Causes
There are several main reasons for the development of frontal sinusitis. These include:
- previously untreated respiratory diseases (sinusitis, sinusitis), accompanied by a runny nose and inflammation of the sinuses;
- penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the paranasal and frontal sinuses.
The infection enters the mucous membrane with blood or from the nasal passages. The ethmoid sinus is anatomically close to the sinus, so frontal sinusitis is often accompanied by polysinusitis. The disease can develop due to hypothermia or after swimming in open water.
In order to get rid of frontal sinusitis, treatment at home is quickly carried out using modern medicines and traditional medicine.
The severity and form of pathology depend on etiological factors. The reasons for the development of frontal sinusitis are:
- prolonged rhinitis caused by an allergen, bacterial or viral infection;
- deviated nasal septum, chronic sinusitis, bronchial asthma;
- infection of the sinuses with staphylococcus or streptococcus;
- respiratory pathology;
- polyps or foreign bodies in the nasal passages;
- injury to the facial bones;
- neoplasm of a malignant or benign nature.
Foreign bodies in the nose often cause the development of frontal sinusitis in children. The inflammatory process can also occur due to decreased immunity.
With frontal sinusitis, the mucous membrane that lines the sinus becomes inflamed. The causes of frontal sinusitis can be varied; the form and severity of the disease depend on them.
- Infection most often causes frontal sinusitis. In this case, inflammation can occur simultaneously in both the maxillary and frontal sinuses. In this case, the patient is diagnosed with sinusitis and frontal sinusitis. The cause may be influenza, ARVI, diphtheria, scarlet fever. The causative agents of viral frontal sinusitis are adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, and coronaviruses.
- Bacterial sinusitis is caused by streptococci and staphylococci.
- The cause of inflammation of the frontal sinus can also be a fungal infection. This happens if there are foci of infection in the human body: carious teeth, abscesses.
- Allergies and bronchial asthma cause inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane. This closes the hole that allows fluid to exit the frontal sinus.
- Nasal polyps (benign, round-shaped growths) can also cause inflammation.
- Injuries to the nose and paranasal sinuses, deviated nasal septum and hypertrophy of the turbinates, and foreign bodies can also cause inflammation of the frontal sinuses.
The most common cause of acute frontal sinusitis is an infectious process that has spread to the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus from the nasal cavity during acute respiratory and other infectious diseases. The causative agents can be viruses, bacteria or microscopic fungi.
Chronic frontal sinusitis develops against the background of incorrect or untimely treatment of the acute form of the disease; it is facilitated by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the paranasal sinuses and/or nasal septum.
The causes of damage to the mucous membrane and the development of frontal sinusitis can be different. Their nature influences the form of the disease and the severity of its course.
Infection
The most common cause of a disease such as frontal sinusitis is infection in the maxillary and frontal sinuses. As a result of inflammation, sinusitis and frontal sinusitis develop.
The disease can be caused by:
- scarlet fever,
- diphtheria,
- ARVI,
- flu.
Among the causative agents of viral frontal sinusitis:
- respiratory syncytial viruses,
- rhinoviruses,
- coronaviruses,
- adenoviruses.
Causative agents of bacterial frontal sinusitis:
- Staphylococcus aureus,
- streptococcus,
- Pfeiffer wand,
- Pneumococcus.
Symptoms of frontal sinusitis in children may appear as a result of exposure to the bacterium Moraxella catarrhalis. In this case, the disease is mild.
Fungi cause inflammation by entering the sinuses through the blood or infectious foci (abscesses, carious teeth).
Rhinitis or bronchial asthma contribute to the appearance of swelling of the mucous membrane and the development of the inflammatory process. As a result, the lumen is blocked, which should ensure the outflow of mucus from the sinus
Injury
Mechanical injuries to the bones of the skull provoke tissue swelling and disrupt blood circulation in the mucous membrane and sinuses.
Polyps
Neoplasms of a benign nature in the nose appear due to degeneration of the mucous membrane. They cause swelling, make nasal breathing difficult and block the outflow of fluid from the sinuses.
This problem can be congenital or acquired as a result of an injury or a previous illness.
Foreign bodies
A foreign object entering the right or left nasal passage causes inflammation. It quickly spreads to the sinuses, causing, respectively, frontal sinusitis on the right or left. This is especially important for small children who may accidentally put small parts in their noses.
Complex treatment
The course of treatment for frontal sinusitis may include not only drug therapy, but also surgery . Surgery is necessary in case of an uncontrolled process when inflammation spreads to nearby tissues.
Keep in mind that it is impossible to cure this type of illness without antibiotics and other medications.
Do not use alternative therapy methods.
Herbs and plants not only will not cure the disease, but will also lead to serious complications. But in some cases, folk remedies can become additional anti-inflammatory therapy.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis should only take place under the supervision of a doctor.
Any self-medication for this type of inflammation is unacceptable.
It is best to treat the acute stage of frontal sinusitis in a medical center, when the patient is under the constant supervision of doctors. In addition, the patient may be prescribed some medical procedures that cannot be performed at home due to the lack of necessary medical instruments.
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the pathological contents in the cavity of the frontal sinus and reduce swelling.
Drug treatment
Standard treatment for frontal sinusitis includes:
- Drops for vasoconstriction: Tizin, Sanorin, Vibrocil, Nazivin, Naphthyzin.
- Drops containing antibiotics: Bioparox, Polydexa or Isofra.
- Systemic antibiotics from the group of tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, lincosamides: Summed, Zinnat, Augmentin, Cephalexin.
- Antihistamines: Tavegil, Suprastin, Loratadine, Claritin, Diazolin.
- Mucolytic agents - Vicks Active, Fluimucil, Fluditek, Bronchobos, Flavamed.
- Homeopathic medicines - Avena-plus, Avia-More, Adam, Gamorin, Gastronal, Dantinorm.
- Antipyretic drugs - Tylenol, Paracetamol, Efferalgan, Analgin, Nise.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - Nasonex, Flixonase.
- Silver-based antiseptics - Protargol and Collargol.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis cannot be comprehensive without antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. Therefore, do not violate the prescribed course of treatment and take all medications in accordance with the dosage.
The usual course of treatment for frontal sinusitis takes about three weeks.
Surgery
If drug treatment does not have the desired effect, the patient may be prescribed surgery.
This is necessary to avoid serious complications, so several additional studies are performed before the operation.
Immediately before the operation, the patient is rinsed with nasal passages to eliminate all germs and viruses in the nasal cavity and cleanse the upper respiratory tract.
also use a catheter to suck out any mucus in the sinus and then rinse it with an antibacterial agent.
To eliminate pus from the frontal sinus, doctors perform a puncture. Thus, pus and other contents leave the frontal part through the anastomosis. After this, the patient is given a drainage and the canal in the frontal part is expanded. If during the operation the presence of polyps or other neoplasms was determined, they are removed during the same period.
Definition of disease
Frontal sinusitis (frontal sinusitis) is inflammation of the frontal paranasal sinus. In recent years, sinusitis has been considered one of the most common diseases in the world. They affect about 10-15% of the population. A tenth of such patients suffer from acute or chronic frontal sinusitis.
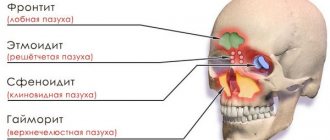
In order to understand the essence of inflammation, let's consider the structure of the frontal sinuses. Adjacent to the nasal cavity are the paranasal sinuses: 2 maxillary, 2 frontal, 2 ethmoidal labyrinths, 1 sphenoid.
The frontal sinuses are cavities in the bones of the skull that open into the nasal passages. Normally they contain air. They perform a number of important functions:
- Humidify and warm the inhaled air.
- Makes the skull bones lighter.
- Protects tooth roots and eyeballs from temperature fluctuations.
- Act as a buffer for facial injuries.
- Acts as a vocal resonator.
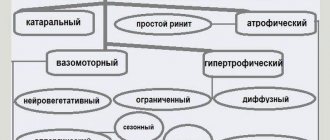
The frontal sinuses are shaped like a pyramid with the base down, which is divided into two parts by a bony septum. The inside is lined with mucous membrane, which is a continuation of the nasal mucosa. But it is thinner and does not contain cavernous tissue. According to the type of inflammation there are:
- Acute catarrhal sinusitis;
- Acute purulent sinusitis (characterized by the accumulation of pus in the frontal sinuses).
Depending on the source of infection in the frontal sinuses, the following are distinguished:
- Rhinogenic frontal sinusitis, which developed as a result of rhinitis;
- Hematogenous frontal sinusitis (develops as a result of penetration of an infectious pathogen into the cavity of the frontal sinus);
- Traumatic (result of injury).
Frontal sinusitis is a form of sinusitis and has the same classification according to the type of inflammation.
The main symptoms of frontal sinusitis in adults have similar manifestations for all types of this disease and are associated with pain in the head. It intensifies when the head is tilted forward, during physical activity, or when touching any part of the nose.
Other signs of frontal sinusitis:
- the light causes pain and a feeling of sand in the eyes;
- the appearance of lacrimation;
- snot may be clear or yellow-brown in color;
- the soft tissues of the nose become swollen, inflamed, and painful, making nasal breathing difficult;
- body temperature remains at high levels on the thermometer;
- feeling weak and drowsy;
- appetite decreases.
Acute frontal sinusitis is accompanied by pain, the intensity of which may vary at different times of the day. The pain intensifies in the morning, after waking up, due to a slowdown in the outflow of mucus. It is concentrated in the temporal zone, orbits. As soon as the sinus is freed from the contents, the pain subsides.
Symptoms of acute sinusitis also depend on the type of pathological process that occurs in the sinuses.
- Exudative sinusitis is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the sinuses and severe pain in many parts of the head. Depending on the type of mucus accumulated in the sinuses, serous, purulent or catarrhal types of the disease are distinguished. The patient's general well-being worsens.
- The productive species is characterized by the proliferation of tissue in the frontal sinuses. In addition to pain, breathing through the nose worsens, a feeling of pressure and discomfort appears.
Catarrhal sinusitis represents the initial stage of the disease. At the same time, nasal congestion, copious thick discharge, and a feeling of fullness in the frontal area are disturbing. If there is no treatment, the risk of developing a purulent form increases.
A dangerous form is acute purulent sinusitis, when pus begins to accumulate in the sinuses due to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. The condition worsens sharply, the body temperature rises, the patient feels sick, has a headache and aches throughout the body.
Chronic frontal sinusitis develops two months after the onset of the acute stage. The reasons for its appearance are associated with ignoring the doctor’s recommendations, or with independent, incorrect treatment.
Of all types of sinusitis, the frontal type is characterized by the most severe form of the course. The formation of the inflammatory process occurs in the mucous membrane covering the frontal sinus. In order to choose the right course of treatment for the symptoms of frontal sinusitis in adults and children, you must first determine its form.
According to its form, the disease is divided into:
- Exudative frontal sinusitis (catarrhal and purulent).
- Productive (parietal hyperplastic and cystic, polypous).
According to localization, experts divide:
- Bilateral frontitis.
- Unilateral (right-sided frontitis and left-sided).
According to the nature of their occurrence, there are the following types:
- medicinal nature,
- fungal etiology,
- developed as a result of injury,
- allergic,
- caused by bacteria
- caused by a virus
- mixed type.
According to the severity of the course, frontal sinusitis is divided into acute and chronic. Let's consider this classification in more detail.
Pathogenic microflora multiply in the frontal sinuses and nasal cavity. In acute cases, inflammation is concentrated in the mucous membrane, passing on its own or as a result of adequate therapy after 2 weeks.
Acute right-sided or left-sided frontal sinusitis is characterized by pressing or aching pain that intensifies during tapping. The discharge comes out with pus, and is especially abundant in the morning, immediately after waking up. I also cough up a lot of purulent sputum in the morning. If you slightly squeeze the bridge of your nose in the area of the inner corners of your eyes, a sharp pain will appear.
Even if the clinical picture is not so pronounced, there is no need to rejoice. Perhaps the second stage of the disease has arrived, more complex and dangerous.
Chronic frontal sinusitis
In the chronic form, the symptoms of frontal sinusitis in adult patients tend to appear and disappear after some time. Under the influence of pathogenic secretions accumulating in the sinus, deformation can occur.
By the way, with chronic frontal sinusitis there may be no nasal discharge at all. The sense of smell practically disappears, it becomes very difficult to distinguish odors. Growing polyps make nasal breathing difficult. If the inflammation spreads to the eye sockets, the eyelids will begin to swell in the morning, and conjunctivitis will develop. Expectorant or antitussive medications do not help get rid of an obsessive cough.
Depending on the nature of the pathological process, frontal sinusitis is divided into acute, recurrent, subacute and chronic.
By prevalence:
- one-sided (left- or right-sided);
- bilateral.
Depending on the etiological factor:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- fungal;
- allergic;
- traumatic;
- mixed.
Along the route of infection:
- rhinogenic – develops against the background of rhinitis;
- hematogenous - the pathogen penetrates the frontal sinus with the bloodstream;
- traumatic – occurs as a result of damage to the skull in the area of the frontal sinuses.
According to the nature of inflammation:
- catarrhal;
- serous;
- purulent;
- polypous (cystic).
The purulent form of frontal sinusitis is the most dangerous, since with inadequate or insufficient treatment it can cause serious complications.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis with antibiotics - a list of effective drugs
The pharmaceutical market offers a large number of medications with an antibacterial spectrum of action. Despite this, not all of them are equally capable of having a positive effect in ridding the patient of frontal sinus sinusitis. Therefore, we will consider the most popular remedies for this disease, the use of which is justified from a therapeutic point of view and allows for a complete recovery in the shortest possible period of time without the risk of relapse . Which antibiotics will help better?
Azithromycin
A universal antibacterial agent that is recommended to be taken both in the first days of the development of frontal sinusitis with a sluggish clinical picture of the disease, and in the event of its transition to an acute form with high fever and persistent pain in the frontal part of the head. It is considered a potent medicine, so the dosage is selected exclusively by the attending physician. In most cases, 1-2 tablets of Azithromycin are prescribed 1-3 times a day. The price of 1 slab of tablets is 80-85 rubles.
Amoxilav
One of the newest antibiotics. The principle of action of this drug is that it acts on the cell of a microorganism and blocks its further division. In this regard, the population of infectious agents is sharply reduced, and the immune system rapidly destroys the remaining number of pathogenic microbes. The drug is available in the form of yellow tablets coated with a protective coating, as well as in the form of intramuscular injections. The cost of the latter is within 195 rubles for 10 capsules.
Amoxicillin
An antibiotic of the penicillin series, which belongs to the aminobenzyl category. It is most effective in the treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis in adults and children. After the tablets enter the patient’s body and the active components of the drug reach the immediate site of inflammation, the protein structure of the bacterial cells is destroyed and the systematic death of the microbes that caused the disease occurs. The cost of the drug in retail pharmacy chains is 100 rubles per 1 pack.
Augmentin
The pharmacological form of Augmentin is yellow tablets coated with a gelatin shell so that the antibiotic components do not dissolve in the stomach, but first enter the intestines and in this part of the digestive system metabolism begins to break down antibacterial substances. In medical practice, it is used to treat the most advanced stages of frontal sinusitis, when purulent contents accumulate in the frontal sinus and there is a real risk of complications. Sold in a cardboard package containing 14 tablets. The price of the medicine is 335 rubles. The drug is effective against microorganisms such as streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus.
ACC
An auxiliary drug that is prescribed to patients with pharyngitis as a medicine that alleviates the patient’s general condition, as well as helping to relieve associated symptoms such as fever, chills, fever, and headache. A bag of white powder is dissolved in 250 grams of water and mixed thoroughly.
Taken as a hot drink, like regular tea. It is not a mandatory element in the overall treatment regimen, therefore ACC is prescribed at the discretion of the doctor. It is not advisable to take it for patients who simultaneously suffer from gastritis, inflammatory processes in the tissues of the pancreas, peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum.
Dioxidine
A broad-spectrum antibiotic used for intramuscular injection. The package contains 10 ampoules. It is used in cases where, based on the results of the examination, it was established that the patient’s frontal sinusitis was provoked by anaerobic microorganisms, staphylococcus, streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Escherichia coli, and Proteus vulgaris. The medication is very effective and in most cases it is enough to take a course of 10 injections for the inflammation in the frontal sinus to completely go away and the patient to return to their normal lifestyle. In combination with another antibiotic, the therapeutic effect is enhanced several times. The cost of one package of Dioxidin is 380 rubles.
Polydexa
Antibacterial drops, the intended purpose of which is the treatment of local inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx. To achieve a positive therapeutic result, you should instill 2-3 drops of the medication into each nostril in the morning and evening. The treatment period ranges from 5 to 7 years. If necessary, the period of therapy can be extended at the discretion of the attending physician. One bottle of Polydex antiseptic drops costs 280 rubles. It is not recommended for allergy sufferers, children under 3 years of age, pregnant women, or breastfeeding newborns.
Rinofluimucil
This is an aerosol that contains antibacterial components. The drug is administered into the nasal canals by spraying. Due to this, the medicine enters the upper sections of the bridge of the nose and reaches the inflamed tissues of the frontal sinus. For adults, the optimal dose is 2 injections of Rinofluimucil into each nostril 3-4 times a day. For children who have reached the age of 5 years and older, the dosage should be 2 times less. The drug should not be taken for longer than 7 days, otherwise the body may become accustomed to the active substances contained in the aerosol. The cost of one can of Rinofluimucil is 390 rubles. Dispensed without a doctor's prescription.
Sinuforte
The drug is produced by the manufacturer in the form of a white powder. Used as a solution for washing the maxillary and frontal sinuses. Effective against purulent and serous sinusitis. Can be used as drops. Before use, the powder must be diluted in saline solution. When preparing the liquid form of the medicine, follow the proportions according to the instructions of the attending physician or follow the information displayed in the instructions for the medicine.
The therapeutic effect of using Sinuforte is that the cyclamen extract, which is part of the medication, activates the secretory function of the mucous membrane of all parts of the nasopharynx and stimulates the body’s independent cleansing of pathogenic exudate, in which an excess amount of pathogenic microorganisms often accumulates. Prohibited for use by pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Sinupret
A completely natural antiseptic drug that is used in the treatment of inflammatory processes occurring in acute or chronic form in the nasopharynx. These are drops that a patient with sinusitis needs to instill 2-3 times throughout the day. The course of treatment is 10 days. If the doctor considers that there is a need to extend therapy, then after a 3-day break Sinupret drops can be used again. Due to the natural therapeutic formula, consisting of extracts of medicinal herbs, the medication is not considered potent and is prescribed to patients diagnosed with mild or moderate frontal sinusitis, when inflammation in the frontal sinus is caused by prolonged hypothermia. Approved for the treatment of children of all age groups. The cost of the drops is 270-280 rubles.
Sumamed
Tablet antibiotic, part of the macrolide group. After oral administration, it is quickly absorbed into the intestinal wall and spreads through the blood, reaching the site of inflammatory damage to the frontal sinus. It helps well in the treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis. This type of antibacterial drug is recommended to be taken strictly at the same time to ensure that a stable concentration of the active components of the drug is maintained in the tissues affected by the disease. The cost of one package containing 10 tablets is 380 rubles.
Suprax
A third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is effective against most pathogenic microorganisms known to science that can cause an inflammatory process in human tissues. The drug has proven itself best in the treatment of acute frontal sinusitis. This is a semi-synthetic antibiotic, produced in the form of tablets, therefore, in relation to its active component - cefixime, even the most drug-resistant bacteria do not have natural immunity. Due to this, an excellent therapeutic result is achieved, and in the process of treating frontal sinusitis. Take 1-2 tablets 3 times a day for 7 days. The price of the antibacterial agent is 420 rubles for 1 package.
Flemoxin
Antibiotics produced by the manufacturer in tablet form. A universal antimicrobial agent in the fight against frontal sinusitis, developing at various stages, from initial to purulent and serous. Take 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. It is considered a generally available drug from its group, since the cost of one package does not exceed 170 rubles. Not used to treat children under 3 years of age.
Ceftriaxone
Antiseptic powder for injection. Before use, it must be mixed with a physical solution. 1 pack of Ceftriaxone contains 5 doses for the preparation of intramuscular injections. This drug is potent, so the duration of 1 course of treatment should not exceed 7 days. Already on the 2-3rd day of therapy, the patient begins to feel that the symptoms of frontal sinusitis are going away, and their overall health is improving. The price of 5 injection doses is 130 rubles.
Tsiprolet
A fluoroquinolone antibiotic that inhibits pathogens from producing their own protein enzyme. Without the presence of the last component, the pathogenic microflora is not able to carry out its division. In this regard, further growth of the inflammatory process and proliferation of infection is impossible. The cost of 1 cassette, consisting of 10 tablets, is 235 rubles.
Ciprofloxacin
It is used for the treatment of frontal sinusitis, both as a main drug and as part of the general treatment regimen as an auxiliary substance. It has virtually no contraindications. Ciprofloxacin should not be taken by patients suffering from an allergic reaction, as well as those with concomitant diseases such as liver and kidney failure. Take 1-2 tablets in the morning and evening at the same time. The price of 1 package of this drug is 110 rubles.
Which antibacterial medication to give preference in treating a patient with frontal sinusitis is determined exclusively by the attending physician.
Each antibiotic for frontal sinusitis and sinusitis is capable of both healing the patient and causing significant harm to his health if the medicine is used without permission without special knowledge in the field of medicine.
Symptoms
The acute form of frontal sinusitis in adults mainly occurs against the background of an untreated cold. Manifested by symptoms such as:
- Intense pain localized around the eyes, in the bridge of the nose and forehead. When tapping or pressing on the forehead, the pain noticeably intensifies.
- A feeling of increasing fullness in the bridge of the nose. This symptom usually intensifies in the evening and when tilting the head.
- Labored breathing.
- Discharge of mucus from the nasal passages.
- Night cough. It occurs due to the fact that in a horizontal position, mucus begins to flow down the back wall of the throat and irritates the receptors of the mucous layer.
- Photophobia and lacrimation.
- Increase in body temperature to 38-39º C.
- Swelling in the forehead and under the eyes.
Acute frontal sinusitis always occurs with symptoms of intoxication. The patient develops severe weakness, his ability to work sharply decreases, and he has no appetite.
The chronic form of frontal sinusitis occurs due to insufficient or improper treatment of the acute form. If the symptoms of inflammation do not completely go away for more than a month, then we can say that acute inflammation has become chronic.
In addition to a runny nose, the following signs indicate chronic sinusitis:
- Decreased sense of smell.
- Severe swelling of the area above the eyebrows and eyelids (especially noticeable in the morning).
- Periodically appearing conjunctivitis.
- Expectoration of viscous, smelly mucus in the morning.
- Constant feeling of lethargy, fatigue.
- Periodic increase in body temperature up to 37.5º C.
- Severe cough, worse in a horizontal position.
In acute frontal sinusitis, patients complain of sharp pain in the superciliary region, which intensifies when tilting the head, during sleep, during palpation, can radiate to the temporal region and is not relieved by taking analgesic drugs. Also, symptoms of frontal sinusitis may include headaches in other localizations, unpleasant bursting sensations in the bridge of the nose, photophobia, pain in the eyes, copious nasal discharge without odor or with an unpleasant odor and particles of pus (with purulent frontal sinusitis), difficulty nasal breathing. These phenomena are accompanied by increased body temperature, cough with sputum in the morning, deterioration of general condition, and sleep disturbances.
In acute frontal sinusitis, patients complain of severe pain in the superciliary area
The clinical picture of chronic frontal sinusitis in adults is less pronounced compared to acute sinusitis. As a rule, the chronic form of the disease is accompanied by inflammation of other paranasal sinuses, especially often the ethmoid sinus (ethmoiditis). The pain in the forehead is aching, intensifies with pressure, and its intensity varies throughout the day.
Discharge from the nose often has an unpleasant odor, and there is a decrease in the sense of smell up to complete loss. Swelling of the eyelids indicates the spread of the pathological process to the orbit. Chronic frontal sinusitis is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. Signs of frontal sinusitis during remission may include a feeling of heaviness in the superciliary area, decreased sense of smell, and nasal discharge.
The primary signs of frontal sinusitis are general in nature and appear due to disruption of the blood flow process in the human body or intoxication. Common symptoms include:
- pain in the forehead, less often in the eyes and temples, appears more often than usual in the morning;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- discharge from the nasal cavity with an unpleasant odor (at the initial stage of the disease, the mucus is clear, but over time pus appears);
- In the morning, purulent sputum is coughed up.
To find out how to quickly cure frontal sinusitis, it is important to correctly determine its type. Let's consider the symptoms and manifestations of the disease in its different types and forms.
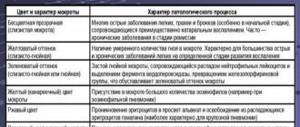
| Frontite type | Characteristic symptoms |
| Single-sided frontal |
|
| Bilateral frontal |
|
| Catarrhal form |
|
| Purulent form |
|
| Acute | Chronic |
|
|
The general signs are:
- pain syndrome that extends not only to the forehead, but also to the temples and eyes;
- swelling of the mucous membrane, which makes nasal breathing difficult;
- morning sputum discharge;
- discharge from the nasal passages (may be mucous or mixed with pus).
In the acute form of the disease, inflammation covers only the mucous membrane and, with proper treatment, resolves within 2 weeks. If therapy was not carried out, and the symptoms weakened but did not disappear, the pathology became chronic. Symptoms also depend on the type of inflammatory process:
- Catarrhal. Here a person feels a headache (usually at night and in the morning). Relief occurs after the mucus drains from the sinuses.
- Purulent. The appearance of copious discharge, throbbing pain near the bridge of the nose, which intensifies when turning the head. Body temperature rises to 39... 40°C. A person may experience a cough at night and in the morning. Fear of light and increased tearfulness are also recorded.
- Unilateral. Body temperature fluctuates between 37...39°C, and discharge appears from one nostril.
In the bilateral form, the pain is felt symmetrically, and mucus flows from both nostrils.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment at home is carried out using rinsing, inhalation, massage and other methods, but after consultation with a doctor. Before carrying out any procedure, the nose must be cleared of mucus and, if there is congestion, drips of a vasoconstrictor should be applied.
Be sure to read:
COPD: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Washing
- In a glass of warm water, dilute a teaspoon of salt, baking soda on the tip of a knife and three drops of tea tree oil. The procedure is carried out using a special device or syringe. Washing is carried out several times a day;
- Sea water. It can be purchased at a pharmacy kiosk. The procedure is carried out three times a day until complete recovery.
Inhalations
- Pour 7-10 bay leaves with water and bring to a boil. Then turn down the heat. Inhalation is carried out under a covered towel for 5 minutes. Repeat as necessary;
- Brew chamomile flowers, add a few drops of tea tree. The procedure is carried out for 5-10 minutes several times a day.
Massage
- From top to bottom, massage the most protruding part of the bridge of the nose with light movements, without pressing;
- Massage the area between the eyes with smooth and gentle movements. Massage helps restore blood circulation and relieve inflammation.
You can also use radish drops. To do this, you need to rinse and peel the black radish well. Then grate on a medium grater and squeeze out the juice. Instill 3 times a day.
Features of the course of frontal sinusitis in children
In children under 5-7 years of age, the frontal sinuses are not developed, so they do not suffer from frontal sinusitis; the disease is detected in primary school and adolescence. Isolated inflammation of the frontal sinuses is rare in children; frontal sinusitis in this age group is much more often diagnosed as a component of pansinusitis.
In general, children are characterized by a severe course of frontal sinusitis with bilateral involvement of the sinuses; the clinical picture is similar to acute respiratory infections, but the disease’s duration is alarming regarding inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, first of all, than that of acute respiratory infections. Specific symptoms of frontal sinusitis in children include:
- persistent headache, aggravated by head movements;
- pain in the projection of the frontal sinuses, aggravated by pressure;
- purulent nasal discharge;
- nasal voice;
- lacrimation;
- cough in the morning;
- stuffy nose and ears.
In children, frontal sinusitis is severe with bilateral involvement of the sinuses
In some cases, children develop conjunctivitis against the background of frontal sinusitis.
There are also a number of nonspecific signs of the disease:
- rise in body temperature (rarely above 38.5 °C);
- pale skin;
- difficulty or complete impossibility of nasal breathing;
- swelling;
- decreased appetite;
- weakness, fatigue;
- irritability;
- sleep disorders.
Frontal sinusitis in children tends to spread to other paranasal sinuses (if it was isolated), as well as to quickly develop into a chronic form.
Pregnant women are strictly prohibited from choosing their own treatment regimen. Most antibiotics are contraindicated for women in the 2-3 trimester. Traditional medicine is also selected individually, based on the general condition of the pregnant woman and the intensity of the disease.
Unlike the signs of the disease in children, the symptoms of chronic frontal sinusitis in adults are less pronounced. The disease progresses much more simply.
Despite the fact that this disease is diagnosed in men and women much more often than in children, adults almost never suffer from bilateral frontal sinusitis. Most often it is not even accompanied by a runny nose.
Many medications are prohibited for use in early childhood, so choosing an effective treatment for the symptoms of chronic frontal sinusitis in adults is much easier.
The symptoms and treatment of frontal sinusitis in children are somewhat different from the manifestations and treatment of the disease in adults. This is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the paranasal sinuses in childhood. In a child under 7 years of age, the sinuses are underdeveloped, so the disease does not manifest itself. But in middle and high school age, the symptoms of the disease in children are more pronounced, and the course of the disease is more severe than in adults.
The main signs of the disease in childhood:
- headache of a long nature, which intensifies when turning the head;
- morning cough;
- nasality;
- purulent discharge from the nasal cavity;
- photophobia of the eyes and lacrimation;
- stuffy ears.
In some cases, with acute purulent frontal sinusitis, conjunctivitis may develop in young patients. The disease is also accompanied by nonspecific symptoms. Among them:
- increase in temperature (up to 38.5 °C),
- inability or severe difficulty breathing through the nose,
- pale skin,
- refusal of food,
- sleep disorder
- weakness and fatigue.
Frontal sinusitis in children quickly becomes chronic, so it is important to start treatment when the first symptoms appear.
Other types of treatment for frontal sinusitis
It is important to understand that a disease such as frontal sinusitis must be treated not only with antibiotics or other medications, but also with auxiliary procedures, such as:
- nasal rinses;
- inhalation;
- physiotherapy;
- surgery.
It should be noted that from everything described above, in case of purulent frontal sinusitis with blockage of the frontal sinus, the most effective procedure will be to pierce the sinus with a special trepanation needle, followed by the release of pus and washing of this sinus. After performing such a manipulation, patients still continue to take antibiotics and other drugs that facilitate the outflow of exudate.
As a rule, after such a procedure there is a significant improvement and even complete recovery, especially with chronic frontal sinusitis. Inhalations, rinsing and physiotherapy for this disease are just auxiliary therapy aimed at improving the general condition.
Possible complications
Frontal sinusitis, like other types of sinusitis, must be treated. Lack of timely and correct therapy, as well as interruption of the course of treatment lead to consequences such as:
- Spread of infection to nearby sinuses. As a result, sphenoiditis, ethmoiditis, and sinusitis may develop.
- Transition of inflammation to the orbit and periorbital areas (abscess of the eyelids, phlegmon).
- Spread of pus into the brain (causing abscesses and meningitis).
The complications of frontal sinusitis that occur in both forms of the disease are quite dangerous. Among the most common:
- infectious damage to the bone walls of the nasal sinus, tissue death and the appearance of a fistula, accompanied by liquid discharge;
- the formation of phlegmon or abscesses associated with the spread of the infectious process to the eye sockets, swelling of the tissue and eyelids, eyelid abscess;
- inflammation of nearby sinuses and the manifestation of sinusitis, sphenoiditis;
- meningitis or brain abscess;
- sepsis.
They are dangerous regardless of whether the disease is chronic or acute. The following complications of frontal sinusitis are distinguished:
- spread of the infectious process to bone tissue;
- infection of the orbit, resulting in the formation of phlegmons and abscesses;
- sepsis;
- meningitis;
- tissue death;
- brain abscess.
If therapy is not started on time, a person may completely lose his sense of smell, his visual acuity decreases, and the bone partitions between the sinuses are destroyed.
In the absence of the necessary treatment, acute frontal sinusitis can become chronic - this is the most common complication. Frontal sinusitis can also be complicated by the following conditions:
- atrophy of the nasal mucosa;
- conjunctivitis;
- phlegmon of the orbit;
- decreased visual acuity;
- photophobia;
- otitis;
- involvement of other paranasal sinuses in the inflammatory process;
- sepsis;
- persistent headaches;
- deterioration of sense of smell; and etc.
Against the background of impaired nasal breathing, chronic hypoxia can develop, in addition, this can lead to obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (“sleep apnea disease”). Involvement of the optic nerve in the pathological process is fraught with a decrease, and in severe cases, loss of vision.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by an ENT specialist who carries out the following diagnostic measures:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor records the patient’s complaints, examines him, and palpates the affected area.
- X-ray of the sinuses. One of the most informative methods that allows you to determine the nature of the inflammatory process and the presence of neoplasms.
- Endoscopy of the nose. In this way, the mucous membrane of the nose and its sinuses is examined. This diagnosis is minimally invasive and reveals abnormalities in the structure of the nasal septum. Endoscopy also helps to determine the exact cause of inflammation.
- Rhinoscopy. The study shows the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence of edema, polyps.
- Ultrasound of the sinuses and forehead. Allows you to determine the extent of the inflammatory process and monitor the progress of therapy.
- CT. Not only determines the localization of inflammation and its causes, but also the severity.
- Diaphanoscopy. Transillumination of the sinuses, used to diagnose children and pregnant patients.
- Thermography. Provides information about temperature in different parts of the body
Additionally, bacteriological culture of nasal secretions, a blood test (to determine the presence of an inflammatory process), and a cytological examination are required.
As mentioned above, before treating frontal sinusitis, you need to recognize it, and this is not always possible to do on time. Often at the initial stage, frontal sinusitis occurs without a runny nose, which greatly complicates the possibility of correctly diagnosing the disease. A specialist, an otolaryngologist, can help with this. Based on a conversation with the patient, based on his complaints, he will make a diagnosis, but additional research will be needed to determine the form and severity of the disease, as well as to choose a course of treatment.
Frontal sinusitis is diagnosed using the following methods:
- Anamnesis collection.
The doctor finds out the nature of the disease, how long ago and against what background the first symptoms appeared, what the patient complains about. - Ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses.
The study, which is carried out using ultrasound sensors, allows you to obtain an image of the lesion. Thanks to this method, it is possible to assess the scale of the inflammatory process and monitor the effectiveness of treatment of purulent frontal sinusitis. - Diaphanoscopy.
The examination is carried out using a tube in a darkened room. A beam of light illuminates the sinuses, allowing one to identify developmental features and areas affected by infection. - X-ray of the sinuses.
A special device is used to take a picture of the head, with which you can:- clearly see the configuration of the frontal sinuses and assess their condition;
determine whether there is inflammation and whether mucus accumulates in the sinuses;
- identify swelling;
- determine whether the frontal sinusitis is bilateral or unilateral.
- Cytology examination of the contents of the nasal cavity.
A sample of the discharge is examined under a microscope, during which the composition of the contents is determined. Based on the study, a conclusion is drawn about the causes of symptoms of frontal sinusitis. - Rhinoscopy.
The use of nasal and nasopharyngeal speculum allows one to identify polyps and thickenings, examine the condition of the mucous membrane, and determine the nature of the discharge and the location of its accumulation. - Endoscopy.
A tube made of flexible material equipped with a camera is inserted into the sinus of the nose. On the monitor, the specialist examines the image and determines the following parameters:- what is the condition of the mucous membrane,
are there any anomalies of the sinus septum,
- what factors caused acute or chronic frontal sinusitis.
- Thermal imaging.
Temperature visualization of various areas, obtained using a thermographic camera, allows us to identify the “hottest” areas that are foci of inflammation. - Examination of nasal discharge for bacteria.
In laboratory conditions, the type of pathological organism that caused the symptoms of frontal sinusitis is determined, and then treatment is prescribed based on data on the sensitivity of the bacterium to antibiotics and other drugs. - CT scan.
A study carried out on a tomograph provides the most reliable and complete information. The specialist gets the opportunity to study the structure of the cranial bones and their features, determine the stage of right-sided and left-sided frontal sinusitis.
The diagnosis is made based on the results of the following studies:
- taking an anamnesis (presence of a previous respiratory disease, sinusitis of another location, duration of manifestations, etc.);
- objective examination;
- rhinoscopic examination (helps determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the nasal cavity);
- bacteriological examination of nasal discharge (makes it possible to identify the infectious pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs);
- general and biochemical blood test, urine test (determines signs of the inflammatory process, allows you to assess the general condition of the body);
- X-ray examination (allows for differential diagnosis of purulent sinusitis and non-purulent forms of the disease, damage to other sinuses, and to determine the presence of curvatures of the nasal septum);
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography (help to identify the anatomical features of the nose and paranasal sinuses and the extent of the pathological process).
Rhinoscopic examination shows inflammation in the nasal cavity with sinusitis
If necessary, additional studies may be used:
- cytological analysis of the contents of the nasal cavity;
- scintigraphy;
- thermography;
- diaphanoscopy, etc.
A differential diagnosis of frontal sinusitis with inflammatory diseases of other paranasal sinuses, trigeminal neuralgia, inflammation of the meningeal membranes, etc. is necessary.
Diagnosis of frontal sinusitis in adults
After establishing all the symptoms and signs of inflammation, the doctor conducts an additional examination. During the examination of the patient’s body, the doctor collects an anamnesis, including establishing all the details of the disease.
After the interview, the patient must undergo rhinoscopy. During this study, the condition of the patient’s mucous cavity and the presence of structural abnormalities are determined. If this cavity and the middle part of the nasal concha are enlarged, it is necessary to determine the presence of pus.
Next, the patient is sent for an ultrasound of this cavity and an x-ray of the frontal sinus is performed. Then the degree of inflammation and the nature of the disease are determined. After the examinations, the patient is prescribed a video endoscopic examination.
During the entire examination, doctors determine the type of bacteria that has spread in the forehead cavity, and also conduct general laboratory tests. In the process of analyzing the mechanism of development of the disease, it is important to establish the absence of a pathological process in the area of the trigeminal nerve and other paranasal sinuses.
After receiving the results, the otolaryngologist establishes a further course of treatment, which consists of drug therapy.
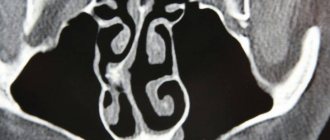
Pay attention to the photo of the frontite:
The location of the frontal sinuses is marked in green.
Prevention
- Timely treatment of respiratory diseases.
- Hardening the body.
- Balanced diet.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Avoiding hypothermia.
Among preventive measures, the main thing is the timely and adequate treatment of colds, which are the main cause of frontal sinusitis.
It is also necessary to strengthen the immune system and harden the body, avoid hypothermia and lead an active lifestyle.
To prevent the re-development of the inflammatory process, the following precautionary measures must be observed:
- strengthen the immune system (harden yourself, eat right, take multivitamins);
- avoid contact with sick people during epidemics of respiratory pathologies;
- maintain an optimal level of humidity in the room, regularly ventilate the rooms;
- promptly treat exacerbations of chronic pathological foci;
- treat rhinitis in the early stages of its development.
Frontal sinusitis is a serious disease that requires medical intervention, so you should not self-medicate.