Acute rhinosinusitis
One of the most pressing problems in the practice of an ENT doctor is acute rhinosinusitis. The disease develops as a result of the inflammatory process in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Recently, the number of diseases affecting the nasal cavity and sinuses has been increasing. Among the total number of patients of otolaryngologists, patients with acute rhinosinusitis account for 60-65%.
acute rhinosinusitis what is it
Surgical treatment
Advanced stages of sinusitis require surgical intervention. The operation usually involves endoscopy. The endoscope is inserted directly into the cavity of the paranasal sinuses.
There are several indications for surgical intervention. Among them, the main ones should be highlighted:
- increase in symptoms of the disease;
- increased body temperature for a long time;
- development of long-term sinus obstruction;
- development of local complications;
- lack of positive results from conservative treatment.
The use of the most modern technologies allows doctors to perform surgical intervention to treat purulent sinusitis in a day hospital.
This method is minimally invasive, so the patient will not have to resort to nasal packing for quite a long time in the postoperative period. In addition, the recovery period lasts much less than with sinus piercing.
The video in this article will demonstrate why sinusitis is so dangerous and why you should not delay its treatment.
Acute rhinosinusitis: risk factors
There are a number of conditions and phenomena that can provoke the appearance of acute rhinosinusitis, as well as aggravate the course of the disease. Such damaging factors include:
- smoking (both active and passive);
- inhalation of irritants;
- violations of the anatomical structure of the nasal cavity - deviated septum, adenoid vegetations, sinus hypoplasia, tumors, curved nasal passages, etc.;
- disturbances of mucociliary clearance;
- immunodeficiency states;
- infectious lesions of the respiratory tract, especially the upper sections;
- allergic rhinitis;
- atopic dermatitis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- dental interventions;
- increased humidity in the premises;
- climate change;
- mental disorders;
- depression;
- anxiety states.
Eliminating the impact of these factors on the human body will prevent the development of acute rhinosinusitis, as well as its complications.
Acute rhinosinusitis: main causes of the disease
The mucous membrane of the nose and paranasal sinuses have functional similarities. Therefore, inflammation of these structures usually occurs simultaneously.
acute rhinosinusitis, symptoms of rhinosinusitis
Important! The term "rhinosinusitis" in modern medicine is considered more accurate than "sinusitis".
Acute rhinosinusitis develops as a result of exposure to a complex of factors:
1. Genetic.
2. Environment - climatic conditions, ecological situation, living and working conditions, use of medications (especially acetylsalicylic acid, antibiotics, hormonal and chemotherapeutic agents), infections.
3. Internal factors - abnormalities in the structure of the nasopharynx.
4. Changes in the rheology of mucus in the nasal cavity (drying or excessive moisture).
5. Random factors - hypothermia, smoking, use of artificial ventilation, etc.
Causal factors lead to changes in the nasal mucosa, which enhances the negative impact of the causative factors. As a result, the following syndromes arise that reduce local immunity and resistance to the development of pathological processes (in particular inflammation):
• disturbances in the rheological properties of mucus in the nasal cavity;
• disruption of the mucociliary transport system;
• decreased activity of the immune system's response to damaging factors.
Despite the fact that the role of infections in the occurrence of acute rhinosinusitis is exaggerated, common etiological factors include the following:
• streptococci;
• viruses;
• fungal pathogens;
• Haemophilus influenzae;
• Moraxella catarrhalis;
• staphylococci.
Important! As a rule, the inflammatory process begins in narrow areas of the nasal passages (middle sections).
In most patients with acute rhinosinusitis, the disease begins as a result of exposure of a pathogenic factor directly to the nasal cavity or sinuses. In more rare cases, the pathological process begins due to the influence of etiological factors through lymph and blood.
acute rhinosinusitis symptoms, treatment of rhinosinusitis
Catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sinuses
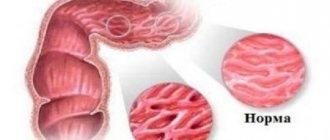
Typically, the disease manifests itself during the cold season, when the protective function of local and general immunity is reduced. The mucous membrane of the respiratory tract becomes more sensitive to pathogenic viruses and bacteria. Catarrhal sinusitis develops against the background of acute rhinitis, colds, and acute respiratory viral infections. Humid and cool air and vitamin deficiency contribute to inflammation of the nasal sinuses.
The sinuses in the bones of the facial skull are not isolated; they are equipped with channels for removing secretions from the sinuses. In the figure, arrows show the movement of mucus in a normal state, red dots indicate blocking of the excretory ducts. The curvature of the nasal septum, nasal polyps, and adenoid growths in children contribute to the stagnation of mucus.
Causes of maxillary catarrhal sinusitis:
- penetration of filling material into the maxillary sinus during dental procedures;
- fistula - an opening between the maxillary sinus and the oral cavity;
- incorrect tooth extraction;
- diseases of the roots of the teeth;
- allergic rhinitis;
- fungal infection.
In case of inflammation, more mucus is produced than in normal conditions. Tissue swelling occurs, the channels are blocked, secretions accumulate in the sinuses, which causes the development of pathogenic microflora. The body increases the production of white blood cells that enter the area of inflammation.
Acute rhinosinusitis: main symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms of acute rhinosinusitis that patients most often complain about are:
1. Nasal congestion.
2. Presence of nasal discharge.
3. Pain or feeling of squeezing on the face.
4. Weakening of the sense of smell or its complete loss.
Additional symptoms, the severity of which depends on the causes of acute rhinosinusitis:
• general weakness;
• feeling of stuffiness in the ears;
• toothache;
• pain in the upper jaw;
• a sore throat;
• elevated body temperature (develops rarely, more often with an infectious or viral nature of the disease);
• purulent discharge from the nose;
• pain in the facial area, which is unilateral (more often with an infectious etiology of the disease);
• unilateral nasal discharge (one half of the nasal cavity is affected, which is often the case with bacterial acute rhinosinusitis);
• swelling of the nasal mucosa;
• nasal voice.
rhinosinusitis symptoms and signs
Important! Symptoms of ARVI (cough, runny nose, fever, weakness, malaise) often accompany acute rhinosinusitis and indicate a viral etiology, which is important when prescribing treatment.
Characteristic symptoms
Regardless of the patient’s age, the symptoms of acute rhinosinusitis are the same, which allows you to understand the severity of the disease and seek medical help in time:
- headache attacks;
- edematous mucous membrane;
- stuffy ears;
- nasality;
- aches, fatigue, weakness, general malaise, decreased performance;
- pain in the paranasal sinuses with the appearance of swelling in the affected area;
- discharge of pus or mucus from the nose;
- elevated temperature;
- loss of smell - partial or complete;
- drainage of accumulated secretions down the nasopharynx.
The difference in symptoms may be explained by the affected area:
- pain concentrated in the forehead area indicates acute frontal sinusitis;
- severe pain, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the sinus area - these are signs of acute sinusitis;
- painful headaches can be symptoms of the development of sphenoiditis;
- nasality most often indicates manifestations of ethmoeditis.
If chronic rhinosinusitis develops, the symptoms are practically the same, but the disease lasts longer.
Polypous rhinosinusitis
The development of polypous rhinosinusitis is observed with weakened immunity and deficiency of immunoglobulin G. As the disease develops against the background of edema, the epithelial tissue thickens with the gradual formation of polyps - specific outgrowths. It is not possible to cure such a pathology with medications, so surgery is prescribed to restore nasal breathing.
Purulent rhinosinusitis
Acute purulent rhinosinusitis develops in adults and children as a result of the rapid proliferation of pathologically dangerous bacterial microorganisms that are localized in the epithelium of the internal surfaces of the nose. To treat inflammatory foci aggravated by a purulent process, antibacterial therapy will be required. An accurate diagnosis is based on collecting secretions that accumulate in the nasal passages and culturing them. Studying the tests allows you to determine the type of pathogen - staphylococci, streptococci, etc., prescribing adequate treatment. The therapeutic complex for the purulent course of the disease, according to indications, includes several medicinal varieties.
- Immunomodulators (for example, IRS-19, Immunal) in combination with multivitamin preparations (Undevit, Triovit, etc.). They help activate the defense mechanism and strengthen the body.
- Antihistamines to reduce swelling. At the same time, they reduce the amount of mucus, restoring free breathing. In treatment, Tavegil, Claritin, Loratadine demonstrate a good effect. Relieve inflammation, moisturize the mucous membranes with nasal drops - Vibrocil, Polydexa. Galazolin, Otrivin, Naphthyzin have a vasoconstrictor effect.
- Mucolytics that promote the removal of viscous secretions. The most commonly prescribed are Mucodin, Fludex, Fluimucil.
- Antibacterial agents designed to eliminate infection. At the first signs, Amoxicillin is used, which has a good anti-inflammatory effect. If a severe degree of the disease is diagnosed, then the inclusion of stronger antibiotics from tetracycline varieties is required in the treatment of acute inflammation with purulent foci.
If the torment causes severe pain, the temperature rises, the doctor prescribes Ibuprofen, Nurofen. The development of purulent rhinosinusitis without proper treatment can lead to dangerous conditions in the form of meningitis and varying degrees of severity of abscesses.
Catarrhal form
Acute catarrhal rhinosinusitis develops against the background of a respiratory disease in the form of foci of inflammation on the mucous membranes (catarrh) of the nose and in the paranasal sinuses. When an acute catarrhal process is diagnosed, the treatment process proceeds fairly quickly, but if left untreated, the consequences can be fraught with serious complications. Along with the general symptoms, the catarrhal form is distinguished by the localization of headaches on the forehead, on one or both sides of the bridge of the nose. Undoubtedly, bilateral rhinosinusitis brings more suffering. A complicated course causes the development of insomnia, the appearance of neuroses, and memory impairment. Catarrhal form is treated at the initial stages with antiviral drugs (Nazoferon, Anaferon, Amizon). They relieve the first symptoms. At subsequent stages of the disease there will be no benefit from them. To combat catarrhal rhinosinusitis, antihistamines (Diazolin, Tavegil, Loratain) are used. Their task is to reduce the swelling process and prevent drug allergies. Mucus secretion in catarrhal form is usually minimal. But if there are any concerns, then vasoconstrictor nasal drops are included in the treatment of rhinosinusitis. You will need vitamins and immune-strengthening medications. Sometimes the chronic course of the disease leads to surgical intervention. Cleansing of pus from the maxillary sinuses is prescribed using puncture under local anesthesia.
Vasomotor form
Vasomotor rhinosinusitis, which develops during a cold, can have bilateral or unilateral damage. This disease is characterized by disturbances in vascular tone. This causes the adjacent mucous membrane to swell. Its swollen surface leads to nasal congestion. The causes of the vasomotor inflammatory process are the unfavorable external environment. In women, this condition may be due to hormonal changes. If not treated in a timely manner, vasomotor rhinosinusitis in children and adults becomes more complicated, and treatment of the chronic process requires more time than in acute forms. Depending on the severity, the doctor prescribes rinsing, antibiotics, etc.
Allergic rhinosinusitis
Allergic rhinosinusitis, symptoms and treatment of which depends on the allergen causing inflammation, is accompanied by sneezing, itching in the nasal passages, watery discharge, and swelling. When starting treatment for rhinosinusitis, the doctor prescribes a special examination, with the help of which the key allergen is identified by testing. This makes it possible to carry out special preventive measures in the future to prevent certain products or substances from entering the body.
Symptoms of complications of acute rhinosinusitis
- periorbital edema;
- exophthalmos;
- double images in the eyes;
- ophthalmoplegia;
- decreased visual acuity;
- Strong headache;
- swelling of the tissues on the face;
- symptoms of meningitis;
- neurological disorders;
- loss of consciousness.
Important! If there are symptoms of complications of acute rhinosinusitis for 3 hours, the patient should be referred to the otolaryngology department.
acute rhinosinusitis in children, treatment and prevention Signs of severe acute rhinosinusitis, including in children:
Complications that may occur after purulent sinusitis
If treatment is incorrect or untimely, the following unpleasant consequences may occur:
- the inflammatory process can spread further, reaching the soft tissues of the face and respiratory tract;
- the process can be complicated by diseases of the ears and eyes, leading to the formation of purulent inflammations, sometimes even leading to loss of vision;
- complications can affect the intracranial space, namely: encephalitis, meningitis, abscess, etc.;
- in severe cases, the infection can lead to blood poisoning and, as a result, death.
As you can see, purulent sinusitis is a serious pathology with insidious consequences, so it is important to understand how to avoid the occurrence of this disease.
Preventive measures help prevent the onset and exacerbation of the disease
Acute rhinosinusitis, treatment tactics
acute rhinosinusitis treatment, causes of rhinosinusitis
Treatment (medical or surgical) of acute rhinosinusitis is always complex. Directions – pathogenetic (impact on the mechanisms of disease development) and symptomatic (elimination of symptoms).
The main groups of drugs that are used in the treatment of the disease:
• nasal saline solutions;
• analgesics;
• antibiotics (limited);
• glucocorticoids (hormonal anti-inflammatory and decongestant) for intranasal and oral use.
Important! There is insufficient evidence of the effectiveness of the use of antihistamines, mucolytics (mucus thinners) and decongestants (vasoconstrictors). The doctor can prescribe such drugs when justifying their need for the patient.
Surgical intervention is used in the following cases:
• ineffectiveness of drug therapy;
• severe rhinosinusitis;
• presence of severe complications of the disease;
• bacterial acute rhinosinusitis due to immunodeficiency and use of immunosuppressants.
Types of surgical interventions for acute rhinosinusitis:
1. Drainage endoscopic interventions in the sinuses.
2. Trepanopuncture of the frontal sinuses.
3. Maxillary-frontoethmoidosphenotomy.
Features of prescribing antibiotics for acute rhinosinusitis
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed for patients with a proven infectious etiology of the disease, as well as for complicated rhinosinusitis.
The drug of choice is amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid (protected aminopenicillins). If there is confirmation that the causative agents of rhinosinusitis are atypical, macrolide antibiotics are prescribed first. Also, macrolide antibiotics are the drugs of choice if there are contraindications for the prescription of amoxicillin.
Second-line drugs are cephalosporins (ceftriaxone), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin).
Important! If the patient is undergoing outpatient treatment, preference should be given to oral forms of antibacterial drugs.
Forms of the disease
There are several main forms of rhinosinusitis, the treatment of which is selected individually. These include:
- Sinusitis catarrhal. The pathology affects the maxillary (maxillary sinuses).
- Ethmoiditis. The inflammation spreads to the ethmoid bone.
- Frontit. The infection is localized in the area of the frontal paranasal sinuses.
- Sphenoiditis. The pathology is localized in the sphenoid sinuses.
Acute catarrhal sinusitis is of 2 types: bilateral and unilateral. Methods, characteristics of the disease and treatment are determined after accurately identifying the type of pathology due to the fact that the sinuses communicate with each other.
Physiotherapy for rhinosinusitis
physiotherapy for rhinosinusitis, acute rhinosinusitis
Physiotherapeutic procedures for rhinosinusitis are prescribed to suppress inflammatory processes, stimulate blood microcirculation and tissue regeneration in the sinuses.
When using any physiotherapeutic procedures, preliminary release of mucus from the paranasal sinuses and nasal passages is required.
To reduce the symptoms of rhinosinusitis use:
- endonasal electrophoresis with the inclusion of various medications;
- darsonvalization (treatment with pulsed currents);
- FUF irradiation of the nasal mucosa;
- biodynamic therapy.
In order to suppress inflammatory processes and symptoms of rhinosinusitis, the following is used:
- medical laser;
- ultrasound treatment;
- UHF;
- centimeter wave therapy.
To strengthen local and general immunity, experts recommend:
- air baths;
- ultraviolet irradiation courses;
- thalassotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser irradiation of blood.
In the chronic form, to relieve symptoms of rhinosinusitis, the following is prescribed:
- warming up using a blue lamp;
- UHF;
- inhalation;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- diathermy.
When analyzing the effectiveness of physiotherapeutic procedures, there was an improvement in the general condition of 45% of patients on the third day, and in 83% of patients after a weekly course of physiotherapy.
EF irradiation of the nasal mucosa, acute rhinosinusitis
Speleotherapy is becoming one of the progressive areas of physiotherapy. The use of this method is based on placing the patient in special conditions
salt cave or mine. Sometimes a specially equipped room is used where antiseptic conditions are created. The walls of such a room are covered with a layer of salt. Therapy requires prescription and supervision by the attending physician. The effectiveness of the method is based on the special properties of salt to suppress harmful microorganisms.
Diagnostics
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, an otolaryngologist does not need only external signs of the disease. The patient must additionally undergo the following diagnostic procedures and tests:
- blood from a finger (glucose level is established, the clinical ratio of vital blood cells - phagocytes, erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, lymphocytes, which play a key role in the formation of a strong immune system);
- selection of purulent mucus secreted from the nasal openings during blowing the nose (in the laboratory, bacterial seeding of biological material is carried out to determine the infectious strain that caused the acute inflammatory process);
- X-ray of the frontal part of the head (in the picture, areas of the paranasal sinuses filled with pus appear in the form of dark spots);
- MRI of the head to determine whether bacterial infection of the bone tissue of the facial disc has occurred, and how extensively the focus of purulent inflammation itself has spread;
- urine, the delivery of which is mandatory for its biochemical examination in order to establish the severity of the current inflammation, and whether this has a negative impact on the functioning of the kidneys.
After receiving comprehensive information on the results of these diagnostic studies, the attending physician has the opportunity to formulate a high-quality therapeutic course with the selection of medications necessary in a specific clinical case.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in children
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in children
The main areas of treatment are:
- suppression of the pathogen and elimination of symptoms of rhinosinusitis;
- shortening the duration of the disease and alleviating the general condition of the child;
- preventing the disease from becoming chronic and developing possible complications.
Drug therapy usually includes the use of antibacterial agents, vasoconstrictors and mucolytics, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs. When selecting a treatment regimen, it is possible to prescribe drugs with both systemic and local effects in combination with physiotherapy.
To remove bacteria and viruses that cause disease from the body, rinsing the nose with saline solutions is used. The absence of side effects on the child's body of preparations based on sea salt allows not to limit their use.
The use of topical antibacterial drugs is practiced in combination with the prescription of antibiotics.
Knowing what rhinosinusitis is, you can choose the right treatment. Various decongestants are used to make breathing easier. They are prescribed to reduce swelling of the mucous membrane.
The list of these drugs includes:
- Oxymetazoline;
- Phenylephrine and similar substances.
It is important to follow the dosage prescribed by a specialist. In young children, some drugs can cause unpleasant side effects.
As part of mucolytic therapy, drugs with thinning, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects are used. The drugs have various dosage forms, which allows them to be used both internally and locally.
use. Acetylcysteine is prescribed to children for the treatment of acute rhinosinusitis. Depending on the degree of damage to the lower and upper respiratory tract, the medicine is prescribed for oral administration in order to actively dilute sputum and achieve a general anti-inflammatory effect.
Ibuprofen or Paracetamol (or their combinations) are most actively used as antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
In addition to medication methods, physiotherapy and herbal remedies are prescribed to strengthen general immunity. The use of any additional treatment methods must be agreed with a specialist. It is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to make an accurate diagnosis.
Complex therapy
Symptoms and treatment of catarrhal sinusitis depend on the location of the inflammation. With sinusitis, in addition to the main symptoms, pain and increased sensitivity of the teeth, coughing at night are troubling. Antibiotics, nasal sprays and drops, antihistamines, and mucolytics are prescribed.
Nasal rinsing is carried out to remove accumulated secretions along with pathogens. Cleansed mucous membranes absorb drugs better. The most commonly used solutions of sea water are Morenazal, Aqualor, Marimer or Aquamaris. You can use saline solution - rinse your nose with it using a special “watering can,” a rubber bulb, or a disposable syringe without a needle. When introducing liquid into the nasal passage, the head is tilted in the opposite direction.
Nasal drops and sprays with sea water or saline do not cause addiction or side effects. Adults and children over 3 years of age can rinse their nose 4–6 times a day.
Vasoconstrictor drugs for the nose:
- Xymelin Extra;
- Nazol Advance;
- Naphazoline;
- Galazolin;
- Nazivin.
These drugs are used to eliminate swelling from the first days of illness, but not more than 1 week. The effectiveness of the drug is reduced, so it should be replaced with other nasal drops that do not irritate the mucous membrane.
Sprays Bioparox, Isofra, Polydexa contain ingredients that act against bacterial infections. Oral antibiotics for catarrhal sinusitis are prescribed in case of purulent exudate. The doctor determines the dosage and duration of use of the medicine on an individual basis.
Auxiliary drugs are used to treat catarrhal sinusitis: expectorants, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic, antihistamines. Some patients need physical therapy: electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation. At home, you can apply a warm compress to the sinus area, but not for purulent inflammation. To restore the immune system, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes.
Sinusitis is easier to prevent than to treat. To prevent catarrhal inflammation, it is recommended to promptly treat dental diseases, influenza or ARVI, allergic rhinitis, and avoid hypothermia.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in pregnant women
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in pregnant women
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in women during pregnancy is a complex process, since there are no structured treatment regimens. Conducting clinical trials is unacceptable for pregnant women.
Current scientific recommendations from medical experts include a description of the various possible risks and consequences of using drugs. There is no substantiated scientific evidence of the effectiveness of the use of saline solutions and homeopathic medicines for rhinosinusitis in pregnant women.
When prescribing treatment regimens, the specialist is guided by a comparative analysis of the planned benefits for the woman’s health and the degree of risk to her fetus.
The development of the disease during pregnancy is possible due to infection, allergic reaction and rhinitis. It is rhinitis in pregnant women that is practically untreatable; it stops some time after childbirth.
Basic rules for the treatment of acute rhinosinusitis in pregnant women:
According to recent scientific research, Okomistin is a local antimicrobial drug, the use of which is allowed during pregnancy. The drug is used in the form of nasal drops.
To ease the general condition and breathing, experts recommend using solutions and sprays based on sea water to rinse the nasal passages.
During pregnancy, special attention should be paid to preventing the disease and strengthening the immune system. This is greatly facilitated by proper nutrition, walks in the fresh air and good sleep.
If an allergic reaction is possible, contact with allergens of both household and natural origin should be avoided.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis with folk remedies
treatment of rhinosinusitis with folk remedies
To combat the inflammatory process in the nasal sinuses, you can prepare a decoction from a collection of herbs:
- chamomile;
- tops of St. John's wort;
- swamp dried grass.
The dry ingredients are mixed in equal proportions, poured with boiling water and left to infuse for 20-30 minutes. After cooling, be sure to strain the product.
Homemade nasal drops include a mixture of:
- sage;
- calendula;
- valerian root;
- eucalyptus leaf.
The dry mixture is also brewed and filtered when cooled. The product is used to instill 2-3 drops into each nasal passage three times a day.
A good result is obtained by simply rinsing the nose with infusion of chamomile, calendula, yarrow or a weak saline solution.
To treat rhinosinusitis, you can use a mixture of celandine juice with chamomile decoction:
- The components are mixed in equal proportions.
- Apply no more than 3 drops of the product into each passage.
- The effect of use will be achieved when using the product at least 5 times a day. However, it is important not to forget that celandine is a poisonous plant. This product should be used with caution.
Differences from other species
Sinusitis has 2 stages of the disease - catarrhal and polysinusitis. Catarrhal sinusitis occurs after a virus enters the nasal sinuses.
At the same time, nasal discharge becomes profuse, but it has a liquid consistency and a transparent color. For catarrhal rhinosinusitis, the doctor usually does not prescribe antibiotics.
If timely and adequate treatment is carried out, then the infection will not have time to join this process and the symptoms of the disease will disappear within 7-10 days.
Otherwise, the disease passes into the infectious-purulent stage and polysinusitis develops.
Most often, polysinusitis begins abruptly on the 7th day. If the causative virus dies and an infection enters the nasal sinuses, polysinusitis occurs on the 10th day.
What does hand dyshidrosis mean? The answer is here.
This color of mucus is explained by the high content of neutrophil cells in it. They are the ones that the immune system produces to eliminate the infection.
These cells contain green granules, which, after their death, color the discharge green.
In addition, catarrhal sinusitis can be distinguished from polysinusitis by symptoms. In the first case they are less pronounced.
Compresses
In folk medicine, compresses are used to relieve inflammation and discomfort associated with swelling of the mucous membrane.
To make a compress, mix wheat flour and honey in equal parts. The compress is applied to the sinuses for 20-30 minutes.
A compress made from black radish is also effective. The root vegetable should be grated on a fine grater. It should be used carefully. The skin must first be lubricated with rich cream or vegetable oil.
Baths with eucalyptus, pine, juniper oil or sea salt give a good effect. They significantly facilitate breathing and have an antiseptic effect.
For general strengthening of the body, you can drink a decoction of chamomile, yarrow, rosehip, as well as herbal teas.
It is recommended to discuss the use of various folk remedies with your doctor. To treat the disease, a competent diagnosis and an integrated approach are important. Consultation with a specialist will help identify the causes of rhinosinusitis, the nature and form of development of the disease. This is a necessary condition for prescribing an effective treatment regimen.
Prevention of rhinosinusitis
prevention of rhinosinusitis symptoms
It is very important to visit a specialist when the first symptoms of rhinosinusitis appear for proper diagnosis and selection of a treatment regimen. Ignoring diseases and self-medication often lead to various complications or the progression of the disease into a chronic form, which will be accompanied by periodic systemic exacerbations.
Timely treatment is one of the important measures to prevent acute rhinosinusitis. Particular importance should be paid to the prevention of the disease in childhood.
Preventive measures include:
- a well-balanced diet;
- active walks in the fresh air;
- hardening;
- timely treatment of respiratory diseases.
An effective method of combating the disease is to strengthen the general immune system. This is greatly facilitated by:
- physical education classes;
- trips to the sea;
- regular intake of vitamins and mineral complexes;
- inclusion of fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet.
Preventive measures to prevent the appearance and development of the disease in adults and children include:
- active physical education and sports;
- healthy lifestyle;
- selection of clothes according to the season;
- regular ventilation and cleaning of the premises;
- walks in the open air;
- a complete diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- use of personal protective equipment during the season of exacerbation of infectious and viral diseases;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules.
The cause of rhinosinusitis is often a defect in the nasal septum resulting from trauma. In this case, you need to consult a specialist, since such defects prevent the free passage of mucus from the sinuses.
Paying attention to your health, an active lifestyle, maintaining personal hygiene and giving up bad habits will be an excellent prevention of the disease.
In the allergic form of rhinosinusitis, measures must be taken to avoid contact with sources of allergies. To determine allergens, you should consult a specialist. Timely consultation will help to avoid complications as the disease develops.