Pain in the perineum is a fairly common symptom that can occur in both women and men, regardless of age. In the vast majority of cases, such a symptom indicates the occurrence of some disease of the genitourinary system. It follows from this that sources for both sexes can be both general and individual.
Most often, in addition to pain, the clinical picture consists of such manifestations as discomfort while walking or sitting for long periods of time, itching and burning in the problem area, as well as disruption of the urination process.
The clinician will be able to make the correct diagnosis and find out the cause only after studying the results of laboratory and instrumental examinations. Treatment is dictated by the predisposing factor, but is often based on conservative techniques.
Causes of acute pain in the perineum
The occurrence of acute, sharp pain in the genital area may indicate the following diseases and conditions:
- Prostatitis.
During an exacerbation of prostatitis, a man experiences intense pain that spreads to the head of the penis and the anus. - Urethritis.
A characteristic feature of pain in urethral inflammation is increased discomfort when emptying the bladder. - Prostate abscess.
The pain is very strong and is one-sided, from the side of the suppuration site. Patients report discomfort in the spine and rectum. The condition is accompanied by difficulty urinating, constipation, hyperthermia (fever) in the area of inflammation. - Prostate cancer.
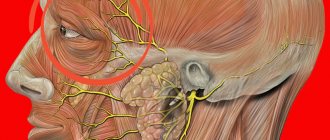
Acute pain in the perineum is a sign of a late stage of oncology (prostate cancer). - Pinched pudendal nerve.
There are many nerve endings concentrated in the perineum. Pinching of any of them causes acute sharp pain, which subsides when walking and intensifies when sitting or lying down. - Pregnancy, postpartum period.
Pain in this area in pregnant women can be caused by compression of the sciatic nerve (during pregnancy) and be a signal for the onset of labor. Acute postpartum pain occurs in women who have suffered multiple ruptures during childbirth. - Perineal injuries.
Any mechanical damage - bruises, ruptures, tissue cuts, etc. , cause sharp pain.
Clinic
Pain syndrome localized in the perineal area is often combined with the following complaints:
- disturbances in urine output (sluggish stream),
- frequent urge to urinate;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- itching and discomfort;
- the appearance of specific discharge from the head of the penis;
- burning in the urethra;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- general symptoms (fatigue, fever);
- rash on the head of the penis;
- erectile dysfunction, ejaculation;
- pus in urine, semen;
- ejaculation with blood;
- increased discomfort during physical activity and intimacy.
Pain in the perineum on the left, right, with irradiation to the penis, scrotum, lower abdomen, rectum, and lumbar region is recorded. The nature of the pain can be acute or chronic, sharp or pulling, bursting or barely noticeable. In addition, for each disease that causes pain in the perineum, specific clinical signs are characteristic, by which the disorder can be recognized and a correct diagnosis can be made. Nagging pain in the groin mainly occurs with chronic prostatitis, inflammatory processes of the urethra in the area of the seminal tubercle, urethritis with a long, asymptomatic course, and with neoplasms of a malignant nature. Acute pain, as a rule, is a symptom of perineal injuries, accompanied by significant bruises and muscle tears. The pain syndrome can be so intense that it provokes loss of consciousness. Sharp pain is also recorded in acute prostatitis and cystitis. With prostate abscesses, they spread to the anus, sacrum, and are accompanied by problems with bowel movements and urination problems. Malignant neoplasms of the prostate do not manifest themselves in the early stages, but in the later stages they cause very intense pain. Neurological disorders are characterized not only by pain, but also by changes in sensitivity and numbness in certain areas of the body (often the inner thigh). Pain in the perineum when sitting indicates compression of the pudendal nerve. They are aching, accompanied by itching, burning, increased sensitivity of the skin, sensation of a foreign body in the external genital area, and constant discomfort. Unpleasant symptoms persist for a long time, cause chronic stress, and are subsequently combined with pain during urination, dysfunction during ejaculation, and bowel disorders in the form of constipation. In addition, such neuropathy can manifest itself as unpleasant sensations in the buttocks and anus, an imperative (false) urge to urinate, and severe pain on palpation in the area of the projection of the ischium.
Causes of nagging pain
In men, aching, nagging pain in the perineum accompanies chronic prostatitis, urethritis and inflammation of the seminal tubercle (colliculitis). Inflammations with constant nagging pain that worsens during defecation include cooperitis. If a man experiences pain after sexual intercourse and is felt in the testicular area, he needs to be checked for varicocele.
In women, nagging pain is observed during pregnancy and can be caused by chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Stitching and aching pain in the perineum can develop with inflammation of the vaginal mucosa (vaginitis).
6-day immersion course
We began treating our first patients with a variety of pelvic floor dysfunctions at Stanford University in 1995 during routine medical appointments. In 2003, we opened a private practice as a 6-day immersion clinical course in Santa Rosa, California. The course, designed for 14 patients and open for a year, eventually implemented the Wise-Anderson Protocol. This protocol teaches patients how to restore the function of chronically tight pelvic floor muscles and reduce anxiety. The Wise-Anderson Protocol, performed independently at home by patients who have been trained by us, has helped many return to normal life. Following the protocol helps patients eliminate the need to seek additional professional help. For ten years, research has documented our results in teaching patients to self-administer the protocol. For further information, please follow the link to our blades page.
For questions about cost and eligibility please fill out the form below, email us at or contact our office at+1 (707) 332-1492.
SYMPTOMS OF PAIN IN THE PERINEUM
(Most of our patients exhibit two or more symptoms)
Urinary frequency and urge to urinate
- Urinary frequency ranges from annoying to debilitating.
- After urinating, patients feel that the bladder has not been completely emptied and they have the feeling that they need to urinate again.
- Patients have to stay close to the toilet.
- Sometimes patients cannot help themselves when they feel the need to empty their bladder.
- Very often, these symptoms disturb night sleep and lead to lack of sleep, because... patients have to get up frequently at night.
Dysuria (pain or burning when urinating)
- Dysuria (pain or burning when urinating) can be very painful and can make urination an ordeal, leading to further pain.
- Pain or burning when urinating is caused by pelvic floor dysfunction.
- Sometimes people experience pain after, rather than during, urination.
- When the problem with chronic spasms and myofascial tension in the pelvic muscles is resolved, for many patients the pain and burning sensation when urinating also goes away.
Nocturia (frequent urination at night)
- Very often, nocturia (frequent urination at night) leads to nervous exhaustion in patients, because. They don't get enough sleep.
- Chronic fatigue from lack of sleep contributes to a vicious circle: tension, pain, defensiveness and anxiety.
Weakened stream and delayed urination
- It is very important to accurately determine the source of this symptom: whether the weakened flow is caused by an enlarged prostate or something else.
- Some patients with pelvic muscle pain experience delays when starting to urinate.
- Retention may also become worse if the bladder does not empty for longer than usual (tension of the muscles that hold urine leads to a spasm that does not immediately relax when urinating).
- A weakened flow can also affect self-esteem and lead to hypochondria, especially in young people.
- If these symptoms are caused by pelvic muscle pain, then when pelvic floor function is restored, the strength of the jet may improve.
Pain while sitting
- When sitting, patients with pelvic pain suffer even more.
- This symptom complicates all aspects of the patient's life.
- Patients have to sit on something soft.
- Pain in a sitting position brings suffering when the patient is forced to sit for a long time behind the wheel or while flying on an airplane.
- Sometimes patients are forced to register for disability, because... they cannot do sedentary work.
- Discomfort/pain while sitting may be worse and may be felt in the front or back of the pelvis, or both.
- Pain while sitting usually gets worse towards the end of the day, after sitting all day.
Pain in the genitals
- Genital pain is usually referred to the anterior levator ani muscle and is easily relieved in some patients
- Men usually experience pain at the tip or body of the penis
- Redness and irritation are sometimes noticeable at the tip of the penis
PAIN IN THE SUPRAPUBIC AREA
- Pain in the suprapubic region is a common symptom and occurs in patients with urinary problems
- Sometimes pressure in this area can be felt in the anorectal area or cause pain in the bladder.
- The pain is felt on one side or in the middle.
Coccyx pain OR Coccydynia
- Pain in the tailbone is a typical symptom.
- Tailbone pain is usually referred from the pelvic floor or the muscles that attach to the tailbone, but not from the tailbone itself.
- Pain in the tailbone can be caused by pain after bowel movements.
Lower back pain
- Low back pain often confuses patients and doctors because... it is reflected from the pelvic floor muscles and does not originate in the lower back itself.
- Discomfort is experienced on one side, but can also migrate.
Groin pain
- Groin pain is often confused with a hernia.
- The adductors are large, strong inner thigh muscles located in the groin area.
- When these muscles are constantly tense and compressed, they are a source of pain and refer pain to the pelvic region, including the rectum.
Discomfort or the appearance or decrease of discomfort after defecation
- The appearance or reduction of discomfort after defecation occurs when tense pelvic muscles relax.
- Discomfort after bowel movements can be especially bothersome if it worsens symptoms throughout the day.
- This symptom, when it appears in the absence of hemorrhoids or anal fissures, has been little studied, but in our opinion it is typical.
- The mechanism of defecation involves filling the rectum with feces, after which the internal anal sphincter and puborectal muscle are commanded to relax, leading to an urgency to defecate.
- After stool passes through the relaxed anal sphincter, the internal anal sphincter reflexively closes.
- We believe that in patients whose symptoms increase after defecation, the internal anal sphincter closes too tightly, i.e. it contracts more than it was before the bowel movement, and this results in a painful spasm.
- In patients whose muscle tension in the pelvis decreases, pain after bowel movements also decreases.
Symptoms migrate or appear in different places
- Pain may occur in different areas of the pelvis or abdomen.
Decreased libido
- Decreased interest in sex is a typical symptom of pelvic pain.
- We believe that low libido is the result of anxiety, low self-esteem and pelvic pain, which interfere with sexual arousal and interest.
- Getting rid of pain and dysfunction of the pelvic muscles also resolves the problem of low libido.
Anxiety and catastrophic thinking
- The worst thing about pelvic pain is the frightening thought that this pain will never go away.
- This fear occupies all the patient’s thoughts, prevents him from living a full life and paints the future in dark colors.
Depression
- Depression includes feelings of helplessness and the inability to change a situation.
- When doctors are unable to help and the patient does not see light at the end of the tunnel, depression and anxiety tend to appear.
Social isolation and difficulties in intimate relationships
- Social isolation is caused by pain, depriving patients of the opportunity to live a full life.
- Chronic pelvic pain negatively affects relationships, including a partner's refusal to have sex, spend time together, travel, parent, and other daily activities.
Violation of self-esteem
- Self-esteem in patients with pelvic pain decreases, because... they worry that people will avoid them.
Sleep disturbance
- Sleep disturbance is a typical symptom
- Many patients wake up anxious, wondering if the pain has gone away and feeling disappointed if it hasn't.
- Patients wake up due to the need to urinate or because of pain and anxiety
- We published an article about increased morning cortisol levels in patients with pelvic pain. Cortisol and Men with Chronic Prostatitis – Poster presented at the Urological Association meeting, 2007
Helplessness and hopelessness
- Helplessness is caused by the patient's inability to stop the debilitating pain.
- Hopelessness occurs when patients begin to think that nothing can help them.
dyspareunia (pain associated with sexual intercourse)
- Patients experience pain during or after sexual intercourse.
- The pain is felt outside or inside the vagina, or in both places.
- When palpating the pain points, the pain can be reproduced.
CT, MRI and X-ray do not reveal any pathology
- The fact that traditional medical examinations, including blood and urine tests, various scans and other tests, do not find any abnormalities in patients with chronic pain syndrome is frustrating for many patients. Traditional treatment, including antibiotics, alpha blockers, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, surgeries and procedures, does not cure pain.
Increased symptoms or pain with stress
- Normal and increased stress lead to increased symptoms.
- When stress causes pelvic pain, it also triggers a tension-anxiety-pain-defense cycle that continues after the stress has passed.
Pain in the genitals
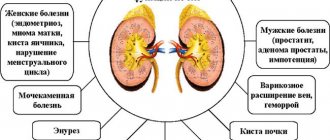
Soreness of the internal and external genital organs is a symptom that can affect both women and men. In the case of women, the main cause of pain and discomfort in the genitals is diseases of the reproductive system - inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries and vagina. Another reason is pathology of the clitoris and labia.
As for men, pain in the genital organs (penis, testicles) can be caused by diseases associated with the prostate gland, seminal vesicles and vas deferens. Let's look at the most common causes of discomfort in the genitals for both sexes.
Pain in the perineum during pregnancy - the cause of pain in the vagina
During pregnancy, a woman experiences such a surge of emotions and feelings that cannot be felt at any other time. Along with enthusiastic emotions and feelings, a woman feels a colossal load on her body, which is sometimes associated with some complications, even physical pain. Although some unpleasant signs and symptoms are typical for a pregnant woman, in certain cases, the presence of discomfort and pain may indicate a serious pathology or problem that is progressing and can threaten the health of mother and baby.
Causes of pain in the genital organs in women
Pain in the genital organs in women can occur with the following diseases and conditions:
- Menstruation .
Nagging and aching pain of varying intensity in the lower abdomen and in the genital area may not have a dangerous pathological basis, but may be a sign of menstrual syndrome. - Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs.
Acute intense pain in this area, spreading throughout the entire lower abdomen, is characterized by inflammation of the uterus and appendages (endometritis and adnexitis). Patients especially complain about the localization of pain in the suprapubic area. An important sign is that the pain tends to gradually intensify. Pain usually develops during the menstrual or postmenstrual period, and also often occurs in women after childbirth. Often accompanied by an increase in body temperature. - Ectopic pregnancy, fallopian tube damage.
The pain in this case develops sharply and is particularly intense, characterized as acute. The condition is very dangerous and requires immediate medical intervention. - Ovarian tumors and twisting of the cyst stalk.
Pain of a tumor nature can manifest itself for a long time as a nagging pain and radiate to the genital area. In later stages, the pain usually intensifies. - Endometriosis.
Pathological growth of the mucous membrane lining the uterus is also accompanied by pain in the vaginal area and external genitalia. - Injuries.
Mechanical damage to the genitals is accompanied by severe pain. - Bartholinitis.
The disease is infectious in nature and causes pain in the external genitalia, which intensifies when walking.
Causes of groin pain
The groin area in humans is designed in such a way that, through pain, it indicates possible diseases. For example, acute - about life-threatening pathologies that require urgent surgical intervention, and dull - indicates the presence of a chronic disease.
As a rule, groin pain in men on the right is explained by pathologies in the reproductive and urinary systems, gastrointestinal tract, nervous and musculoskeletal systems. Each is worth studying separately.
urinary system
In most cases, diseases of this organ are different in women and men.
However, there are also similarities. For example, inflammation in the bladder is characterized by pinpoint colic, which gets worse when going to the toilet. This pathology is called cystitis. With urolithiasis, blood appears in the urine, and during urination, sharp colic appears in the right ureter and lumbar region. The worst thing is bladder cancer, and until malignant cells begin to spread to organs located in the immediate vicinity are affected, a person will not know about its presence. When pain in the groin on the right in men radiates to the leg, one can judge urethritis or inflammation of appendicitis, especially if it is accompanied by fever and nausea.
Digestion
An inguinal hernia on the right side is formed when internal organs and even the peritoneum protrude into the groin canal. The development of such a pathology begins as a result of the thinning of certain places of the peritoneal walls from the groin, in other words, the deepening of their spaces.
It is worth understanding that with this disease a small protrusion appears, which is not always accompanied by pain. But in more advanced situations, when the hernial sac is compressed, then pain of a localized or diffuse nature will appear.
In addition, there are a number of diseases associated with digestion:
- intestinal obstruction;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- malignant tumor in the colon;
- chronic constipation.
Musculoskeletal and nervous systems
In these systems, the list of diseases is too small, but very serious. For example, nerve damage in the lumbar plexus area is possible. It is characterized by decreased sensitivity and colic in the groin, which can be localized both in the lower abdomen and in the upper thigh.
With injuries to the groin area, a person experiences slight swelling and increased pain during movement. This pathology is most often found in professional athletes.
Reproductive system
This is an absolutely individual organ and the diseases that women have are not at all characteristic of men. The only similarity is the formation of sexually transmitted diseases, which are usually caused by sexually transmitted infections. The presence of symptoms directly depends on the type of pathogen.
- Acute prostatitis is an inflammatory process in the prostate gland caused by microbes. Symptoms: stabbing pain appears in the perineum and groin, and the urge to urinate becomes more frequent and difficult. With prostate adenoma, the growth of glandular tissue increases, and the bladder is compressed, which is the cause of pain during emptying. The most unpleasant thing is prostate cancer, when malignant neoplasms force a man to have bowel movements more and more often, despite cramping pain.
- Testicular torsion - when the testicles are rotated, the spermatic duct is twisted. Symptoms of its occurrence are dizziness and piercing pain, which may be accompanied by vomiting.
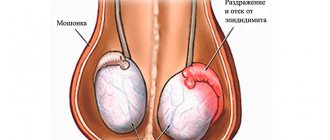
- Epididymoochitis is an inflammatory process in the epididymis and testicles. The pathology is severe: acute pain in the scrotum and increased body temperature to 38 degrees and above.
Pain in the groin on the right in men radiates to the testicles and perineum intensifies with a full bladder and ejaculation. This is an infectious nature of inflammation of the seminal vesicles, also accompanied by increased pain during urination.
Causes of pain in the genital organs in men
Representatives of the stronger sex often encounter pain syndrome of genital localization, which can be caused by various factors - from excessive stress to tumor processes. The most common causes of pain in the male genital organs:
- testicular torsion;
- epididymitis, which is a consequence of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- malignant and benign testicular neoplasms;
- inguinal hernia;
- varicocele - a condition associated with the expansion of venous structures;
- spermatocele is a disease of a cystic nature;
- Peyronie's disease, accompanied by curvature of the penis;
- inflammatory processes such as balanitis and balanoposthitis, etc.
Examination for pain in the perineum and genital organs in men and women
Treatment of any pathologies in the organs of the genitourinary system is carried out by highly specialized doctors: for men - a urologist, for women - a gynecologist. When visiting a doctor, you will need to undergo an examination, tests and ultrasound. According to a short examination program, it is enough to undergo a pelvic ultrasound, take a smear for infections and urine.
If the cause is not found, further research will be required. The doctor may prescribe:
A timely visit to the specialists of the Diana Medical Center will provide an opportunity not only to get rid of pain in the perineum and genitals, but will also eliminate the root cause of the development of such an unpleasant symptom.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
source
What inflammation causes pain in the lower abdomen in women?
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a group of diseases associated with infection. This is evidenced not only by world experience, but also by the experience of gynecologists.
Women encounter infections everywhere. It is impossible to live in completely sterile conditions. Bacteria are everywhere, in the water of rivers, lakes and even the sea. Despite the belief that “salt water kills everything.” This is far from true, considering that in nature there are bacteria that live even in sulfuric acid... Even in your own bathroom, not to mention the toilet, which not only you can use.
If you read reports on bacterial cultures from Jacuzzi pipes in which water stagnates, it turns out that there are a lot of bacteria and fungi there. The moment the Jacuzzi is turned on, all bacteria rush out along with the stagnant water. Unfortunately, the first place they can attack is the female genitals.
Practice shows that 65% of women who come with pain in the lower abdomen, itching, irregular periods, foreign odors and discharge are diagnosed with an infection: pathogenic flora, which is not typical for this part of the body.
Perineal pain
Pain in the perineum is a fairly common symptom that can occur in both women and men, regardless of age. In the vast majority of cases, such a symptom indicates the occurrence of some disease of the genitourinary system. It follows from this that sources for both sexes can be both general and individual.
Most often, in addition to pain, the clinical picture consists of such manifestations as discomfort while walking or sitting for long periods of time, itching and burning in the problem area, as well as disruption of the urination process.
The clinician will be able to make the correct diagnosis and find out the cause only after studying the results of laboratory and instrumental examinations. Treatment is dictated by the predisposing factor, but is often based on conservative techniques.
Causes and treatment of prostate pain after ejaculation
If the prostate hurts after ejaculation, this may be evidence of many pathologies of the male genitourinary system.
It is not possible to determine a specific disease by symptoms alone, because other manifestations may be similar. In some cases, the pathology may not be isolated or may be caused by another pathology.
Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a fairly large number of diagnostic procedures that will help to accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Causes
The causes of pain in the prostate or perineum after ejaculation are always due to a pathological process. Most often these are:
- Vesiculitis (spermatocystitis) is an inflammation of the seminal vesicles.
- Orchitis is inflammation of the testicles.
- Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis (has similar symptoms to orchitis).
- Testicular torsion (the easiest pathology on this list to diagnose).
- Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland, one of the most likely diseases with this symptom.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a tumor of the prostate, better known as an adenoma.
- Prostate cancer.
- The most common sexually transmitted diseases are chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis.
There is no simple way to independently identify a specific disease. A burning sensation in the prostate after ejaculation is one of the common characteristic signs of each of them; other symptoms can also be common, so a comprehensive diagnosis is required.
Separately, we can highlight another cause of pain in the perineum after ejaculation - mechanical injury.
Diagnostics
If your prostate hurts after sex or other unpleasant sensations occur in the perineum, you should first be examined by a urologist.
The appointment begins with the patient telling about his complaints and taking an anamnesis. Next, a visual examination of the genital organ, palpation of the scrotum and prostate gland will be carried out. Already at this stage it is possible to detect testicular torsion. If this diagnosis is not confirmed, additional laboratory and instrumental examinations will be prescribed:
- General urine and blood tests.
- Biochemistry of blood.
- Microscopic analysis and bacterial culture of prostate secretion.
- Spermogram.
- Ultrasound, TRUS, CT or MRI of the pelvic organs.
- Urography and uroflowmetry (study of urination).
- Urethral swab (to check for STDs).
- Biopsy (if PSA blood test results are ambiguous and there is a suspicion of prostate cancer).
This number of procedures is necessary because most diseases require confirmation by several examinations to make an accurate diagnosis, and in some cases there may be several pathologies.
Often they can be interrelated, for example, a sexually transmitted infection can cause, in addition to its own symptoms, prostatitis or orchitis, or orchitis can arise as a complication of prostatitis with ineffective treatment.
Treatment
Therapy is carried out depending on the diagnosis of the disease. Most often, treatment is carried out using conservative methods - medications are prescribed, and physiotherapeutic procedures may also be prescribed.
Medicines usually include the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics (if the disease is caused by infection);
- antispasmodics;
- analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In the most complex or advanced cases, surgical intervention may be prescribed. Most often this occurs with purulent orchitis or late stages of hyperplasia and prostatitis.
Taking into account the specifics of diseases and their impact on psychological health, psychotherapy may be prescribed.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of genitourinary system diseases in men, it is recommended:
- exclude unprotected sexual intercourse;
- avoid prolonged abstinence or excessively intense sex, as well as interruptions of sexual intercourse;
- support the functioning of the immune system;
- lead an active lifestyle (but too much exercise can also cause problems);
- watch your diet, give up bad habits;
- avoid local and general hypothermia, as well as overheating of the body;
- prevent injury to the perineum (this is possible during horseback riding, cycling, long-term driving or lifting heavy objects).
Source: https://prostatity-net.ru/prostata/simptomy/bol-posle-semyaispuskaniya.html
Etiology
The most common causes of pain in the perineum are the course of one or another disease that affects the genitourinary system, which has a different structure in men and women, therefore the sources of such a symptom will be divided into several groups.
The first category includes pathological conditions for which division by gender does not make sense. These include:
- prolonged effects on the body of low temperatures;
- injury or injury to the perineum;
- diseases affecting the skin, in which boils, condylomas or papillomas form;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular, the formation of hemorrhoids of external and internal localization, proctitis and paraproctitis, as well as anal fissures;
- chronic pelvic pain syndrome;
- poor nutrition;
- traumatic sexual contact;
- some STDs, such as gonorrhea or trichomoniasis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- previous surgical interventions on the genitourinary system;
- malignant neoplasms or cancer metastasis;
- poor nutrition;
- osteochondrosis;
- helminthic infestation;
- intestinal obstruction;
- inguinal hernia;
- inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes.
Perineal pain in men can also be caused by the following predisposing factors:
- acute or chronic form of prostatitis;
- the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the urethra, testicles or seminal tubercle;
- abscess or prostate cancer;
- pinching of the pudendal nerve;
- prostate adenoma and cysts;
- cystic neoplasms in the testicle, epididymis or spermatic cord;
- the presence of epididymitis or orchiepididymitis;
- vesiculitis;
- injury to the scrotum or penis;
- testicular torsion;
- enlargement of the veins of the testicle, which is also called varicocele.
Pain in the perineum in women is caused by the following reasons:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- inflammation of the fallopian tubes or vagina;
- rupture of an ovarian cyst - in this case, pain will be felt not only when walking, but also during or after sex, or in cases of prolonged sitting. Pain can be localized on both the left and right, which indicates an affected ovary;
- endometriosis;
- cystitis;
- cancer of the uterus;
- gynecological diseases that disrupt the normal microflora of the vagina;
- varicose veins of the perineum.
In addition, a similar symptom in females can occur during menstruation or during pregnancy.
Separately, it is worth noting about pain in the perineum during pregnancy. Depending on the time of occurrence, this symptom appears:
- before childbirth - pain indicates that the woman will become a mother in the next few days, and the baby is very close to the birth canal. Despite the fact that pain in the perineum before childbirth cannot be called normal, it is not a cause for concern;
- directly during pregnancy - often occurs around the 35th week of intrauterine development of the fetus, since from this period the female body prepares for labor, namely the hip bones move apart. In addition, a similar symptom is expressed if the sciatic nerve is compressed. However, not in all situations such a symptom is considered normal - pain in the perineum in the early stages acts as an alarming signal indicating the likelihood of miscarriage;
- after the birth of a child - is also considered a normal, but unpleasant consequence of labor. Very often, childbirth leads to various injuries, ruptures and other phenomena. Often, pain in the perineum after childbirth goes away on its own a few days after the baby is born.
What are the reasons for pain in the side?
There are many reasons why a person experiences pain in the groin area. Based on which system in the body fails, all these factors can be divided into several groups:
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Lesions of the urinary system.
- Problems in the male genital organs.
- Nerve damage.
- Malfunctions of the musculoskeletal system.
Groin pain in men can be caused by diseases of the digestive system: intestinal obstruction, chronic constipation, colon cancer. But the most common causes of painful discomfort are appendicitis and inguinal hernia. Many people who have pain on the right side of their abdomen immediately begin to suspect appendicitis, since this is the most obvious symptom of the disease. When the appendix is inflamed, right-sided pain radiates to the groin or leg. Men also often suffer from a left-sided hernia, which is accompanied by groin pain.
Common causes of groin discomfort are problems of the genitourinary system. In this case, men suffer from bladder or urethral cancer, urolithiasis, urethritis and cystitis. The easiest way to identify cystitis. In addition to pain in the groin area in men, the process of urination becomes frequent, and it is accompanied by piercing pain.
Prostate adenoma
Among the problems of the reproductive system are prostate adenoma, vesiculitis, acute prostatitis, balanoposthitis, and testicular torsion. With them, the man experiences pain in the right groin or in the left - depending on the place where the problem is localized. Venereal diseases are also common among representatives of the stronger half of humanity. When a person is sick with genital herpes, chlamydia or gonorrhea, in addition to their visible signs, manifested in changes in the external integument of the genitals and discharge from them, a sign is pain in the groin in men.
Compression of the nerve roots in the spine, lower back or sacrum is also accompanied by pain in the groin. And groin injuries manifest as discomfort when the lower limb is moved to the side. A man suffering from radiculitis and arthritis also experiences heaviness and pain in the groin.
Varicose veins, considered a female disease, also affects the stronger sex. It, usually concentrated in the lower leg (calf), can spread to the thigh area. Men of different ages are also susceptible to the effects of such a disease as varicose veins of the testicles.
Pulling in the groin in men in all these cases.
Classification
Depending on the predisposing factor, pain in the perineal area in men and women is divided into:
- primary – formed against the background of various neurological disorders or direct trauma to this area;
- secondary - it is such if it radiates with damage to other internal organs, for example, the prostate, uterus or bladder.
By origin, a similar symptom occurs:
- visceral – the main cause is irritation of nerve endings localized directly in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- psychogenic – often occurs in the absence of a particular illness, in individuals with certain character traits, or as the body’s response to a stressful situation;
- neurogenic - develops when nerve tissue is damaged in a given area.
Depending on the nature of the manifestation, there are the following types of pain syndrome:
- nagging pain in the perineum - may indicate an oncological process;
- bursting pain – very often experienced by women during vaginitis. Pain of the bursting type is also present shortly before childbirth;
- sharp pain in the perineum - caused by urolithiasis and cystitis, bruises and hematomas;
- shooting pain;
- dull pain in the perineum - often develops due to inflammation of the organs located in this area;
- aching pain - most often occurs against the background of urological problems, which means that it is typical for men. In women, aching pain is associated with stretching or swelling of the birth canal.
According to the duration of the expression, they are distinguished:
- acute pain in the perineum - bothers a person for several minutes or hours, but not more than a day;
- chronic pain in the perineum - is such if it is mild and has been present for three or more months.
What is the cause of itching and pain?
Painful sensations in the intimate area bother many representatives of the stronger sex. They arise for various reasons. Burning and itching are associated with irritation of nerve endings. They are not capable of causing severe pain, but can be a symptom of a serious pathology.
The most common causes of discomfort in the perineal area in men are the following:
- urethritis and other diseases of infectious origin;
- genital injuries;
- varicocele;
- hypothermia;
- hernia;
- BPH;
- stones in the kidneys;
- prostate inflammation
- venereal diseases. For example, syphilis or genital herpes;
- long-term abstinence;
- orchitis;
- osteochondrosis.
Also, the cause of discomfort may be pelvic pain syndrome. This condition is typical not only for men, but also for women. It is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen that radiates to the perineum. It is often impossible to diagnose the disease in patients with this syndrome. Therefore, doctors prescribe treatment that is aimed at relieving unpleasant symptoms.
Most often in men, urethritis, prostatitis and adenoma occur. Pain sensations for different pathologies are slightly different. For example, in acute prostatitis, pain in the perineum is sharp and radiates to the scrotum, penis, bladder area, and anus. If prostatitis is chronic, the discomfort will be insignificant, the pain will be nagging, aching, which periodically decreases and sometimes intensifies. There is often a burning sensation between the legs and itching.
Normal and enlarged prostate (adenoma)
Acute urethritis often occurs with sharp and burning pain that occurs at the beginning of urination. Many patients with sexually transmitted diseases experience a burning sensation in the urethra or perineum. With varicocele (or varicose veins), pain appears after sexual intercourse. It is mild and goes away after a while.
With extensive tissue damage in the intimate area, sharp pain and burning occurs in the testicles in men and adolescents. This pathology increases the likelihood of impaired development of the genital organs in children, which can ultimately lead to infertility.
Orchitis is caused by viruses. It often develops as a complication after rubella and mumps. With this disease, the organ enlarges, the skin of the affected area becomes hyperemic, and pain appears.
If discomfort occurs in the right or left side, this means that the damage to the organ is one-sided.
A hernia is characterized by pain when walking. Malignant neoplasms are asymptomatic in the first stages. But over time, after or during sexual intercourse, burning and pain appear.
Symptoms
The clinical picture that complements perineal pain in men and women will differ depending on what disease caused the main symptom. It follows that the symptoms will be individual in nature.
However, it is worth highlighting the most common symptoms:
- spread of pain to the lumbar area, lower abdomen and pelvic area;
- frequent and painful urge to urinate, including at night;
- a feeling of cutting and burning during emptying of the bladder;
- itching in the perineum;
- periodic or constant pathological discharge from the vagina or urethra, which may have a specific color and smell;
- the presence of impurities of pus or blood in urine or semen;
- false urge to defecate;
- feeling of a foreign object in the rectum;
- increase in body temperature;
- enlargement of the affected testicle;
- increased intensity of pain during sex or physical activity;
- significant redness of the penis or labia;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes
The inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes is called salpingitis. It is associated with the penetration of infection into them through the genitals, vagina or abdominal cavity.
Pathologies are indicated by signs; the features of their appearance depend on the form of the disease, the pathogen that caused the infectious process, and the presence of other diseases of the female reproductive system. The main signs of salpingitis include :
- the lower abdomen may pull;
- the pain is localized in the groin area, perineum, can be left- or right-sided, discomfort can affect the lower back;
- vaginal discharge appears (purulent, cheesy, foamy, watery).
Similar article - Tukofit candles reviews who helped
Patients have complaints that cramping pain occurs in the perineal area. There is a burning sensation and itching in the perineum. The pain becomes especially intense during sexual intercourse.
Antibiotics are prescribed to treat salpingitis. Anti-inflammatory drugs and antipyretics help get rid of pain in the perineum. Immunomodulators are indicated. Surgical removal of the damaged section of the fallopian tube is used.
Diagnostics
Only a clinician can find out the cause of pain in the perineum. For an initial consultation, you should go to a therapist, who, after conducting an initial diagnosis, can refer the patient for additional examination to the following specialists:
- urologist;
- gynecologist;
- oncologist;
- surgeon;
- proctologist;
- obstetrician-gynecologist - if there is pain in the perineum during pregnancy;
- pediatrician - in rare cases of the appearance of a similar symptom in children.
Such doctors will prescribe specific laboratory and instrumental examinations, but the basis of the primary diagnosis will be:
- studying the medical history and life history of the patient - to detect a disease that could lead to pain of various types in the perineal area;
- a thorough physical examination, namely gynecological and urological, digital examination of the rectum and palpation of the lower abdomen. This will often indicate which side the affected ovary or testicle is on;
- a detailed survey of the patient - to determine the nature of the pain, the presence and severity of additional symptoms;
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- taking a smear for flora from the urethra and vagina;
- blood biochemistry;
- blood test for hormones and tumor markers;
- microscopic examination of feces;
- X-ray and ultrasound of the peritoneum or pelvic organs;
- colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy;
- irrigoscopy and gastroscopy;
- cystography and FGDS;
- CT and MRI.
Haemorrhoids
An ailment such as hemorrhoids often causes pain in the perineum during pregnancy. An insidious disease can occur at the beginning, middle or end of pregnancy.
The causes that give rise to the development of hemorrhoids include:
- Chronic constipation;
- Physical inactivity;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- Problems with excess weight;
- Hormonal changes.
Every expectant mother should know that hemorrhoids can and should be treated during pregnancy. If the necessary therapy is not provided in a timely manner, the disease will progress to a later stage, which is difficult to cure. Or it will lead to problems like this :
- Complex inflammatory process;
- Infections;
- Anemia;
- Anemia;
- Fetal hypoxia.
Signs of illness
At the initial stage of development, hemorrhoids do not show obvious symptoms, so the woman does not pay due attention to minor discomfort.
Then the disease manifests itself:
- Deterioration of general health;
- Perineal pain;
- Painful sensations during defecation;
- Discomfort when walking.
The more advanced the form of the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms. Therefore, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor, because only a specialist can help get rid of this problem.
Treatment options
Timely access to a hospital will relieve unbearable perineal pain thanks to conservative treatment methods. Based on the stage and trimester of pregnancy, the doctor will prescribe suppositories and ointments to the patient .
If the stage of hemorrhoids is very advanced, doctors will be forced to resort to surgery. Modern medicine is filled with various methods that will not harm either the expectant mother or the baby.
Treatment
To relieve cutting, stabbing, bursting and other types of pain in the perineal area, conservative methods are used, including:
- taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, using rectal suppositories and local ointments;
- use of traditional medicine recipes;
- physiotherapeutic procedures, in particular microwave, laser therapy and magnetic therapy;
- diet therapy - to avoid the development of complications from certain diseases.
Almost all therapeutic methods are prescribed by the attending physician individually for each patient. The only exception is folk remedies, which involve the implementation of sitz baths with the addition of:
- chamomile and calendula;
- potassium permanganate and soda;
- oak and yarrow bark;
- flax seeds and horse chestnut;
- St. John's wort and elderberry;
- lingonberry and hop leaves.
The main indications for surgical intervention are the detection of oncological formations or cystic tumors, urolithiasis and the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
Pain in the perineum during pregnancy requires careful monitoring by the attending physician when using medications and traditional recipes. The operation, if necessary, is performed only after the child is born.
Which doctor should you visit if a symptom appears?
- diseases of the prostate gland - prostate (in men), most often - chronic prostatitis or inflammation of the seminal vesicles;
- postoperative pain in the perineum - developing in women: after natural childbirth, during episiotomy;
- lesions of the urethra, for example, acute urethritis;
- development of ulcers (abscesses) as complications of prostatitis and other inflammatory diseases;
- damage to one or more bulbous-urethral glands - in men (cooperitis);
- traumatic injuries to the prostate – prostate gland and urethra – urethra;
- inflammation/injury of the pudendal nerve;
- damage to the skin in the perineal area (the presence of inflammatory processes of bacterial or viral, fungal etiology);
- benign and malignant neoplasms (prostate cancer).
If a man or woman notices that there is a painful sensation in the perineum, postponing a visit to a medical facility is prohibited.
A symptom may indicate the development of a number of pathologies that can cause significant deterioration in health for a long period and occur with serious complications. It is impossible to independently determine the cause of the pain, and it is dangerous to ignore the situation when the perineum hurts. If the perineum hurts, you should make an appointment with a therapist, urologist, gynecologist, or surgeon. After examining the patient, the doctor will refer him for diagnostic procedures and prescribe laboratory tests. Patients may need to see other specialists:
- traumatologist;
- dermatologist;
- venereologist;
- andrologist;
- neurologist;
- proctologist;
- endocrinologist;
- oncologist;
- allergist;
- infectious disease specialist
Treatment of a disease accompanied by pain in the perineum begins only after confirmation of an accurate diagnosis.
The list of diseases when the perineum hurts in a man or woman also includes:
- intestinal obstruction;
- oncological processes;
- diseases transmitted through sexual contact (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis);
- condylomatosis, the presence of papillomas in the perineal area;
- anal fissure;
- proctitis or paraproctitis;
- cystitis;
- formation of boils;
- osteochondrosis.
One of the “common” diseases is cooperitis or inflammation of the Cooper gland. The main complaint during its development is pain in the perineum after sex, there are other signs.
There are “male” pathologies when the perineum hurts:
- cyst, abscess, prostate tumor;
- testicular torsion;
- varicocelle;
- epididymitis;
- the presence of cystic formations in the genitals.
Women experience pain in the perineum if they have:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- active growth or rupture of a cyst in the ovary;
- varicose veins of the perineum;
- endometriosis.
The symptom of pain in the perineum accompanies the period of pregnancy, labor, and pain persists after childbirth.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent people from having problems with perineal pain, it is recommended:
- lead an active and healthy lifestyle;
- avoid hypothermia;
- engage in protected sex to prevent STDs;
- eat properly and balanced;
- If possible, avoid perineal injuries and stressful situations;
- ensure early diagnosis, timely and comprehensive treatment of all diseases that can lead to the appearance of such a symptom - for this you should undergo a full medical examination several times a year.
As for the prognosis of pain in the perineum, it will completely depend on the disease of the genitourinary system that acted as the etiological factor. Seeking qualified help at the first manifestation of such a sign greatly increases the chances of a favorable outcome.
source
What to do when your lower abdomen hurts?
You need to know the enemy by sight, especially when it comes to treating pain in the lower abdomen. If there are complaints from the female genital organs, the first thing to do is consult a gynecologist, undergo a gynecological ultrasound and get tested.
Most inflammatory diseases in gynecology, in some cases, are already visible at the stage of transvaginal ultrasound examination. The cause of inflammation is revealed by laboratory examination.
A qualified examination, a gynecological ultrasound and a laboratory not only determine the presence of inflammation, but also establish its cause.
But if someone thinks that this inflammation can be cured with simple anti-inflammatory drugs, this is far from true. Inflammation can be reduced. But, for quality treatment, you will need to understand what bacteria caused the inflammation?
It is known that gynecological inflammations can be specific and nonspecific. Sexually transmitted diseases are commonly called specific inflammations. The second group includes diseases that are caused by “banal” flora: Escherichia coli, streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, candidiasis (thrush), etc. In gynecology, they are often called nonspecific inflammations. Although such inflammations are caused by a specific foreign flora. Rather, no attention is paid to such “banal” flora and “relieve” inflammation using methods without the use of antibacterial drugs. Such flora may not be detected, including by not complying with certain standards of examination and laboratory diagnostics.
The condition of a woman’s genitourinary system is a very important issue. Many body functions depend on it: psychological state, sexual, reproductive function, pregnancy, child health.
Ideally, a woman should always monitor her health and, if she suspects any disease, be sure to consult a doctor.
Pain in the perineum in women
The perineum is the diamond-shaped area between the anus and the genitals.
Pain in the perineum in women is a symptom of many different pathological conditions.
The perineum is where most of the pelvic muscles are attached.
Therefore, it has many sources of referred pain (i.e., arising in women in another place, the pain radiates to the perineum).
Characteristics of perineal pain in women
When making a diagnosis, the doctor pays special attention to the characteristics of pain, establishing their type:
- acute (lasting up to several hours and sudden onset) or chronic, disturbing patients for several months;
- rather mild or very painful;
- not changing their intensity and worsening in sitting/standing positions, when cycling;
- sharp, aching, pulling, etc.;
- spilled and localized, etc.
Causes of pain in the perineum in women
In women, the causes of such a condition as pain in the perineum include disorders:
- gynecological;
- urological;
- neurological;
- vascular, etc.
Acute sharp pain in the perineum in women, associated with gynecological problems, may be a consequence of:
- inflammatory diseases of the uterus;
- acute vulvovaginitis;
- inflammation of the Bartholin glands;
- injuries or surgical interventions in the pelvic area, etc.
Pain in the perineal area in women is also associated with inflammation of the urethra and rectum.
With infectious (bacterial, fungal, viral) diseases.
With skin diseases (boils, benign formations).
With the manifestation of chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Nagging pain in the perineum in women often characterizes the course of a chronic process.
The same chronic urethritis, proctitis, etc.
Aching pain in the perineum in women can normally be observed in the postpartum period, during ovulation.
Such pain tends to spontaneously decrease in intensity.
Ovulatory pain can be one-sided.
For example, pain in the perineum on the right in women for 2 to 3 days in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
Pain in the perineum in women during pregnancy
Painful sensations in the last weeks of pregnancy are also common.
When the descending fetus puts pressure on the surrounding tissues, and the pelvic bones begin to move apart.
Most often, such manifestations are stabbing in nature.
More intense pain is observed if a pregnant woman has varicose veins.
Sharp pain in this area during pregnancy can be caused by compression of a nearby nerve by the fetus.
Unpleasant sensations intensify immediately before childbirth.
In the postpartum period, almost all women who give birth experience perineal pain.
More intense symptoms are associated with trauma during childbirth, less intense symptoms are associated with swelling and tissue overstretching.
Tears and sutures prolong the period of pain.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome in women
With this syndrome, persistent pain in the lower abdomen radiates to the groin and perineum.
However, it is not possible to identify the organic cause of the condition.
Soreness in the perineum has a shooting, pulling character.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
PID is a whole group of diseases.
Includes pathologies such as salpingitis, oophoritis, endometritis, pelvic peritonitis, tubo-ovarian abscess.
With this pathology, pain in the lower abdomen, often associated with menstruation, radiates to the perineum, as well as the sacrum and lower back.
Itching, heat, and bloating may be felt in the perineum.
Vulvovaginal pain
Vulvovaginal pain that can radiate to the perineum includes:
- vulvodynia – pathology with unexplained pain in the vulva;
- dyspareunia – pain during sexual intercourse;
- vaginismus - painful muscle contractions at the entrance to the vagina;
- pain associated with PID, injuries, neoplasms and other diseases.
Coccydynia
Coccydynia is pain in the coccyx, often associated with hypertonicity of the pelvic floor muscles and usually caused by nerve injury.
One of the manifestations of the condition is spasm of the perineal muscles.
Forces patients to use special soft pillows when sitting for long periods of time is necessary.
Gynecologist, obstetrician-gynecologist Popelnitskaya Natalya Olegovna talks about what to do for pain in the perineal area in women
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by a gynecologist
Garyaeva Irina Vladimirovna
Perineal neuralgia
Perineal neuralgia is also known as cyclist's syndrome.
Caused by compression of the pudendal (genital) nerve by ligaments, muscles, and tumor formations.
Including malignant ones.
May develop after injury.
It is characterized by severe discomfort in the perineum, worsening in a sitting position.
What should a pregnant woman do if she has severe pain in the pubic bone?
Simple recommendations will help relieve pain and improve your general condition.
Wearing a special bandage is the best way to relieve stress from the pelvis and thereby reduce pain. The bandage is selected according to size for each woman. The bandage should provide good support for the lower back, but not tighten the growing tummy.
. You can wear a bandage from 18-20 weeks of pregnancy.
All pregnant women will benefit from yoga or special gymnastics for expectant mothers. You can exercise at home or in a fitness center under the guidance of an experienced instructor. You are allowed to start training after 14 weeks of pregnancy.
Swimming is a great way to relieve tension from the bones and ligaments of the pelvis. You can sign up for water aerobics for expectant mothers or practice in the pool yourself.
The future mother's diet should be complete and varied. Proper selection of dishes will help to avoid micronutrient deficiencies and rapid weight gain. In winter and spring, do not forget about taking multivitamins.
Pain in the pelvic bones is a situation that can overshadow the whole long 9 months. To prevent the problem from becoming acute for the expectant mother, you need to start taking care of your health even before conceiving a child. Adequate physical activity, a balanced diet and weight control are what will help a woman feel good throughout pregnancy.
Natural causes of discomfort in the perineum
Pain in the perineum in women is rarely the result of normal physiological processes. They should not cause concern unless they are unbearable and pass quickly.
- Injuries. A bruised or sprained muscle causes serious physical discomfort. Girls often suffer from them after playing sports without proper warm-up. Damage can also occur during a gynecological examination or during active sexual intercourse.
- Pregnancy. The larger the fetus becomes, the more it puts pressure on surrounding tissues. This sometimes causes unbearable pain, but doctors cannot help in such a situation. All that remains is to wait for the child to change his body position. In the later stages, pain in the perineum indicates an imminent birth, and in the early stages it can be a sign of a threatened miscarriage.
- Period. During menstruation, the uterus gets rid of excess blood, endometrial particles and unfertilized eggs. These days, her cervix opens up, which causes nagging pain in the perineum in women. In addition, discomfort is felt in the lower abdomen and lower back. Monthly unbearable pain along with heavy bleeding indicate pathologies of the reproductive organs.
Constipation
The causes of pain in the perineum during pregnancy may lie in constipation, from which many pregnant women suffer. Some people assume that such phenomena are considered normal during pregnancy, but they are deeply mistaken. Constipation can lead not only to perineal pain, but also to more serious disturbances in the functioning of the body.
In the early stages, the causes of constipation can be considered:
- Unbalanced hormonal levels;
- Malnutrition;
- Taking prescribed medications.
In later stages, constipation may occur:
- Reduced physical activity;
- Change in fetal position;
- Disturbed emotional background.
Signs of illness
When a pregnant woman experiences constipation, it is difficult to ignore. Secondary manifestations of the disease include:
- Perineal pain;
- Bloating;
- Discomfort;
- Feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- Sometimes, loss of appetite.
It is strictly not recommended to ignore such a problem as constipation, because they threaten the appearance of:
- Hemorrhoids;
- Ailments of the female organs;
- Toxic poisoning;
- Premature birth;
- Threats of miscarriage.
Treatment options
You can get rid of perineal pain caused by constipation during pregnancy with the help of laxatives, which must be prescribed by the attending physician.
Promotes proper functioning of the body:
- Foods containing a lot of fiber;
- Drinking plenty of fluids;
- Some physical activity.
By adhering to all the necessary recommendations, the woman will forget about the unpleasant sensations and give birth to a healthy child.
Pain in the perineum as a sign of pathology
Most often, discomfort in the groin area is a sign that all is not well with your health. Usually the matter is not limited to pain; there are other unpleasant symptoms.
- Bartholinitis. Inflammation of the gland, which is located at the base of the labia. The affected area noticeably thickens and increases in size, it can even completely block the entrance to the vagina. Of course, such a neoplasm does not go unnoticed. It interferes with walking and rubs against underwear. The most accurate description of the symptoms is that a dense ball can be felt on the labia.
- Inguinal athlete's foot. A fungal disease that affects the skin in large folds. It occupies large areas, causing constant discomfort. Itchy and flaky spots appear on the epidermis, which merge with each other, forming rings with healthy skin inside and a red border outside.
- Ectopic pregnancy. With this pathology, the fertilized egg is attached not to the wall of the uterus, but inside the appendage. The growth of the fertilized egg provokes tissue stretching and severe pain. Brown discharge is observed. If medical attention is not provided in a timely manner, the pipe ruptures, accompanied by significant bleeding.
- Diseases of the urinary system. The urethra is located above the perineum, and pathological processes in it are reflected by pain in this area. Unpleasant sensations can also be a sign of cystitis or pyelonephritis. Women with such problems experience pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, frequent urge to urinate, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. There may be a discharge streaked with blood.
- Intestinal pathologies. Some disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract are associated with constipation. Fullness of the intestines causes a feeling of constriction, and difficult passage of hard feces provokes pain in the anus and perineum.
- Diseases of the reproductive system. Discomfort in the groin area in women often occurs as a result of pathological processes in the uterus and fallopian tubes. The growth of the endometrium, neoplasms on the walls and cervix lead to heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding against the background of severe pain.
- Pinched nerve. Pain in the perineum when sitting in women may indicate a pinched sciatic nerve. In this case, the groin area becomes numb, and there is a sensation of a foreign body in the rectum and vagina. Sitting and lying down provide relief.
- Varicose veins Veins can also expand in the pelvic area. This problem most often affects pregnant women and overweight women. The pathology leads to disruption of the blood supply to the reproductive organs, which is manifested by the following symptoms: acute PMS; perineal sensitivity; cycle disruption; copious discharge; urinary disturbance; feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area.
If women have pain in the perineum, do not put off visiting a gynecologist. Unpleasant sensations in this place are often a signal of the development of a pathological process. The source of the problem can be in any organ of the pelvic floor, so it is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms for a correct diagnosis.
source
How to reduce pain?
In cases where there is pain between the legs during pregnancy, a woman needs to do the following:
- normalize the daily routine;
- ensure adequate sleep at night;
- move more and be outdoors;
- eat well and avoid excessive drinking and eating before bed;
- before going to the maternity hospital, you can reduce pain by eating your favorite food, walking a little, holding your tummy;
- the use of relaxation techniques to relieve emotional stress.
If your groin hurts during pregnancy, it is important to perform a set of exercises recommended by your gynecologist. They are designed to stretch and increase the elasticity of the muscles and ligaments of the pelvis and hip joints. Exercises should be done with pleasure, understanding that they will reduce discomfort in the perineum and facilitate the process of childbirth.
The simplest and safest are shallow squats with knees wide apart and leg swings in a standing position. It is better to perform the exercises with your hand resting on the back of a chair. The load must be dosed by a doctor. The appearance of unpleasant sensations serves as a signal to immediately stop exercising.
In the presence of varicose veins, venotonics and vascular drugs are prescribed for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes, which will not harm the unborn baby. Wearing a bandage that supports the stomach and prevents it from sagging helps a lot.
Any pain is a signal of trouble and serves as a reason to treat yourself with increased attention, especially for expectant mothers. If pain occurs at the beginning of pregnancy, is accompanied by vaginal discharge and a disturbance in the general condition, you should urgently contact an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Timely prescribed therapy in a hospital setting will prevent miscarriage and save the baby’s life. The fact that the perineum hurts during pregnancy can be regarded as normal only in the later stages, but in any case, an examination is necessary so as not to miss the pathology.
Author: Olga Shchepina, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Every woman is a continuator of the family, and therefore many are interested in the question of why the perineum hurts during pregnancy. Unfortunately, it is impossible to avoid perineal pain during pregnancy, because during this period, women’s bodies change greatly. But such sensations also cannot be called the proper norm, because sometimes perineal pain during pregnancy indicates disorders or pathologies that require immediate treatment.