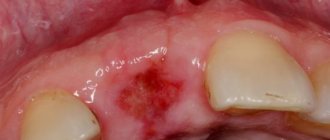
Antibacterial treatment
Taking antibacterial medications is not necessary in all cases of glossitis treatment.
The need for such therapy is determined by the doctor, and indications for prescribing antibiotics are purulent and phlegmonous processes, when the inflammatory process spreads not only to the deep tissues of the tongue, but also to neighboring areas (oral cavity, chin, neck). Antibacterial agents are also prescribed to patients with high fever, enlarged peripheral lymph nodes and signs of intoxication. What drugs are used according to indications for the treatment of glossitis:
- Doxycycline is a drug from the tetracycline group, which is taken 100-200 mg per day, divided into 2 doses. Contraindications: pregnancy, children under 8 years of age and allergic reactions to the drug.
- Suprax is an antibacterial drug related to cephalosporins; it should be taken orally at a dose of 800 mg per day, in one or two doses, for 7-10 days in a row.
- Rocephin is an analogue of Ceftriaxone, also belongs to the group of cephalosporins, 2-4 g are administered intramuscularly or intravenously throughout the day until the general condition is normalized and the inflammatory process subsides.
- Tetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is not prescribed for fungal and viral etiologies of the disease; it is taken 250–500 mg three times a day, the dosage and duration of treatment depends on the severity of the clinical picture.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
If glossitis is accompanied by purulent-phlegmonous complications, this is often a reason for surgical intervention. Then antibacterial therapy is carried out during the recovery period, using one or two drugs at once, selecting them after analyzing the flora for sensitivity.
Causes of erosion on the tongue
The main factors leading to the appearance of various lesions in the oral cavity, mainly localized in this area of the digestive tract, include:
- Mechanical, thermal or chemical injury;
- Herpes virus;
- Stomatitis;
- Malignant tumor of the tongue;
- Syphilis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
The causes of ulcers on the tongue also include allergic reactions to food or hygiene products, problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Which doctor treats glossitis and when should you contact him?
When suspicious ulcers are discovered on the tongue, many begin to ask a completely logical question regarding which doctor to turn to for help. In such a situation, you can, of course, immediately make an appointment with a dentist, but it is not a fact that the pathology was caused by a dental problem, and this specialist will be able to provide the necessary assistance.
It is better to first consult with your attending physician - after a visual examination, he can send the patient for additional examination, the necessary tests, or immediately refer him to a highly specialized doctor: a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, immunologist, or again to a dentist.
The formation of strange suspicious spots, plaque and ulcers on the surface of the main speaking organ, the occurrence of obvious pain, burning and tingling sensations - all these are signs of tongue pathology. If we are talking about glossitis, then it can be an independent disease, since it is a secondary sign of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems.
Symptoms of tongue inflammation
The tongue becomes bright red or burgundy. With anemia, the tongue becomes covered with a pale coating. The tongue may increase in size and become soft. There are difficulties in chewing, swallowing, and speaking.
If you experience one or more of the above symptoms and they do not disappear within 24 hours, you should definitely see a doctor.
Consultation with a specialist is also necessary if you have difficulties with the processes of inhaling air, swallowing or speaking. If you have symptoms of tongue inflammation, you should consult a doctor.
The dentist will examine the area of inflammation of the tongue, determine the presence or absence of papillomas, ask the necessary questions to identify the causes of the infection, or prescribe the necessary tests to identify a systemic disease.
Catarrhal glossitis
The most common form of the disease, in which the inflammatory process does not spread to the deep layers of the tongue. It occurs in acute and chronic forms. The acute form is caused by poor oral hygiene, poor-quality fillings, and improperly installed orthodontic appliances and dentures.
It may develop after a burn from hot drinks or food, or chemical contact with an acid or alkali. The first sign is pain in the tongue, which intensifies when talking or eating food (rough or spicy). Catarrhal glossitis of an infectious nature has a characteristic localization on the back or side surface of the tongue.
In this disease, the surface of the mucous membrane is hyperemic, the tongue is somewhat enlarged and swollen (tooth marks are visible on the lateral surfaces). A few days after the start of the process, the back is covered with a coating consisting of a large number of desquamated epithelial cells. Enlarged mushroom-shaped papillae are clearly visible against the background of plaque. The patient is bothered by moderate drooling.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the causes of the taste of wormwood in the mouth
The chronic inflammatory process occurs with the death of filiform papillae and bright red spots appear on the back of the tongue. Later, the fungiform papillae also die, and the spots merge. The tongue looks mirror-smooth and bright red, as with erythematous glossitis. The thinned mucous membrane of the tongue tends to form cracks, and when injured, ulcers occur.
Chronic inflammation is associated with burning and pain in the tongue, which can be constant or appear periodically. The mucous membrane is sensitive to external irritations, so spicy, spicy, hot and salty foods cause unbearable pain. A common complaint is dry mouth, which makes speech difficult, as well as lack of appetite.
Diagnosis by type of lesion
Sometimes the appearance of an ulcerated tongue can tell you what pathology led to such symptoms.
- Red ulcers become noticeable when the digestion process or the functioning of the endocrine glands is disrupted;
- Bloody blisters on the surface of the tongue indicate problems with the circulatory system. The walls of the capillaries are thinned, which leads to the formation of hematomas with minor trauma during eating or brushing teeth;
- Blisters on the tongue with transparent contents appear as a result of a burn;
- A small papular rash in different parts of this organ is caused by the herpes virus;
- Small white ulcers on the tongue indicate the development of candidiasis, problems with the gallbladder, kidneys, liver or intestines;
- Purulent formations on the sides and at the root of the tongue indicate the development of an abscess.
This area of the oral cavity is constantly exposed to various factors, which significantly complicates the healing of ulcers of various origins. Carrying out diagnostic measures and taking a detailed history will help the specialist understand the cause of problems with the surface of the tongue and select the appropriate set of medications to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Treatment of candidiasis
Externally, the oral mucosa is treated with a solution of borax in glycerin at a 10% concentration. You should also rinse your mouth with chamomile decoction, soda solution and irrigate the mucous membrane with 2% boric acid. Tablets for oral administration with antifungal effect:
- Nystatin is a rather old, but proven and effective remedy for Candida fungus, tablets with a dosage of 250-500 thousand units. taken 3–4 times a day, it is not recommended to crush or chew them beforehand; the course of treatment is 10–14 days.
- Lamisil - tablets that need to be taken one per day (active substance content 250 mg), the course of therapy depends on the depth of damage to the epithelial layers and the duration of the disease.
- Terbinafine is a fungicidal agent, which will take from a week to 1-2 two months to be treated, take one tablet once a day with a dosage of 250 mg.
It must be remembered that candidal glossitis often accompanies long-term infectious diseases, for which the patient uses large doses of antibiotics. Sometimes it is enough to cancel antibacterial agents and apply external treatment to the tongue several times so that the symptoms of glossitis go away on their own.
How to deal with glossitis
A list of diagnostic procedures prescribed by the dentist that help determine the nature and depth of the lesion:
- cytological studies
- bacteriological techniques
- anticardiolipin testing
- analysis for Treponema pallidum - the causative agent of syphilis
- infectious diseases are detected using polymerase chain reaction
The therapy is complex; pathological disorders caused by primary diseases are necessarily corrected (treated):
Plaque that occurs when the tongue becomes inflamed is removed with a cotton swab soaked in trypsin. When erosive and ulcerative formations create pain, then applications with Iruksol will be the best option to combat plaque.
At the end of the procedure, treatment with an antiseptic solution is required to avoid re-entry of infectious agents and further complications.
Among medical prescriptions: vitamin A, rosehip oil. The combined use of these components accelerates the recovery of cells affected by glossitis and reduces pain.
In addition, systematic rinsing throughout the day with a weak solution of furacilin and potassium permanganate helps minimize pain. In case of severe pain, antiseptic application procedures (Lidocaine) are added to therapy.
In case of weak immunity, immunomodulatory drugs are indicated.
Possible difficulties with breathing (difficulty) are an argument for prescribing hormonal medications. At a short interval, in order not to provoke the “death” of tongue cells, Prednisolone and Hydrocortisone ointments are allowed for therapy.
The problem of glossitis can be solved if the therapeutic process starts on time. Adequate correction of the primary disease, which served as a catalyst for inflammatory phenomena in the tissue structures of the tongue, will avoid possible negative consequences:
Preventive measures: systematically (twice a year) visit the dental office, maintain hygiene. The risks of tongue inflammation will decrease after quitting smoking. It is necessary to exclude spicy foods and strong alcohol, which will reduce the chances of developing glossitis. Mashed potatoes, slimy porridges, pureed soups are welcome.
General principles of treatment
To select an adequate treatment for tongue glossitis, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis in time. In some cases, when the symptoms are severe and the development of the disease was preceded by external factors (burn of the mucous membrane, injury from braces, prosthesis or filling), only a dentist can determine the diagnosis.
If during the examination a concomitant disease of an acute or chronic nature is revealed, which provoked the development of glossitis, then the therapy will have two directions - basic and symptomatic. Basic therapy aims to improve the functioning of the affected systems and organs, and symptomatic therapy is intended to relieve signs of glossitis as a concomitant pathology.
Treatment includes the following points:
- complete sanitation of the oral cavity;
- treatment of the mucous membrane with antiseptic solutions;
- applications with painkillers and restorative drugs;
- treatment with agents for healing and regeneration of the mucous membrane;
- taking vitamin complexes;
- antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal treatment, depending on the type of pathogen;
- taking immunomodulators.
During treatment with medications and external preparations for applications and rinses, the patient is prescribed a gentle diet that excludes spicy, hot, sour and salty foods, too hot and irritating foods, as well as solid foods. During treatment, heavy physical and emotional stress should be avoided in order to increase its effectiveness. Any changes in health status should be reported to your doctor.
Signs and methods of treating tongue diseases
The action of external and internal factors individually or in combination causes various pathologies, among which the most common are infectious, congenital and chronic glossitis, leukoplakia, as well as a symptom complex called glossalgia.
Infectious glossitis
Infectious diseases of the tongue can be recognized by photos and descriptions, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
White coating with a cheesy consistency, as in the photo.
Removing plaque is accompanied by pain and bleeding. Children often have fever.
Rashes in the form of small watery blisters, as in the photo.
If they open, erosions appear on the tongue. The rash is painful and accompanied by fever.
The tongue becomes inflamed, red spots appear, in place of which bubbles up to 1 cm in diameter develop, as in the photograph.
When the blisters open, ulcers form.
| Name of the disease | Pathogen | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Candidiasis (thrush) | Fungal infection – Candida albicans | Lubricating the inflamed areas with antifungal ointments, rinsing with soda solution, Furacilin or manganese. | |
| Herpetic glossitis | Herpetic viral infection – Herpes simplex virus | Taking antiviral drugs orally, lubricating the rash with antiviral ointments, rinsing the mouth with Chlorhexidine. | |
| Streptococcal impetigo | Bacterial infection – streptococci | Taking antibiotics orally and in the form of ointments, rinsing the mouth with Furacilin, soda or manganese solution, Chlorhexidine, chamomile decoction. |
Additionally, symptoms accompanying the inflammatory process are treated: for fever, an antipyretic is used, for unbearable pain, analgesics are used, and more fluids should be drunk to prevent dehydration. Regular oral hygiene helps eliminate infections and ulcers on the surface of the tongue.
Catarrhal and ulcerative glossitis
Catarrhal and ulcerative glossitis are also infectious diseases of the tongue, the symptoms and treatment methods of which are similar to the infectious diseases described above.
But the cause most often lies not in infection of the epithelium of the oral cavity itself, but in the complication of general infectious processes (ARVI, influenza) or inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. This diagnosis is often found in smokers and people who abuse alcohol. With the catarrhal form of glossitis, taste perception changes, pain appears, and tingling occurs. Inflammation causes swelling, which leaves teeth marks on the sides of the tongue. A dense layer of white plaque accumulates on the root of the tongue.
If left untreated, catarrhal glossitis turns into an ulcerative form with the formation of bleeding ulcers covered with a layer of dead epithelium and the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
In case of catarrhal and ulcerative forms of glossitis, it is necessary to treat both the general disease, which entails pathological changes in the tongue, and external manifestations (erosions). May be assigned:
- Antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs by mouth.
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptics and herbal decoctions to eliminate inflammation and heal ulcers that have affected the human tongue. You can use chamomile.
- If plaque accumulates, wipe it off with clean gauze.
Desquamative glossitis
In diseases of the digestive organs and metabolic disorders, diathesis, dysbacteriosis, inflammation of the tongue may be accompanied by a change in the location of the grooves and thickening or desquamation of the papillae.
Subsequently, pink and red spots appear on the surface, clearly delimited by whitish ridges. This set of symptoms is called “geographical tongue.” To eliminate the pathology, it is necessary to treat the disease that led to such changes. Depending on the cause of the pathology, the patient is prescribed different groups of drugs:
- Antiallergic.
- Vitamin.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Probiotics to eliminate dysbiosis.
For local treatment of a sore tongue, rinsing with antiseptics and lubricating the mucous membrane with a vitamin A preparation are used.
Congenital abnormalities of the tongue
Rhomboid glossitis is caused by congenital features of muscle development.
It appears as a growth on the back of the tongue (near the root) up to 10 mm in length, characterized by a glossy surface of bright red color. Folded glossitis is characterized by congenital uncharacteristic folds on the tongue, although the mucous membrane is of normal color. In the absence of other diseases, this feature does not cause discomfort, but metabolic disorders and vitamin deficiencies can provoke keratinization and cracking of the surface of the folds.
Treatment may include the following:
- If such diseases are complicated by infection or cracking of the tongue, it is necessary to treat the oral cavity with antiseptics.
- For vitamin deficiencies, a special diet and taking vitamins in the form of medications are indicated.
- For rhomboid glossitis, cryotherapy is used. To avoid complications, patients with such problems are not recommended to smoke.
Hairy black tongue
The name of this tongue disease is explained by its photo and description of the symptoms. The tongue does look hairy, but this effect occurs due to the pathological growth of papillae on its back closer to the root. They can reach 2 centimeters in length. Gradually these structures die off and turn black.
The cause of this pathology is metabolic disorders or taking medications harmful to the body. Tobacco smoke and alcohol, which affect the body for many years, can provoke the growth and death of papillae. Doctors admit that the disease may be caused by genetic mutations.
This disease is treated with antiseptic drugs to wash away plaque and keratolytic agents. Papillae that become inflamed and die can be removed using cryodestruction. You need to follow a gentle diet, stop smoking and spicy irritating foods.
Leukoplakia
This tongue disease most often occurs in men in adulthood and is usually associated with metabolic problems or diseases of the digestive system.
Leukoplakia does not cause pain, but the patient may feel discomfort when eating spicy food. Symptoms of this tongue disease can be seen in the photo on the right. The mucous membrane of the organ becomes covered with whitish plaques, which spread to other parts of the oral cavity and may appear in the corners of the mouth. After a few weeks, the affected epithelium thickens. Treatment of the causative disease is necessary. The affected areas of the tongue are cleaned with:
- Laser therapy.
- Radio waves
- Electroexcision method.
- Diathermocoagulation method.
If the doctor suspects the cells have degenerated into malignant ones, surgical treatment will be performed.
Glossalgia
This problem with the tongue is caused by frequent injuries in the mouth or serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs; the pathology most often affects elderly patients. Glossalgia is not a separate disease, it is a complex of symptoms characteristic of certain diseases.
With glossalgia there are practically no visible external signs - redness or the appearance of ulcers. Only in some severe cases there is a grayish coating. The manifestation of the pathology is felt by the sick person himself: the tongue becomes painful in one place, or the pain spreads throughout the entire muscle. Due to dry mucous membranes, severe itching or tingling occurs, and the discomfort usually increases with excitement.
Sometimes the pain syndrome disappears on its own, but it is unacceptable to ignore such signs of the disease without attention and accurate diagnosis. The dentist must carry out a complete sanitation of the mouth, check the condition of the dentures, if any, as they can cause permanent injury. When an internal disease is detected, the detected problem must be treated. If the tongue hurts very badly, the discomfort is eliminated with the help of analgesics.
The oral cavity can be exposed to various harmful influences, therefore, to prevent tongue diseases in humans and eliminate their symptoms, comprehensive health care is necessary. If signs of illness appear, you should consult a doctor and carefully follow his instructions. In order not to miss the initial stages of pathologies, you need to carefully look at the surface of the tongue in the mirror from time to time.
Consequences and complications
In the absence of adequate treatment, there is a possibility that the acute form of catarrhal glossitis will become chronic. In patients with rhomboid and folded glossitis, chronic mucosal candidiasis is detected, which is a complication of these forms. In isolated cases, malignant degeneration of rhomboid glossitis is possible.
Complications in the form of phlegmon or abscess are extremely rare and are possible only in the absence of treatment in weakened people leading an asocial lifestyle. The abscess is manifested by throbbing pain and severe swelling of the tongue. The process of eating is disrupted and difficulties arise when speaking.
Causes
- Bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, etc.).
- Viruses (herpes).
- Fungi (yeast-like genus Candida).
- Injuries to tongue tissue (thermal and chemical burns, mechanical damage).
Under the influence of nicotine and alcohol, the risk of developing glossitis increases.
Glossitis is a symptom of certain diseases and conditions of the body:
- lack of vitamins (A, E, B12 and folic acid);
- anemia;
- scarlet fever and measles;
- diphtheria;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- helminthic infestations;
- lichen planus;
- allergy;
- stomatitis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- taking antibiotics;
- rheumatism, etc.
Inflammation of the tongue - how to deal with glossitis
Inflammation of the tongue is an infectious pathological condition called glossitis, characterized by disturbances in the tissue structure of the tongue and changes in color.
The development of the inflammatory process entails a lot of negative symptomatic manifestations that complicate the normal functioning of this muscular organ.
List of emerging “troubles” associated with glossitis:
- loss of sense of taste
- increased blood supply to the vascular system
- the tongue turns red and stings, burns and swells
- the resulting painful discomfort provokes difficulties while eating (problematic swallowing, chewing food)
- increased salivation
- difficult to have a conversation
The disease, which is a variant of stomatitis, can develop against the background of other inflammatory problems of the oral cavity.
Inflammation of the tissues of the tongue, in the case of infectious penetration of parasitic microorganisms, is classified as a separate, independently developing “pathological unit” called glossitis.
At the same time, the inflammatory process can become a consequence of systemic pathology present in the body.
The onset of inflammatory phenomena in the tissues of the tongue is due to the following causative factors:
- Mechanical damage (minor trauma) of the tongue opens the “doors” wide for the invasion of pathogenic microflora (bacteria, viruses), which provokes the development of glossitis. It is possible to injure after an injection with a sharp fish bone, illiterate selection of dentures, and finally the sharp edges of destroyed teeth and fillings.
- The risk of damage increases in people who abuse alcohol and are heavy smokers.
- Ignoring the basics of oral hygiene - brushing with someone else's toothbrush, excessive use of mouth rinses, inadequate reaction of the body to toothpaste.
- Hot food, drinks - burn.
- Weakened immunity, dysbacteriosis.
Anti-inflammatory and painkillers
To reduce the level of inflammation in the oral cavity and eliminate pain, drugs from the antimicrobial groups, NSAIDs, as well as anesthetics in the form of gels and ointments are needed. They are also used for tissue swelling and other unpleasant consequences of pathology. Here is a list of necessary drugs:
- Tantum Verde is a spray from the indazoles group that has not only an analgesic, but also an antimicrobial effect. Effectively stops the inflammatory process in the oral cavity, stabilizes the condition of cells. Contraindicated for children under 3 years of age and for people with allergies.
- Ketoprofen is a remedy that reduces the level of inflammation, eliminates pain, and reduces fever. Thanks to its complex action, it improves the patient’s well-being and relieves the characteristic symptoms of glossitis. Not used for severe gastrointestinal diseases, pregnancy, lactation and renal dysfunction.
- Cholisal is a gel with antimicrobial and analgesic properties, which is applied to the surface of the mucous membrane 2-3 times a day until a lasting effect is achieved.
- Kamistad is a gel that contains chamomile extract to achieve an antimicrobial effect and the anesthetic component benzocaine. The product cools the damaged mucosa well, relieving pain and healing the affected layers of the epithelium.
- Hexaspray - used as a spray, thanks to a special spray nozzle. It has a powerful anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and analgesic effect. The product is contraindicated for children under 2.5 years of age and for patients sensitive to the components.
To cleanse the oral cavity of microbial plaque, reduce inflammation and pain, use Lizak lozenges. This fungicidal agent is effective against bacterial, fungal and viral forms of glossitis, but is not prescribed to children under 4 years of age.
Classification
Diamond-shaped - the appearance is due to chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Characteristic clinical signs:
- thickening of the epithelial layer
- formation of diamond-shaped zones
- the color of the affected area ranges from red to dark blue
With this option, the following scenarios are possible:
- formation of lumpy growths on the surface of the tongue
- the appearance of warty or papillomotous whitish growths
- the affected area atrophies, becoming smooth
The disease can “get a foothold” on a chronic basis, and there is a high probability of relapses.
Villous form - caused by a fungal infection, or systematic minor damage to the surface of the tongue.
As a result, thread-like clusters of taste buds located inside visible elevations (bulges) on the surface of the mucous membrane of the tongue increase in size and become dark.
Later they harden and keratinization is detected.
In addition to the above mentioned causal factors, catalysts for development can become:
- addiction to alcohol
- “friendship” with a cigarette
- taking medications
Geographic - the affected areas of the epithelial layer alternate with foci of swollen lingual papillae that have grown from inflammation. This set of pathological disorders is similar to the geographical outlines of the continents on the globe.
The medical name for this form of glossitis is desquamative, and among the causes that provoke its development are:
- chronic gastrointestinal pathologies
- pregnancy
The following were found guilty of formation:
- hematological pathologies
- presence of parasitic microorganisms, helminthic infestations
- liver problems
- impaired metabolism
The development of the geographical type of glossitis is caused by focal destruction (violation of the integrity) of the epithelium. As a result, bright red spots appear on the side of the tongue. There is a burning sensation and moderate pain.
The Gunter form is evidence of a deficiency of B vitamins in the body (9, 12), which leads to smoothing. The surface of the tongue is comparable to a polished crimson hue.
Interstitial - a bell (symptom) indicating the possible presence of a sexually transmitted disease called syphilis.
The affected areas are replaced by connective tissue, which tightens the tongue. The lack of adequate therapy results in oncological problems. Diseased cells acquire the properties of a malignant tumor and become cancerous.
Prevention
Preventive measures can prevent the development of inflammation:
- oral hygiene using high-quality care products;
- preventive examinations at the dentist with sanitation of foci of infection in the oral cavity;
- identification and timely treatment of diseases of internal organs that cause glossitis;
- rejection of bad habits;
- limiting/excluding from the diet foods with chemical additives, overly spicy foods and sweets.
From childhood, you need to develop the habit of brushing your teeth in the morning and at night (using an irrigator), using dental floss, and rinsing your mouth after every meal. Children need to be weaned from the habit of biting their nails and putting their fingers in their mouth.
Particular attention is paid to oral care with a folded tongue, this was mentioned above. If you have dentures, they also need to be treated with antifungal agents. Patients with the papillomatous form of rhomboid glossitis, taking into account the possibility of its malignancy, should be registered at the dispensary with periodic examinations every six months.
Other drugs
In addition to treatment with the listed agents, therapy for glossitis involves the intake and use of other drugs, depending on the clinical need:
- antihistamines - for the allergic nature of the disease, these are Claritin, Zyrtec, Loratadine, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine;
- hormonal - in severe forms of the disease, accompanied by shortness of breath and severe swelling of the throat mucosa, these are Prednisolone and Hydrocortisone;
- antiviral - Interferon, Cycloferon, Viferon, used for the viral nature of the disease;
- immunomodulators - necessary in cases where glossitis acquires a chronic etiology and manifests itself in relapses against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity, these are Immunal, Bronchomunal, Echinacea tincture;
- healing agents – rosehip and sea buckthorn oil, vitamin A;
- vitamin complexes – are prescribed in almost all cases of glossitis; it is especially necessary to replenish the body’s reserves of B vitamins and iron (with concomitant anemia).
In the form of applications that are applied to the tongue, the drugs Lidocaine in 2% concentration, Trimecaine in 2% concentration and Novocaine are used. These substances are part of many anesthetic gels, which are necessary for patients with glossitis, because most often the disease causes acute pain. It must be remembered that successful treatment of glossitis involves complex therapy, depending on the root cause of the disease.
If the pathology develops simultaneously with dysbiosis, treatment is carried out by a gastroenterologist. Blood diseases, and at the same time signs of glossitis, are the prerogative of a hematologist. And so on, depending on the factor that provoked the inflammatory process in the cavity of the tongue. Self-medication and ignoring the symptoms of the disease are strongly discouraged, since poorly treated glossitis can be complicated by phlegmon, abscess and even blood poisoning.
We suggest you read why a child’s tooth hurts after pulpitis treatment
Questions and answers on the topic “Inflammation of the tongue”
Question:
Hello!
Can there be a burning sensation of the tongue with esophagitis? Answer:
Hello! Esophagitis may be accompanied by a burning sensation of the tongue. But often this symptom can be a sign of another disease, for example, inflammation of the tongue. A burning sensation of the tongue may occur with chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis. With gastritis, the absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract, including vitamins, may be impaired. Due to a lack of vitamin B12, B12 deficiency anemia develops, in which the papillae of the tongue often atrophy. In this case, pain and burning occur, the tongue becomes bright red and very smooth. To diagnose the disease, you need to take a blood test and contact your doctor for help.
Question:
Hello!
For a week I took antibiotics flemoxin and clarithromycin (with Enterol and Linex, respectively) to treat Helicobacter pylori infection and cervical lymphadenitis. On the penultimate day of taking antibiotics, the coating that was constantly on the tongue completely disappeared and the tongue became smooth and bright burgundy in color. Inflammation has appeared and the tongue is constantly stinging. It looks like it's a little swollen, but I'm not sure. If you don’t eat anything, then the tongue seems closer to pink, but smooth and without the slightest coating. After any meal it becomes bright burgundy and hurts (burning and stinging). The food is completely dietary, nothing spicy, salty, etc. (not allowed according to gastroenterology). I visited the dentist and they said that it looked more like an allergic reaction and they prescribed suprastin and a sage rinse. I already started taking Suprastin along with antibiotics, but rinsing doesn’t help yet. Eating is very painful. What can you recommend in this situation? Answer:
Hello! Your condition is most likely caused by taking a lot of antibiotics. The microflora of the oral mucosa is probably disrupted. I think that after stopping the drugs everything will return to normal. At this stage, use dental ointments and gels that are sold in pharmacies.
Question:
Hello!
In the morning I discovered a thick white coating on my tongue and my tongue was very inflamed. The plaque was removed, small hemorrhages formed under it (the tongue began to bleed slightly). The papillae on the tongue have enlarged and are very annoying. When eating food I feel bitterness in my mouth. When examining the tongue, all papillae are visible as red grains. I drink suprastin and rinse my mouth with soda and chlorhexidine. The third day and no improvement. What it is? Which doctor should I contact first? Answer:
Hello, You need to consult a gestroenterologist.
Question:
Hello!
About a month ago inflammation appeared on the tongue. I went to the doctor and said it was a stomach problem. Prescribed Linex and Ultop. There was no pain and there was no discomfort. Now, after the treatment, the inflammation has not gone away and red dots have appeared and the tip of the tongue stings a little. And it seems to me that there are rashes on the palate too. Who is better to contact and what to do? The doctor said that it is not contagious, but I am still worried. Thank you! Answer:
Hello. Consultation with a dentist, ultrasound OBP, FGDS, CBC, biochemistry (liver tests).
The most effective drugs
Drug treatment of glossitis involves the use of such common drugs as Vinizol, Chlorhexidine and Solcoseryl. Each of these drugs has its own functions, but their combined use can increase the effectiveness of symptomatic treatment of glossitis. Vinisol is widely used in the treatment of burned surfaces, ulcerative lesions that do not heal for a long time, as well as for the speedy restoration and healing of tissue.
The release form of the drug is a spray, the composition includes the components vinylin, propellant, citral and linethol, and the product itself has powerful anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. The drug must be sprayed onto the inflamed surface of the tongue 1-2 times a day, the duration of spraying is several seconds.
The next product is Solcoseryl, a gel for healing and rapid tissue regeneration. Its beneficial properties:
- heals damaged mucous membranes;
- improves metabolism in epithelial cells;
- improves the supply of tissues with oxygen and nutrients;
- increases the amount of collagen fibers produced;
- stimulates cell renewal.
In addition to the listed properties, Solcoseryl gel creates a thin film on the surface of the mucous epithelium that prevents infectious agents from entering the layers of damaged tissue. Before using the drug, it is also necessary to clean the surface of plaque. Treatment with the gel is carried out three times a day until a positive effect is obtained in the form of drying of ulcers and healing of cracks in the tongue.
The drug affects a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative microbes, but is powerless against fungal infections. Cases of an allergic reaction to Chlorhexidine are extremely rare; the product should be used three times a day; it is also suitable for lubricating the mucous membranes and irrigating.
List of sources
- Mironova V.V., Solomatina N.N. Anomalies of tongue development and its diseases // Textbook for practical classes in dentistry. 2020.- 29 p.
- Karakov K.G., Vlasova T.N., Lavrinenko V.I. Independent and symptomatic glossitis in the clinic of therapeutic dentistry // Textbook. Stavropol, Publishing and Information, 2020. – 102 p.
- Borovsky E.V., Mashkilleyson A.L. Diseases of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and lips. // M., 2001, 73-90.
- Redinova T.L. “Diseases of periodontium and oral mucosa” // Textbook. Izhevks, 2020. – 160 p.
- Anisimova I.E. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa // Textbook. Medical book, 2008. – 194 p.
Diagnostic methods
The first diagnostic step for any pathology associated with such discomfort is a visual examination of the oral cavity. You can see a physician, dentist, or otolaryngologist. Based on the characteristic symptoms, the doctor will make a diagnosis and provide referrals for clinical tests if necessary.
If the cause of the pain is an inflammatory process in the oral mucosa or gums, then a consultation with a dentist is necessary, who, after examining and clarifying the disturbing symptoms, prescribes appropriate treatment. During the examination, the doctor carefully examines the color of the tongue and its shape, determines the type of plaque and the presence of formations on its surface (papillomas, blisters, ulcers). In case of injury to the root by elements of the system, it is corrected.
The examination of the tonsils is carried out by an otolaryngologist using spatulas, a curved probe, with which a sample of the contents is taken for bacterial examination. The doctor examines the ear canals and nasal cavity to identify diseases. If a malignancy is suspected, a biopsy is prescribed. A bacterial smear allows you to identify the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to antibiotics that will be used in treatment.
If, after studying the patient’s medical history, it is determined that he has any chronic disease that could cause pain at the root of the outgrowth of the floor of the oral cavity, then consultations with the following specialists are prescribed:
- endocrinologist (endocrine system pathologies),
- gastroenterologist (gastrointestinal problems),
- an allergist participates in treatment when candida stomatitis, allergic manifestations are detected,
- in case of diagnosing malignant neoplasms or tumor-like growths, the doctor refers the patient to an oncologist,
- neurologist,
- nephrologist,
- cardiologist,
- if surgical intervention is necessary (additional goiter, oncology), an examination by a surgeon will be required.
In this case, narrow specialists use the following diagnostic methods:
- blood chemistry,
- determination of hormone levels,
- Ultrasound of the abdomen, throat and salivary glands,
- gastroscopy.
Surgery
Some forms of glossitis can be treated surgically. With a folded form, sometimes they resort to surgery - suturing the grooves, after which laser evaporation is performed. If there is a tendency to grow papillomatous and tubercular forms of rhomboid glossitis, the formations are also subject to excision. This is done to prevent degeneration of the overgrown tissue.
The most effective are laser evaporation, the use of radiosurgery or cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen. Liquid nitrogen causes freezing and rejection of growths. The postoperative period is relatively easy and consists of the use of local anti-inflammatory procedures, a gentle diet, and restriction of motor activity of the tongue. After all surgical interventions, the patient must carefully monitor the oral cavity and be sure to clean the tongue.
In rare cases, with persistent pain in the tongue, novocaine blockades of the lingual nerve area are performed. Depending on the patient’s condition, the course may be 3-10 injections.