Precancerous breast diseases are a common pathology among women. With hormonal and genetic disruptions, or the negative impact of the environment on a woman’s body, they turn into a malignant tumor. Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment of precancerous conditions helps to avoid surgical intervention and prevent the development of oncology.
In the “Bulletin of the Russian Scientific Research Center named after. N.N. Blokhin" Professor Yakovleva and a team of authors published a study stating that precancerous pathologies are the most important risk factor for malignancy of benign breast formations.
The structure of the mammary glands
Your knowledge of breast structure will determine which procedures you choose to maintain and improve your bust shape: some of them (such as exercises and creams) will be completely ineffective for enlargement or tightening.
The main task of women's breasts is to produce and supply colostrum and milk for feeding the baby. The second most important option is obtaining sexual pleasure, because the breast is an entirely erogenous organ. The third, traditionally, is aesthetic – both men and girls themselves love to look at beautiful female breasts.
Breasts cannot be pumped up, lifted or enlarged through exercises or techniques because they have no muscles. It consists of adipose and glandular tissue, and only under it on the ribs lies the pectoralis minor and major muscles. On top, the entire structure is covered with a thin layer of dermis. There is no point in doing exercises to increase size, but you can use them to strengthen the chest muscles and connective tissue to prevent sagging, and even slightly lift them after feeding.
The structure of the mammary glands
From the concept of additional
- or lost lobes of G. the concept of “accessory glands” should be distinguished: the latter always have a nipple and an excretory duct (see below). Each lobe G. Breast_Gland g. consists of smaller formations - lobules (acini s. lobuli), and the latter - from alveoli (alveolae). That. The mammary gland is a complex alveolar gland. The alveoli are lined with a single-row cylindrical structure. Breast_Gland glandular epithelium. The height of the cells of this layer is different;
- it depends on the presence and amount of secretion and ranges between 2 and 15 c. The cell nuclei are round or oval, sometimes somewhat flattened, contain 1-2 nucleoli and delicate chromatin\'yu Cshg Ch yun 1 1 1кн i 1 geshtaya v provet Fig. 1 Additional lobule (axillary) of the mammary gland of a nursing woman. (According to Seitz'y.) •—<«« I ig „U l O—1 p In I C b II 1IBI I state; A'-
- alveoli, but prepared for secretion; m—large duct. (From Koelliker.) alveoli, during secretion, are filled with fat drops of varying sizes.
At the same time, the lumens of the alveoli expand and fill with a homogeneous mass containing leukocytes and fat drops. At rest, the alveoli largely remain solid, i.e., they lack a 16S lumen (see Figure 2). Around the alveoli there is a membrane, which, according to some authors, consists of smooth muscle fibers, and according to others, of connective tissue. This is the Breast_Gland, its own membrane of the alveoli, its membrana propria.
In the layer between the epithelium and this v/// *i shell, the so-called myo-_g epithelial cells are described. By anastomosing with each other, they form a network that plays the invisible role of a supporting device. 3. Scheme of output research institutes. Conclusion in the Pro-ducts of the mammary gland: Mammary_Gland CURRENTS IN THE DEPTH OF YOU-1—nipple muscles; 2—sinus rTnqTT„ pchttprloy-lactiferus, or milk tanks SINGLE-LAYER tanks. (According to Boanet.) CYLINDRICAL. epithelium and are surrounded, like the alveoli, by their own membrane (membrana propria). Approaching the skin, after its expansion into the sinus lactiferus (see Figures 3 and 4), the duct replaces
What affects size and elasticity?
Your weight can affect your bust size: breasts are an extremely fat-sensitive organ. When a woman loses weight sharply and significantly, her breasts disappear before problem areas, and when she gains weight, they return, but the kilograms do not go only to the upper part of the body - they are evenly distributed throughout it in accordance with the type of figure.
If your glandular tissue predominates, then weight swings will not affect the appearance and elasticity of the bust. The glands are responsible for producing milk. They are collected into 20 lobes, which are located in a circle from the nipple-areola area. After the birth and feeding of the baby, the areola and nipple may acquire a rich scarlet or brown tint and a clear border.
Cost of correction
The cost of the operation may vary depending on the type of tubulation and the severity of the defects.
Approximate prices:
| Type of intervention | Price |
| Mammoplasty (endoprosthetics) | 120,000 – 240,000 rub. (including the cost of prostheses) |
| Periareolar mastopexy | 165,000 – 245,000 (excluding cost of prosthesis) |
| Vertical mastopexy | 210,000 – 220,000 (without implants) |
| Anchor mastopexy | From 240,000 rub. |
The total amount includes the cost of consultation, examination, anesthesia and the implants themselves. If a complex intervention is planned, the patient will need to pay for her hospital stay.
Breast self-examination
To prevent the development of unpleasant breast diseases, women are advised to examine themselves in the chest and armpits, where the lymph nodes are located. In infectious diseases they can increase.
Breasts may hurt due to approaching menstrual periods, during pregnancy, or due to diseases of the mammary glands, spine and cardiovascular system. Thus, osteochondrosis of the thoracic region can radiate pain to the chest, which can be confused with cardiac pain. In the chest area there are nerve fibers and intercostal nerves, which can signal with painful sensations about problems of a very different nature.
Treatment
A secerating mammary gland is a sign of a particular ailment that should be treated. If the discharge is purulent, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. Sometimes surgery is required to wash out the purulent focus. For ectasia, surgery and antibiotic therapy are resorted to.
If the cause of the discharge is a papilloma located inside the duct, then the only way out in this situation is surgery. For mastopathy, drug therapy is usually used, but sometimes surgery cannot be avoided. Galactorrhea requires taking medications that stabilize hormonal levels.
Cancer is a common cause of breast discharge. With this diagnosis, the following treatment methods are used:
- surgical removal of the tumor;
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy.
Breast shapes
In addition, in order to know the structure of the mammary glands, it is useful for a woman to navigate the shape of her breasts.
- Disc-shaped - the chest is attached to the body with a wide diameter, it is flat and low.
- Hemisphere - has approximately the same height and diameter.
- Pear-shaped - the height of such a breast is greater than the width of its base.
- Mastoid - similar to a pear, but the nipple is directed downwards.
Some people classify women's breasts according to their resemblance to fruits: apple, pear, melon, etc. Forms are individual, just like their owners, and there is no single concept of “ideal breasts.” At the same time, breasts can change throughout life: weight changes, a woman becomes pregnant, gives birth, and breastfeeds babies. By the way, the fetus develops a mammary gland already in the fifth month of the mother’s pregnancy.
Breast shapes
Types and symptoms
Precancer is represented by pathologies manifested by similar clinical symptoms:
- Mastopathy. This is a disease of the connective tissue fibers that make up the mammary gland. It is accompanied by a loss of breast shape, accompanied by a violation of the outflow of secretions - female breast milk.
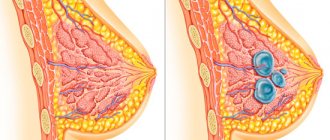
- Fibroadenoma. This is a benign neoplasm, characterized by the appearance of compactions in different quadrants of the organ. The tumor does not hurt and can be accidentally detected during an ultrasound examination.
- Cystic formations. They have mild clinical symptoms - they do not hurt and do not manifest themselves in any way. Occasionally there is a fluctuation - a feeling of fluid in the chest.
Mastopathy and its risks
Mastopathy occurs in women after childbirth, as the breasts change shape and hormonal levels change.
This is a precancerous condition of the mammary gland, which is characterized by a change in the shape of the organ and its dysfunction. The pathology is due to the fact that after childbirth a woman’s hormonal background changes dramatically. Her estrogen levels drop, and to replace them, hormones are produced that are responsible for the production of women's breast milk. The resulting hormonal imbalance provokes stretching of connective tissue fibers and loss of elasticity and shape in the pectoral muscles. The breasts sag, become flat and resume their shape only when their glands are filled with secretions. Inflammatory processes rarely accompany the disease, but in this case, gene and chromosomal mutations can form in mastocytes, provoking cell degeneration.
Breast cysts
These structures, which are cavities filled with exudate, do not manifest themselves for a long time. They are noticeable only during ultrasound examination, when round-shaped hyperechoic darkening is visualized. They most rarely degenerate into malignant neoplasms, since they do not contain a specific cell pool that can mutate. But if milk stagnation occurs as a result of impaired outflow, the cystic cavities can become infected, become inflamed and develop into cancerous tumors, which often metastasize.
Fibroadenomatosis of the parenchyma
Most often, precancer occurs in the form of benign neoplasms that fill most of the gland - fibroadenomas. Adenoma can also occur in the prostate, pancreas, thyroid and other organs that have endocrine functions. Specific cells of the female breast that produce milk after the birth of a child also have these properties. In addition, there are a lot of them, which means the likelihood of spontaneous mutations increases. Like adenomatous formations in other endocrine organs, these structures in the chest do not hurt for a long time and do not manifest obvious clinical symptoms. Therefore, the primary diagnosis is mainly determined during a routine examination by a gynecologist or antenatal clinic doctor.
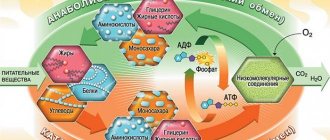
Functions of the mammary glands
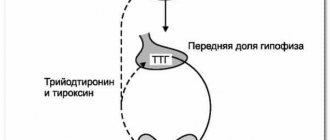
Physiological processes in the mammary glands are subject to the hormonal system - more than a dozen hormones affect breast growth, milk production, the menstrual cycle and menopause. The key hormone is estrogen, which affects cycle regularity, libido, weight and other metrics of women’s health.
- Lactation
The main option of the breast is lactation. While carrying a child, a woman’s breasts enlarge due to the growth of glandular tissue (fat tissue too, because the expectant mother is actively gaining weight). Between the lobes there are special ducts that will transport milk to the nipple. The percentage of glandular tissue is largely influenced by genetics. Women with a predominance of glands over fat have almost no difficulties with breastfeeding.
To stimulate breastfeeding, the baby needs to be applied to the breast more often, and to stop lactation, the child must be weaned off little by little, applying it less often. The glandular tissue decreases due to a decrease in milk production, the size returns to the prenatal norm, and feeding is completed.
- Erogenous zone
The breast is not only a feeding tool, but also an important erogenous zone, the most sensitive element of which is the nipple. The skin here is thin, so it responds to stimulation quickly: the nipple hardens and protrudes, the areolas become brighter. In addition, there are many nerve endings that respond to excitement. If a partner strokes the breast, caresses it with his tongue and lips, a surge of the intimacy hormone oxytocin occurs in the body - much the same happens when a mother feeds her child. The hormone tones the uterus and works as a pain reliever. If a woman is pregnant, breast stimulation can contribute to premature labor or miscarriage.
Functions of the mammary glands
Does breast shape matter for sex?
There is no connection between a woman's sexuality and her bust size. It is a stereotype that men like a full bust. Tastes, like bodies, are different for everyone. Much more important is the healthy appearance of the breasts, their elasticity and shape. A large bust has its drawbacks, for example, a tendency to early ptosis - breast sagging under its own weight.
Breast sensitivity during sex depends on the excitation and inhibition of a woman’s nervous system, her libido, the quality of stimulation, the air temperature in the room and other factors.
Pregnancy and breasts
During pregnancy, the mammary glands begin to intensively develop secretions so that the breasts are ready to feed before childbirth. After the birth of a baby, the mother feels roughness in her breasts, tenderness and pain for several days until she finally feeds the newborn. First, the glands secrete colostrum - a nutritional concentrate, a real storehouse of substances useful for the growth of a child, and on the third or fourth day they begin to produce milk.
When the baby is 9 weeks old, the mother's breasts are at the peak of milk production - up to one and a half liters per day. During this time, it is important to support lactation with energy from food and sleep. The diet should be balanced and satisfying, include dairy products, lean meat, starchy vegetables, and yeast-free bread. Tears and nervous shock, quarrels, lack of sleep, low-calorie diet, and illness can disrupt lactation.
Pregnancy and breasts
Norm and pathology
A huge number of women are unhappy with the way their breasts look. But if external criteria for beauty are very subjective, medical parameters are precise and cannot be justified by taste. There is a clear division into normal, individual normal and pathology of the mammary glands. Pathological conditions include various neoplasms, nodes and cysts, the formation of additional glands, excessive breast growth, atrophy and others.
What is important to know:
- breast size depends only on the amount of glandular and adipose tissue, their ratio, which is dictated by genetics and weight;
- the elasticity of the breast depends on the connective capsule and the ligaments that hold it;
- it is impossible to pump up the chest - there are no muscles there;
- diets are not effective - the bust goes away first of the problem areas;
- temporary loss of shape during lactation is normal;
- Bust enlargement during pregnancy is normal;
- breast asymmetry is normal;
- age-related changes and ptosis after 45 years are the norm.
Developmental anomalies[ | ]
Nipple line
- Amastia - atrophy of the mammary glands, unilateral or bilateral, is observed extremely rarely.
- Macromastia[en] is excessive (up to 30 kg) enlargement of the mammary gland, usually bilateral.
- Polymastia[en] - accessory mammary glands. Most often found in the armpits.
- Polythelia is the presence of accessory nipples located along the nipple line
. - Flat or inverted nipples, which can cause difficulty breastfeeding.