The child’s enamel is just forming, and the immune system is weak, so the child’s body is not able to fully resist cariogenic microbes. It's no surprise that tooth decay is one of the most common problems for which parents bring their children to the dentist. In this article we will look at the causes, forms, symptoms and methods of treating caries in children.
Some parents believe that caries in baby teeth does not need to be treated, since they are temporary and will fall out anyway. However, this opinion is wrong. If the disease is neglected, complications may develop that can affect the molars and oral tissues.
In this article
- Causes of caries in children
- Types and forms of caries in children
- What is bottle caries?
- Symptoms of caries in children
- Treatment of caries of primary teeth
- Treatment of caries of molar teeth in children
- Complications of caries in children
First, a few words about what caries is. This pathology is a slow process of destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth - dentin. It occurs due to the entry of cariogenic microorganisms into the oral cavity. They may not be dangerous to human health, but under certain conditions they begin to actively reproduce. The acid released by these bacteria eats away at the enamel and gradually begins to destroy the enamel and hard tissues of the tooth.
The child’s immune system has not yet strengthened; his body cannot fully resist bacteria, so he is more vulnerable to carious processes. At the same time, caries develops faster in children than in adults. In this regard, it is necessary to start treating it as early as possible. Otherwise, you will have to treat concomitant diseases.
The main factor that provokes the development of caries is bacteria, but there are other causes of caries.
Causes of caries in children
The factors causing carious lesions are the same in children and adults. But the child’s enamel and immunity are weak, so this disease is diagnosed more often. In general, general and local causes of caries development are distinguished. Among them:
- Poor oral hygiene. Food debris remaining on the teeth and in the interdental spaces is a favorable environment for the proliferation of cariogenic microbes.
- Metabolic disease. Because of this, the enamel may not receive enough nutrients, it becomes weak and cannot cope with the spread of bacteria.
- Genetic abnormalities that cause enamel destruction: ectrodactyly, amelogenesis imperfecta, dysplasia, etc.
- Poor nutrition. Children tend to eat a lot of sweets, and the main source of food for cariogenic microorganisms is carbohydrates. The more a person consumes them, the faster bacteria multiply.
- Disruption of the salivary glands. Saliva washes away germs from the oral cavity and neutralizes their waste products. Due to insufficient salivary fluid production, the number of bacteria in the mouth increases.
- Taking medications that affect the level of calcium and fluoride in the body, which are necessary to strengthen the enamel.
Thus, tooth decay is not only caused by germs and poor hygiene. It can be triggered by other dental pathologies and systemic diseases. Depending on the causes, health status and a number of other factors, caries in a child takes one form or another. There are many varieties of this disease. Let's describe some of them.
Prevention of childhood caries
Even during pregnancy and breastfeeding, mothers should eat a balanced and rational diet. Then monitor your baby’s diet. This is quite significant in shaping the body’s resistance to various diseases, including dental ones.
Brush your baby's teeth twice a day every day. Be sure to sweep with a brush.
Types and forms of caries in children
There are several classifications of carious lesions that help determine the stage of the disease and the method of its treatment. Depending on the form of caries, it can be:
- Acute: develops rapidly - within 14 days, going through almost all stages of the disease.
- Chronic: characterized by slow destruction of enamel and dentin. It often occurs in cases where the cause of the pathology is eliminated, but not its consequences.
- Multiple: appears on different sides of one tooth or several teeth at once.
- Secondary: occurs under a filling.
According to the localization of the pathological process, caries in children is classified into the following types:
- cervical: at or under the gum;
- interdental: between two teeth;
- fissure: in the depressions on the chewing surface.
Dentists often use the classification developed by the American doctor Green Black when diagnosing caries. He divided the forms of carious lesions into classes:
- 1st: localized in fissures;
- 2nd: develops between the molars;
- 3rd: occurs between the incisors;
- 4th: affects the edges of the front teeth;
- 5th: appears in the cervical region;
- 6th: affects the cutting edges of the incisors.
Each class is characterized by corresponding symptoms. Having determined the degree of pathology, the doctor chooses a treatment method.
What it is?
Superficial caries is characterized by the appearance of a yellowish carious spot on the surface of the enamel. A feature of this disease is the absence of damage to the deep layers. This stage is transitional, that is, in the absence of treatment for superficial caries, the infection gradually moves deeper and affects the entire tooth.
Most often, superficial caries is localized in depressions, the so-called fissures. According to statistics, initial carious lesions are observed in 85% of the population, but not everyone knows about it. For the same reason, many patients come to the dentist too late, when the tooth is completely susceptible to deep caries.
What is bottle caries?
There is another type of childhood caries - bottle caries. It occurs in children after the eruption of baby teeth, when the baby is breastfed or bottle-fed. This disease usually occurs as a result of feeding a child before bedtime. While he sleeps, bacteria begin to multiply in his mouth.
Often this form of carious process affects the cervical area. Gradually, caries spreads along the entire circumference of the crown. First, white spots appear, then they darken and destroy dentin. The child constantly cries, especially during meals, sleeps poorly and tries to refuse food. This indicates increased sensitivity of the enamel. Left untreated, it can lead to premature loss of baby teeth.
Causes
Caries in young children is a complex disease that instantly affects several teeth at once. Many kids cannot explain that a baby tooth is bothering them. They are capricious, refuse to eat or chew on one side.
Among the causes of caries of primary teeth in children are:
- influence of dietary carbohydrates;
- genetics;
- immaturity and inferiority of bone tissue due to dental caries in children;
- using cutlery contaminated with bacteria;
- improper use of pacifiers.
According to statistics, the main factor of the disease is insufficient oral hygiene and excessive consumption of sweets. About 7 out of 10 children suffer from this disease. Fermentation acids destroy enamel, creating a favorable environment for pathogenic bacteria. After eating, the pH of saliva drops, and food debris is an excellent environment for the rapid growth of pathogenic organisms.
It is important for parents to remember: they themselves can become a source of caries in the front milk teeth and other rows of teeth. Adults infect their children through kissing, eating food with them from the same dishes using the same cutlery.
Genetic conditioning is also a sufficient factor that provokes caries in a child (since tooth enamel is formed in utero). Smoking and taking medications also interfere with the development of dental elements.
Caries of primary teeth in young children is associated with insufficient mineralization. Teeth erupt “immature”, “ripening” in the oral cavity. This period is considered the most susceptible to caries. The disease is provoked by various diseases, the use of medications, and fluoride in food.
Dmitry Sidorov
Orthopedic dentist
Sleeping with a bottle provokes tooth decay in children under 3 years of age, so you need to remove it from the baby’s mouth while he sleeps. Or simply not teach him to fall asleep with a bottle.
Prolonged contact with sweet liquid leads to damage to the front teeth. Children are not recommended to snack on carbohydrate foods between meals. You cannot eat fruits, cookies, dried fruits, or marshmallows. You can offer sweets after breakfast, making sure to rinse your mouth after eating.
Symptoms of caries in children
Signs of the disease depend on its degree. The following stages of caries are distinguished:
- Initial (white or chalky spot stage). White spots indicate areas of enamel demineralization. They look matte in contrast to the rest of the tooth surface, which is shiny. There is no pain or hypersensitivity at this stage, since the pathological process does not affect dentin.
- Superficial. The lesions acquire a dark tint. The enamel is destroyed more severely, and areas of hard tissue are exposed. At this stage, there is increased sensitivity of the tooth to sweet foods.
- Average. Caries covers all layers of enamel, penetrating deeper into dentin. The tooth begins to react painfully to hot and cold food. The pain disappears after eliminating this irritant. Average caries ends with the formation of a so-called hollow - a brown cavity.
- Deep. The carious lesion affects the dentin to almost its entire depth. A thin wall remains between the pathological cavity and the pulp. There is complete or partial destruction of the dental crown. The disease is accompanied by acute pain, not only due to exposure to irritants, but also at rest. In some cases, pain cannot be relieved with analgesics. The tooth may split into several parts.
To detect caries at the first stage, you need to visit the dentist every six months. At the very beginning, the pathology develops asymptomatically, so only a doctor can identify it. A tooth can be treated at almost any stage of disease progression. If left untreated, there is a risk of tooth loss and the development of other oral diseases.
Superficial caries: main symptoms
At the stage of formation of a chalk spot, which is not yet caries, as a rule, no symptoms occur. Unpleasant sensations begin to appear directly during the development of carious lesions. The main symptoms of superficial caries are:
- the appearance of visible changes in the enamel surface: spots, dots, irregularities and chips;
- the occurrence of sensitivity to temperature changes and to the action of mechanical irritants (for example, a toothbrush, dental floss);
- short-term pain when eating certain types of food (for example, sweet or sour);
- frequent food getting stuck in a certain tooth;
- bleeding, inflammation of the gums.
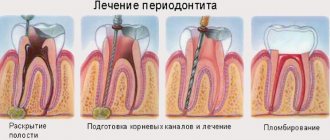
Treatment of caries of primary teeth
Children are usually afraid of dentists, so it is advisable to identify caries at an early stage in order to carry out non-invasive treatment. It is based on remineralization therapy: the enamel is artificially saturated with minerals - fluorine, magnesium and calcium, strengthening it and thereby protecting dentin from destruction. The child is prescribed 10 sessions of 10-15 minutes each, during which the doctor applies a solution with minerals to the tooth.
If caries has reached the middle or deep stage, filling is required. The procedure is carried out according to a standard algorithm. First, the doctor numbs the area of the jaw with an injection, then cleans the cavity of necrotic tissue, treats it with an antiseptic and dries it. Next, a filling is placed on the tooth. Once hardened, the dentist grinds and polishes it.
When treating a child’s teeth, the removal of pathological tissue is carried out manually, so as not to damage the weak enamel and once again not to frighten the little patient with a drill. The hardness of the filling must be lower than the hardness of the enamel, otherwise there is a risk of splitting it or damaging the oral mucosa.
Treatment of caries of molar teeth in children
At the initial stage, the dentist carries out remineralization, and at the middle and deep stage, he places a filling. When treating molars, a filling is selected from a composite material whose hardness is not lower than the hardness of the enamel. In other words, exactly the same filling occurs as during dental treatment for adults.
Baby teeth begin to fall out in a child at the age of 5-6 years, and are completely replaced by molars by the age of 12. Parents should ensure that the first teeth do not fall out prematurely, as the process of replacing them should occur naturally. We list the possible complications of caries in children.
Stages and signs
In the fight against childhood caries, there are several main stages: initial, middle and deep.
Within the initial stage, two main forms of transformation of children's teeth occur: the mottled stage and the superficial stains. From the very beginning, white chalky spots appear on the upper incisors, which do not cause any harm. However, in the future they grow and turn into carious cavities.
Quite often, dental changes begin with abrasions and softening of the enamel. This process can continue for a year. The first forms of caries should be distinguished through examination from diseases such as fluorosis and enamel hypoplasia.
The best method for diagnosing the presence of diseases is ultraviolet stomatoscopy. In the case of healthy teeth, the latter will be illuminated with a light, greenish tint, with hypoplasia - with a dark, green color, and with caries, the tissue will not be visible at all.
Did you know? Scientists note the first widespread prevalence of caries in the 19th century, when the massive “expansion” of sugar began.
In order to moisten a baby tooth, you need to use a special medical solution. All areas that are demineralized due to disease damage should be painted depending on the stage. If therapy is carried out on time, this pathology can be eradicated.
During the middle phase, softened dentin appears. There are no painful forms of manifestation in this disease. Nevertheless, this pathology is very dangerous for a child’s teeth, since it can develop into a deep form in the shortest possible time.
In the case of preparation of deep parts of the cavity, acute pain may occur. This is the main symptom of the moderate form. If there is no reaction to preparation, it is not caries that develops, but pulpitis or periodontitis.
At a deep stage , the main component of dentin is destroyed, as a result of which acute pain occurs and the sensitivity of the teeth greatly increases: both hot and cold. This process often transforms into pulpitis. Treatment of primary teeth in children directly depends on the condition of the pulp itself.
Please note that infection in a carious cavity often causes complications with constant runny nose, sinusitis, otitis media, sore throat, and even with intestinal infection, gastroenteritis, intestinal dysbiosis
Complications of caries in children
Advanced caries in children can cause the following problems:
- Pulpitis is an inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth, which can become purulent. This disease can lead to the development of systemic infection.
- Early loss of baby teeth. A child may develop a malocclusion if their baby teeth fall out before the age of 5. In addition, the permanent tooth in such cases often grows in the wrong direction.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Experiencing discomfort when chewing food, the child swallows it in pieces and increases the load on the stomach.
To prevent these consequences, bring your child to the dentist every 6 months, even if there are no symptoms of tooth decay.