition is alleviated. It is due only to an improvement in well-being when the proliferation of pathogens stops. If you do not complete the course of therapy, the inflammatory process will manifest itself with renewed vigor;
- Regarding the temperature reaction, the recommendations of experts are as follows: it helps the body quickly cope with pathology by accelerating metabolism, if it does not rise above 38.5 degrees. This temperature reaction should not be “knocked down” unless absolutely necessary;
- Diseased lung tissue is considered susceptible to injury. When using antibiotics and sulfonamides, it can quickly become affected, so it is necessary to monitor the dynamics of therapy using chest radiography in two projections (direct and lateral);
- Any methods of treating lung diseases require precise adherence to the dosage of medications. In order to prevent a decrease in the concentration of the drug in the pathological focus, the pharmaceutical industry has carefully worked out the dosage, which is indicated in the manufacturer’s instructions;
- Prescribing medication in large doses must be justified. It should be understood that it will cause partial destruction of the tissue. However, when the patient’s life is threatened, one has to choose the lesser of two evils.
Analyzing the above recommendations regarding the methods and methods of treating pneumonia, it is difficult to imagine how these mechanisms can be implemented at home. Nevertheless, doctors need to do this, since a person’s life hangs in the balance.
The best drugs for pneumonia
Most antibiotics that are suitable for bacterial pneumonia are prescription drugs.
Their incorrect use can significantly harm human health.
The drug and its dosage must be selected by a specialist.
Treating pneumonia is difficult, so you should listen to your body - sometimes a drug that is suitable for all indicators does not help.
In this case, you need to consult a doctor to select another remedy, or consult with several specialists.
Some drugs are available over the counter, but most of them can only be used in a hospital setting.
Your doctor may prescribe different antibiotics:
- macrolides;
- penicillins with beta-lactase inhibitors;
- tetracyclines;
- respiratory fluoroquinolones;
- Generation 2 or 3 cephalosporins.
Combined semisynthetic penicillins are prescribed against some pathogens, for example Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
These medications include:
- amoxicillin (Flemoxin Solutab, Hiconcil);
- piperacillin and tazobactam (Tazocin);
- oxacillin;
- oxacillin and ampicillin (Oxamp, Ampiox);
- ampicillin and sulbactam (Unazin, Sulacillin);
- amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate (Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Co-Amoxiclav).
If cephalosporins are required for treatment, then a drug from one of four groups of such drugs is selected.
Most often used:
- Cefuroxime (Zinacef, Ketacef - II generation);
- Zinnat (Cefuroxime Axetil - II);
- Cefaclor (Ceclor - II);
- Ceftriaxone (Lendatsin, Rotsedin, Forcef, Ceftriabol – III generation);
- Cefotaxime (Claforan - III);
- Sulperazone (cefoperazone and sulbactam - III);
- Cefoperazone (Cephobid - III);
- Cefixime (Cefspan, Suprax - III);
- Ceftibuten (Cedex, III);
- Cefipin (Maxipim, IV);
- Cefpir (IV).
Of the tetracyclines, Doxycycline (Vibramycin, Unidox Solutab) is considered the best in the treatment of pneumonia, and among monobactams, Aztreonam (Azactam).
Of the aminoglycosides, it is worth noting Amikacin (Amikin), which is prescribed if inflammation is caused by gram-negative microorganisms.
If the strains of identified bacteria are resistant to cephalosporins, carbapenems are used:
- Meropenem (Meronem);
- Tienam;
- Impenem (cilastatin and imipenem).
If pneumonia is caused by pneumococci, then fluoroquinolones are suitable - Levofloxacin (Tavanic) or Moxifloxacin (Avelox).
Among the expectorant drugs that are popular and available in pharmacies:
- Ambrohexal;
- Ambrobene;
- Halixol;
- Bronchosan;
- Lazolvan;
- Bronchohex;
- Mucosolvan;
- Gedelix;
- Sinupret.
To treat viral pneumonia without a bacterial infection, you do not need to take antibiotics.
- Acyclovir for chickenpox and herpes;
- Gancilovars for cytomegalovirus;
- Tamiflu or Relenza for influenza A and B.
Antibiotics for pneumonia in adults
Antibiotic treatment of pneumonia in adults: scheme and course. Treatment of pneumonia is carried out mainly ... “Read more”
Which doctor should I contact with symptoms?
Modern treatment of pneumonia at home requires the doctor to have extensive practical experience. Home therapy has its advantages and disadvantages:
- When observing bed rest, a person is in a more comfortable environment;
- Relatives and the doctor should monitor the slightest changes in the person’s condition;
- It is necessary to constantly monitor blood pressure;
- Deterioration of the condition requires mandatory hospitalization;
- Mental agitation of the patient indicates toxic damage to the brain. In such a situation, it is necessary to immediately diagnose the pathology of the lungs and brain;
- A constant flow of clean air is ensured into the room where a person is located, so the room is ventilated several times a day.
The course of home therapy for pneumonia is somewhat longer than hospital therapy.
A significant advantage of treating pneumonia at home is the ability to organize a rational and proper diet. The patient's food should be low in calories with limited carbohydrate intake.
In the first days, during the course of antibacterial therapy, the patient’s appetite decreases. You should not insist on eating. His diet during this period of time consists of fruits and vegetables. In the future, you can add chicken broth and natural juices.
Traditional methods may also be included in the course of treatment. A well-known drink made from milk with raspberries and honey, tea with rose hips - these methods have the right to exist, since they have been tested by the practical experience of traditional healers over several centuries. Their use should be discussed with your doctor.
Home physical therapy methods for treating pneumonia
To speed up the healing process, you can resort to simple methods of home physiotherapy:
- inflating balloons. To improve bronchial patency, you can inflate balloons or soap bubbles 3-5 times a day;
- massage. If the patient is on the mend, it will be useful to use massage to better remove mucus from the lungs and warm up. To do this, you can use vacuum cans that are moved along the back in the lung area; honey, which has a warming effect and gives vitality, or essential oils that kill harmful bacteria in the air, relieve swelling and make breathing easier;
- mustard plasters, compresses. Also used if a person has already felt relief;
- inhalation. Birch or eucalyptus leaves are used for them;
- body position. If pneumonia has persisted, the patient should be placed in such a way that the upper part of the body is lower than the lower part. This will make it easier to remove mucus from the bronchi.
Diagnostics and therapy in medical institutions
To treat pneumonia in a medical facility, you should first contact your local physician. How does a doctor diagnose pneumonia?
- Examine the patient;
- Perform percussion (finger tapping of the chest);
- Listen to breathing with a phonendoscope (auscultation);
- Order a chest x-ray;
- Perform laboratory tests.
After receiving the results of clinical and instrumental research methods, the therapist will make a diagnosis and determine the severity of the disease.
For mild pneumonia, the therapist will independently treat the patient. If a person has moderate or severe pneumonia, he will be sent for consultation to a pulmonologist, who will refer him for hospitalization to the pulmonology department. This is necessary in order to promptly provide, if necessary, artificial ventilation (in case of respiratory failure).
Thus, pneumonia can be treated at home and in a hospital setting. In any case, the course of therapy should be comprehensive and based on WHO recommendations.
Possible complications
Timely treatment is the key to ensuring that the disease goes away without serious consequences. Sometimes the cause of complications is the perception of relief as complete recovery. If the patient stops treatment quickly, complications arise. Pathogenic microbes multiply unhindered, and the infection becomes chronic.
Complications after pneumonia in adults are expressed in malfunctions of the respiratory system and the body as a whole. The most threatening are pulmonary edema, pleurisy, acute respiratory failure, meningitis, pericarditis and gangrene.
Discharge from hospital
After undergoing drug treatment and upon completion of physical procedures, when the doctor ascertains a stable condition, the recovery process is confirmed by tests, and the patient is prepared for discharge.
Such a certificate allows you to resume attending preschool educational institutions, and for adults to return to work. An extract is also issued in cases where a patient is transferred from a full hospital to a day hospital for further monitoring.
Despite the completed therapeutic process, recovery from the disease can occur over a period of several months to a year (this depends on the severity of the pathology suffered). All this time, the person is registered at the dispensary, periodically takes the necessary tests and undergoes other examinations.
During the recovery period, it is important to follow a sleep and rest schedule, eat right, give up bad habits, ventilate areas where you frequently spend time, take walks in the fresh air and dress according to the weather (prevent hypothermia).
During periods of seasonal epidemics, vaccination against diseases of the respiratory organs and viral pathways is especially recommended for persons who have had pneumonia.
A stay in a sanatorium and therapeutic exercises make rehabilitation effective.
Author: Glushko Raisa Therapist, pulmonologist, immunologist
Source
Pneumonia is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the lungs that can affect any age and social group of people. There are a number of different criteria that allow you to assess whether a patient with pneumonia needs hospitalization in a specialized department. Treatment of pneumonia in the hospital is carried out for patients with a severe course of the disease, at risk of developing complications, or in the presence of serious concomitant pathologies.
Why does pneumonia occur?
Pneumonia can result from many different causes. Overview of Pneumonia. The severity of the disease and the method of treating Pneumonia largely depend on which factor caused the pneumonia.
Viral pneumonia
It is this type of pneumonia that Pediatric Pneumonia most often occurs in children under 5 years of age.
The causative agents are influenza viruses, herpes, adenoviruses (causing colds) or, for example, coronaviruses - the same SARS‑CoV‑2. Whatever virus causes pneumonia, the signs of pneumonia will be the same. The Clinical Presentation and Immunology of Viral Pneumonia and Implications for Management of Coronavirus Disease 2020.
Bacterial pneumonia
There are many bacteria that can attack the lungs. For example, pneumococci (Streptococcus pneumoniae) or staphylococci.
Bacterial pneumonia is the most common Pneumonia Symptoms and Diagnosis type of pneumonia in adults.
Typically, bacterial pneumonia occurs when the body is weakened for some reason: after an illness (for example, ARVI), surgery, due to poor nutrition, age, bad habits (these include smoking and alcohol abuse) or immune disorders.
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Mycoplasmas are bacteria without cell walls. They usually cause pneumonia with the lungs Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections. Fast Facts, almost imperceptible cold-like symptoms.
Unofficial Don't miss the first signs of pneumonia The name of this type of pneumonia is “walking pneumonia”: the disease is often carried on the legs, without even thinking about the need for bed rest.
Fungal pneumonia
Such Pneumonia. What Causes of Pneumonia pneumonia most often occurs in people with chronic illnesses or severely weakened immune systems (such as HIV), and in those who regularly inhale spores of certain fungi from contaminated soil or bird droppings.
Aspiration pneumonia
Occurs when foreign substances accidentally enter the lungs - food, drink, vomit, saliva. Most often, this happens to people who have something (for example, brain damage, alcohol or drug intoxication) that disrupts the normal functioning of the gag or cough reflex.
Forecast
The prognosis for the course and duration of pneumonia depends on many factors:
- type of pneumonia (out-of-hospital/intrahospital),
- pathogen,
- age of the patient (in older people it is more severe and the incidence of death is higher),
- the presence of concomitant diseases and their course (exacerbation/remission),
- state of the immune system,
- start time of treatment,
- development of complications (abscess, empyema and others).
Typically, patients with mild to moderate severity have a good prognosis and recovery time is rapid. In patients with risk factors and concomitant diseases, acute pneumonia can take a protracted course and the risk of complications is much higher.
Important! With timely treatment, in most cases complete recovery occurs.
Efficiency mark
The effectiveness of treatment is assessed based on the severity of the inflammatory process. Accordingly, the doctor must identify the intensity:
- shortness of breath;
- suffocation;
- cough;
- other symptoms.
It is important to determine whether there is hypotension, tachycardia, respiratory failure and other conditions of a similar type. If the symptoms subside, the treatment is correct. If no changes are observed, or they intensify, new studies are prescribed, based on the results of which a different therapeutic model will be selected.
Treating pneumonia is not an easy task. An integrated approach is required. Self-therapy will not lead to anything good. You need to contact a pulmonologist.
Lecture: “Community-acquired pneumonia: diagnosis and treatment from the perspective of evidence-based medicine.”
Treatment of pneumonia at home and in hospital