Infectious diseases of the kidney system can have various symptoms, causes of their formation and cause serious complications. The most common infectious disease is pyelonephritis of the upper urinary canals. Adolescent children are at risk of developing this pathology, due to the development of the urinary system and organs, women under 30 years of age (reason for the onset of sexual activity, pregnancy) and men with problems with the prostate gland. A kidney infection can cause inflammation of the urinary tract, as well as blood clots entering the kidney. In this article we will tell you what kind of kidney infection there is, we will analyze the causes of its occurrence, symptoms and treatment.
What kidney diseases can there be?
The kidneys are constantly in contact with toxic substances and other harmful compounds, which is why the urinary system is susceptible to dangerous ailments. Kidney diseases cause dangerous manifestations and disrupt the functioning of all body systems, which is why you should immediately proceed to treatment, since every day of delay reduces the chance of recovery. However, first of all, it is necessary to determine an accurate diagnosis, since each disease requires individual therapy.
Different diseases may present differently, but typically the patient will experience severe pain and excessive swelling, often requiring hospitalization. An acute form of the disease can be cured through special therapy, but chronic diseases are exclusively supported with the help of special means. As a rule, a patient is diagnosed with the following kidney diseases, the symptoms of each disease are different, these diseases include:
- urolithiasis disease;
- nephroptosis;
- pyelonephritis;
- nephrolithiasis;
- hydronephrosis;
- polycystic disease;
- glomerulonephritis;
- malignant formations;
- renal failure;
- violation of metabolic processes.
Different kidney diseases can present in different ways, usually the patient experiences severe pain and excessive swelling
Signs of kidney disease directly depend on the disease that develops in the body, as well as on the degree of damage. It is very important to correctly diagnose the disease and clarify its type so that treatment is effective, fast and affordable. Not everyone knows what kidney diseases are, let’s look at the most famous and common of them.
Vascular kidney diseases
With vascular disease, not only the arteries can suffer, but also the organs that they nourish. Thus, when the renal arteries and veins are damaged, pain may develop that resembles the symptoms of kidney disease.
Atherosclerosis of the renal arteries
A classic example in this regard is atherosclerosis of the renal arteries. The disease manifests itself against the background of already existing atherosclerosis in other large vessels, and with a predisposition to it.
In the lumen of the renal artery, as in other vessels, cholesterol plaques can form, which interfere with normal blood flow.
At the initial stage, blood still enters the kidney, although in a reduced volume, but as the plaque grows or breaks off and obstructs the vessel, it can completely block the supply to the kidney. As a consequence of this, the kidneys cease to perform their function. Against this background, the acute manifestation of a pain symptom begins.
How does the disease manifest itself? In kidney disease, symptoms are characterized by pain in the lower back and kidneys, while the patient has all the signs of hypertension. A diagnosis can be made after receiving test results. Also, after Doppler sonography, doctors determine the location of the obstructed passage of blood, which finally confirms the diagnosis. Treatment of the disease is based on general medications that are prescribed for vascular atherosclerosis, but surgical treatment may be necessary.
Renal artery thrombosis
If renal artery thrombosis occurs, you must immediately call an ambulance. In case of pathology, a blood clot, brought here with the bloodstream, gets stuck in the arterial lumen. And if in wider vessels the thrombus passed unhindered, then in the place of narrowing of the vessel it has a detrimental effect on the body, cutting off the blood supply to the kidney.
Patients first of all complain that their kidneys hurt badly. The discomfort becomes so all-encompassing that some people do not know how to identify pain in the kidneys - it hurts in the side, in the lower back, in the abdomen, and can radiate to the back.
Since the symptoms are similar to appendicitis, the final diagnosis is made in the clinic, where the patient will be given first aid, pain relief will be relieved and, if necessary, prepared for surgery.
Urolithiasis disease
This disease is polyetiological, in other words, a number of different factors lead to its occurrence. As a rule, urolithiasis develops in people whose age is in the range of 20-45 years, but men are diagnosed with the disease 3 times more often than the fairer sex. The reasons that contribute to stone formation include the following factors:
- heredity;
- drinking liquids that contain large amounts of mineral salts;
- impaired water regime, which is typical for those who consume a small amount of water;
- a passive lifestyle in which there is no physical activity;
- poor nutrition, consisting of foods high in purine compounds (meat, beans, spinach).
Also, factors that increase the likelihood of urolithiasis include various diseases of internal organs and the most important systems in the body:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract: cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis;
- acquired and congenital pathologies of the ureters and kidneys;
- diseases of the stomach and digestive tract: pancreatitis, gastritis, hepatitis;
- problems with metabolic processes: hyperparathyroidism, gout.
Prevention of urolithiasis
The above problems lead to changes in the acid balance in the body, due to which solid deposits accumulate. Symptoms of kidney disease can be very diverse; for some time the disease does not make itself felt at all, and then acquires acute symptoms, up to renal colic and even kidney block. As a rule, patients complain of the following manifestations:
- a feeling of cutting and burning in the pubic area and urethra during urination, this manifestation can be explained by the spontaneous removal of small stones, otherwise they are also called “sand”;
- pain in the lower back, which is especially pronounced when changing body position, drinking plenty of liquid, and also with a sharp shake. In this case, pain is only the result of the movement of neoplasms;
- increase in body temperature - the body cannot fail to respond to the presence of solid deposits, as a result of which an inflammatory process occurs precisely in the place where the stone comes into contact with the mucous surface, often an infection is added to this process;
- Renal colic is one of the most unpleasant signs of how kidney disease manifests itself. In this case, the patient feels severe pain in the lumbar region, which is associated with the movement of a solid formation along the ureter, sometimes the pain spreads to the abdominal cavity and even the lower extremities;
- There is a change in the color of the urine, and you can also notice the presence of blood or whole clots in the urine; this manifestation is combined with renal colic.
The nature of the pain and its location provides the specialist with useful information, thanks to which he can clarify the degree of damage to the body and the type of stones
. The last factor plays a huge role, since the characteristics of the treatment will depend on it. Stones can be located in the ureter, kidney or bladder. The doctor’s assumption about the preliminary diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted by ultrasound and radiography.
After clarifying the diagnosis and the characteristics of the stones, you can proceed to treatment. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the pain syndrome; for this, analgesics are used; if the patient has an attack or renal colic has acquired an acute form, then the medical institution may even use narcotic substances to avoid painful shock and other serious complications. In this case, antispasmodic drugs have proven themselves well; they provoke the independent elimination of small stones from the body.
To dissolve stones, medications are used that change the acid balance. The product is selected based on the type of stones; there are several varieties:
- oxalate;
- phosphate;
- cystine.
Stones in the kidneys
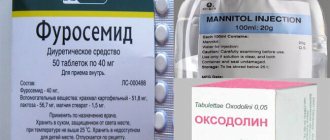
To dissolve the latter, Uralit and Tipramine are used, oxalate stones are dissolved by Prolit, various kidney preparations are used, and phosphate stones are destroyed by Marilin. The drug is selected by a nephrologist or urologist based on the results of a blood and urine test of the patient. Conservative methods include the use of physiotherapy: patients are prescribed amplipulse therapy, magnetic therapy, inductothermy, etc.
If there is no pain syndrome, then folk remedies can be used to prevent relapses. If phosphate stones are present, a positive effect can be achieved by using decoctions based on barberry or rose hips. Combined herbal preparations are used, based on several plants that have diuretic, uroseptic and antispasmodic properties.
Large drops do not dissolve, so radical methods are used to remove them, that is, surgery. The calculus is removed from the kidney by small size in the renal pelvis. There are other methods, when an incision is made through the kidney; in special cases, the stone is removed from the ureter. Recently, lithotripsy has been actively used, the principle of which is based on the creation of a powerful shock wave.
A modern, minimally invasive, high-tech technique for removing kidney stones - laser lithotripsy
Urolithiasis is a disease characterized by the presence of hard deposits in the urinary system. Symptoms of kidney disease manifest themselves in the form of pain, temperature, changes in the color of urine and more serious manifestations, such as inflammation. Treatment should be started immediately, since the disease progresses every day and affects new tissue.
Kidney infection: Causes, Prevention and Treatment
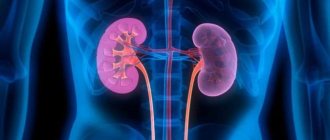
A kidney infection occurs when bacteria or viruses enter the kidneys. The medical name for this phenomenon is pyelonephritis. It can affect both kidneys at once, or only one of them.
What is a kidney infection?
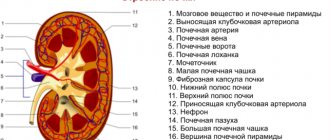
People are born with two kidneys, although you can live with just one. The kidneys filter the blood, remove waste, and produce urine. They are part of the urinary tract, which in addition to the kidneys consists of the ureters, bladder and urethra. The shape of the kidneys resembles a bean and the size of a fist. They are located on either side of the spine just below the rib cage.
A kidney infection occurs when bacteria or viruses enter the kidneys. The medical name for this phenomenon is pyelonephritis. It can affect both kidneys at once, or only one of them.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a kidney infection include:
- elevated temperature
- pain in the back, side or scrotum
- chills
- nausea and vomiting
- painful and/or frequent urination
- cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- blood or pus in the urine.
Symptoms may vary depending on age. Children and older adults may have no urinary tract-related symptoms at all. Other symptoms may include slurred speech, dizziness, or confusion. Most often this happens due to dehydration. If any of these symptoms occur, seek help immediately.
Reasons for development
A kidney infection can be caused by viruses or bacteria. Most often it becomes E. coli (Escherichia coli)
.
This bacterium can enter the kidney (or kidneys) from any part of the urinary tract, for example, from the bladder. Often a kidney infection is a consequence of a urinary tract infection.
Women are more susceptible to both types of infection due to anatomical features.
Diagnostics?
It is extremely important to quickly identify a kidney infection and begin treatment immediately. The doctor diagnoses it based on the results of blood and urine tests. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe other diagnostic procedures. These include ultrasound, x-ray or computed tomography. All of them will allow you to obtain an image of the organs of the urinary system.
Is it possible to prevent the development of infection?
To reduce your risk of developing a kidney infection, you should:
- To drink a lot of water.
- Urinate after sexual intercourse.
- Don't ignore the urge to urinate.
- Avoid douching and contact of scented products with the genital area.
- Wipe the genital area from the vagina to the anus, and not vice versa (for women).
Although anyone can develop a kidney infection, certain people are at increased risk. In general, the risk of developing a kidney infection is higher if you:
Treatment
The main treatment for kidney infection is antibiotics. There are different types of antibiotics. Some of them turn out to be more effective, some less.
Antibiotics are available in tablet form and in the form of preparations for intravenous injection. Cases of severe infection require intravenous administration of the drug and often require hospitalization.
This mainly happens when the patient is severely dehydrated or elderly.
It is necessary to strictly follow medical instructions regarding taking the prescribed drug. It may take several weeks for the infection to completely clear. At the same time, you cannot stop treatment ahead of schedule even if the symptoms disappear.
Subsequently, the doctor will probably order tests for you to make sure that the infection is completely cured.
In addition, additional medications or treatment procedures may be prescribed to eliminate the cause of the disease or factors associated with it.
Consequences
Most people who experience a kidney infection recover successfully and subsequently lead full lives. You should be prepared for the possibility that a kidney infection may develop again. Discuss effective prevention methods with your doctor.
Questions to ask your doctor
- How much water should you drink daily?
- What antibiotic is best for kidney infection?
- What is the likelihood that a kidney infection will lead to chronic kidney disease?
Loading…
Source: https://mojdoktor.pro/pochechnaja-infekcija-pielonefrit/
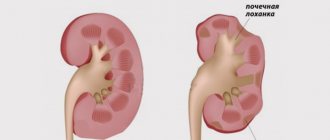
Nephroptosis
Nephroptosis is a pathological process in which the kidney has increased mobility, manifested in the form of movement of the organ beyond the boundaries of the anatomical bed. Moderate and minor nephroptosis occurs without symptoms; if hemodynamic and urodynamic disturbances occur, pain in the lumbar region occurs, and hematuria, pyelonephritis, nephrolithiasis, arterial hypertension, and hydronephrosis may also occur. Nephroptosis can be diagnosed using ultrasound, angiography, excretory urography, nephroscintigraphy and MSCT. Surgical treatment may be required if secondary changes have occurred; as a result of manipulation, the kidney is fixed in the correct position; this procedure is called nepropexy.
During normal development of the body, the kidney has a fixed mobility: during physical stress or during breathing, the kidneys move within certain limits; they do not exceed the height of one lumbar vertebra. If in a vertical position of the body the displacement of the kidney is more than 2 centimeters, and during forced breathing - more than 3-5 centimeters, then we can talk about the presence of nephroptosis.
Symptoms of kidney nephroptosis
As a rule, the left kidney is 2 centimeters higher than the right; in childhood, the kidneys are much lower than normal and occupy the correct position only by 8-10 years. In the anatomical bed, the kidneys are fixed by fascia, perinephric fatty tissue and ligaments. Nephroptosis is diagnosed much more often in women than in representatives of the stronger sex, and damage occurs on both sides simultaneously.
Nephroptosis is a completely acquired disease; its development is caused by pathology of the peritoneal ligaments, renal bed, as well as fascial and fatty structures. Increased mobility of the kidney may depend on a decrease in the fat capsule or incorrect localization of the vessels of the renal pedicle. Many people have kidney pain, the symptoms of the disease and treatment have several individual characteristics and nuances.
Nephroptosis develops against the background of a slight tone of the abdominal muscle tissue, and it can also occur against the background of a sharp decrease in body weight, increased physical activity, and damage to the lumbar area. Nephroptosis is often diagnosed in people with systemic weakness of the ligamentous apparatus and connective tissue. This ailment is often associated with a person’s professional activity: drivers due to constant vibrations and shaking, loaders as a result of physical stress, doctors and hairdressers, since their activities involve prolonged standing in an upright position.
Nephroptosis in women develops during pregnancy, especially after the birth of a large fetus.
Nephroptosis is combined with all sorts of anomalies of the musculoskeletal system - absence of ribs or violation of the location of the lumbar vertebrae. During puberty, nephroptosis can develop in adolescents with a constitutional asthenic appearance, and also with intense changes in the proportions of the body during growth.
Nephroptosis in women develops during pregnancy, especially after the birth of a large fetus.
At the initial stage of the disease, when breathing, the kidney is palpated through the abdominal wall of the anterior cavity, but when exhaling, the organ disappears in the hypochondrium. If the patient is in an upright position, then the patient may experience unilateral nagging pain in the lumbar region, discomfort, and also heaviness in the lower abdomen; if one takes a lying position, the symptoms of kidney disease disappear.
Treatment of nephroptosis is carried out using conservative and surgical techniques
If bilateral nephroptosis occurs, then symptoms of renal failure occur, such manifestations include chronic fatigue, ascites, headache, swelling of the extremities, nausea and dizziness. Such patients may require hemodialysis or even a kidney transplant. Diagnosis of nephroptosis is based on the patient’s complaints; visual examination, instrumental diagnostics, palpation of the kidney and laboratory tests are also of great importance. Research is carried out when the patient takes not only a supine, but also an upright position.
General symptoms
Pain
They are characteristic of most kidney diseases. Stretching of the organ capsule or compression of the peritoneum by enlarged kidneys, damage to the urinary tract leads to painful sensations.
It happens on one or both sides. Unilateral pain can occur with pyelonephritis or urolithiasis, when only one kidney is affected. Most other ailments are always based on damage to organs on both sides, so the nature of the pain is bilateral.
Recommended topic:
Kidney pain and fever
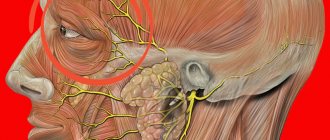
Irradiation is possible to the abdomen, groin, labia or testicles.
Acute pain is typical for urolithiasis when stones move; in other cases, the nature of the pain is dull and aching.
Often back pain is a manifestation of neurological changes in the lumbar spine. The differential diagnosis algorithm includes a survey, examination with palpation, and the appointment of blood, urine and biochemistry tests.
Acute pain in the lower back
Urinary disorders
Observed when the paths of urine outflow are narrowed by tumors, stones, an enlarged uterus, with torsion of the ureters, with impaired urine formation in the kidneys as a result of autoimmune, bacterial damage, as well as in the final stage of chronic diseases.
Changes in urination are often associated not only with the functioning of the kidneys, but also with the bladder, adrenal glands, and brain.
Changes in urine parameters
Allows you to determine the presence of renal pathology, often, although not in all cases, can indicate the cause of the disease. Not always any elements in urine analysis are a signal of impaired functioning of the urinary system.
Changes in urine parameters
Blood occurs during the disintegration of tumors, stones, cysts - it is almost impossible to accurately indicate the origin and level of hemorrhage by the number of red blood cells. Bleeding may be noticeable to the naked eye in the form of brownish clots, scarlet urine, or detected only in laboratory results. Intermittent symptom.
Bacteria are observed with pyelonephritis, but, like leukocytes, they can be the result of insufficient hygiene before collecting material for analysis.
Temperature rise
Occurs in bacterial diseases or during acute inflammatory processes.
A nonspecific symptom, the presence of which alone cannot confidently indicate renal pathology.
Blood pressure surges
Hypertension is characteristic of severe renal tissue damage or organ failure. Disorder in the regulation of the release and reabsorption of ions, the synthesis of certain hormones that affect vascular tone, leads to poorly controlled hypertension.
Sometimes the cause of high blood pressure is a narrowing of the lumen of the renal arteries.
Nausea
Nausea and vomiting
Often observed with prolonged and intense pain, when irritation from the nerves surrounding the kidneys is transmitted to other fibers going to the stomach and intestines. Also, with severe intoxication, in which the elimination of toxic substances and excess trace elements is impaired, the toxic effect on the centers of the medulla oblongata causes vomiting.
Edema
Present during exacerbation of the chronic course of the disease or in the acute period of kidney damage. A distinctive feature is the appearance of edema in the morning, and not in the evening, as with heart failure or varicose veins.
Severe swelling occurs when the main urinary organs are unable to do their job, which is the main symptom of end-stage failure.
Skin change
Impaired renal activity leads to an increase in toxic substances in the blood that affect the functioning of other organs and systems. Often the manifestations of skin changes are based on improper kidney function. This may include dryness, peeling, rashes, increased pigmentation, and a tendency to fungal diseases.
It should be borne in mind that many manifestations of impaired kidney function may be similar to the symptoms of other diseases. It is difficult to make a correct diagnosis at home; you should consult a local doctor or urologist.
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is a disease that is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process that occurs when harmful bacteria spread in the urinary system. As a rule, the causative agent of the disease is Escherichia coli; they are diagnosed in large quantities in the patient’s urine. This disease is characterized by a severe course, it is accompanied by serious pain, and the patient’s well-being worsens daily. Great importance depends on preventive measures, because the disease is easier to prevent than to cure.
The causes of pyelonephritis are pathogenic bacteria; they enter the urethra through the urinary system, then penetrate the bladder. After this, the pathogen spreads to higher systems, resulting in pathogenic bacteria entering the kidneys. About 90% of pyelonephritis occurs due to Escherichia coli, that is, bacteria that multiply in the intestines and enter the urethra from the anus during defecation. This phenomenon explains the intensity of the disease in women, which is associated with the close location of the anus near the external genital organs, as well as the urethra.
So we looked at what symptoms occur in kidney disease, and also looked at detailed methods of treating the disease. From everything it follows that first of all you need to determine the type of illness, and then draw up a detailed treatment plan. This is done by the attending physician after the patient goes to a medical facility. In some cases, the disease is such a serious pathological process that the patient can only be cured through surgical intervention. After surgery, you need to go through a rehabilitation period to ensure the body recovers.
Causes of infectious inflammation
The causative agent of pyelonephritis is most often streptococcus, staphylococcus, E. coli.
An inflammatory process in the kidneys can be caused by problems in the intestines, uterus, dental caries, and even the presence of an ordinary boil. The causative agent of pyelonephritis is most often streptococcus, staphylococcus, and Escherichia coli. The main causes of kidney infection are:
- decreased immune system;
- kidney stones;
- the presence of various bladder infections;
- diabetes;
- genetic abnormality of the organ;
- cysts in the organ;
- anemia or anemia;
In men, the penetration of bacteria occurs through the prostate gland or urethra, then the bacteria rise through the urinary tract.
For information! Most often, the infection affects two organs, disrupting the functionality of all systems and the body as a whole. The urinary system is especially affected.
Microorganisms that cause kidney inflammation
The cause of pyelonephritis is pathogenic microbes. From birth, a person lives in close interaction with various bacteria and viruses, which are the most ancient forms of life. However, most of them do not have any negative effects. Only a certain group of microorganisms are pathogenic, capable of causing inflammation of the renal cups and pelvis in humans.
Bacteria are the most common cause of pyelonephritis. They are not always guests who enter the body from the outside. In most cases, a person lives with them in close proximity. Bacteria normally live in the oral cavity, on the surface of the skin, and inhabit the intestines. All of them are under careful control of the immune system, which does not allow them to penetrate beyond certain limits.
Beneficial bacteria help the body function
This balance benefits both the microscopic inhabitants and the larger human organism. The bacteria that make up the normal microflora are provided with food and a permanent place of residence. They daily train the immune system to recognize friends and foes, prevent the penetration of pathogens and help digestion in the intestines. However, among the undoubtedly beneficial bacteria there are species that are opportunistic. With any weakening of immune control, they can cause the development of the disease.
Bacteria are the only cell in which the processes of nutrition, reproduction, and metabolism occur. These microorganisms, as a rule, do not destroy kidney tissue, but they poison them with toxins released in large quantities. Bacteria can differ in shape, method of nutrition and chemical transformations that form the basis of metabolism. These properties make it possible to divide microorganisms into types.
Bacteria is a single-celled microorganism
Rod-shaped bacteria
The main causative agent of pyelonephritis is Escherichia coli, which normally inhabits the human digestive tract. This bacterium belongs to the opportunistic species and requires constant monitoring by the body's immune system.
Escherichia coli is the most common cause of pyelonephritis
Klebsiella is a rod-shaped bacterium. It lives mainly in the respiratory tract - pharynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. However, in some cases it causes inflammation in the kidneys. Another type of stick is the proteus. It can live in the human intestine, but it rarely causes pyelonephritis.
Klebsiella causes infectious inflammation of the kidneys and respiratory tract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a pathogen that in most cases causes infectious diseases that develop within hospital walls. Pyelonephritis is no exception. These bacteria are massively resistant to antibiotics, making them extremely difficult to control.
Cocci
Another cause of pyelonephritis is cocci. Some of their species are absolutely useful and exist unhindered as part of the normal microflora. However, two representatives cause dramatic negative changes when they enter the kidney tissue - streptococci and staphylococci. Under a microscope, they resemble balls collected in chains or clusters in the form of a bunch of grapes. These bacteria actively produce toxins that cause the development of symptoms of pyelonephritis.
Staphylococcus aureus often occurs in clusters
Pneumococcus is a type of streptococcus, which often causes not only pneumonia, but also the development of pyelonephritis. Kidney disease can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, in this case, the inflammation is purulent in nature (apostematous nephritis, renal carbuncle, paranephritis).
Intracellular forms
Among bacteria there are a number of species leading a rather extravagant existence. They penetrate into the cell, are released from the outer shell and become inaccessible to the action of antimicrobial drugs. Such microorganisms include pathogens of genitourinary infections - chlamydia and mycoplasma.
Chlamydia and mycoplasma exist inside the cells of the host body
Viruses
Viruses are a special form of life. They do not know how to feed and reproduce on their own. They begin their life activity when they enter the human body. The virus penetrates the cell and forces it to perform only one task - to reproduce its own kind. This process most often leads to the death of body tissue. Viruses are extremely difficult to fight because antibiotics have no effect on them. The body's only chance is protection with the help of the interferon protein, which destroys the infectious agent inside the cell. Pyelonephritis can be caused by influenza viruses, parainfluenza, enteroviruses, rhinoviruses, and adenoviruses.
The virus contains an envelope and genetic material
Preventive and therapeutic measures
Treatment of renal diseases involves a complex of measures from conservative therapy to surgical intervention.
A common feature of both treatment and prevention of kidney diseases is minimizing the load on the urinary system. In this regard, the following recommendations are proposed:
- eliminate a sedentary lifestyle to prevent urine stagnation;
- adherence to a therapeutic diet, the main feature of which is a decrease in the amount of protein foods, an increase in the amount of fiber, and drinking plenty of fluids;
- decoctions and teas from medicinal plants can cleanse the body of toxins.
If you have kidney disease, you should try to avoid hypothermia, and if you have a cold, do not carry it on your feet, so as not to cause complications. You should not self-medicate if renal colic occurs; only a doctor will be able to determine the true cause of the disease and prescribe the appropriate course of treatment.