A condition in which the foot flattens and rolls inward is called hallux valgus.
This pathology leads to the fact that the heel begins to rest on the floor only with its inner edge. The deformity can be valgus or varus. In the latter case, the foot falls not inward, but outward from the conditional center line of the body. Hallux valgus is often accompanied by a deformity of the big toe.
Description of the pathology
Hallux valgus is a specific disease that results in a violation of the correct position of the feet and toes. The main symptom of the disease is the deviation of the foot from the central axis of the body, as well as a decrease in its height. Due to these changes, the foot and the phalanx of the first toe take an incorrect position . The foot turns inward, and the first phalanx of the big toe turns outward. The reason for this is an increase in the angle between the metatarsal bones.
In the mid-19th century, this pathology was associated with wearing uncomfortable shoes. At the beginning of the 20th century, the disease was described by the Russian scientist Albrecht. He associated it with gout.
It is worth noting that hallux valgus deformity of the first toe appears mainly in women whose age exceeds 30 years. At the same time, doctors found that the pathology is more common among European and American women. It is much less common in Asian and African women. Most likely, this geographical division is due to the characteristics of the shoes worn.
The older a person gets, the more likely they are to develop hallux valgus.
Many people consider this disease to be purely cosmetic. But in reality this is not the case. Pathology over time causes pathological changes in all elements of the foot. Ligaments and tendons are damaged, all bones and joints are deformed. All this leads to the development of the following serious diseases:
- Deforming arthrosis.
- Chronic bursitis.
- Exostosis of various origins.
- Combined flatfoot.
- Varus displacement of the metatarsal bones.
For this reason, treatment for hallux valgus should begin as early as possible.
How does valgus develop?
Problems are often caused by wearing high-heeled shoes. They shift the entire body weight to the forefoot, increasing pressure on the joints. The front arch of the foot (transverse arch) falls. The ends of the toes lie on the ground. The fingers have a skewed outer position. The stretching of the tendons causes the thumb to move out of the joint - just like a bow bent by a band - inwards towards the other fingers.
The adjacent fingers are forced out by the thumb, which rushes inward and then becomes deformed as a result of valgus. The big toe tendon lies at an angle to the metatarsophalangeal joint. The sesamoid bones, which control the tendons of the toes, are not symmetrically placed with the big toe, but are noticeably shifted. The toe rotates from the metaartophalangeal joint, just as the bow is increasingly tensed by the string.
The deformity is caused by signs of wear and tear in the hallux joint: changes in the position of the big toe can lead to arthritis and hallux rigidus. Hallux valgus is often accompanied by painful bursitis and arthritis. A hump appears on the inside of the foot, it protrudes strongly at the metaartophalangeal joint.
Causes of deformation
This pathology can be congenital or acquired. In some cases, the parents themselves are to blame for the appearance of hallux valgus in children. They strive to teach the child to walk as quickly as possible, so they put him on his feet. In this case, the baby’s musculoskeletal system cannot withstand the load, resulting in significant deformation.
Congenital causes of deformity include genetic predisposition and disorders of intrauterine development. In both cases, the pathology is diagnosed in children in the first months of life. The pathology cannot be eliminated without surgery, so doctors perform surgical correction as soon as possible.
Acquired valgus of the legs appears against the background of insufficient development of tendons . The causes of the pathology can be:
- Excess weight.
- Scoliosis.
- Past polio.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Connective tissue dysplasia.
- Long-term wearing of a cast after an ankle injury.
- Diabetes.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Various infectious and viral diseases.
- Congenital hip dislocation.
- Excessive leg tension.
- Osteoporosis.
- Hypermobility of joints.
- Gout.
- Inflammation of the joints due to psoriasis.
- Arthritis.
- Flat feet.
- Multiple sclerosis.
Very often the cause of foot deformation is poor shoes. When buying shoes, adults do not pay attention to how the heel is fixed and what rigidity it has.
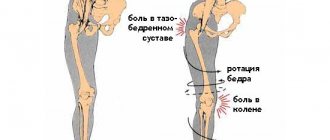
Correction of valgus deformity of the lower extremities and legs
True X-shaped curvature (valgus deformity) is manifested by the presence of a distance between the feet with the knees tightly closed in a free stance.
Classification of leg shape (Artemyev A.A., 2001):
- Perfect legs;
- True O-shaped curvature (varus deformity);
- False curvature;
- True X-shaped curvature (valgus deformity);
Below is a video on how to fix crooked legs
Correction of X-shaped legs. Part 1. Dangers and consequences
Correction of X-shaped legs. Part 2. At what age should surgery be performed?
What is X-shaped curvature
This classification allows you to independently determine the shape of your legs and make a decision about correcting the curvature.
The “ideal” shape of the legs involves the closure of the knees, calves and feet and the presence of three spaces between them.
True X-shaped curvature is manifested by the presence of a distance between the feet with the knees tightly closed in a free stance. Conventionally, we can assume that an axis deviation of 10-15° is a cosmetic problem, and more than 15° is an orthopedic problem. With pronounced curvature, we are already talking about valgus deformity.
How common are X legs?
The shape of the legs is an ethnic characteristic. X-shaped curvature of the legs is more common among residents of European countries. Owners of such legs seek surgical correction approximately 10-15 times less frequently than those with O-shaped curvature of the legs. It is difficult to say how often X-legs occur among all people, but men resort to the services of surgeons approximately 2-3 times more often than women.
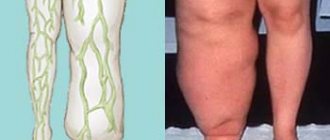
Manifestations and consequences of valgus curvature of the lower extremities
An interesting observation is noteworthy: in trousers, legs with slight valgus deformity appear straight. Straight legs, especially in thin people, look a little like wheels in trousers. With severe hallux valgus, X-shaped legs, on the contrary, are not only very noticeable in trousers, but even make it difficult to wear clothes. A very common reason for seeking surgical help, especially among men, is problems in choosing fashionable clothing.
Valgus deformity upon in-depth examination is accompanied by underdevelopment of the condyles of the femur or tibia, as well as flat feet. With age, these features can lead to the development and progression of various pathological conditions, and therefore require as early correction as possible.
Three options for correcting the shape of the legs
You can be sure that we will make perfect legs in almost any case (see photo.). The point is how long this process will take. We offer three ways to correct leg varus deformity:
- Ilizarov correction (see details below);
- Express method;
- Improved express method.
If you think you have false curvature, look here.
Features of correction of X-shaped legs
The principle of surgical treatment is the same as when correcting O-shaped legs - only the direction of displacement is exactly the opposite.
Appearance of a 38-year-old man with severe hallux valgus before and after correction.
During the correction process, the legs can be lengthened in order to improve appearance.
Appearance and radiographs of a 56-year-old man with X-shaped legs before treatment and after correction (leg shape correction + lengthening 4 cm).
Surgical correction of the lower leg is technically simpler and has much fewer complications than surgery on the hip. However, with severe valgus deformity, it is necessary to correct the specific segment that is curved.
Radiographs of a man with valgus post-traumatic deformity of the right hip before surgery, during correction with the Ilizarov apparatus and after treatment
Considering that the principle of correction of X-shaped curvature of the legs is the same as for O-shaped curvature, the main features of the operation and postoperative management, as well as the cost of treatment however, in the treatment of both types of deformity.
Additional information and frequently asked questions
At the decision-making stage and during the correction process, additional questions often arise. The answers to them are on a separate page. Here you can find out what kind of examination you need to undergo before the operation, how to take photos correctly for an absentee consultation, and much more.
Hallux valgus is often understood as a deformity of the foot, including the first (big) toe (hallux valgus). Both valgus deviation of 1 toe and deformation (valgus and varus) of the knee joints are phenomena of the same order. They refer to static deformations, and the reason lies in the peculiarities of the development of connective tissue. This cannot be considered a pathology. In many cases these are developmental features. However, with age, such deformities can lead to serious problems. If one of these diseases is detected, additional examination is necessary to identify other deformities.
Such static deformities can be detected in early childhood. The child must undergo additional examination to exclude any pathology. If you suspect a child, you should see an orthopedist at least once a year.
Trying to cure severe deformities with exercise is a misconception. If there is severe deformity, other treatment options, including surgery, should be considered.
If you want to study the problem in more detail, we recommend that you refer to this book:
If you are interested in the problem under consideration and would like to receive additional information or professional advice, call
Classification of foot valgus
There are many types of bow legs. All of them are directly dependent on the reasons that caused them. Doctors distinguish the following types of valgus:
- Static. Curvature of the legs appears against the background of curvature of posture.
- Structural. Appears with a pathological location of the talus. From birth she occupies a vertical position.
- Compensatory. The pathology occurs due to a shortened Achilles tendon and an oblique position of the ankle.
- Paralytic. This is a consequence of encephalitis or polio.
- Spastic. Appears with muscle spasms.
- Hypercorrectional. This type of valgus appears due to a mistake by doctors who incorrectly treated clubfoot.
- Rachitic. As the name implies, curvature appears with rickets.
- Traumatic. This is the result of injuries of various types.
There are several degrees of foot deformation. All of them have their own clinical manifestations and characteristics. Taking them into account, doctors distinguish 4 degrees of pathology:
- The first degree is diagnosed when there are changes in the joint at the site of deformation. This leads to mobility of the sesamoid ligament, which provokes subluxation of the foot and deviation of the first phalanx by 15°.
- In the second degree, further displacement of the tendons occurs, while they pull along all the joints of the first finger. The angle of deflection of the latter reaches 20°.
- The third degree is characterized by the vulnerability of the ligamentous apparatus and bones of the foot. They can no longer cope with the loads placed on them. Finger deflection reaches 30°.
- The fourth degree is the final stage of deformation. It marks the development of severe consequences.
Each stage of the disease has its own symptoms. At first they are barely noticeable, but gradually become more serious and begin to cause significant inconvenience to the patient.
Symptoms of the disease
Valgus of the foot manifests itself with unpleasant symptoms. In the initial stages of the disease, the patient experiences constant discomfort and cannot get rid of it. Later, he encounters pain, which in severe cases becomes permanent.
Most patients also experience the following symptoms:
- Pain when wearing any shoes.
- The length of the foot changes. This makes choosing shoes very difficult.
- The insteps of my feet hurt a lot at the end of the day.
- The first and second toes are severely deformed.
- Painful calluses may appear on the first finger.
- Signs of circulatory problems appear.
- Arthrosis develops.
- Corns appear in the heel area.
It is worth noting that such symptoms are similar to many other diseases. For this reason, if you experience pain or strange bumps on your fingers, you should not self-medicate, but rather consult a doctor. The sooner a correct diagnosis is made, the better.
Signs
It is impossible to confuse hallux valgus with other orthopedic pathologies. The disease is characterized by an X-shaped curvature of the big toe and a decrease in the height of the longitudinal arch. The metatarsus “spreads out”, the range of motion of the ligaments and tendons increases. Hallux valgus pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a characteristic bone develops in the area of the thumb;
- the affected joint turns red, swells, and hurts;
- the position and shape of other toes changes;
- corns and calluses appear;
- pain, heaviness in the legs, and fatigue are observed.
Establishing diagnosis
Detection of hallux valgus is carried out in several stages. First, the doctor collects anamnesis. He talks with the patient, identifies subjective symptoms and possible causes of pain. Then the doctor conducts an external examination. And first of all, he evaluates the patient’s gait. It can be used to determine the degree of violations. The position of the big toe and its range of motion in the joint must be studied.
As a rule, after this the doctor can already make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm it, the following studies are carried out:
- Computer podometry. This procedure allows you to determine the distribution of load on the bones of the foot and identify pathological changes even in cases where there are no obvious clinical manifestations of pathology.
- Radiography. The photographs clearly show a decrease in the arch and a violation of the relative position of the parts of the foot.
- Ultrasound. This type of research is rarely used. Ultrasound is mainly used in cases where it is necessary to study the condition of the ligaments and muscles of the lower leg.
All these research methods make it possible to exclude various neoplasms, inflammatory processes in the periosteum and foci of necrosis.
The information obtained during diagnosis allows the orthopedic traumatologist to determine the optimal treatment for hallux valgus in adults.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, the following instrumental studies are carried out:
- radiography of the lower extremities in three projections, which will display the position of the feet relative to each other;
- computer plantography, which is carried out on a special platform, leaving a foot print on it; the method allows you to assess the condition of the feet and the distribution of the load on them;
- computer podometry, which helps to identify primary changes in the structure of the foot, to prevent the development of the disease;
- MRI or CT to assess the condition of soft tissues.
During the initial examination, the orthopedist determines the mobility of the joint and the mobility of adjacent fingers. A consultation with a neurologist is also necessary to identify nerve damage involved in the pathological process. The disease is differentiated from arthritis, gout, deforming osteoarthritis.
Methods of treating the disease
Foot and big toe valgus can be treated without surgery. But only in the initial stages of the disease. Advanced forms of planovalgus deformity have to be treated surgically.
Conservative therapy
Such treatment is possible only in the initial stages of the disease. It is based on reducing the load on the foot. This can be achieved in different ways. The main one is choosing the right shoes. It should have a wide toe.
Doctors also prescribe patients the use of special orthopedic devices:
- Finger pads. They reduce pressure on the joint capsule.
- Spacer products that allow you to redistribute the load on the foot.
- Arch supports for interdigital ridges and finger correctors. They stop further deformation.
Orthopedic products quite effectively eliminate the intensity of pain, but they are not able to completely eliminate the pain syndrome. Therefore, in the process of therapeutic treatment, doctors resort to NSAIDs: Diclofenac, Ibuprofen.
If non-steroidal drugs do not help, then corticosteroid injections are prescribed: Diprospan, Hydrocortisone. These drugs are very effective in treating pain.
Also, with conservative treatment, patients are prescribed therapeutic massage and special gymnastics. The exercises in the latter are simple and are aimed primarily at eliminating deviation of the thumb.
Surgical intervention
Doctors know more than 100 methods of surgical elimination of hallux valgus. However, in practice only a few of them are used. Methods used include:
- Exostectomy. It involves excision of part of the metatarsal bone.
- Osteotomy. Surgeons remove part of the phalanx.
- Arthrodesis. During the operation, doctors artificially block the mobility of the first finger.
- Reconstruction of the bones of the thumb.
- Resection arthroplasty.
- Installation of an endoprosthesis instead of the affected joint.
It should be taken into account that in some patients the bunion on the big toe may reappear after surgery. Therefore, it is very important that patients follow the rules of postoperative rehabilitation. They are simple:
- You can move your foot only on the second day after surgery.
- You can get up and walk only on day 10. When walking, be sure to use a stick or crutches.
- Full load on the foot can be given only after 30 days.
- You can return to sports after 6 months.
- Wearing shoes with heels is allowed 1 year after surgical treatment.
During rehabilitation, it is recommended to undergo shock wave therapy. It will improve blood circulation, relieve swelling and reduce the intensity of pain after surgery.
Preventive measures
The main rule of prevention is regular observation by an orthopedist-traumatologist. The doctor will determine the development of pathology at an early stage and will be able to prevent its further development.
The second rule is an important rule of prevention - wearing comfortable shoes that eliminate the possibility of foot deformation. It is best to buy such shoes in specialized institutions.
It will also not be superfluous to plan your working day. This is especially important for people who, due to the nature of their work, have to spend a lot of time on their feet. Such patients should learn to set aside time in their work schedule to periodically relax their legs.
And most importantly, at the first signs of curvature of the feet, you should immediately contact qualified specialists. Self-treatment can cause very unpleasant consequences.