Pancreatitis is caused by self-destruction of pancreatic tissue by activated enzymes. Activation of enzymes that break down proteins and fats occurs in response to inflammatory changes in tissues.
Pancreatic changes in the activity of the pancreas occur as a response to the vigorous activity of enzymes. Excessive enzyme activity develops due to a number of factors:
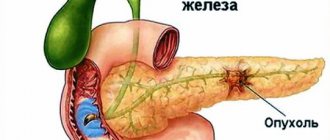
Pancreatic tissue
- Mechanical destruction. It consists of blocking the duct and blocking the outflow of gland juice. Develops due to adjacent diseases of the bile ducts and edema. Injuries are distinguished separately.
- Neuroendocrine disorder. General disorders of the body's hormonal function - fat metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism. Reasons: abuse of fatty foods, alcohol.
- Toxic and allergic disorders. Allergic reactions to systemic drugs, droppers.
Regardless of the factor in the development of pain, a pancreatic attack is often caused by a combination of factors and a negligent attitude towards health.
Types and forms of manifestation of pancreatitis
According to the nature of the clinical course, pancreatitis can manifest itself:
- in acute, acute recurrent form;
- chronic and chronic complicated form.
The development of the disease occurs in a consistent progression, gradually moving from one form to another. According to the nature of the damage to the pancreas, indicating the size of the damage to the organ, the following are distinguished:
- An edematous form of pancreatitis, in which the characteristic islands of necrosis are not observed.
- Destructive form caused by small-focal, medium-focal, large-focal and total-subtotal lesions (of all parts of the pancreas).
Within the framework of the clinic of the acute process of the disease, certain phases of the course of pancreatitis in adults are noted:
- Enzymatic – the duration of the flow phase does not exceed 5 days.
- Reactive – the duration of the course is from 1 to 2 weeks.
- Sequestration, manifesting itself after 2 weeks after the onset of the disease.
- Initial, occurring after 6 months or more from the onset of the disease.
An important clinical point is mortality from pancreatitis. It can be early, caused by a severe nonspecific stress reaction of the body, and late, provoked by the development of various forms of purulent-septic complications, manifested as a result of the development of purulent-necrotic parapancreatitis.
Is it possible to stop the progression of the disease?
Doctors note that chronic pancreatitis can be kept under control if treatment is detected and started on time. Timely seeking medical help increases positive prognoses and reduces the occurrence of dangerous consequences. It will not be superfluous to visit health resorts.
What to do to further support the body? The question is relevant if the acute pain has gone away, but the threat of return remains. Drugs for pancreatitis are not the only panacea. A visit to a special sanatorium will help you recover quickly.
The first signs and symptoms of pancreatitis in adults
The disease is not easy to diagnose, but it can be identified by characteristic signs. The first symptoms of pancreatitis may appear:
- Severe pain in the abdomen, extending to the thoracic, dorsal and subscapular areas, covering the heart area. In this case, the pain syndrome cannot be relieved with analgesics.
- Frequent foamy, mushy stools with pieces of undigested food and an unpleasant fetid odor. Characterized by alternating constipation with diarrhea.
- Heartburn, nausea and constant rumbling in the stomach.
- Unpleasant belching and foul-smelling exhaust gases.
But the main sign of the first symptom of pancreatitis is increased pain after eating. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply and is accompanied by frequent vomiting.
You can suspect the onset of pancreatitis based on some external signs such as:
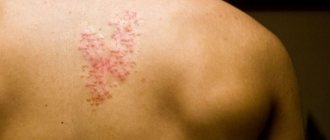
- the appearance of small red spots on the body (back, chest, abdomen);
- a feeling of dry mouth and a white coating on the tongue;
- skin turgor and symptoms of vitamin deficiency.
In addition to the primary symptoms, you can add general symptoms characteristic of inflammatory processes of the pancreas.
- fever and hyperhidrosis, manifested by profuse sticky and cold sweat;
- manifestation of hypotension and hypertension;
- hardening of abdominal muscle tissue;
- shortness of breath and rapid weight loss;
- intolerance to food odors.
The main difference between the various forms of pancreatitis is the nature of the pain syndrome and the clinical course of the disease.
In the acute form of pancreatitis, pain symptoms appear constantly, it can be intense, or cutting and dull. Soreness manifests itself in the reflection zone of the area of the gland that has undergone an inflammatory reaction - under the left or right ribs. Pain in the epigastrium, or girdles, manifests itself as a result of total-subtotal damage.
Exacerbation of pain is provoked by alcohol, a nutritious diet rich in fats and “aggressive” foods that cause increased secretion of pancreatic juice. In the absence of timely assistance, the development of painful shock, loss of consciousness and mortality of the patient is possible.
In chronic pancreatitis in an adult, pain accompanies the patient for many years, especially aggravating a quarter of an hour after eating provocative food. In this case, the duration of pain can last several hours or even days. Its intensity decreases when bending or squatting.
- In addition to pain, changes in coloration of the skin are noted.
This process is caused by pathological processes in the bloodstream caused by inflammatory processes in the pancreas, promoting hemorrhagic effusion under the skin. The skin of the face becomes pale and subsequently sallow in color. In the lumbar and umbilical area, the skin turns blue or acquires a “marble” color. In the groin area - a green-blue hue.
Compression of the bile duct by the inflamed gland can cause yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (sclera) - evidence of the development of a sclerosing form of the disease.
With a healthy stomach and stomach, the human digestive system can even digest foreign objects. But inflammatory reactions in the pancreas can lead to tissue necrosis and complete destruction of the gland. Therefore, with the manifestation of the first symptoms of pancreatitis in adults, treatment must begin immediately, so as not to have to be treated for complications later.
What does the pancreas do?
It has two main functions:
- regulates sugar levels due to the release of insulin;
- participates in the food processing system in the duodenum.
Pancreatitis involves a failure of the digestive system due to disruption of the pancreas, resulting in an excessive accumulation of enzymes in the duct. In this situation, the iron secretes juice, which destroys tissue and impairs its functionality. The connective tissue begins to replenish the damaged cells, but this process only recreates the volume, but does not restore the ability to produce hormones. New cells cannot perform the functions of their dead predecessors. And as a result, digestion loads the remaining cells, causing acute inflammation of the pancreas.
Pancreatitis can occur in acute or chronic form. Like other diseases, the first stages are characterized by attacks. And only in the absence of treatment can they become chronic.
What to do during an attack of pancreatitis?
Everyone should know what to do during an attack of pancreatitis. A person’s life may depend on correct actions. The first thing to do is call an ambulance, and before it arrives:
- The patient should be put to bed. Positioning yourself with your knees pressed to your chest will relieve pain. Rest and limitation of movements are necessary.
- A cold compress should be applied to the epigastric area. This will reduce pain and partially reduce inflammation and swelling of the pancreas.
- Pain and muscle cramps (spasms) can be relieved with Drotaverine, Spazmalgon or Maxigan.
The main rule should be remembered - when symptoms of an acute attack of pancreatitis appear, first aid is determined by three components - absolute rest of the patient, cold to the site of inflammation and a starvation diet.
Treatment of pancreatitis, drugs and nutrition (diet)
Therapy for inflammation of the pancreas should take place in a hospital setting. The treatment strategy for pancreatitis in adults is based on the use of individually selected medications. Including:
- Antispasmodic drugs that relieve pain - “Phenicaberan”, “Drotaverine”, “Sparexa” or “Duspatalin”. Anticholinergic drugs - “Gastotsepina”, “Metapina”, “Chlorosil”. Pathological pain is relieved with Ranitidine and Famotidine.
- Complex treatments for the treatment of pancreatitis are selected according to the prevalence of inflammatory damage to the gland. To stop inflammatory processes, anti-enzyme therapy drugs are prescribed - “Trypsin”, “Kontrikala”, “TrazilolA”, “Gordoxa”, “Pantripin”, “Aspakarma”. Their action is aimed at reducing pain, swelling and microcirculatory disorders.
- Blockers and antisecretory drugs. Blockers - Nexium and Omeprazole, Omez or Rabelok. Cytostatic drugs - “Gordoxa”, “Kontrikala”, “Pantripina”, “Trazylol”, “Amidopyrine”, “Ftorafura”.
- An effective treatment for pancreatitis is pancreatic enzymes. Prescribed to reduce the load on the inflamed gland and in case of its secretory failure. These can be drugs - “Biozima”, “Vigeratina”, “Gastenorma”, “Creona”, “Mezima”, “Pancreatin”, “Penzital”, “Ermital”).
- In addition to treatment, drugs are prescribed to normalize acidity in the digestive organs - Cimetidine, Almagel or Maalox, Famotidine, Gastal and Phosphalugel.
- Drugs that help improve the functions of the gastrointestinal tract - prokinetics “Itopride”, “Motilium” or “Cerucal” and vitamin complexes.
- In severe chronic clinical conditions caused by disorders of the digestive functions, intravenous “parenteral” nutrition is prescribed – solutions of “Alveein”, “Alvezin” or “Aminosol”.
Drug therapy is extensive and justified, but no drugs will help get rid of inflammation of the pancreas without following a diet and nutritional rules.
Nutrition and diet for pancreatitis, sample menu
In case of exacerbation of the disease, in the first three days only drinking regime is allowed - plain water, non-carbonated mineral water or rosehip decoction. The most gentle diet menu for pancreatitis is table No. 5 according to Pevzner. The diet consists of a predominance of protein and vitamin foods with a limitation of carbohydrates and fats.
Dietary meals include up to 6 times a day in small portions, warm. The diet includes:
- Vegetable and cereal soups with lean meat, dairy first courses.
- For the second course, any products made from non-fatty meat or fish, and an omelet made from one egg white are prepared. Pasta dishes, rice, oatmeal, semolina, buckwheat or pearl barley porridge can be served as a side dish. From bakery products - crackers or dried bread.
- Among dairy products, slightly acidic fresh cottage cheese, yogurt, 1% kefir, non-spicy and non-fat lightly salted cheese, and skim milk can be offered.
- Vegetables and fruits allowed include dishes made from potatoes, beets, carrots and pumpkins, zucchini and sour apples.
- Dessert may consist of fruit and vegetable juices, decoctions and compotes of dried fruits and rose hips, tea with added milk. Jam and honey, jelly from sweet fruits and berries are allowed.
Cooking techniques: boiling, simmering, baking and steaming.
The list of foods allowed for consumption is quite wide, and an approximate menu for such a diet for pancreatitis of the pancreas may consist of various products. Eg:
- The first breakfast menu includes carrot and apple salad, steamed meat cutlets.
- 2nd breakfast – one apple.
- For lunch you can prepare mashed potato soup, boiled low-fat fish with milk sauce, rice porridge and fruit jelly.
- The afternoon snack menu includes dried fruit compote and cookies.
- For dinner you can eat buckwheat porridge and drink a glass of mineral water.
- Before bed - a glass of kefir.
Variations of the proposed products can be very diverse. By following such a diet, the treatment will be most effective and will proceed without complications (for more details, see diet table 5).
Prognosis for treatment of pancreatitis
No doctor can predict the outcome of this pathology. The prognosis depends on many factors: the presence of alcohol dependence and diabetes mellitus, the form of the disease and the prevalence of the inflammatory process, the age at which the disease was detected, adequate treatment and the patient’s adherence to a gentle diet.
Even if pancreatitis is detected in adolescence, following all the rules of treatment and diet will allow you to live long and happily.
We can definitely say that no treatment will help with alcohol addiction. Such patients, as a rule, live 10-20 years less than their peers.
Tags: stomach, pancreas
- Gas formation in the intestines: causes and treatment,…
- Vasomotor rhinitis - symptoms and treatment in adults...
- Rhinopharyngitis - symptoms and treatment in children and adults
- Vitamin deficiency - symptoms, photos on the skin, treatment for children and...
- Urticaria in adults: photos, symptoms and treatment,…
- Tracheobronchitis - types, symptoms and treatment, drugs