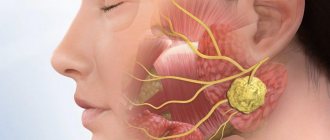
A tooth abscess is an infection caused by the accumulation of purulent mass in the alveoli. The disease is penetrating in nature and can spread to bone tissue. In difficult situations, suppuration even reaches the brain tissue, causing severe pain. Below is information about how dental abscess is treated.
Causes
Penetration of microbes into the tooth through enamel lesions is the main cause of an abscess.
Other provoking factors: violation of the integrity of the tooth, periodontal disease, dental diseases, poor brushing of teeth, damage to the oral mucosa, poor brushing of teeth, concomitant diseases, gingivitis, chronic infectious processes.
Patients with severe forms of diabetes mellitus or tumors are at risk for developing an abscess on the gums. Radiation and chemotherapy impair the functioning of the immune system.
Classification: periodontal tooth abscess, flux extends only to the gums, periapical form.
Abscess after tooth extraction
After an operation to remove a tooth, a purulent abscess may begin in the injured areas of the tissues of the oral cavity, gums and cheeks. An unhealed wound is a favorable environment for the development of bacteria, therefore, in its place or in the depths of a tooth pocket, suppuration quickly forms, which, in the absence of appropriate treatment, can “spill” into the soft tissues.
The cause of an abscess after tooth extraction is most often the patient’s negligent attitude to the doctor’s recommendations. The procedures prescribed by him must be strictly followed, otherwise repeated surgery cannot be avoided.
If you start the process, even strong antibiotics will not help. Therapeutic measures aimed at removing purulent formations consist of opening and cleansing the abscess cavity, followed by anti-inflammatory therapy.
Symptoms
The abscess always spreads to only one tooth. Infection of adjacent areas is possible if the disease is started or self-medicated. The following signs indicate the formation of an abscess:
- Pain while chewing food.
- Migraine.
- The tooth begins to hurt when pressure is applied.
- Increase in body temperature.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Unpleasant aroma.
- Enlargement of the gums in the affected area. In the absence of necessary therapy, a small abscess with a light tip may form.
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
- Throbbing pain is transmitted to the gums. Unpleasant sensations subside for a while and recur with increased intensity.
Patients often request tooth extraction due to severe pain . In some cases, swelling on the face forms and nervousness increases. A person may complain of poor sleep, a feeling of discomfort when consuming cold or hot food.
Harmful bacteria destroy dental nerves. After this, the patient stops feeling throbbing pain. This condition does not mean that the disease disappeared on its own - without medications and a dentist. The pathology progresses, spreading deeper to the lower jaw bone.
As the disease spreads, intoxication, provoked by microbial waste products, increases, the patient begins to feel sick, chills and weakness appear.
Types and symptoms of the disease
Dental abscess is divided into three types depending on location. There are gingival, periodontal and periapical forms. They are characterized by a complex of specific symptoms, if detected, you should immediately seek medical help. You can clearly see the symptoms in the photo accompanying the article. The main features are:
- loss of natural pigmentation of the tooth (if the case is advanced);
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- smell of rot from the mouth;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- swelling, redness, swelling of the gums near the affected tooth;
- sleep and appetite disorders;
- fever, fever, chills;
- increased sensitivity of the diseased tooth to hot and cold;
- acute pain when chewing food;
- a constant aching pain is felt in the affected area.
In some cases, the damage extends only to the soft tissue of the gums. In this case, the bone and periodontal ligament are not affected. Then the doctor will diagnose a “gingival abscess,” also called gumboil. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply, sometimes suddenly. The main characteristic sign is an edematous, swollen cheek on the affected side.
Periapical
A periapical tooth abscess develops directly in its pulp, then spreads through the alveolar bone to nearby gum tissue. It has pronounced symptoms - the patient feels severe pain, comparable to electric shock, when the affected tooth is exposed to cold or hot. An abscess can be eliminated either through an incision in the damaged tissue or through an open cavity in the diseased tooth. If the pathology is advanced, then the infected dental element is removed.
Periodontal
Sometimes the inflammatory process begins in the periodontal pocket.
Over time, inflammation spreads towards the roots. With this form, the patient notes that the tooth located in the lesion becomes unusually mobile, pus is released, there is constant dull pain, general malaise, fever, chills, and bad odor from the mouth. With mechanical impact on the diseased area, the pain intensifies. With a periodontal abscess, it is important to open the abscess in time. If this can be done before the pulp becomes infected, then the tooth will not have to be removed. When an abscess is identified, the dentist will develop a treatment strategy based on the form of the disease, the degree of its development and the causes that provoked the pathology. The inflammatory process itself does not go away, even if the abscess has opened without outside intervention - the focus of the disease remains. You cannot limit yourself to symptomatic treatment. It is necessary to identify the source of inflammation and remove it. It should be remembered that in advanced and severe forms it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
Therapeutic methods
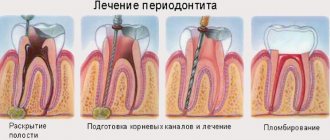
The dentist will perform a drainage procedure, after which he will fill the damaged tooth and install a crown. The doctor drills out the diseased tooth, then cleans the cavity of pus and treats it with an antiseptic. If the case is advanced, then the tooth is removed, and the drainage procedure is carried out through the alveolus. The doctor may also prescribe laser treatment, rinsing and physical therapy.
Antibiotics and other drugs
He will take into account the patient’s age, the shape and degree of development of the abscess, as well as the individual characteristics of the body. Antibiotics may be given as tablets or injections. The following drugs show the greatest effectiveness:
Surgical intervention
Surgery is a last resort.
This type of treatment is resorted to only in cases where the development of the disease threatens the health and life of the patient, or conservative therapy does not produce the expected effect. Emergency surgery is performed when pus spreads to the neck, jaw or brain of the patient. The intervention makes it possible to avoid death, but the disease itself does not eliminate it. In such advanced cases, a biopsy is often performed - this way the cause of the development of a tooth abscess can be accurately determined and an effective treatment strategy can be selected. Another type of surgical intervention indicated for tooth abscess is removal of the affected element. Extraction is carried out after a comprehensive examination, if diagnostics have shown the impossibility of saving the tooth - for example, the pulp is severely infected. Also, in case of an abscess, the abscess is often opened and the cavity is subsequently cleansed of pus.
Read also: How to kill a nerve in a tooth yourself
How to reduce pain?
Taking painkillers in itself is not part of the treatment of the inflammatory process, but it helps to alleviate the patient’s condition and relieve the most unpleasant symptom – pain. Such drugs are also indicated after surgery. It must be remembered that Aspirin should not be taken during the postoperative period. In addition, it is unacceptable to take analgesics before visiting a doctor; the drug will distort the clinical picture. Dentists recommend:
- Ibuprofen. The daily dose is 3 – 4 tablets per day. Tablet form should not be taken by children under six years of age; suppositories and suspension should not be taken by infants under 3 months.
- Analgin. 0.5 - 2 tablets at a time, but no more than 8 pieces during the day. You can give it to a child on the recommendation of a doctor - the solution is used in the first year of life, suppositories - from 12 months, tablets - for children aged 10 years and older.
- Paracetamol. An adult or teenager over 12 years of age can take up to 8 tablets (500 mg) or 20 tablets (200 mg) per day. Paracetamol for children is produced for the treatment of children; it can be given from 2 years of age.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine cannot replace drug treatment or surgery. Homemade recipes can be used to relieve symptoms and speed up the healing process. It is impossible to apply heat to the affected side of the face - this will aggravate the course of the disease. Cold will help relieve swelling and pain. Also recommended are rinsing the mouth with a solution of soda and salt, decoctions of medicinal herbs, and propolis. Compresses made from grated onions or potatoes help well, you can also apply aloe leaves.
First aid
A dental abscess requires special attention if caries is present. It is this disorder that allows the infection to spread to the pulp.
If you cannot visit a doctor, you can use the following means:
- You can apply a cotton swab soaked in oil with clove extract to the sore tooth, hold it for 20 minutes, and rinse your mouth with water. This remedy eliminates infection, relieves pain, and avoids various complications.
- Several clove buds should be chewed for 2-3 minutes 4-5 times a day.
- A peeled geranium leaf should be crushed, applied to a sore tooth, and removed after 5 minutes.
- Apply a little ginger to the gum for 15 minutes. This is a wonderful antiseptic.
To prevent an abscess from developing, you need to regularly care for your oral cavity. Contact a specialist at the first signs of minor chips on your teeth.
Diagnosis of periodontal abscess
Diagnosis of periodontal abscess includes anamnesis, clinical examination, dental radiography, as well as additional laboratory and instrumental research techniques. During examination, a dental therapist or periodontist reveals the presence of painful bulging of the gums in the area of certain teeth against the background of swollen, hyperemic mucosa. In case of periodontal abscess, the dental-epithelial junction is disrupted, the transitional fold is smoothed. Teeth are mobile (grade 2-3). Horizontal percussion is positive. With periodontal abscess, the depth of periodontal pockets varies from 3 mm to 6 mm and above, the contents are granulation tissue and purulent discharge. There is also displacement of the teeth, which leads to the development of traumatic occlusion.
X-ray examination of periodontal abscess reveals widening of the periodontal fissure, destruction of the cortical plate with uneven vertical resorption of the spongy substance of the interdental septa, the formation of intra-alveolar pockets and diffuse osteoporosis of the remaining spongy substance. The hygiene index of the proximal surfaces of teeth during the formation of periodontal abscess is unsatisfactory. The papillary-marginal-alveolar index (PMA) exceeds 50%, which indicates a pronounced inflammatory process that involves the interdental papillae, marginal margin and alveolar part of the gums. The gingival sulcus bleeding index (SBI) with the development of periodontal abscess sharply exceeds the norm.
In blood tests in patients with periodontal abscess, changes appear that are characteristic of a nonspecific inflammatory process. There is an increase in leukocytes, an increase in ESR, and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. Using molecular genetic research (quantitative PCR), it is possible to identify the qualitative and quantitative composition of the anaerobic microflora of the periodontal pocket. The results of the analysis indicate the prevalence in periodontal abscess among other periodontal pathogens of such bacteria as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Bacteroides forsythus, the relative content of which in the total bacterial mass steadily increases by more than 100 times.
With the help of cytological examination, along with a variety of microflora, a large number of destroyed neutrophilic granulocytes are detected. The phenomena of phagocytosis during the formation of periodontal abscess are not pronounced. The study of saliva by chemiluminescence confirms the activation of lipid peroxidation processes, which indicates an exacerbation of inflammation. Periodontal abscess must be differentiated from acute periodontitis or exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, suppuration of the jaw cyst, periostitis, osteomyelitis. Consultation with a dental surgeon is necessary.
Treatment
Treatment of a tooth abscess is fraught with danger, which is why no one does it. If you try to open an abscess, you can cause more infection and injure the nerve. Therapy is selected individually , its main task is to protect the tooth and prevent complications. For this reason, they first get rid of infection, localized inflammation and intoxication. It is better to treat with medications. Therapy is carried out according to the selected treatment.
Surgery involves opening the abscess and cleaning out its cavity. The gums in the area of the abscess are opened, the inflamed tissue is removed, and disinfected. Laser therapy treats dental abscess and is used for drainage. This technology is painless and healing is quick.
Canal drainage is used if there is a chance to remove the resulting pus and not cut the gum. After cleaning, an antiseptic mixture is used. Then it is often necessary to choose a crown for the tooth. If the drainage does not bring the desired results, it will need to be removed.
After this, secondary cleaning of the wound from inflamed tissue is carried out. Treatment does not end with a visit to the dentist. The doctor determines the period during which the patient will have to carefully monitor personal hygiene. Medicines that are good at preventing the spread of infection are Metronidazole, Amoxicillin, Trimox . At the same time, use painkillers.
After completing the course, it is recommended to choose vitamins that stimulate the protective functions of the immune system. Teeth should be brushed twice a day. From traditional medicine, decoctions based on oak, sage, calamus root, and chamomile .
The salt mixture or Furacilin also has disinfecting properties. These products are good for rinsing your mouth. To recover faster, the procedure should be performed every 2 hours.
With complex treatment, the symptoms will be eliminated on the 2nd day, and the consequences of the abscess will be completely eliminated in a week.
Inflammation that occurs in any part of the human body, including in the oral cavity, is always a painful, unpleasant and completely unexpected process. After reading this article, you will not only be able to determine if you have an abscess based on its characteristic signs, but you will also be able to understand what types of dental abscesses there are, what complications may arise, and how to treat it at the Alfa Medica clinic in St. Petersburg.
What is a dental abscess?
A dental abscess is an acute inflammatory process in the root area of a tooth, in other words, a small accumulation of pus that causes acute pain. The causes of inflammation can be both dental diseases and damage to the soft tissues and mucous membranes of the oral cavity. An unscrupulous dentist using unsterile instruments can cause an infection. And even boils that appear in the mouth area can ultimately lead to an abscess, not to mention failure to comply with the rules of oral hygiene.
As a rule, an abscess is characterized by sharp throbbing pain in the area of one specific tooth. In this case, the process of chewing food that gets on this tooth becomes simply impossible. After a short period of time, the pain intensifies, and a very painful compaction forms on the soft tissues around the tooth. If you do not consult a doctor in time, the development of the abscess will progress, which will negatively affect the general condition of the person. We list the risk factors leading to the occurrence of the disease:
What are the main reasons for the development of a tooth abscess?
- Various types of untreated dental diseases - advanced caries, pulpitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, granuloma, dental cyst, etc.
- Mechanical injuries leading to tooth chipping or fracture
- Infection transmitted by the bloodstream during common infectious diseases (sore throat, flu, etc.)
- Damage to the skin or oral mucosa
- Formation of boils on the skin in the jaw area
- Infection through injections (for example, during pain relief for dental procedures)
These factors cause a violation of the integrity of tooth enamel, opening the way for bacteria to reach the dental pulp and the development of inflammatory processes. If the inflammatory process is not stopped in time, the infection can subsequently spread to the periodontitis tissues holding the tooth in the alveolus and to the jaw bone, which will cause even more serious consequences - for example, oral phlegmon.
What are the main symptoms of a tooth abscess?
- Prolonged, severe, sharp, aching or throbbing pain in a tooth
- Pain when pressing on a tooth, particularly when chewing
- Increased tooth sensitivity to temperature stimuli (hot and cold)
- Regular feeling of bitterness in the mouth
- Constant general malaise and discomfort
- Sleep disturbance, appetite
- Temperature increase
- Formation of an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth
- Noticeable enlargement of cervical lymph nodes
- Redness and swelling of the gums
- Formation of an open ulcer with purulent discharge on the surface of the gum
- Edema and swelling of the soft tissues of the face in the jaw area
If the affected tooth root dies as a result of the development of the inflammatory process, the pain in the tooth and some other symptoms may stop. However, this is only a temporary external improvement. At the same time, the infection continues to actively develop, affecting ever deeper tissues of the tooth and jawbone.
How to treat a tooth abscess?
A tooth abscess is diagnosed quite simply. Suspicion of a tooth abscess may arise already during the first examination of the patient based on external symptoms: pain in the tooth (increased by tapping), redness and swelling of the gums, ulcers on the gums, discharge of pus, etc. If necessary, an x-ray can be taken, which will finally confirm the diagnosis or identify some other disease with similar symptoms. Treatment of a tooth abscess is aimed primarily at eliminating the source of infection in order to save the tooth and prevent further complications.
Often, there is a need to drain the abscess, for which a root canal procedure is performed, with the help of which, in addition to draining the abscess, necrotic root tissue is also removed. After this, the tooth is filled and, if necessary, an artificial tooth crown is installed. In some cases, when the infection has developed quite severely, the risk of complications is very high, and saving the tooth turns out to be problematic, the tooth that is the source of the infection may be removed. In order to suppress the infection, the patient may be prescribed a course of antibiotics during treatment of a tooth abscess. To relieve pain caused by an abscess and reduce discomfort, dentists recommend regular rinsing of the mouth with a warm water-salt solution or taking analgesics available in pharmacies without a prescription.
What is the prevention of tooth abscess?
Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. Following simple rules will help you avoid encountering such an unpleasant phenomenon in the future:
- It is always necessary, regardless of the circumstances, to maintain oral hygiene, brushing your teeth with fluoride-containing toothpastes at least twice a day;
- visit the dentist at least once every six months for preventive examinations;
- regularly clean your teeth from plaque and tartar;
- promptly repair cracks and chips of enamel;
- eat healthy foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
Complications
Advanced disease leads not only to tooth decay. The accumulation of infection over time will lead to the following problems:
- The inflammation deepens and spreads to bone tissue . The infection can spread along the nerve fibers of the face and spread to the whole body.
- Pneumonia.
- Blood poisoning . This disease can develop as a result of pathogenic microorganisms entering the blood. This often leads to septic shock or death of the patient.
- Formation of a fistula in the oral cavity - suppuration will be continuous, which will fundamentally undermine the immune system and provoke an infectious complication.
- Phlegmon . Purulent inflammation spreads over a large area, swelling, intoxication occurs, and problems with swallowing function and breathing appear.
- Meningitis . Inflammation often occurs in the brain due to a dental abscess. In difficult situations, death is possible.
- Bone marrow infection.
- Meningitis develops if the illness continues for too long.
- Teeth rarely fall out , only in the most advanced cases. Sepsis, heart disease, and diabetes may develop.
- Brain abscess . The abscess can expand and reach the brain. Patients experience severe pain and frequent epileptic seizures.
- The acute form affects bone and soft tissue . This threatens brain inflammation and osteomyelitis.
If you notice signs of a tooth abscess, you should immediately contact an orthodontist. The complication is developing rapidly, delay is unacceptable.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Normally, the microflora of the oral cavity is constantly inhabited by a mass of bacteria and microbes that contribute to the smooth operation of body functions.
However, under the influence of provoking factors, a colony of pathogenic microorganisms begins to actively multiply.
Penetrating into the periodontal pockets of the gums, harmful bacteria cause inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane, up to the formation of a purulent abscess.
The reasons that provoke the formation of an abscess in the soft tissues of the periodontium are of two types - exogenous (external) and endogenous (internal).
Exogenous factors:
- Inflammation of the gums due to dental diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis).
- Mechanical damage - trauma, chemical and thermal burns of the mucous membrane.
- Doctors' mistakes - incorrectly selected or installed prosthesis, braces, overhanging fillings, malocclusion.
- Often an abscess appears against the background of a complex tooth extraction, especially the 8th molar.
- Entry of a foreign body into the gum pocket (food particles, dental fragments, etc.).
- Hypothermia or overheating of the body.
Endogenous factors:
- Tendency to frequent infectious diseases.
- Chronic dental diseases, for example, advanced caries, moderate or severe stage of periodontitis.
- Disturbances due to hormonal imbalance or metabolism.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system, immunodeficiency state of any etiology.
- Deep location of dental plaque.
- Insufficient outflow of purulent exudate.
- Bruxism is grinding of teeth during sleep, causing teeth to become loose.
Traditional medicine
Many doctors allow treatment of acute purulent forms of tooth abscess in the home. Using traditional medicine recipes helps eliminate inflammation. This measure is temporary; you will still have to make an appointment with a doctor.
Constant pain and swelling can be eliminated with an ice compress . It should be applied to the cheek or jaw - in the area of the inflamed area. It is strictly forbidden to use a heating pad or hot compresses, as this will only spread the infection further.
Anesthetics help relieve pain: metamizole sodium, Nise, lidocaine mixture.
The general condition is improved by antipyretics and drugs to reduce swelling. For rinsing, you can use a solution of soda and salt, aloe juice, decoctions of propolis, eucalyptus . For compresses, use grated potatoes, apply it to the sore spot, and tie this mass for 3-4 minutes. An aloe dressing is also effective. You need to apply it directly to the source of infection. An onion compress prevents the development of an abscess. The plant needs to be grated or finely chopped and applied to the sore spot.
You cannot open the flux without the help of a specialist or try to treat a dental abscess on your own.
Submucosal abscess
It occurs as a result of untreated subperiosteal abscess, when the periosteum separates from the bone and undergoes necrosis. Pus spreads under the mucous membrane of the gums into the vestibule of the mouth.
Clinical symptoms
The mucous membrane in the area of the alveolar protrusion is blown out, becomes thinner, takes on a bright color, and sometimes accumulated pus is visible through it. Spontaneous pain subsides, leaving only a slight pressing pain. The temperature disappears or only slightly increases, the inflammatory effusion in the surrounding tissues also disappears, and facial swelling decreases.
Treatment
There is no need for wound drainage during surgery. At the same time or after eliminating the acute inflammatory symptoms, the cause of the infection is removed, as in the treatment of a subperiosteal abscess. If the cause remains unresolved, a fistula remains on the mucous membrane, which will temporarily close spontaneously.
Prevention
- Visit the dentist regularly - at least once every six months.
- Timely sanitization of the oral cavity and treatment of gum diseases.
- Use halogen paste after meals or at least twice a day.
- Use dental floss regularly.
- Remove plaque from teeth.
- If enamel defects are detected, you need to contact an orthodontist.
Causes of pus accumulation
A dental abscess does not appear by chance. The causes of occurrence are a complex issue that experts constantly face. They study them carefully, helping patients receive comprehensive information. It is necessary to study the basic principles of prevention to get rid of the consequences and discomfort.
- Advanced dental diseases;
- Mechanical damage to the gums and oral cavity;
- Boils on the jaws;
- Infection due to injections.
These cases suggest that you should take your own gums seriously. An abscess may appear unexpectedly, and its treatment will require a lot of time and patience. The pain becomes insignificant, but this does not mean that the process has stopped. It is most practical to think about prevention, rather than bring your own condition to a critical point.
Types of tooth abscess - video
Treatment of a tooth abscess is considered difficult and painful. To avoid having to use therapeutic measures, it is better to follow prevention tips. The main task is to constantly maintain oral hygiene.
The main cause of suppuration is non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. Treatment of dental abscess should only be carried out by a qualified professional. Rarely are patients allowed therapy at home. The most effective is a comprehensive treatment method.
Periodontal abscess
Periodontal abscess is a complication that occurs during an exacerbation of the inflammatory-destructive process in periodontal tissues, characterized by a limited accumulation of purulent exudate. The formation of periodontal abscesses is promoted by deep pathological pockets and hard subgingival deposits. In the vast majority of cases, acute periodontal abscesses occur. Cold (chronic) periodontal abscesses are extremely rare. Frequent relapses of exacerbations of chronic periodontitis are observed in 30% of periodontal patients. Both men and women suffer equally. The peak incidence occurs in the autumn-spring period.
Symptoms and pathogenesis
Through damaged enamel or gum tissue, pathogenic microbes penetrate into the alveolar process. They multiply in the soft pulp of the tooth, stimulating the formation of pus. If there is no way out for it, the inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissues - periodontitis, jaw bones, neighboring teeth.
Manifestations of a developing abscess:
- Pain when pressing on a tooth, most often occurs during eating;
- Swelling of gum tissue, cheeks;
- Throbbing pain when not eating;
- The appearance of a hyperemic compaction in the affected area;
- Increased temperature sensitivity;
- The appearance of bad breath;
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- Hyperthermia, feverish state;
- Poor general health, restless sleep;
- Upon visual examination, you can see an open wound with purulent discharge.
The onset of the disease is associated with the appearance of severe pain. As the pain intensifies, swelling and hyperemia of the gums develop, and then the swelling spreads to the tissues of the cheek.
Treatment of diseases by dentists
Tooth abscess shows clear symptoms. If a person is faced with this dental disease, he needs to urgently go to the clinic. The rapid development of the disease leads to a sharp deterioration of the situation, so the smile can be saved only in the early stages. What treatment methods do doctors use?
- Drug treatment;
- Drainage;
- Root canal therapy;
- Removal of a tooth.
Medicines, in particular dental drops, are designed to combat symptoms, so they are not considered as the basis of a course of treatment. Medical practice is usually based on drainage, but widespread delaying usually leads to categorical removal. Such troubles remain a problem, so they should be foreseen.