In the modern world, endocrinology problems come to the fore. About 50% of the world's population has experienced this pathological condition. The insidiousness of this pathology lies in the fact that the primary symptom complex is practically absent, and the first stage of the inflammatory process goes unnoticed. All age groups of the population are susceptible to this disease. Next, we will look at the causes and consequences of such an inflammatory process as an enlarged thyroid gland.
Self-diagnosis
It is important to know what may indicate possible problems, which symptom of an enlarged thyroid gland you need to pay attention to first.
So, at home you can only try to palpate this organ. It is located in the neck, just behind the thyroid cartilage, which moves during swallowing. If you place your hand so that your thumb is to the left of the cartilage, and the other 4 are to the right, you can feel a formation that has a soft consistency. This is the organ we need. To understand whether there is an increase in the lobes of the thyroid gland, you need to know what size it should be. So, normally it is as long as the outer phalanx of the thumb - the one on which the nail is located. If it seems to you that it is larger, then it is better to make an appointment with an endocrinologist who can conduct a professional examination.
During self-diagnosis, you can evaluate its density and check for the presence of nodes. Ideally, it is soft and elastic. In other cases, it is necessary to see a doctor. This symptom of an enlarged thyroid gland cannot be ignored. After all, its dense structure may indicate oncology. It is also important to ensure that it moves with the thyroid cartilage during swallowing.
Notice the soreness. Normally, during manual examination of the gland, only discomfort should be present. In all other cases, a visit to the doctor becomes mandatory.
Why the thyroid gland enlarges, symptoms
Regardless of age and gender, an enlarged thyroid gland is an alarming signal of serious pathologies or diseases within the body.
Often, the increase occurs unnoticed and goes through several stages.
Why does the thyroid gland enlarge?
The endocrine gland is responsible for the synthesis of hormones that control the functioning of homeostasis - self-regulation and the ability to maintain a constant internal state through reactions aimed at maintaining balance and dynamics.
The slightest malfunction leads to endocrine disorders. The thyroid gland is the main and largest organ of the endocrine system (slightly smaller in women than in men).
As you age, the thyroid gland may drop slightly.
In the first stages, an enlargement of an organ cannot always be noticed: a person does not even suspect that changes are occurring inside, leading to an imbalance in tissues or systems.
Any excess in size (starting from the third stage) is diagnosed by doctors as a goiter. The most common type of disease is a thyroid nodule.
Features of the structure of the lobes - the right one is slightly larger than the left due to the greater formation of blood vessels. The main reason for the growth of tissues and their compaction is iodine deficiency.
The gland controls metabolic processes, nourishes cells with vitamins and iodine, which is produced by the hormones thyroxine, calcitonin and triiodothyronine. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine are the main sources of iodine. Failure of two hormones leads to adverse consequences.
Typically, the weight of the thyroid gland does not exceed 30 g, but it may increase during pregnancy.
It is worth noting that the enlargement of the organ occurs precisely because of iodine deficiency.
How to determine an enlarged thyroid gland - stages
At the first stage, slight changes in the structure can be noticed when swallowing: the isthmus stands out (there is a constant lump in the throat), nothing changes upon palpation.
At the second stage, the lobes of the organ are felt during palpation (located on the sides of the isthmus), and they can also be seen when swallowing. The structure of the neck itself remains the same.
At the third stage, the neck swells, noticeably increases in size, and the thyroid gland comes forward.
The fourth stage - the lobes of the gland extend far forward.
At the fifth degree, the increase is so strong that it becomes difficult to swallow food.
Due to the tumor, the larynx and trachea are compressed, the voice may partially disappear or become hoarse, the neck area becomes overgrown with a massive “collar”, swells, shortness of breath, suffocation, and cough appear (one of the main signs that is often ignored).
Symptoms of an enlarged thyroid gland in men and women
Are common:
- Hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- weakness, broken state;
- disruptions in heart rhythm;
- causeless aggression;
- sexual dysfunction (loss of desire);
- the tongue swells (tooth marks are visible along the edges);
- proper sleep is disturbed;
- hair splits and falls out.
An enlarged thyroid gland can be a sign of diseases such as:
- Hypothyroidism (rapidly gaining fat mass);
- hyperthyroidism (severe weight loss occurs, the body's endurance increases, but the condition is temporary).
Diffuse enlargement of the organ (tissues of the lobes rapidly grow in all directions) depends on many external factors: hormonal imbalance (especially after 45 years), poor nutrition, unfavorable environmental conditions or a weakened immune system.
Cancerous formations are provoked by the colloid form of the disease, and with hypothyroidism iron deficiency anemia often develops. The hereditary factor is of great importance.
Diagnosis of the thyroid gland - which doctor to consult
A doctor who treats diseases of the endocrine system is an endocrinologist.
You can find out about the condition of the thyroid gland using an ultrasound examination. You can also determine the enlargement of the gland using special tables.
Blood is taken for analysis to detect thyroid-stimulating hormone, an additional scan of the thyroid gland is performed (a radioactive iodine solution is injected), and if necessary, a computed tomography scan and biopsy are prescribed.
For treatment, hormonal drugs and tablets (thyreostatics) are selected that increase the level of iodine in the body. Levothyroxine is prescribed if treatment does not have the desired effect.
Treatment of the thyroid gland at home
Products high in iodine are sea fish, cranberries, kelp (seaweed), bananas, radishes, corn (sweet), beans, eggplant, tomatoes, bell peppers, potatoes, oranges, chicken fillet.
Products that do not allow iodine to be fully absorbed: cabbage (white cabbage, broccoli, Brussels sprouts), flaxseed, peanuts.
Regular table salt can be replaced with iodized salt. It is very important not to delay contacting a specialist - in case of complications, tissue inflammation is possible - autoimmune thyroiditis, you can find out about the features of the disease here.
Surgery on an organ is performed in exceptional cases (cancer, rapid tissue growth, a node exceeds 3 cm, co-occurrence of autoimmune thyroiditis, a tumor blocks the natural access of oxygen).
A cancerous tumor can be removed in 95% of cases without consequences.
Treatment of the thyroid gland largely depends on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the person. You cannot cure the disease on your own.
Read with this article:
Pancreatitis: symptoms, treatment, diet
Stomach ulcer: symptoms and treatment
Source: https://xn--80ajamitfn6b.xn--p1ai/uvelichennaya-shhitovidnaya-zheleza/
Reasons for the increase
Having figured out which symptom of an enlarged thyroid gland cannot be ignored, it is also important to understand what led to the problems. So, first of all, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient, asking whether he has a genetic predisposition. But, besides heredity, there are other reasons. Enlargement of the thyroid gland may be due to a violation of the iodine absorption mechanism or due to too low intake of this trace element in the body.
A goiter can also form as a result of excessive radiation to the neck or head area. Sometimes the causes of problems lie in excessive stress, prolonged depression, and nervous breakdowns. Hormonal imbalances in the body also lead to the appearance of goiter.
Degrees of enlargement of the thyroid gland
Under normal circumstances, the thyroid gland is invisible and practically cannot be felt.
The classification of goiter sizes includes 3 degrees of gland enlargement:
- Zero degree. There is no goiter at this stage, the organ can be palpated.
- First degree. The goiter is not visualized when the head is in a normal position; an enlarged gland is palpable.
- Second degree. The goiter is palpable and quite noticeable to the naked eye.
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland allows you to accurately determine the size of the organ. In this case, the initial examination does not allow us to adequately assess the position, because it depends on several factors that determine the error.
Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland is more often diagnosed in women. Similar changes occur under the influence of autoimmune antibodies. The reason is often hidden in genetic predisposition. Such a pathology requires observation and treatment. In the absence of therapy, undesirable consequences cannot be ruled out. Treatment in most cases gives a positive result and leads to recovery.
Nodular deformity is often diagnosed. These changes are noticeable upon palpation, the organ has a soft structure, and the nodes are more rigid. Nodes can be single or multiple, malignant and benign. The node may fill with fluid – a manifestation of a cyst. Deformations of this kind can be provoked by stress, mental and physical stress, and nutritional disorders.
At the zero stage of the disease, the patient does not notice any changes. After some time, the node begins to put pressure on nearby organs, which causes discomfort. As the formation grows, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced. In the early stages of the pathology, the patient is under the control of an endocrinologist, and conservative methods of therapy are used. If the nodes grow, their malignant nature is proven, an operation is performed and an oncologist is involved in therapy.
An increase in the proportions of the thyroid gland can provoke changes in the functioning of the endocrine system. The gland includes 2 lobes, and if one of them begins to change its size, they speak of a pathological process.
Women are more likely to experience an enlarged thyroid gland due to hormonal changes in the body. Accelerated growth of the thyroid gland has been noted in the following situations:
- puberty;
- pregnancy;
- postpartum period;
- menopause
Women must remember the necessary control of the functioning of the endocrine system, protect the body from infections, and prevent the development of iodine deficiency; to do this, they need to include foods rich in this element in their daily diet.
Men are much less likely to hear that their thyroid gland is enlarged. This is due to the fact that their thyroid gland is slightly different from women's. In men, the increase is visualized in the early stages, and this helps to start treatment in a timely manner. Goiter grows equally in both sexes, so it is extremely important to consult a doctor and determine the reasons for the enlargement of the thyroid gland. The signs of an enlarged thyroid gland are no different.
Types of goiter
Depending on the clinical picture, doctors distinguish several stages.
At grade 0, manual examination does not detect problems with the thyroid gland. It is of normal size without any formations. Stage 1 enlargement of the thyroid gland is characterized by minor changes that can be felt. But the shape of the neck is not changed; no deformations can be seen with the naked eye.
Stage 2 is characterized by a noticeable enlargement of the organ, which leads to the appearance of bulges on the skin. The neck becomes deformed. It is impossible not to notice a grade 2 goiter.
Experts also distinguish diffuse and nodular changes. In the first case, the iron increases evenly. Diffuse goiter is also divided into toxic and non-toxic. The nodular form of the disease is characterized by a limited area of gland enlargement. There is also a mixed type of goiter. There are signs of both diffuse and nodular enlargement.
Classification of problems
As a result of the examination, the endocrinologist must not only determine the degree of enlargement of the thyroid gland, but also identify a euthyroid, hypothyroid or hyperthyroid state. The symptoms of a goiter will depend on the changes that have occurred in this organ.
Euthyroid enlargement usually goes unnoticed by patients. People, as a rule, don't complain about anything. But in such patients there are disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and signs of myocardial pathologies. There may also be problems with metabolic processes.
Hyperthyroid goiter is less common. But it is worth noting that such enlargement of the thyroid gland is diagnosed more often in women than in men. Patients may complain of periodic shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and sweating. Also with this form of the disease, trembling of the fingers is noted.
Hypothyroid goiter has a number of clinical signs, but they may not appear in the early stages. In more advanced forms, diagnosis is quite simple. Patients have a somewhat puffy face, dry skin, and pale skin. There is also increased hair loss.
Causes and treatment of an enlarged thyroid gland
An enlarged thyroid gland is often diagnosed with a disease such as endemic goiter, a symptom of which is also a change in the shape of the neck. This pathology most often develops against the background of iodine deficiency in the body. This trace element plays a very important role, since it is necessary for the production of sufficient quantities of thyroid hormones. Iodine mainly enters the human body with food (up to 90% of the required volume). 4-5% of the required amount of this element comes with water, and the remaining 4-5% with air. Epidemic goiter occurs in the majority of the population who live in a region characterized by insufficient iodine in the environment. Therefore, this disease is very common, especially in some areas.
Classification of goiter based on thyroid hormone levels
With an enlarged thyroid gland, endemic goiter develops in children or adults, which can affect the functioning of the human body in different ways. This type of pathology, in turn, is divided into several varieties depending on the resulting hormonal background:
- hypothyroid type. Accompanied by a decrease in the production of thyroid hormones. This condition is called hypothyroidism;
- euthyroid type. With the development of this condition, the thyroid gland enlarges, but the hormones are normal;
- hyperthyroid type. With an increase in the volume of the thyroid gland, an increased production of its hormones is observed. This type of disease is typical for older people.
Classification of goiter depending on the type of pathology
If the thyroid gland is enlarged, after certain diagnostics it is possible to determine the specific type of developed pathology:
- diffuse goiter. The thyroid gland is enlarged evenly in all directions;
- nodular goiter The enlargement of the thyroid gland occurs locally. One or many formations of a dense structure are observed;
- mixed goiter. Characterized by the presence of diffuse nodular pathology. Quite common among the population.
The thyroid gland can also be affected by other types of goiter. The colloid form is characterized by the presence of benign formations (one or many). The polynodous type of goiter is characterized by its multinodular nature. You need to understand that the colloid form of the disease along with cystic degeneration poses a particular danger to humans. The follicular variety is also found. In addition, it is customary to distinguish a sporadic form, such as toxic goiter. Pathologies of a mixed nature are quite common.
Toxic goiter of the diffuse type is in most cases diagnosed in women whose age ranges from 20 to 30 years. This pathology develops against the background of autoimmune processes in the body. Diffuse toxic goiter is accompanied by a significant increase in the right and left lobes of the thyroid gland.
The pathology of the nodular toxic form is accompanied by the formation of an adenoma with the presence of one or more nodules. This condition is characterized by an increase in the concentration of thyroid hormones. Endemic goiter develops in regions with insufficient iodine content in food, water, and air among a large number of its inhabitants. With this pathology, the thyroid gland increases rapidly without lifestyle adjustments or specific treatment. The epidemic is common in many areas around the world.
Classification of goiter depending on the location of the pathology
An enlarged thyroid gland in men or women can be localized in certain areas, and therefore the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- classically located goiter. The pathology is located on the anterior wall of the gland;
- dystopic goiter. This disorder develops from the embryonic folds of the body;
- partially substernal type;
- ring shape;
- single sided type. The pathology is localized on the right or left lobe of the thyroid gland;
- double sided type. Both the right lobe and the left lobe of the thyroid gland are affected.
Stages of goiter development
The following degrees of development of the disease are distinguished:
- When diagnosing a person and identifying this degree, we can say that he is completely healthy. In this case, the gland fully complies with the norms and does not have any pathological changes;
- 1. Visually, the formation is invisible, but is determined by palpation and is visible during swallowing;
- The formation is detected by visual examination, the appearance of the neck does not change;
- When diagnosing this degree, thickening of the neck is observed;
- A pronounced pathology that changes the contour of the neck;
- A goiter that compresses the esophagus and trachea.
Causes of enlarged thyroid gland
Why can the thyroid gland become enlarged? Such a negative process can be caused by either one specific cause or a combination of factors, which is why a comprehensive diagnosis of endemic goiter is indicated. Examination of the patient’s body allows us to determine the development of certain pathological processes that affect the treatment method.
The following are the causes of an enlarged thyroid gland:
- hereditary factors;
- a certain genetic defect affecting the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones. The produced substances are unable to fully perform their assigned functions;
- the possibility of goiter may increase significantly when drinking water is contaminated with humic substances, nitrates, and urochrome. Calcium also negatively affects the process of iodine absorption by the thyroid gland. It can also be found in large quantities in water;
- A person's risk of developing goiter will increase if they do not have sufficient amounts of certain minerals in their food and environment. Such substances include zinc, manganese, selenium, cobalt, copper, molybdenum. An imbalance of these minerals in the body leads to an enlargement of the thyroid gland - the cause of this phenomenon is a violation of the synthesis of thyroid hormones;
- the use of certain medications that block the absorption of iodine by the thyroid gland;
- inclusion in the diet of foods with goitrogenic properties. They disrupt the normal production of thyroid hormones. Various types of cabbage (Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli), turnips, horseradish, lettuce, rapeseed and others have such negative properties;
- when exposed to infectious, inflammatory processes, a phenomenon such as an enlarged thyroid gland is often observed;
- little-known causes of endemic goiter - the presence of helminthic infestations, unsatisfactory living conditions (both sanitary and social);
- The main reason for the development of this pathology is a lack of iodine in the human body, which must be supplied in sufficient quantities with food. This makes it impossible for the normal production of thyroid hormones. The development of diffuse endemic goiter associated with iodine deficiency occurs due to an increased concentration of thyrotropin in the blood. By increasing the size of the thyroid gland, the body tries to compensate for the insufficient production of hormones. Also, with such changes, a low concentration of iodine in this organ is observed. Normally it should be 500 mcg per 1 g of tissue;
- insufficient production of thyroglobulin, which is typical for some regions. This negative factor contributes to thyroxine deficiency;
- autoimmune causes. In some patients, changes in immune functioning are observed. The thyroid gland produces substances that are identified by the body as foreign. As a result, the immune system produces special antibodies to neutralize them. This leads to decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism).
Symptoms of this pathology
How can you tell if a person’s thyroid gland has become enlarged? Certain signs indicate this. Symptoms of an enlarged thyroid gland largely depend on the degree of development of the pathology, its cause and the consequences it causes. In most cases, the signs of this disorder are:
- with an enlarged thyroid gland (a symptom of this pathology is the presence of a characteristic lump on the neck), it can not only be clearly felt, but also seen;
- the appearance of a feeling of a foreign body in the trachea, problems with swallowing;
- excessive formation of fat deposits due to impaired carbohydrate metabolism. In this case, obesity can be both external and on internal organs (visceral);
- with pathologies of the thyroid gland, the symptoms of which are an increase in its size, a decrease in the volume of muscle mass is observed;
- fat metabolism in the human body is disrupted. This means that the concentration of substances of lipid origin – cholesterol, triglycerides and others – increases in the blood. As a result of such a violation, the risk of developing a heart attack, atherosclerosis, angina pectoris and other diseases increases;
- decreased intellectual abilities, fatigue;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- the presence of muscle weakness, brittle bones, delay in the physical development of children;
- constant feeling of cold;
- development of infertility in men and women. The risk of spontaneous abortion, fetal abnormalities, or the birth of a child whose weight exceeds 4.5 kg also increases.
Diagnostics
How to determine an enlarged thyroid gland in order to prevent the development of unpleasant complications of this condition? How to find out what degree of pathology and whether it poses a danger? To do this, the following diagnostic methods are shown:
- external examination of the patient with palpation of the neck;
- Ultrasound, which allows you to accurately determine the degree of enlargement of the gland, the shape of the goiter, the presence of nodules or any other formations;
- determination of hormone levels. Most often it is necessary to determine the concentration of T3 and T4;
- thyroglobulin analysis. The more it is, the expression of iodine deficiency;
- biopsy of tumor formations of the thyroid gland if a malignant process is suspected;
- radioisotope scanning.
Drug treatment
What to do if the thyroid gland is enlarged, and this is confirmed by ultrasound diagnostics? What drugs are indicated for this? With an enlarged thyroid gland, treatment depends on the identified pathologies. What is endemic goiter, and how to eliminate this disease, only an endocrinologist can say more accurately. It is prohibited to treat this pathology on your own.
In many cases, the following medications are indicated:
- Iodomarin, Iodine balance, vitamin containing complexes. The iodized preparation saturates the body with a sufficient amount of iodine, which is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. Vitamin-containing complexes are indicated for better absorption of this microelement (indicated for stage 0-1 goiter);
- thyroid preparations containing synthetic tetraiodothyronine. This hormone is necessary for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland in women or men. In some cases, it is indicated for stage 1 goiter and for more serious pathologies.
For endemic goiter, treatment lasts on average from 6 months to 1 year. This term depends on the severity of the patient's condition. All the time, when unpleasant symptoms develop and treatment occurs in a conservative way, the endocrinologist monitors the patient to prevent the occurrence of dangerous complications of the disease.
Surgery
If the use of vitamin and mineral preparations does not produce results and the goiter is actively progressing, a decision may be made about surgical intervention. A significantly enlarged gland compresses the surrounding vessels, nerves, and respiratory tract, which not only reduces the patient’s quality of life, but also poses a danger to life.
Surgery is also indicated for the formation of an autonomous adenoma, frequent recurrences of goiter and other negative factors. In the presence of malignant processes, the thyroid gland is removed completely or subtotal resection is used.
Prevention
Prevention of endemic goiter presupposes a rational diet. The foods a person eats must contain large amounts of iodine. These include:
- baked potato;
- prunes;
- cranberries;
- seafood;
- turkey breast and others.
If necessary, vitamin-containing complexes are prescribed. Such drugs can be used for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. Vitamin containing complexes with iodine can prevent the development of goiter in residents of areas that are susceptible to the development of this disease. It is also necessary to monitor your weight, exercise, and give up bad habits.
Symptoms of euthyroid enlargement of the gland
The clinical manifestations of the disease will directly depend on which particular form has developed. For example, euthyroid goiter does not manifest itself in any way. Even a blood test for thyroid hormones cannot diagnose it. Most often, such an increase looks like a noticeable cosmetic defect. The thyroid gland is clearly visible on the neck. Photos of people with this particular disease are most common. The increase can be so great that the gland compresses the vessels, reducing the lumen of the trachea and esophagus. In this case, a person may complain of difficulty breathing and swallowing.
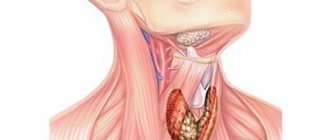
What is the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland, or thyroid gland, belongs to the endocrine glands of internal secretion, which do not have excretory ducts for the produced secretory substances.
They go directly into the blood, lymph, tissue and cerebrospinal fluid.
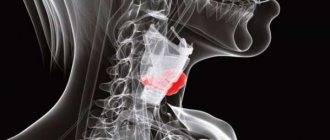
The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck, on the thyroid cartilage (hence its name). The location of the thyroid gland is related to age.
For example, in children it is located above the thyroid cartilage. In older people, it sometimes descends into the mediastinum. This is a symmetrical organ, shaped like an outstretched butterfly.
With its winged lobes, the iron envelops the trachea on both sides, while its middle part, the isthmus, is located on its front part. The weight of this small organ is from 20 to 60 grams.
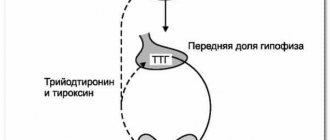
Signs of hyperthyroiditis and hypothyroiditis
A detailed survey of the patient and collection of complaints allows the endocrinologist to establish a preliminary diagnosis. Thus, hyperthyroid goiter is characterized by hyperfuction of the thyroid gland. Patients in most cases complain of bulging eyes, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, accelerated metabolic processes, and increased appetite.
Hypothyroid goiter manifests itself differently. Even increased sleepiness is a symptom of an enlarged thyroid gland. In addition, the disease is manifested by hypotension, hair loss, a feeling of dry mouth, some lethargy, flatulence, and constipation. Patients are often diagnosed with anemia based on test results. Some even experience hearing loss. This is possible due to swelling of the eustachian tube.
Purpose of the gland
It is important to understand that thyroid diseases affect the functioning of the entire body as a whole.
Thus, this organ is responsible for the normal, stable functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. It also controls protein synthesis, which takes place at the cellular level, and the consumption of phosphates, calcium and oxygen. In order to prevent problems in time, you need to know how an enlarged thyroid gland manifests itself. Symptoms (treatment should be aimed at correcting the functioning of this organ) can be varied. They vary depending on the type of disease. In cases where the thyroid gland stops working normally, weight changes, and problems with mental and energy status are observed. Thus, if not detected in time, the disease can lead to obesity, serious problems with the heart, hair loss, sexual disorders and other health problems.
Importance of treatment
If the endocrinologist notices at least one symptom of an enlarged thyroid gland, he will most likely send you for tests. In this case, it is necessary to donate the main hormones responsible for its functioning. The doctor may also order an ultrasound examination of this gland. With the help of blood tests, you can determine how much the level of hormones responsible for its functioning has changed. And ultrasound allows you to accurately determine the stage of the goiter and identify even small nodules.
After the final diagnosis is made, do not try to self-medicate and under no circumstances refuse hormonal therapy. In most cases, only with its help can you reduce the load on the thyroid gland. Prescribed hormones can fill the body's needs and thereby improve its functioning. But they must be taken regularly. Periodically, the endocrinologist will recommend retaking the tests. This is necessary to adjust the dosage of hormones. In addition, treatment can be aimed at eliminating the causes that led to the disorders.
Preventive measures
To avoid an enlarged thyroid gland, you must adhere to the following recommendations from endocrinologists:
- Find out what level of iodine is entering the body at the place of residence - it also depends on how clean the ecology of the region is and what the composition of the water is. You can obtain such information either from the department of the sanitary-epidemiological service or from an endocrinologist.
- Replace regular table salt with sea or iodized salt. Please note: this salt has a very peculiar taste, which discourages many people from consuming it. You can combine both types of salt - for example, use iodized salt only in spicy dishes and broths.
- There should be seafood on the table at least 2 times a week. Let it be a simple kelp salad (seaweed) or fried squid in batter - the necessary dose of iodine will be delivered to the body.
- You can prevent enlargement of the thyroid gland by regularly eating nuts. You can use any type of nuts, but it is better to focus on walnuts.
- At least once a year you need to visit an endocrinologist for a preventive examination - the doctor will be able to detect an enlarged thyroid gland at an early stage and, by prescribing iodine-containing drugs and diet, adjust the functionality of the organ.
An enlarged thyroid gland is a rather unpleasant pathology that can lead to serious disruptions in health and the usual rhythm of life. But at the same time, endocrinologists assure that by adhering to a certain diet and constantly taking hormonal or iodine-containing medications, you can live a long life even with this disease.
It is important to detect the problem at the very beginning of its development, so you can periodically diagnose it yourself. You just need to feel your own thyroid gland and make sure that it is mobile, painless, the lobes are well palpated and soft/elastic. If any of these “points” confuse you, or if you feel, in addition to discomfort, there are pronounced painful sensations, then a visit to the doctor should not be put off for long. You can get more information about inflammation of the thyroid gland by watching this video:
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category.
35, total, today
( 64 votes, average: 4.61 out of 5)
How much iodine does a person need: signs, consequences and prevention of iodine deficiency
How to stimulate the production of growth hormone?
Related Posts
Therapy methods
In order to choose the right treatment, you need to know what exactly influenced the changes and identify the causes. Enlargement of the thyroid gland requires not only competent prescription of medications, selection of the required dosage of hormonal drugs, but also lifestyle correction.
If the doctor talks about treatment that can help eliminate the causes of problems, then you need to be prepared to change your diet and a number of habits. It is important to increase your activity and strive to change your metabolism.
Endemic goiter appears in most cases due to insufficient iodine intake in the body. In this case, doctors can prescribe appropriate medications, for example, it could be Iodomarin.
But when hyperthyroid goiter appears, it is necessary to adjust the functioning of the thyroid gland so that it produces less hormones. These drugs are called thyreostatic drugs. These may be medications “Tyrozol”, “Metizol”, “Mercazolil”. The active ingredient in them is thiamazole. The doctor may also prescribe Propicil. The active ingredient in it is called propylthiouracil. Treatment with such drugs can last 1-1.5 years, depending on the degree of enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroid goiter requires a different approach to treatment. To normalize the condition, thyroxine is needed. The most well-known remedy that can restore the level of this hormone in the body is L-thyroxine. The use of vitamin complexes is also important. The body must receive sufficient amounts of vitamins B, A, and C. If the disease is accompanied by anemia, then iron supplements are prescribed.
Causes and degrees of enlarged thyroid gland
Malfunctions of the endocrine system can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, it is important that every person pays close attention to any changes in the body. The reasons for the enlargement of this gland may be different, but among the most common, doctors identify the following factors:
- iodine deficiency in consumed food and water;
- exposure to unfavorable environmental conditions;
- heredity and predisposition;
- deficiency of vitamin D, as well as the microelements selenium and fluorine;
- chronic stress, psychological disorders, depression;
- constant severe overwork;
- lack of physical activity, inactivity;
- menopause in women, accompanied by disruptions in the hormonal system.
Surgical intervention
In some cases, the goiter is so enlarged that it can compress internal organs, squeeze arteries, trachea and esophagus. A growing thyroid gland can also sometimes cause cosmetic defects. The photo gives a clear idea of how enlarged this organ can be. So, in some people, egg-sized increases are visible in the neck area.
In such situations, conservative therapy is unlikely to be appropriate. True, in a number of situations the surgeon’s knife can be replaced with radiation therapy.
Problems in children
Problems with the thyroid gland can begin at any age. But in children they cause a number of problems that cannot be corrected later. Thus, an enlarged thyroid gland in children can negatively affect both the mental and physical development of the baby. It is also this organ that is responsible for metabolic processes, the state of the immune system, and heart function.
There are a number of symptoms that may indicate that a child has problems with endocrinology. It is better to go to the doctor if the baby has become lethargic, allergic reactions that are unusual for him have begun to appear, and infectious diseases have become more frequent. The skin may be dry, but in some cases it becomes moist and swollen. Short stature is also a clear sign of problems. It is also advisable to consult an endocrinologist if, based on tests, the doctor diagnoses anemia in the baby.
Only a pediatric specialist should treat children. He may conduct a manual examination, recommend a test for hormone levels, or go for an ultrasound examination. Only a pediatric endocrinologist can interpret all the results, taking into account the age of the child and the clinical picture that he saw during the examination.