Composition and release form
The instructions for use of Diroton contain information that this drug is available in only one form. Composition of tablets:
| Description | White flat tablets in the shape of a disk, pentagon or quadrangle |
| Concentration of lisinopril dihydrate, mg per piece. | 2.5, 5, 10 or 20 |
| Auxiliary components | Calcium dihydrate hydrogen phosphate, magnesium stearate, corn starch, talc, mannitol |
| Package | Blisters of 14 pcs., 1, 2 or 4 blisters per pack |
Directions for use and dosage
The tablets are taken orally, regardless of meals, preferably at the same time of day.
For all indications, Diroton is prescribed once a day; the dose and period of treatment are determined individually by the doctor.
The initial dose of the drug for the treatment of chronic heart failure is 2.5 mg, its increase can begin after five days of controlled use. The maintenance daily dose of Diroton is from 5 to 20 mg.
Treatment of renovascular hypertension and pathologies with increased activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is recommended to begin with taking 2.5-5 mg of the drug per day. To determine the correct maintenance dose, it is necessary
monitor kidney function, blood pressure dynamics, and potassium concentration in the blood serum.
According to the instructions for Diroton, for essential hypertension the initial dosage is 10 mg. The therapeutic effect occurs after 2-4 weeks of use, this should be taken into account when prescribing a maintenance dose. If the clinical effect is insufficient, it is recommended to combine Diroton with other antihypertensive drugs. The maximum dose should not exceed 40 mg.
The use of Diroton as part of complex therapy for acute myocardial infarction is 5 mg on the first and second days of treatment, then the drug is taken at a dose of 10 mg per day for 6 weeks. For patients with low blood pressure, treatment is carried out at a dose of 2.5-5 mg, and in case of persistent arterial hypotension, the drug must be discontinued.
To stabilize the condition of diabetic nephropathy, patients are prescribed 10 mg tablets.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The drug Diroton reduces the formation of angiotensin, which leads to a reduction in the release of aldosterone. This increases the production of prostaglandins. The medication reduces blood pressure and preload in the pulmonary capillaries. Diroton dilates arteries more than veins. The drug begins to act within an hour, reaches its maximum effect after 6.5 hours and maintains it throughout the day.
According to the instructions, in the treatment of arterial hypertension, the result appears in the first days of therapy, a stable condition is observed after a month and a half. If you abruptly stop the drug, your blood pressure will not increase significantly. The use of Diroton reduces albuminuria, normalizes the functions of damaged endothelium during hyperglycemia, does not change blood glucose levels and does not lead to hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus.
After taking lisinopril, it reaches its maximum concentration after seven hours, its average absorption is 25%, and does not depend on food. The substance is not metabolized in the body, it is excreted by the kidneys, the half-life is 12 hours. Clearance and absorption of the active component are reduced in old age. Hemodialysis is used to remove lisinopril from the body.
Indications for use
According to the instructions for Diroton, the drug is prescribed to patients:
- As part of complex therapy of chronic heart failure;
- In the case of renovascular and essential arterial hypertension;
- In the treatment of acute myocardial infarction as a prevention of heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction, as well as to maintain hemodynamic parameters in a stable state during the first day of therapy.
The use of Diroton for diabetic nephropathy is indicated for:
- Treatment of arterial hypertension in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- Reducing albuminuria in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with normal blood pressure.
How to take Diroton
The tablets are taken once a day, regardless of eating at the same time. For essential hypertension, the patient receives 10 mg, the maintenance dose is 20 mg, the maximum daily dose is 40 mg. The effect of therapy becomes visible after 0.5-1 month of taking the tablets. If the result is insufficient, it is allowed to combine Diroton with other antihypertensive drugs.
If the patient received diuretics before treatment with the drug, then their use should be stopped 2-3 days before. If this is not possible, the initial dose of Diroton is 5 mg per day. For renovascular hypertension, 2.5-5 mg per day is prescribed. In case of renal impairment and renal failure, the dose of lisinopril is determined individually, depending on clearance and creatinine level.
According to the instructions, if the patient has chronic heart failure, the initial dose is 2.5 mg per day. The dosage can be gradually increased after 3-5 days to a maintenance dose of 5-20 mg. If diuretics are taken at the same time, their dose is reduced. Before starting treatment and during it, it is necessary to monitor the level of sodium and potassium in the blood, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
In case of acute heart attack, 5 mg is prescribed on the first and second days, 10 mg on the third, the maintenance dose is 10 mg once a day for a course of at least 1.5 months. For low systolic pressure (less than 120 mmHg), a low dose of 2.5 mg per day is prescribed. When the indicator decreases to 100 mm Hg. Art. The maintenance dose is reduced to 5 mg per day, and to 90 mm Hg. Art. -therapy is stopped.
Article on the topic: Prednisolone - instructions for use, composition, release form, indications, dosage and price
For diabetic nephropathy, patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus receive 10 mg once a day, gradually increasing the dose to 20 mg. The instructions for use of Diroton also contain special instructions:
- Often, pressure decreases when fluid volume decreases while taking diuretics, reducing the amount of salt, dialysis, or vomiting. In severe chronic heart failure, blood pressure drops sharply. In such patients, treatment with Diroton is carried out with caution. Similar rules must be followed when treating patients with coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular insufficiency.
- A transient hypotensive reaction is not a reason to stop taking the next dose of the medication.
- According to the instructions, before starting therapy, sodium concentration should be monitored or the lost volume of fluid and nutrition should be replaced.
- Symptomatic arterial hypotension is treated with bed rest and combination syndrome with intravenous saline.
- According to the instructions, you should not take the pills if you have cardiogenic shock or proteinuria.
- In cases of bilateral renal artery stenosis or single renal artery stenosis, drug-induced hypotension may lead to decreased renal function.
- In some patients, during therapy with Diroton, angioedema of the face, lips, tongue, and limbs developed. It can be eliminated by taking antihistamines, administering epinephrine or adrenaline, and glucocorticosteroids.
- When desensitization against arthropod allergens is carried out, treatment with ACE inhibitors should be interrupted to avoid hypersensitivity reactions.
- During treatment with the drug, a dry, prolonged cough may occur.
- During therapy with the drug, it is prohibited to drink alcoholic beverages, and caution should be exercised when playing sports in the heat.
- If adverse reactions from the central nervous system develop, you should stop driving.
Diroton tablets 20 mg No. 28
Pharmacological action Diroton
ACE inhibitor. Prevents the formation of angiotensin II from angiotensin I. Diroton reduces the vasoconstrictor effect of angiotensin II, reduces the level of aldosterone in the blood plasma, reduces peripheral vascular resistance, increases cardiac output without changing heart rate. Improves intrarenal dynamics. The maximum antihypertensive effect is observed after 6 hours and continues for 24 hours after taking the drug. The duration of action of Diroton depends on the dose and averages more than 24 hours. The effectiveness of the drug is maintained during a course of treatment. When the drug is abruptly discontinued, there is no significant increase in blood pressure.
Pharmacokinetics of Diroton
Suction and distribution
After taking the drug orally, lisinopril is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Eating does not affect the absorption of lisinopril. The bioavailability of the drug is 25-50%. Cmax in blood plasma is reached after approximately 7 hours. Does not bind to blood plasma proteins. Metabolism and excretion
Lisinopril is not biotransformed in the body. Excreted by the kidneys. T1/2 is 12 hours.
Indications Diroton
– arterial hypertension (as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs); – chronic heart failure (as part of combination therapy for the treatment of patients taking digitalis and/or diuretics).
Dosage regimen Diroton
For essential hypertension
in patients not receiving other antihypertensive drugs,
Diroton is prescribed at an initial dose of 10 mg/day.
The maintenance dose is 20 mg/day. The maximum daily dose is 40 mg. For the full development of the effect, 2-4 weeks of treatment with the drug may be required (this should be taken into account when increasing the dose). If the use of Diroton at the maximum dose does not cause a sufficient therapeutic effect, then an additional prescription of another antihypertensive drug is possible. In patients who have previously received diuretics,
they must be discontinued 2-3 days before starting Diroton.
If it is impossible to cancel diuretics, the initial dose of Diroton should be no more than 5 mg/day. In this case, after taking the first dose, medical supervision is recommended for several hours (the maximum effect is achieved after approximately 6 hours), because Symptomatic hypotension may develop. For renovascular hypertension or other conditions with increased function of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system,
Diroton is prescribed at an initial dose of 2.5-5 mg / day (under the control of blood pressure, renal function, potassium levels in the blood serum).
The maintenance dose is set depending on the dynamics of blood pressure. In patients with renal failure and patients on hemodialysis,
the initial dose is set depending on the creatinine clearance values. The maintenance dose is determined depending on the dynamics of blood pressure (under the control of renal function, potassium and sodium levels in the blood plasma).
| 10-30 | 2.5-5 |
| <10 (including patients after hemodialysis) | 2.5 |
For heart failure
it is possible to use Diroton simultaneously with diuretics and/or cardiac glycosides. If possible, the dose of the diuretic should be reduced before starting Diroton. The initial dose of Diroton is 2.5 mg/day, subsequently it is gradually increased to 5-20 mg/day. The maximum daily dose is 20 mg. The drug should be taken 1 time/day in the morning, before or after meals, preferably at the same time.
Side effects of Diroton
From the side of the central nervous system:
dizziness, headache.
From the digestive system:
diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.
From the respiratory system:
dry cough.
From the cardiovascular system:
orthostatic hypotension, chest pain, tachycardia.
From the hematopoietic system:
agranulocytosis, decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit (especially with long-term use);
increase in ESR (1 case described). From laboratory parameters:
hyperkalemia, increased levels of creatinine, urea nitrogen (especially in patients with kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, renovascular hypertension).
Allergic reactions:
skin rash, angioedema (0.1%).
Other:
feeling of weakness; arthralgia (1 case described).
Contraindications Diroton
– history of angioedema during treatment with other ACE inhibitors; – severe renal dysfunction; – bilateral renal artery stenosis or stenosis of the arteries of a single kidney with progressive azotemia; – condition after kidney transplantation; – azotemia; – hyperkalemia; – stenosis of the aortic mouth (or similar obstructions to blood flow); – primary hyperaldosteronism; - childhood; – hypersensitivity to lisinopril and other ACE inhibitors.
Pregnancy and lactation Diroton
The use of Diroton during pregnancy is possible only for health reasons. If it is necessary to use Diroton during lactation, the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be decided.
Special instructions Diroton
Diroton is prescribed with caution for diseases accompanied by fluid loss (increased sweating, diarrhea, vomiting), and with previous diuretic therapy, because the risk of developing arterial hypotension increases. In these cases, after taking the first dose, medical supervision is indicated for several hours. The drug should be prescribed with caution to elderly patients. Before starting treatment, sodium levels should be normalized and/or fluid lost should be replaced if possible, and the development of antihypertensive effects should be carefully monitored. In case of renal artery stenosis (especially with bilateral stenosis or stenosis of the artery of a single kidney), water and electrolyte imbalance, the use of Diroton can lead to impaired renal function, the development of acute renal failure, which is usually reversible after discontinuation of the drug. During major surgical procedures or when using opioid analgesics that cause arterial hypotension, Diroton blocks the formation of angiotensin II with compensatory release of renin. Arterial hypotension caused by this mechanism is eliminated by replacing lost fluid. If arterial hypotension develops, the patient should be placed in a horizontal position with legs elevated, and if necessary, an infusion of saline solution is administered. With the development of angioedema, adequate emergency therapy is necessary (administration of adrenaline, corticosteroids, antihistamines). When using the drug under dialysis conditions with a polyacrylic-nitrile membrane, the development of anaphylactic shock is possible, so it is recommended either to use other membranes or prescribe other antihypertensive drugs. Control of laboratory parameters
During treatment with the drug, the peripheral blood picture should be monitored.
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The question of the possibility of engaging in potentially hazardous activities should be decided only after assessing the patient’s individual response to the drug.
Overdose of Diroton
Symptoms:
arterial hypotension.
Treatment:
restoration of water and electrolyte balance. If necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy. Lisinopril is eliminated from the body during hemodialysis.
Drug interactions Diroton
When Diroton is used simultaneously with potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium preparations or table salt substitutes containing potassium, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases, especially in patients with impaired renal function (therefore, these combinations are prescribed with caution, monitoring potassium levels in blood plasma and kidney function). When Diroton is used simultaneously with diuretics and antihypertensive drugs, an additive antihypertensive effect is observed. There is evidence that Diroton does not interact with NSAIDs. With simultaneous use, Diroton may enhance the hypotensive effect of ethanol. Pharmacokinetic interaction
When Diroton is used simultaneously with lithium preparations, the excretion of lithium from the body may decrease (therefore, the level of lithium in the blood plasma should be regularly monitored). With simultaneous use of Diroton with diuretics, the excretion of potassium from the body decreases.
Conditions and periods of storage of Diroton
The drug should be stored in a dry place at a temperature of 15° to 30°C.
During pregnancy
Diroton is a medication contraindicated during pregnancy because its active substance is found in the placenta. If a patient receiving treatment with the drug becomes pregnant, then therapy is interrupted as early as possible. If ACE inhibitors are taken during the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, the fetus has a risk of decreased blood pressure, renal failure, hyperkalemia, and cranial hypoplasia. Sometimes therapy can lead to intrauterine death of the embryo. The use of the product is not recommended by the instructions during breastfeeding.
Drug interactions
The instructions for use of Diroton talk about its drug interactions with other drugs. Combinations and effects:
- Combining the drug with potassium-sparing diuretics, Spirnolactone, Amiloride, Triamterene, potassium supplements, and potassium-based salt substitutes increases the risk of developing hyperkalemia.
- The combination of the drug with β-blockers, slow calcium channel blockers, diuretics, antihypertensives, vasodilators, phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, ethanol, barbiturates enhances its hypotensive effect.
- Simultaneous use of Diroton with gold preparations leads to nausea, facial flushing, arterial hypotension, and vomiting.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, estrogen, and adrenergic agonists reduce the antihypertensive property of the drug.
- The combination of tablets with lithium preparations increases the cardiotoxicity and neurotoxicity of lithium.
- Antacids and cholestyramine reduce the absorption of lisinopril.
- The drug can enhance the neurotoxic effect of salicylates, weaken the effect of oral hypoglycemic agents, norepinephrine, epinephrine, anti-gout drugs, and oral contraceptives. It increases the likelihood of developing side effects of cardiac glycosides, the effect of peripheral muscle relaxants, and reduces the excretion of quinidine.
- The combination of Diroton with Methyldopa causes hemolysis.
special instructions
Indapamide
When thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics are prescribed to patients with impaired liver function, hepatic encephalopathy may develop, especially in the presence of electrolyte imbalance. In this case, it is necessary to stop using diuretics.
Cases of photosensitivity have been reported with the use of thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics. If photosensitivity develops during therapy, discontinuation of these drugs is indicated. If it is necessary to continue treatment, it is recommended to protect the skin from sunlight or artificial UV radiation.
The sodium content in blood plasma must be determined before starting treatment. Regular monitoring of this parameter is indicated throughout the entire period of therapy. All diuretics can cause hyponatremia, which can sometimes have very serious consequences. Constant monitoring of sodium content in blood plasma is necessary, because at the beginning of therapy, such a decrease may not be accompanied by the appearance of pathological symptoms. Sodium monitoring should be carried out particularly carefully in patients with cirrhosis and in elderly patients.
During therapy with thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics, a sharp decrease in the potassium content in the blood plasma, as well as the development of hypokalemia, is possible. The risk of hypokalemia should be reduced as much as possible (
It has been reported that thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics reduce the excretion of calcium by the kidneys, leading to a non-significant temporary increase in plasma calcium. Clinical hypercalcemia may result from previously undiagnosed hyperparathyroidism. In this case, it is necessary to discontinue diuretics before examining the function of the parathyroid glands.
Monitoring glucose concentrations is indicated in patients with diabetes mellitus, especially in the presence of hypokalemia.
Patients suffering from gout may experience an increase in the frequency of attacks or an exacerbation of gout.
Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics are most effective in patients with normal or slightly reduced renal function (plasma creatinine in adults
At the beginning of treatment, patients experience a decrease in GFR due to hypovolemia, which may be associated with loss of water and sodium ions due to the action of diuretics. In this regard, an increase in the concentration of uric acid and creatinine in the blood plasma is possible. In the absence of renal dysfunction, such transient functional renal failure usually resolves without complications, but the general condition of patients may worsen in the presence of renal failure.
It is possible for athletes to test positive for doping tests.
The drug contains lactose, so it should not be taken by patients with rare hereditary galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Lisinopril
Most often, a significant decrease in blood pressure is associated with hypovolemia caused by the use of diuretics, reducing the amount of salt in food, dialysis, diarrhea or vomiting. In patients with chronic heart failure, regardless of whether it is associated with renal failure, arterial hypotension may develop. It has been found that in patients with severe heart failure, this condition occurs more often due to the administration of high doses of diuretics, hyponatremia or impaired renal function. In such patients, careful medical supervision is required (careful selection of doses of lisinopril and diuretics is indicated). The same instructions apply to patients with coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular insufficiency, in whom a sharp decrease in blood pressure can lead to myocardial infarction or stroke.
If there is a significant decrease in blood pressure, the patient must take a horizontal position; it is possible to administer a 0.9% sodium chloride solution intravenously. Transient hypotensive reactions are not a contraindication to the next dose of lisinopril.
In patients with chronic heart failure with normal or reduced blood pressure, the use of lisinopril may lead to a decrease in blood pressure; this usually does not serve as a reason to discontinue the drug. If arterial hypotension is accompanied by clinical manifestations, dose reduction or discontinuation of lisinopril should be considered.
In patients at risk of developing symptomatic arterial hypotension (on a low-salt or salt-free diet), regardless of the presence of hyponatremia, as well as in patients receiving high doses of diuretics, it is necessary to achieve compensation for these conditions (hypovolemia or sodium deficiency) before starting treatment.
Monitoring of the effect of the initial dose of lisinopril on blood pressure is indicated.
For acute myocardial infarction, standard treatment is recommended (thrombolytics, acetylsalicylic acid, beta-blockers). Lisinopril can be used in combination with intravenous nitroglycerin or transdermal nitroglycerin. In patients with acute myocardial infarction and the risk of further deterioration of hemodynamics, worsening of symptoms after the prescription of vasodilators, lisinopril therapy should not be started. These patients include patients with systolic blood pressure
In patients with chronic heart failure, a significant decrease in blood pressure during the administration of ACE inhibitors can lead to worsening renal dysfunction. Cases of acute renal failure have been reported.
In patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or renal artery stenosis of a single kidney, an increase in serum urea and creatinine concentrations was observed during the use of ACE inhibitors; Usually such disturbances were temporary and ceased after discontinuation of therapy. They occurred more often in patients with renal failure.
In patients with acute myocardial infarction and severe renal impairment (serum creatinine concentration >177 µmol/l and/or proteinuria >500 mg/day), lisinopril is contraindicated. If renal dysfunction develops during treatment (serum creatinine concentration >265 µmol/l or doubling compared to the initial value), discontinuation of lisinopril is indicated.
In rare cases, during the use of ACE inhibitors, including lisinopril, the development of angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, epiglottis and/or larynx has been reported. In such cases, immediate discontinuation of lisinopril is required; Monitoring the condition of patients until symptoms are completely resolved is indicated. Typically, angioedema of the face and lips is temporary and does not require treatment; however, antihistamines may be prescribed. Angioedema of the larynx can cause death. Swelling of the tongue, epiglottis, or larynx can lead to secondary airway obstruction. In this case, it is necessary to immediately administer 0.3-0.5 ml of a 1:1000 solution of adrenaline subcutaneously, and also ensure patency of the airways. It was reported that angioedema occurred more often in black patients receiving ACE inhibitors than in patients of other ethnic groups. In patients with a history of angioedema not associated with taking ACE inhibitors, the risk of developing angioedema when using ACE inhibitors is higher.
In very rare cases, patients taking ACE inhibitors may develop life-threatening anaphylactic reactions during desensitization with hymenoptera venom, so it is necessary to temporarily discontinue ACE inhibitors before desensitization.
Anaphylactic reactions have also occurred in patients undergoing hemodialysis using high-flux dialysis membranes (eg, AN69) with concomitant use of ACE inhibitors. In such patients, the use of other dialysis membranes or other antihypertensive drugs is indicated.
Therapy with ACE inhibitors may cause cough, which should be taken into account when carrying out differential diagnosis. A prolonged dry cough usually stops after stopping ACE inhibitors.
The use of antihypertensive drugs during major surgery or during general anesthesia can lead to inhibition of the formation of angiotensin II due to compensatory secretion of renin. The significant decrease in blood pressure associated with this effect can be prevented by increasing blood volume. Patients taking ACE inhibitors should inform the surgeon/anesthesiologist before undergoing surgery (including dental procedures).
Cases of hyperkalemia have been reported. Risk factors for hyperkalemia include renal failure, diabetes mellitus, therapy with potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene and amiloride), use of potassium supplements and potassium-based salt substitutes, especially in patients with impaired renal function. If combined use of lisinopril and these drugs is necessary, regular monitoring of potassium levels in the blood plasma is indicated.
It has been proven that the simultaneous administration of ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists or aliskiren increases the risk of arterial hypotension, hyperkalemia and renal dysfunction (including acute renal failure). Therefore, it is not recommended to prescribe ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, or aliskiren for dual blockade of the RAAS. If there are absolute indications for double blockade of the RAAS, it should be carried out under the careful supervision of a specialist with frequent monitoring of blood pressure, renal function and electrolyte levels. ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists should not be used concomitantly in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There is no data on the effect of lisinopril on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. However, the possibility of dizziness should be taken into account. In this regard, care must be taken when driving vehicles and operating machinery. Indapamide does not cause impairment of psychomotor functions, however, in some patients, with a decrease in blood pressure, various individual reactions may develop, especially at the beginning of therapy or when an additional antihypertensive drug is prescribed to the main treatment regimen. In this case, the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery may be reduced.
Side effects
The instructions for use of the drug contain side effects that may develop during therapy. These include:
- myocardial infarction, decreased pressure and blood flow, heart failure, chest pain, bradycardia, tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension;
- nausea, increased activity of liver enzymes, vomiting, hyperbilirubinemia, abdominal pain, jaundice, dry mouth, hepatitis, diarrhea, pancreatitis, dyspepsia, taste disturbance, anorexia;
- hair loss (alopecia), urticaria, itching, photosensitivity, increased sweating;
- confusion, mood lability, muscle twitching, paresthesia, drowsiness, increased fatigue;
- apnea, dyspnea, bronchospasm, dry cough;
- erythrocytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, agranulocytosis, neutropenia;
- allergies, angioedema, vasculitis, eosinophilia, anaphylactic shock;
- decreased potency, uremia, anuria, oliguria;
- hyper- or hypokalemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyponatremia, hypercholesterolemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperuricemia, hypochloremia, hypercalcemia;
- arthralgia, myalgia, arthritis;
- fever;
- exacerbation of gout.
Article on the topic: Ginos tablets - a serious natural drug for the brain and central nervous system
Contraindications
Prohibitions on the use of Diroton are a history of idiopathic angioedema, hereditary angioedema, age under 18 years, hypersensitivity to the components of the composition or other ACE inhibitors. The instructions allow you to use the product with caution when:
- condition after kidney transplantation;
- hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy;
- renal failure;
- aortic stenosis;
- scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- primary hyperaldosteronism;
- coronary heart disease;
- arterial hypotension;
- cerebrovascular insufficiency;
- inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis;
- hyponatremia;
- in old age.
Analogs
You can replace the medication with other drugs from the group of ACE inhibitors with the same or another active component . These include:
- Aurolaise is a drug against hypertension;
- Vitopril – tablets to lower blood pressure;
- Dapril is an antihypertensive drug based on the same component;
- Lisinocor is a drug for the treatment of hypertension.
Which is better - Diroton or Lisinopril
Diroton's analog Lisinopril is similar to the original. Both drugs are available in tablet format, taken once a day, but Diroton is prescribed 10 mg per day, and Lisinopril only 5 mg. The effect of both medications develops within 2-4 weeks of treatment. Otherwise, the indications, contraindications and effects on the body of the drugs are similar, because they have the same active substance.
Anti-pressure tablets Agen: instructions for use
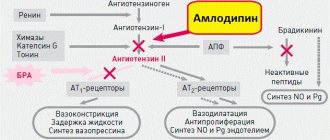
"Agen" - blood pressure tablets produced by the Czech company. Today there are many analogues of the same substance under different names, so you should know that “Agen” is the Russian “Amlodipine”.
The agent is used in the treatment of angina pectoris, although the name sometimes means nothing to Russian citizens. Indeed, it is not easy to understand the variety of analogues that contain the same active ingredient.
Anyone who periodically or systematically experiences ailments associated with high blood pressure knows firsthand about such a drug as amlodipine. The substance “amlodipine” is a derivative of dihydropyridine and, by binding to its receptors, has a blocking effect on calcium channels. This inhibits the transition of calcium into the smooth muscle cells of the heart and blood vessels, which produces a relaxing effect and ensures access of oxygen to the myocardium.
For the first time, this substance was obtained by the world's largest pharmaceutical company (USA) and is produced under the name “Norvasc”. The drug called simply “Amlodipine” or with the prefix “Prana”, “Vero” is produced in Russia. You can also find Russian-made Amlotop on the shelves of pharmacies, which is an analogue of the same amlodipine.
The world-famous Hungarian pharmaceutical company produces a similar drug “Normodipin”, and the Czech “Zentiva” produces “Agen”. Therefore, which one to use depends on which manufacturer the patient has more confidence in. Naturally, domestic medicines are several times cheaper than their foreign counterparts.
The pharmacy sells white, oblong tablets “Agen 10” and “Agen 5”, which differ from each other in the content of the active ingredient amlodipine besylate. Typically, one side of the tablet is divided by an indentation and is “engraved” with the letter “A” with the corresponding number. The drug is available in blisters of 10 pieces, which are packed in cardboard boxes of 1 and 3 blisters.
The Czech company also produces a drug called Amlodipine. Although the active ingredient is the same, you should carefully study the accompanying instructions when purchasing “Agen”. The instructions for use of each drug require familiarization, because they differ slightly.
"Agen" is used for high blood pressure, angina, both stable and vasospastic. The substance amlodipine acts slowly, due to which the pressure does not drop sharply, but the norm taken once a day is valid throughout 24 hours. People suffering from angina pectoris using the drug can count on increased physical activity and a prolonged state of remission.
Absorption of amlodipine occurs in the gastrointestinal tract over a long period of time and is almost 90%; its maximum content in the blood plasma is detected after 6 - 12 hours, although the effect is noticeable by the patient after 2 hours. When taken regularly over a week, exactly the concentration that is necessary to maintain balance is achieved.
Depending on the patient’s condition, with high blood pressure, “Agen” is used both as monotherapy and in combination with other drugs that lower blood pressure. The initial dose for hypertension is considered to be 5 mg; if the patient does not have intolerance to the components of the drug, then, if necessary, the dose is increased to 10 mg. Intolerance to amlodipine will immediately make itself felt in the form of nausea, dizziness, shortness of breath, increased heart rate, and drowsiness. Sometimes symptoms such as hair loss and itching on the surface of the skin occur.
Given the normal effect of the drug on the body, it in no way has a negative effect on concentration and memory. Therefore, driving a vehicle or performing work that requires mental concentration while using "Agen" is not prohibited.
Agen is a tablet, the instructions for use of which recommend not exceeding a daily dose of 10 mg. An overdose is fraught with an excessive decrease in pressure with the appearance of signs of tachycardia.
The daily norm is accepted regardless of eating food once a day. The tablet must be taken with water. The drug should be used with extreme caution by pregnant and lactating women, as well as those under the age of 18, since safety has not been fully established. The use of "Agen" is not recommended for people who suffer from diabetes mellitus, acute myocardial infarction, or severe hypotension.
Contraindications include hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, chronic heart failure, and serious disorders of the liver and kidneys. But, at the same time, the drug "Agen" does not require a dose reduction for patients in old age and with partial renal impairment. Although in some cases the dose is reduced when the patient is underweight, short in stature and has impaired liver function. In any case, it would be a good idea to monitor your body weight throughout the entire intake of the drug and see a dentist to prevent bleeding gums.
With the simultaneous use of calcium, the effect may be noticeably reduced, since amlodipine will not be able to block increased amounts of calcium. Combining this drug with others containing lithium can also cause nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness.
Like all medicines, “Agen” should be stored in a place out of reach of children, out of direct sunlight at a temperature not exceeding + 25 degrees.
When using “Agen”, you need to understand that its use is unacceptable from time to time, just to bring down high blood pressure once. "Agen" - blood pressure pills aimed at long-term therapy.
Price
You can buy Diroton tablets online or in pharmacies at a cost that is affected by the level of the active component and the volume of the pack. Approximate prices in Moscow:
| Concentration of lisinopril, number of tablets in a pack | Internet price tag, rubles | Pharmacy cost, rubles |
| 10 mg 56 pcs. | 530 | 550 |
| 20 mg 56 pcs. | 753 | 780 |
| 5 mg 56 pcs. | 359 | 380 |
| 20 mg 28 pcs. | 419 | 450 |
| 5 mg 28 pcs. | 211 | 250 |
| 10 mg 28 pcs. | 295 | 315 |