2298
0
Peripheral lung cancer is caused by unfavorable living conditions, including various types of pollution. This oncology also manifests itself due to poor heredity or due to hard work in relevant areas of activity, which include:
- work related to places concentrating large amounts of dust;
- professions that involve severe stressful situations that are repeated with great frequency;
- work at chemical plants or other hazardous production facilities.
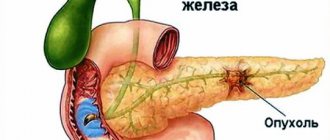
Unlike the central location of the disease, peripheral cancer manifests itself later. In this case, the tumor itself does not reach the lumen of the bronchus, spreading very slowly inside the affected part of the body and often showing its existence at a stage close to critical. Pain endings are absent in the lung tissues and, therefore, do not give the body timely alarm signals. Due to the delayed appearance of external symptoms, such hidden oncology is much more dangerous than the more obvious central one.
Forms of the disease in question
Tumor processes in the lungs are diverse. Peripheral lung cancer has several types. The cortico-pleural appearance is an oval-shaped formation that grows in more than one node. This neoplasm grows directly into the chest, after which it is located in the so-called subpleural space. The resulting pathology belongs to the squamous cell type of cancer. The structure of the tumor is homogeneous; it has a lumpy inner surface and poorly distinguishable contours. The tumor can grow both into adjacent ribs and into the bodies of adjacent thoracic vertebrae.
The so-called cavitary form of peripheral lung cancer is characterized by the absence of symptoms. It is detected at later stages, when pathological processes have become irreversible. Cavity formations are formed inside the pulmonary sections, having the shape of a ball, a lumpy outer surface and poorly distinguishable contours. The growth of the tumor leads to the proliferation of formations with parallel thickening of their walls.
Causes of pathology
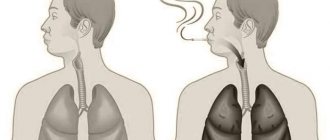
The main reason for the development of such pathology as peripheral lung cancer is smoking. Moreover, not only those people who smoke themselves get sick, but also those who inhale tobacco smoke. According to some researchers, passive smoking is even more dangerous in terms of the development of lung cancer than active smoking, so it is worth considering whether to be near the person smoking a cigarette or to give him the opportunity to smoke it alone.
However, not only active and passive smoking leads to lung cancer. The disease can also develop in people who inhale asbestos dust for a long time (working in industries) or in those who are exposed to arsenic, chromium, radon or nickel.
The risk of oncology in the lungs is also inherent in people who work in hazardous chemical industries and constantly inhale vapors of various chemicals. Danger also awaits those who work in excessively dusty areas, regularly inhaling dust into the lungs, thereby disrupting the normal blood supply in them.
Peripheral tumor
People living in large cities suffer from lung cancer more often than residents of small cities, which is associated with inhalation of large amounts of harmful substances in the city atmosphere. The average age of patients suffering from this disease is 40–50 years, but women, especially smokers, are more often affected. Sometimes it happens that the disease is detected in a person who has never smoked and led a healthy lifestyle. Scientists still cannot explain why this happens - they are inclined to an unfavorable environment and a weak human immune system.
Factors such as:
- hereditary predisposition (the presence of this pathology in relatives increases a person’s chances of contracting it);
- chronic inflammatory processes in the bronchi and lungs.
Oncology of the upper lobe of the left lung
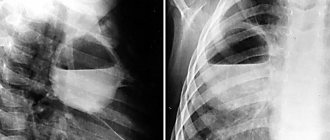
In people with this type of cancer, X-rays clearly show blurred contours, an irregular shape of the formation and its heterogeneous structure. The pulmonary roots are expanded due to the influence of the vascular trunks. In most cases, the lymph nodes remain the same size (in the case of lower lobe cancer, the situation is the opposite).
As for oncology of the upper lobe of the right lung, it is in many ways similar to the previous pathology, but it is diagnosed much more often. The formation of the nodular form occurs in the terminal bronchioles. The disease makes itself felt after the soft lung tissues germinate. X-ray examination allows us to examine a formation that has a nodular shape, clear contours and a bumpy surface. Sometimes the edge of the tumor contains a small depression. The presence of such a depression indicates that a large vessel has entered the node.
Peripheral cancer: prognosis
This type of oncology is considered to be the most difficult to treat malignant tumors. Even in the early stages, peripheral cancer is difficult to treat, including due to the low sensitivity of infected lung tissue to chemotherapy drugs. In case of timely intervention in the ongoing disease process, chances of survival are present with a limited cancer process.
If a rounded darkening appears on the images, with a clearing in the center, or if an uneven scalloped contour of the cavity is detected on the x-ray, treatment of peripheral cancer turns out to be difficult, because These signs indicate the transition of the disease to the dangerous third stage.
Tumor collapse and centralization syndrome
When the pathogenic formation reaches a large size, the pulmonary blood supply deteriorates, and this leads to tumor disintegration. The decay occurs gradually with the formation of cavities inside the tumor node. Due to the unevenness of the process, small tumor masses remain on the walls of the cavity. When small cavities merge into one, the stage of major decay begins. At the end, the phase of the so-called central decay begins. Thanks to the examination, it is possible to identify the presence of a cavity formation with thick walls; There is a horizontal liquid level inside it. The course of the described pathology is similar to the course of an abscess. A person’s temperature rises, the expectoration becomes purulent (sometimes there is blood in the secreted mucus).
Complications and consequences
If the rehabilitation course is successfully completed, the patient will be able to live for another five years, after which remission may last if there is no worsening of the diagnosis.
Despite the destruction of cancer cells and optimization of the body’s functioning, certain complications associated with the activity of internal organs may arise. We are talking about failure of the liver, kidneys, pulmonary and other types of failure. A separate recovery course and preventive measures will allow you to cope with the presented processes. They will provide an opportunity to strengthen the body, normalize metabolism and improve the general health of the patient.
Symptoms of the described deviation
In the early stages of peripheral lung cancer, a person may suffer from shortness of breath and chest pain. There is often expectoration of blood. The progression of the pathology leads to an increase in temperature and copious sputum production. After a certain time, secondary symptoms are added to the main symptoms, which appear after the pathogenic formation grows into adjacent tissues, as well as nearby organs.
Atelectasis - forms after the tumor grows inside the bronchus. This germination disrupts the pneumatization of lung tissue.
Syndrome of neurological abnormalities - progresses when metastases enter the brain. The syndrome is characterized by signs of paralysis of the phrenic and recurrent nerves.
Perifocal inflammation - forms in situations where a focus of pneumonia forms around a tumor node. Symptoms include hyperthermia, cough with sputum production.
Pleural effusion is a deviation that cannot be treated by pleural puncture. After a certain time after removal, the pathology develops again.
Pancoast syndrome - manifests itself in the form of atrophy of the muscles of the upper extremities; There is often pain in the shoulder girdle area. Progresses in the presence of apical oncology, affecting the nerves and vessels of the shoulder girdle.
The so-called mediastinal compression syndrome makes itself felt by difficulty swallowing and pain in the chest area.
Preventive measures
Prevention measures should be observed by healthy people to prevent the primary development of the tumor, as well as by patients who have already survived lung cancer to prolong remission. Doctors recommend following these rules:
- Once every six months, undergo fluorography.
- Have your entire body examined at least once a year.
- Eat properly.
- Avoid contact with harmful substances or follow instructions for working with chemicals and poisons.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- To live an active lifestyle.
It is also important to promptly treat any pathologies of the respiratory organs. If diseases are left unattended, favorable conditions may be created for the development of the tumor process.
Differential diagnosis
In accurately identifying the pathology in question, bronchographic as well as radiation examination is of enormous importance. Thanks to such procedures, it is possible not only to diagnose the presence of cancer, but also to determine its form. If a person suffers from central cancer, x-rays will show insufficient ventilation of the lungs, atelectasis of lung tissue, narrowing of the central bronchi, and abnormal sizes of mediastinal lymph nodes. The tumor will have poorly distinguishable contours, as well as a heterogeneous structure. An x-ray will be able to show decay cavities with poorly visible contours; in addition, it will allow you to examine the node against the background of lung tissue. Bronchographic examination will provide consideration of multiple bronchial amputations; in addition, it will show narrowing of the small bronchi.
Development factors
The formation of this type of cancer is influenced by factors such as nicotine addiction, which provokes not only peripheral lung cancer, but also other types of disease. No less probable reasons should be considered:
- negative conditions associated with the environment, namely air pollution, gas pollution, etc.;
- negative working conditions, which are characterized by a significant accumulation of dust and small volatile components;
- asbestosis, which is a condition that develops due to the inhalation of small particles of asbestos;
- genetic predisposition.
Chronic lung diseases should be considered another factor in the development of peripheral lung cancer. They cause permanent inflammation, which increases the likelihood of developing lung cancer. The viruses presented can penetrate cellular structures and increase the likelihood of cancer.
Particular attention should be paid to the symptoms that appear in this case and relate to the lower and upper areas.
Surgery
• removal of the pulmonary lobe (the most common procedure);
• tumor removal - this type of operation is usually performed on elderly people or patients with concomitant disease that prohibits extensive abdominal surgery (due to danger to life);
• complete removal of the lung - such an intervention is carried out in the 2nd and 3rd stages of cancer development;
• combined surgery – involves removal of the tumor, as well as affected neighboring organs and tissues.
Treatment options
In order to eliminate negative symptoms and stop the growth of malignant neoplasms and metastases, complex treatment is indicated. It must remain this way at any stage for the prognosis to be positive. Surgeries and radiation therapy are giving way to modern methods of treating lung cancer. Despite the introduction of new treatment methods, surgery for patients with resectable lung cancer is perceived as a radical method.
Within the framework of its use, there are prospects for 100% cure.
Radiation therapy demonstrates ideal results when implementing a radical treatment program in the primary stages, namely the first and second.
The next effective method is chemotherapy, which uses Doxorubicin, Vincristine and other drugs. They are prescribed if there are contraindications to surgery and radiation therapy. Oncologists pay attention to the fact that:
- the presented therapy involves up to six cycles of chemotherapy with breaks of 3-4 weeks;
- absolute resorption of the tumor occurs rarely, only 6-30% of patients experience objective improvement;
- When combining chemotherapy with radiation (probably synchronous or sequential use), better results can be achieved.
A combination treatment is used, which includes, in addition to radical and surgical, other types of effects on the tumor. We are talking about the local and regional affected area, which can be used by external beam radiation therapy and other similar methods.
The combined technique involves the use of two different types of influences, which are aimed at local and regional foci. We are talking about surgical and radiation treatment, radiation, surgery and then radiation. Such combinations make it possible to compensate for the limitations of any of them used separately. It must be emphasized that it is permissible to talk about the presented method of treatment in a situation where it is used according to the algorithm that was developed at the very beginning of therapy for the lower and upper areas.