Total information
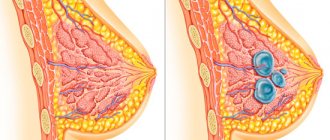
Adenosis of the mammary gland is a benign formation, which is hormonally dependent in nature, which is confirmed by the manifestation of clinical symptoms in the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
Pathology occurs in women of reproductive (childbearing) age. Most often it is detected in patients aged 30-40 years - up to 70% of all patients with this diagnosis fall into this age category.
Important
If a woman suffers from any gynecological disease, then the incidence of mammary adenosis is, according to various sources, from 90 to 100%. In other words, all patients with diseases of the genital area should be examined for the presence of mammary adenosis.
This condition develops not only as pathological, but also physiological. Breast adenosis is normally observed in:
- girls during the period of menstruation;
- women in the first trimester of pregnancy.
In both of these cases, the manifestations of adenosis regress and disappear on their own after the hormonal levels are equalized. However, in this condition, monitoring by a gynecologist is necessary, since pathological adenosis of the mammary glands can develop against the background of physiological one.
Treatment
The following treatment options are possible:
- Surgical intervention. When single nodular formations are detected, radical surgical interventions, as a rule, are not resorted to. However, the patient must be regularly monitored by a specialist. The minimum number of visits to a mammologist per year is 2. If a sclerosing form is detected, it must be surgically excised. The operation can be performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the indications. After removal of a benign tumor, it is necessary to take painkillers orally.
- In many cases, the use of hormonal therapy produces positive results. It is preferably recommended to take oral contraceptives or progestin drugs. On average, positive results are observed after 50-60 days of treatment.
- Homeopathic medicines. These medicines are made from natural ingredients. They can have a significant therapeutic effect.
- Vitamin complexes. Prescribed to normalize metabolism and strengthen immunity. Do not use without the consent of the attending physician.
- Diet food. Proper food will not only allow you to recover as soon as possible, but will also have an overall beneficial effect on the body. It is necessary to avoid eating fried, fatty, spicy foods. Do not get carried away with smoked or salted foods. They can cause fluid stagnation and cause swelling.
The disease causes discomfort to a woman and can be the first sign of impending breast cancer. The disease develops without severe symptoms. To prevent it, all women, starting from a very early age, need to carefully monitor their health. However, it is worth noting that adenosis extremely rarely degenerates into a malignant formation. In many cases, for example, during pregnancy, the disease goes away on its own.
Causes
The immediate cause of the described condition is an imbalance in female sex hormones - in this case the following are observed:
- excess estrogen;
- lack of progesterone.
Etiological factors have been identified that cause hormonal imbalance, and therefore are indirect causes of mammary adenosis. This:
- metabolic disorders;
- complicated gynecological and obstetric history;
- taking certain medications;
- gynecological pathology;
- some somatic diseases - those that are not related to a woman’s genital area;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- bad habits.
Of all types of metabolic disorders, obesity is the most important in the development of hormonal imbalance. The connection is that adipose tissue is capable of producing estrogens. With every extra kilogram in obesity, the synthesis of estrogen increases almost proportionally. In this case, relative (not always pronounced) hyperestrogenism develops - but it is enough to provoke the development of mammary adenosis. At the same time, the amount of progesterone in the blood remains at a normal level.
Factors of a burdened gynecological and obstetric history, against the background of which a hormonal imbalance develops, leading to the development of mammary adenosis, are:
- abortions;
- late pregnancy;
- refusal to breastfeed.
Both spontaneous abortions (miscarriages) and artificial ones (performed in a clinic for medical reasons) lead to hormonal imbalance. A particularly pronounced provoking factor is termination of pregnancy in its late stages (15-22 weeks). It leads to a very drastic hormonal change in the body, while compensatory mechanisms are not triggered, and the body is not able to instantly correct the existing malfunction. The level of sex hormones returns to normal gradually, during which time endocrine problems have time to develop - in this case, with such a consequence as adenosis of the mammary glands.
The described pathology develops during late pregnancy, since in women over 35 years of age, ovarian function begins to fade, and the likelihood of developing hormonal imbalance increases. When pregnancy occurs, the work of the ovaries is activated - this leads to a postpartum failure in the production of estrogen and progesterone, as a result, a hormonal imbalance develops.
note
If you refuse to breastfeed, the concentration of prolactin increases, which causes stagnation of milk in the milk ducts. Due to such stagnation, the ducts become clogged and dilate, and this, in turn, leads to the formation of cysts and further disruption of the internal structure of the mammary glands with the formation of adenosis.
It is often indicated that the cause of adenosis may be postpartum agalactia - a complete lack of milk production. In fact, adenosis of the mammary glands can simply occur against the background of agalactia - but it is not its direct cause, but only a “beacon” about the possibility of its development. Adenosis and agalactia are two consequences of hormonal imbalance . Agalactia develops due to a lack of progesterone, which regulates the development and “specialization” of mammary gland parenchyma cells, as well as due to an excess of estrogens. In her case, with hyperestrogenism, the stroma (connective tissue base) of the glands grows, and the lack of progesterone provokes the uncontrolled growth of the glandular epithelium.
The development of mammary adenosis can be caused by uncontrolled use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs), drugs that prevent the development of unwanted pregnancy. The reason is that when taking COCs, the individual characteristics of a woman’s body and non-compliance with the dosage regimen may not be taken into account. This leads to hormonal imbalance and the development of dysplastic processes in the mammary glands.
Of all the gynecological diseases, the most common cause of mammary adenosis is:
- endometrial hyperplasia - growth of the inner layer of the uterus;
- ovarian tumors – both benign and malignant;
- Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor that develops in the muscular layer of the uterus;
- Endometriosis is the appearance of endometrial cells in unusual places throughout the body.
Somatic diseases can act as triggers for mammary gland adenosis (in the literal sense - triggers) - these are pathologies that in themselves are not the cause of the described disease, but are capable of starting the pathological process. Most often, such triggering pathologies are:
- hypertension - a pronounced persistent increase in blood pressure;
- pancreatic diseases;
- liver pathology;
- chronic stress;
- sexual disorders.
Most often, of all the factors of unfavorable environmental conditions, the development of mammary adenosis is provoked by an increase in the amount of harmful substances in the atmosphere and water.
Bad habits that can provoke the development of the described disease are not only smoking, alcohol abuse and drug use, but also persistent chronic sleep disturbance (constant lack of sleep due to domestic and work circumstances, lack of satisfaction with sleep), as well as regular dietary disturbances (particularly eating unhealthy foods).
Causes
The main factor is a change in the secretion and ratio of hormones in the female body. Excess estrogen and prolactin have a negative effect on the mammary glands and reproductive system; often the condition of the breast is adversely affected by diseases of the thyroid gland, problems with the pituitary gland and hypothalamus.
Doctors often identify several negative factors that increase the risk of hormonal imbalance. If a woman can exclude or significantly limit the influence of a complex of causes, then nodular formations and areas of proliferation may disappear when the hormonal levels stabilize.
What is breast fibrosis and how to treat connective tissue growths? We have the answer!
Read about the characteristic symptoms and effective methods of treating mastodynia in women at this address.
Adenosis develops more often in women:
- against the background of stress, overwork, excessive nervousness, lack of sleep;
- under the influence of high background radiation;
- for chronic pathologies and tumor processes that negatively affect the production of hormones;
- against the background of chest hypothermia;
- with poor nutrition, a predominance of “fast” carbohydrates, smoked meats, fatty foods, fast food, fried foods, baked goods and chocolate in the menu;
- for injuries and bruises of the mammary glands;
- against the background of severe obesity, if the body mass index is significantly higher than normal;
- with prolonged and active smoking;
- as a consequence of hormonal imbalance with frequent abortions;
- if a woman begins sexual activity late, sexual contacts occur irregularly or are absent.
Diseases:
- pathological growth of the endometrium;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the genital area;
- dysfunction of the ovaries;
- endocrine pathologies: hypothyroidism, tumor process in the adrenal glands, hyperprolactinemia, damage to the pituitary gland, thyrotoxicosis and others.
READ ALSO: What are microcalcifications in the mammary gland and how to get rid of salt deposits in the breast
Development of the disease
Cyclic changes that occur in the mammary glands are regulated by such active biological substances as:
- hypothalamic releasing factors;
- follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH);
- luteotropic hormone (LH);
- prolactin;
- human chorionic gonadotropin;
- glucocorticoids;
- progesterone;
- thyroid hormones;
- pancreatic hormones.
The main factors in the development of the disease are:
- hyperestrogenemia – excess estrogen;
- progesterone deficiency.
In this case, hyperestrogenism can be:
- absolute;
- relative.
Exposure to estrogen causes the milky ducts to grow as their cells multiply more. The consequences of a lack of progesterone are as follows: it normally inhibits the activity of estrogen, which means that due to a deficiency of progesterone, the already excessive effect of estrogen on the mammary glands is further enhanced. In fact, the cells multiply uncontrollably and uncontrollably. From the point of view of the structure of breast tissue, it looks like this:
- the connective tissue inside the lobules of the mammary gland grows and swells;
- glandular cells rapidly develop in the milk ducts - because of this, their blockage and expansion described above occur, and then - the proliferation of glandular tissue.
There are several types of mammary adenosis - they are distinguished by:
- area of gland tissue damage;
- histological (tissue) structure.
According to the prevalence of the pathological formation, two forms of the described pathology are distinguished, such as:
- focal (or local). In this case, a large mobile formation in the form of a ball or disk is formed in the mammary gland. The node itself consists of individual lobules and is covered with a fibrous capsule;
- diffuse. It is characterized by the fact that several areas of compaction are formed in the mammary gland at once, while their shape and boundaries are unclear and blurred. Such seals grow in different places of the mammary gland and are unevenly located in the tissues.
Based on the tissue structure (the type of cells that have grown), the following types of adenosis are distinguished:
sclerosing. Individual areas of the mammary gland lobules (also called acini) grow. At the same time, the overgrown connective tissue puts pressure on the acini, but their shape does not change;
- apocrine. With this type of pathology, epithelial cells of one type turn into epithelial cells of another - namely apocrine cells, which secrete secretions. In terms of tissue structure, this type of adenosis is similar to infiltrating cancer, which can cause confusion in the diagnostic process. It should be recalled that, unlike infiltrating cancer, apocrine adenosis is a benign disease;
- ductal Its development is based on the expansion of the milk ducts. This type of pathology is similar to sclerosing adenosis;
- microglandular. It is characterized by a chaotic proliferation of small ducts throughout the mammary gland, but sclerosis and tissue compression are not observed;
- adenomyoepithelial. With it, separate foci of growths form in the tissues of the mammary gland. Such adenosis is quite rare and is mainly combined with the formation of adenoepithelioma, a benign neoplasm of the mammary gland.
Classification of pathology
All damage to the epithelium during benign processes is divided into 3 types:
- Growth without active proliferation.
- Proliferation without atypia.
- Atypical hyperplasia.
With adenosis, there is no active cell proliferation, so it is the least dangerous in terms of malignancy. There are 2 main forms - diffuse and local adenosis of the mammary gland.
Diffuse, or focal, adenosis of the mammary gland is associated with degeneration of the myoepithelium.
Glandular tissues develop according to the type of cystic fibrous changes. Diffuse adenosis of the mammary gland is usually moderate, and the lumps have unclear shapes and boundaries, but they are distributed throughout the breast.
As it develops, the affected area increases. With such processes, damage occurs not only to the glandular tissue, but also to the milk ducts. As a result, papillomas develop inside them in the form of epithelial outgrowths.
In the local form (local adenosis of the mammary gland), limited compactions can occur in any lobe of the gland, so their structure is lobular.
The formations are relatively large, each lobule is surrounded by a layer of fibrosis (capsule). Between the lobules there are myoepithelial cells.
The compaction affects only a separate area, so focal asymmetry of the mammary glands is noted. Depending on the affected part, this form has several subtypes:
Sclerosing adenosis of the mammary gland
Affects lobules. There is a rapid proliferation of fibrous tissue.
The nodules in this form are very dense, small and mobile. Active tissue growth is observed in the thoracic ducts, as a result of which intraductal papillomas appear, and the ducts themselves are overgrown with epithelial cells.
Lymph nodes are usually not affected. Pain in the chest appears in the first half of the MC.
One gland enlarges more than the other. The tumor spreads to several ducts of the gland. The seal is mobile and has clear boundaries.
Apocrine adenosis
The nodes are contained by the lobule of the mammary gland; they are easily palpated and located along each lobule. Intraductal papilloma is covered with epithelium and muscle epithelial cells (ductal hyperplasia of the mammary glands). Often it reveals an altered glandular epithelium, which has acquired similarities with the epithelium of apocrine glands (apocrinization of the epithelium).
Adenomyoepithelial form
It has no specific localization and is rare. Seals from epithelial cells form randomly.
Microglandular form
It occurs even less frequently, with epithelial compactions formed in the smallest ducts. Fibrous tissue becomes permeated with small round nodules, which are located frequently and there are many of them.
Tumor-like type
The compaction is small, resembles a disk, and does not make itself felt in any way. X-rays help identify pathology. According to morphology, there are altered epithelial cells.
Tubular form
It differs from others in microcalcifications and 2 layers of epithelium. A mass of identical retracted tubes is formed in the gland.
Symptoms of breast adenosis
The clinical picture of mammary adenosis manifests itself with similar symptoms as with other types of mastopathy. Symptoms may vary depending on the form of the disease.
The general signs of the described pathology are:
- mastodynia – soreness and engorgement of the glands, as well as increased sensitivity of their skin;
- discharge from the nipple.
Characteristics of pain:
- by localization - in the area of development of the pathological focus;
- by distribution - the entire mammary gland may hurt;
- by nature – aching, pressing;
- intensity – moderate, intensifies on the eve of menstruation;
- by occurrence - may develop with a delay.
If a local form of mammary adenosis is formed, a formation is detected in it. Its characteristics are as follows:
- in shape - round or irregular;
- in size - from 1 cm in diameter and more;
- consistency – dense;
- by structure – lobular structure;
- in terms of mobility – mobile;
- in relation to the surrounding tissues - not fused to them.
note
With the local form of adenosis, there are no signs such as the release of mucus or milk from the nipple, deformation of the skin and enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes. There is also no pain on palpation.
If the diffuse form develops, the following symptoms appear:
- pain;
- swelling of the mammary gland before menstruation;
- nipple discharge;
- formations in the gland in the form of nodules.
Characteristics of pain:
- by localization - diffuse, throughout the mammary gland;
- by distribution - they can spread to the tissues of the chest wall adjacent to the mammary gland;
- by nature – aching, pressing;
- in terms of intensity – moderate;
- in terms of occurrence, they generally develop with a delay.
Characteristics of discharge:
- by color - yellow or colorless;
- consistency – liquid;
- in quantity - not abundant.
Characteristics of formations:
- in quantity - several;
- in form - without a specific shape and clear boundaries;
- by size - different sizes. The nodules that are nearby may merge - it seems that a large tumor has formed;
- consistency – dense;
- structure - homogeneous;
- in terms of mobility – mobile;
- in relation to the surrounding tissues - not fused to them.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of mammary adenosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, anamnesis (history of the disease) and the results of additional examination methods - physical, instrumental and laboratory.
A physical examination reveals:
- upon examination - the size and shape of the mammary gland, the condition of the skin, nipple and areola, the presence or absence of discharge from the nipple;
- on palpation - consistency, presence of formations, pain.
Instrumental diagnostic methods that are prescribed when breast adenosis is suspected are:
- mammography – a comprehensive examination of the breast;
- biopsy – removal of breast tissue and subsequent examination under a microscope.
During mammography, diagnostic methods are used such as:
- X-ray mammography - X-ray examination of the breast (photos are taken in two or three projections);
- Ultrasound mammography – using ultrasound, areas of compaction are identified in the breast tissue and assessed;
- tomosynthesis - the method is based on creating a two-dimensional image of the mammary gland, which evaluates its internal structure;
- magnetic resonance (MRI) mammography – a method of tomographic examination of the mammary gland;
- optical mammography – the condition of breast tissue is studied using optical equipment.
The following laboratory research methods are also important in the diagnostic process:
general blood test - helps to distinguish the described pathology from a malignant tumor. If a malignant neoplasm has developed, the ESR increases significantly, and in the late period of disease development the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin decreases;
- the content of sex hormones - determine the level of estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteotropic hormone (LH), and according to indications - the level of thyroid and adrenal hormones;
- cytological examination - a smear of nipple discharge is examined under a microscope, its cellular composition is determined;
- histological examination - the degree of cell proliferation is determined in a biopsy specimen under a microscope.
If there are any somatic diseases, in order to identify them, examination methods such as:
- blood chemistry;
- blood sugar test;
- general urine analysis
and others.
If necessary, a consultation with a gynecologist, oncologist and endocrinologist is prescribed.
Treatment with folk remedies
With the initial development of adenosis, the use of folk healing decoctions and compresses helps to completely get rid of the pathology. In later stages, herbal remedies can only be used as an adjunct to medications.
For internal use, the following home recipes are used:
- Chestnut (horse) decoction. For 5 tbsp. chestnut inflorescences take 1 liter. purified water. Bring to a boil over low heat, pour into a thermos and leave for 8-12 hours. Drink 1 tbsp. every hour throughout the day. The next day, prepare a new decoction. Duration of treatment – 7 days.
- Burdock infusion. 10 g required. pour chopped fresh burdock leaves with boiling water (200 ml). Leave for 3 hours, filter and take 15 ml. 20-30 minutes before meals. The duration of the course is 10 days.
- Collection. Mix 1 tbsp. nettle, plantain and sage and 2 tbsp. wormwood. For brewing, take 1 tbsp. 250 ml mixtures. boiling water, leave for 1-1.5 hours. The drink is drunk during the day, 1/3 of the prepared volume at regular intervals, the course is 1 month.
For external treatment, traditional healers recommend:
- Beetroot and honey application. You will need 3 parts raw beets and 1 part honey. Pass the vegetable through a meat grinder (you can grate it on a fine grater), add honey, mix. Apply the resulting paste to the chest in the place where the lump is located (at night). Compresses should be done every other day for 2-3 weeks.
- Simple compresses. It is useful to apply a mashed cabbage leaf (only juicy layers from the middle of the vegetable) or freshly picked burdock to the chest. Their insides can be greased with natural honey, grated carrots and beets can be added, or castor oil can be poured over them - the compositions can be alternated.
- Salt lotion. Dissolve 3 tbsp in a liter of lukewarm water. salt (you can take any), soak a towel or clean cloth in the liquid, then apply it to the sore chest for 5-6 hours. The course is a week.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of mammary adenosis is most often carried out with such diseases and pathological conditions of the mammary gland as:
- adenoma – a benign tumor of glandular tissue;
- fibroadenoma is a benign tumor of glandular and connective tissue;
- cyst - a cavity formation with liquid contents inside;
- cancer is a malignant tumor that grows from epithelial cells.
Main signs and symptoms
Breast adenosis is determined by the general symptoms of mastopathy, which include:
- chest pain that worsens before the onset of menstruation;
- swelling and hardening of the mammary glands during menstruation;
- various types of discharge from the nipples;
- the appearance of compactions that can be detected by touch;
- pain when feeling the chest.
Certain forms of adenosis development manifest themselves in different ways, respectively, with certain symptoms expressed to a greater or lesser extent.
nipple discharge pain when palpated
Complications
The most common complications of mammary adenosis are:
- inflammatory diseases of the mammary gland;
- its deformation;
- cyst formation;
- formation of papillomas in the milk ducts - short outgrowths of a benign nature;
- Breast cancer – the likelihood of its occurrence in the presence of the described pathology increases 5 times. The frequency of malignant degeneration depends on the intensity of cell proliferation. Thus, non-proliferative forms (in which cells practically do not grow) become malignant in 0.86%; if moderate proliferation is observed, breast cancer occurs in 2.5%; with severe proliferation, a cancerous tumor develops in 32% of cases.
Treatment of mammary adenosis
The choice of treatment method for adenosis (conservative or surgical) depends on the form and nature of the disease being described.
With the development of a diffuse form, conservative treatment is used. It is based on the following purposes:
- correction of diet - limiting animal fats, carbohydrates, increasing the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits;
lifestyle correction - if he is sedentary, then it is necessary to increase physical activity;
- weight normalization;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- hormonal drugs;
- sedatives;
- vitamins - in particular, A, E, C, P and B vitamins;
- minerals.
If a mild form of the disease has developed, monophasic combined oral contraceptives are prescribed, the course of treatment is 6 months. If a more severe form of the disease has developed, the course of treatment is at least 3 months.
With the development of a focal form of mammary adenosis, surgical treatment is used. In this case, a sectoral resection of the gland is performed - excision of the formation within healthy tissue.
Effective treatments
Basic Rules:
- dietary nutrition;
- taking vitamins and minerals;
- normalization of the psychological microclimate in the family and work team;
- reduction of physical activity;
- walks in the air;
- sufficient time for night rest;
- taking phytoestrogens;
- use of herbal decoctions and sedatives;
- receiving oral contraceptives and hormonal drugs to stabilize the level of regulators;
- weight loss to optimal levels;
- elimination of nervous overload;
- treatment of infectious pathologies that provoke inflammation in the mammary glands;
- control of chronic diseases;
- therapy of endocrine pathologies, against the background of which the functionality of the ovaries, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and other endocrine glands changes;
- carrying out specific therapy when confirming the malignant nature of the disease.
Learn about the signs and symptoms of testicular cancer in men, as well as cancer treatment options.
Methods for treating multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland with folk remedies are written on this page.
Go to https://vse-o-gormonah.com/zabolevaniya/simptomy/nedostatok-joda.html and read about the signs of iodine deficiency in the body in women and methods of replenishing the microelement deficiency.
Prevention
The prevention of mammary adenosis is based on such actions and measures as:
- competent planning of pregnancy in order to prevent abortions;
- planning your first pregnancy before age 30;
- correct selection of hormonal contraceptives, adherence to their dosage regimens;
prevention of gynecological, endocrine and somatic diseases, and if they occur, timely diagnosis and adequate treatment;
- breastfeeding the child for at least 6 months;
- regular breast self-examination;
- regular visits to the gynecologist - at least once every six months;
- compliance with work, sleep, rest, and nutrition regimens;
- rejection of bad habits.
The main causes and risks of the disease
Breast adenosis occurs mainly in women aged about forty years. The main reason for its development is a change in hormonal balance. In this case we are talking about sex hormones.
At the same time, the main risk group includes women experiencing menopause and menopause, sometimes pregnant women and young girls during puberty.
pregnancy menopause
The development of the disease can be provoked by the following phenomena:
- premature and induced births, late-term abortions;
- late first pregnancy (around 40 years);
- absence of pregnancies throughout a woman’s life;
- refusal of breastfeeding and lack of breast milk production.
You can also automatically fall into a risk group if you have:
- overweight;
- gynecological health problems;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- general weakening of the immune system;
- use of certain methods of contraception. overweight problems in gynecology
Forecast
The prognosis for breast adenosis is favorable for health and life with early diagnosis and adequate, timely treatment. The development of any complications is possible in advanced cases.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
9, total, today
( 39 votes, average: 4.97 out of 5)
Galactophoritis: causes, symptoms, treatment
Mastoptosis: causes, types, methods of treatment