Modern diagnosis of syphilis and evaluation of results – Venereology
Venereology / April 20, 2006 01:01
Diagnosis of syphilis is based on clinical and laboratory data. The diagnosis of syphilis is made only after laboratory confirmation, i.e.
detection of pale treponema in the discharge of chancre, erosive, papules in primary and secondary syphilis, and serological examination data.
Serological reactions are an extremely valuable method not only for confirming the diagnosis of syphilis, but also for monitoring the dynamics of its course under the influence of treatment and determining whether the disease is cured.
The standard components of the complex of serological reactions (CSR) for ascertaining a syphilitic infection are currently supplemented by treponemal reactions: RIBT (treponema pallidum immobilization reaction), RIF (immunofluorescence reaction).
The Wasserman reaction (RW, PB) is based on the phenomenon of complement fixation.
For its production, cardiolipin antigen is used, which is a cholesterolized alcoholic extract from bovine heart muscles and has similar antigenic properties to Treponema pallidum.
Wasserman reaction
Complement is bound by a complex (lipoid antigen and reagin of the test serum). To indicate the formed complex, a hemolytic system (sheep red blood cells and hemolytic serum) is used.
In addition to the complement fixation reaction with cardiolipin and treponemal antigens, the CSR group also includes a glass reaction (express method). The severity of hemolysis during RV is indicated by pluses: sharply positive - 4 +; positive - 3 +; weakly positive - 2 + or 1 +; negative - .
It is also important to stage the reaction using a quantitative method, i.e., with various dilutions of serum (1:10; 1:20, etc. up to 1:320).
The large number of standard serological reactions is explained by the antigenic mosaic nature of Treponema pallidum, due to which a corresponding multiplicity of antibodies (complement-fixing, agglutinins, precipitins, immobilins, antibodies that cause immune fluorescence, etc.) appears in the blood serum of patients.
At each stage of syphilis, certain antibodies may predominate and, therefore, reactions with some antigens may already be positive, while with others they may still be negative.
In addition, the relative specificity of standard serological reactions makes it necessary to use not one of them, but a complex of reactions, in order to avoid diagnostic errors. CSRs become positive at the end of the 3rd or during the 4th week after the appearance of chancre.
These reactions are sharply positive and in a significant dilution of sera in almost all patients with secondary fresh (98-99%), secondary recurrent (100%), tertiary active (70-80%) and tertiary latent (50-60%) syphilis.
However, CSR is not a strictly specific set of reactions for syphilis. They may be positive in patients with leprosy, tuberculosis, brucellosis, malaria, lupus erythematosus, as well as in cases of pneumonia, liver diseases, cancer, after drinking alcohol, fatty foods, during pregnancy, especially in the second half, as well as during the first 2 weeks after birth.
With age, the number of nonspecific false-positive DCS results increases.
For a substantiated diagnosis of syphilis, along with CSR data, clinical data, test results for Treponema pallidum in the manifest manifestations of primary and secondary syphilis, data from other serological reactions - RIBT and RIF are taken into account.
RIBT is based on the phenomenon of immobilization of Treponema pallidum by immobilisin-type antibodies found in the blood serum of patients with syphilis. A suspension of pale treponema obtained from the tissues of syphilitic orchid drolck is used as an antigen for RIBT.
Treponema pallidums, after adding the patient’s blood serum to them, stop moving, i.e., they become immobilized. The results of the reaction are assessed as a percentage: positive RIBT is stated when immobilization is from 51 to 100%.
Treponema pallidum, weakly positive - from 31 to 50%, doubtful - from 21 to 30% and negative - from 0 to 20%. The reaction is carried out under conditions of anaerobiosis. Immobilisins appear in the blood serum of patients later than other antibodies, so RIBT becomes positive later than CSR and RIF.
RIBT is the most specific of the existing reactions to syphilis. Its main purpose is to recognize false-positive results when performing CSR. This is especially important for patients in whom syphilis occurs latently without external manifestations, but with damage to internal organs or the nervous system.
RIBT is of particular importance in recognizing false-positive CSR results in pregnant women.
It should be remembered that nonspecific positive results of RIBT are also possible in patients with sarcoidosis, lupus erythematosus, tuberculosis, cirrhosis of the liver, etc. However, in these diseases, RIBT is weakly positive (from 30 to 50%) and never reaches 100%.
When treated with antibiotics, the results of RIBT become negative. Therefore, studies using RIBT are carried out only after 7 days, if water-soluble antibiotics were administered, and 25 days after the end of treatment with durable antibiotics.
RIF is a more sensitive reaction, so it is positive already in the primary seronegative period of syphilis in 80% of patients. In terms of specificity, RIF is inferior to RIBT, which does not allow it to replace RIBT, although its technique is much simpler.
The reaction is carried out in several modifications: RIF-10, RIF-200 and RIF-abs. (absorbed). RIF-10 is more sensitive, while RIF-200 and RIF-abs. more specific.
The principle of the reaction is that a specific antigen (treponema pallidum) is combined with the patient’s blood serum (antibodies) and anti-species fluorescent serum (rabbit serum against human globulins combined with fluorescein, a substance that glows under ultraviolet light). With a positive reaction, in a fluorescent microscope you can see a yellow-green glow of pale treponema, since they are surrounded by fluorescent antibodies clinging to them. The degree of luminescence is assessed by pluses, as with CSR. A positive reaction is stated as 4 +, 3 + and 2 +. If the degree of luminescence is 1 + and there is no luminescence, the reaction is considered negative. In secondary syphilis, RIF is positive in almost 100% of cases. It is always positive in latent syphilis (99-100%), and in tertiary forms and congenital syphilis it is positive in 95-100%.
Express method (microreaction on glass). In this reaction, as well as in CSR, cardiolipin antigen is used, one drop of which is mixed with 2-3 drops of the blood serum of the person being examined in the wells of a special glass plate. The reaction proceeds by the precipitation mechanism.
The total duration of the reaction is 10-40 minutes. The result is assessed by the density of the deposited sediment and the size of the flakes; the severity of the reaction is indicated by pluses: 4 +, 3 +, etc., like the DAC.
The microreaction on glass is less specific for patients with syphilis than RV, but is slightly superior in sensitivity. False-positive results are obtained more often with the express method than with the RT method.
Therefore, this method is approved for use only as a selection reaction during mass examinations of the population, clinical examination and examination of patients in clinical diagnostic laboratories of somatic hospitals.
A definitive diagnosis of syphilis based on this method is prohibited. Only the express method cannot be used when examining donors, pregnant women, or for monitoring after treatment of patients with syphilis.
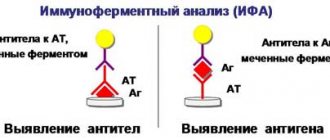
To diagnose syphilis, you can use other methods: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with a microprecipitation reaction (RPM) or a passive hemagglutination reaction (RPHA) with RMP (including foreign analogues of RMP - RPR or VDRL).
When conducting clinical-serological monitoring after specific treatment (to determine the effectiveness of therapy), a quantitative study of bladder cancer is allowed (study of the titer of the reaction over time). Enzyme immunoassay (ELISA, Elisa).
The principle of the reaction is to combine the syphilitic antigen, sorbed on the surface of a solid-phase carrier, with the antigen of the test blood serum and identify the specific antigen-antibody complex using anti-species immune serum labeled with an enzyme. The sensitivity and specificity of ELISA are similar to RIF.
Passive hemagglutination reaction (RPHA). The macromodification of this reaction is called TRHA, the micromodification is called MNA-TP, and the automated version is called AMNA-TP. Scientists have developed a domestic diagnosticum for RPHA from pathogenic and cultured Treponema pallidum.
High sensitivity and specificity of RPGA have been established, especially in late forms of syphilis. The ease of production, low cost and high sensitivity of RPGA makes it possible to use it as a screening reaction for syphilis.
RPGA is provided in qualitative and quantitative versions; there are macro- and micromodifications.
IgM serology. In recent decades, the dynamics of antibody formation in the body of patients with syphilis before, during and after treatment has been widely studied.
This is due to the fact that in patients who have been fully treated for syphilis, positive results of specific serological reactions to syphilis remain for a long time.
which complicates the solution to the issue of cure of patients, as well as the diagnosis of early congenital syphilis. Differential diagnosis of disease relapse and reinfection is also difficult.
When studying the formation of antibodies in the body of patients with syphilis, it was found that specific antibodies are produced first after infection. IgM, detected already in the second week after infection and reaching its maximum concentration in the blood at 6-9 weeks. After 6 months
after the end of therapy in most patients they are not detected in the blood. In the fourth week after infection, the body begins to produce specific IgG. This type of immunoglobulin is detected in greatest quantities 1-2 years after infection.
It should be noted that specific IgM ceases to be produced when the antigen disappears from the body, and the secretion of IgG continues by clones of memory cells.
In addition, large IgM molecules do not pass through the placenta from mother to fetus, and therefore their presence in the child is used to determine whether the child is infected with Treponema pallidum. Due to the fact that the concentration in the blood of specific
IgM naturally decreases over time; an increase in the titer of these antibodies can serve as an auxiliary sign of the presence of a relapse of the disease or reinfection. In 1977, 19S IgM-TA-abs. was proposed, then 19 IgM-TPHA.
These tests are based on the separation of test sera into 19S IgM and 7S IgG using gel filtration and detection of the former using the immunofluorescence method and hemaglucination test. In 1980 V.
Schmidt described the hemadsorption reaction on a solid-phase carrier of IgM-SPHA, which combined elements of ELISA and RPHA, and in 1983 E. Lindeschmidt proposed IgM-TP-ABS-Elisa. A.
Luger (1981) determined that to establish the activity of a specific process in the central nervous system, it is important to determine IgM by staging 19S IgM-SPHA. Particular attention is paid to seroconversion due to syphilis in infants whose mothers received antisyphilitic treatment.
The diagnosis of congenital syphilis is often made erroneously in healthy newborns based on the detection of IgG-AT, which enters the child’s blood through the placental barrier from mothers with syphilis.
Additional IgM-AT testing and the use of combinations of different tests are required to exclude congenital syphilis in infants born to mothers treated for syphilis who have positive first serologies but no clinical symptoms.
The passive hemagglutination reaction in the serodiagnosis of syphilis (RPHA), in contrast to RIF and ELISA, is distinguished by its methodological simplicity, speed of obtaining results and high reproducibility. Considering these qualities, RPGA should be used as a screening test for mass examinations for syphilis.
The principle of the method is that when blood serum containing specific antibodies interacts with red blood cells sensitized by Treponema pallidum, their characteristic agglutination is observed. Sensitization of erythrocytes can be produced by antigens of pathogenic and cultural strains of Treponema pallidum.
RPGA is a valuable diagnostic test at all stages of syphilis, and is especially sensitive in late forms of syphilis.
Source: https://health.sarbc.ru/sovremennaya-diagnostika-sifilisa-i-otsenka-rezultatov.html
Hematological (clinical) blood test: interpretation in adults according to the norm in the table
Like other laboratory blood tests, the test is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. Laboratory assistants make a report on the hematological blood test with a detailed transcript. The attending physician receives information on the same day after a few hours or the next day. Common indicators that we want to know after a general blood test include:
- hemoglobin;
- volume of red blood cells;
- color index;
- reticulocyte concentration;
- volume of platelet molecules;
- ESR;
- leukocyte formula, including a transcript of the control blood test for neutrophils (ne).
Hematological blood test (transcript, table)
Important! Today, it is not possible to obtain detailed information according to the clinical picture of the patient’s health condition through another blood test.
CSR blood test: what is it and when is it taken?
It is very important to recognize the disease in time. At some point, a person may be referred for a DAC blood test, which can determine whether a person has syphilis or not.
When is a blood test for CSR prescribed?
Purpose of analysis
There are several indications when it is necessary to donate blood to determine the presence or absence of syphilis in the human body.
Such indications include:
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse (both casual and not). People do not always protect themselves during sexual intercourse, and therefore the risk of contracting syphilis increases several times.
- Preparation before surgery, when it is very important for doctors to know about the general condition of the human body and whether they need to take any extra safety measures to avoid becoming infected themselves.
- Pregnancy, during which it is very important to conduct a complete diagnosis of the expectant mother’s body and understand how great the chances are of bearing the baby. And besides, syphilis poses a danger to the child, and therefore, in some cases, this may prompt termination of pregnancy.
- Pregnancy planning. This process is designed to ensure that future parents consciously undergo examination in order to approach the issue of conception seriously. During this event, all possible diseases are identified, as well as existing infections that need to be treated immediately.
- Ulcers on the genitals, which may indicate the presence of a serious and dangerous disease.
- Copious discharge from the genitals of various types.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, mainly in the groin area.
- A rash on the body that may be accompanied by severe itching.
- Painful sensations in the bone area.
Also, blood testing for syphilis (DBS) is given at every preventive examination for one purpose, in order to detect the problem in time.
Preparing and interpreting a blood test
How to properly prepare for donating blood for a DBS test
It is very important to follow all the doctors’ recommendations in preparing for the test. The reliability of the results obtained sometimes depends on this.
A patient who has received a referral for a CSR test must refrain from eating food at least 8 (and preferably 12) hours before the procedure itself, as this can sometimes lead to either a false-positive or false-negative test.
If a person cannot avoid eating for such a long period of time (for example, diabetics or pregnant women), then it is necessary to exclude tea, coffee, and any juices. You are allowed to drink only plain water (boiled or filtered).
At the moment when scientists received such a method for diagnosing syphilis, it became possible to detect it even with a latent course.
The Wasserman reaction is of particular importance for any venereologist because:
- It allows you to determine even the moment of infection, of course, not with an accuracy of days, but the approximate interval and duration of the disease is quite good.
- It is possible to determine the presence of syphilis even if it occurs in a latent form.
- This is the only normal indicator of how effectively the treatment is proceeding and whether there are positive dynamics.
More information about the analysis can be found in the video.
Also, the doctor is guided by the results of the analysis when carrying out preventive measures at the source of infection, which is also important. Patients are accustomed to the fact that the test result can be either positive or negative. But with syphilis the situation is a little different.
A negative result can occur either in the complete absence of infection or in early primary or late tertiary syphilis.
As for a positive result, it indicates that the infection is present in the body (depending on the accuracy of the indicators), or that the person is at the stage of recovery or in the first year after treatment. That is, when receiving the result of the analysis, it is impossible to say with certainty whether a person is healthy or not. Especially when it comes to patients undergoing treatment.
In the event that a person was not tormented by symptoms and did not undergo any treatment, and his analysis was negative, then this indicates a complete absence of the disease.
False positive reaction
There are a number of diseases and reasons due to which a DAC blood test may show a false positive result. Of course, this shocks a person, but it does not mean hopelessness.
A false positive result may occur in the following cases:
- During pregnancy, since the body is under heavy stress at this moment.
- For diabetes mellitus.
- For tuberculosis of any form.
- In the presence of malignant tumors in the body (oncology).
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages.
- With viral hepatitis, when the liver does not work as the body requires.
- For pneumonia, especially in severe forms.
Also, a false positive result can be observed in people after vaccination, so if you receive such a result, you need to tell your doctor about it. As for false negative results, this is very rare.
A blood test is a very important diagnostic method that allows you to detect the disease in time and begin treatment.
Of course, the disease is not always detected at an early stage. That is why every year, especially if you have had casual sex, you need to take a blood test so as not to bring the disease to a severe stage, at which it is already problematic to be cured.
Source: https://DiagnozLab.com/analysis/clinical-tests/blood/ksr-analiz-krovi-chto-eto-i-kogda-sdaetsya.html
Treatment
The main therapeutic actions in the treatment of this age-related disease are aimed at restoring bladder function. The main thing is to reduce its contractile activity. For each elderly person, individual treatment is selected depending on the type of incontinence. Medications include calcium channel blockers, smooth muscle antispasmodics, and anticholinergic drugs. In case of serious dysfunction of the sphincters, surgery is sometimes resorted to, but this is extremely rare. Treatment of concomitant diseases, such as vaginitis or atrophic urethritis, significantly improves the condition of older people. Obesity also causes involuntary urination, so it is important to reduce body weight.
It is quite possible to combat urinary incontinence in older people. Firstly, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner. Secondly, loved ones can provide significant help. It is necessary to teach an elderly person to use special urological pads that protect against unpleasant odor and urinary dermatitis, and to limit his intake of liquids, especially before bedtime. Urinary incontinence is a manifestation of natural aging of the body, so you need to treat it with understanding. Take care of yourself!
Urinary incontinence is three to five times more common in older women than in men of the same age. “Age-related weakness” of the bladder complicates the life of 80% of the fair sex after 50 years.
Incontinence happens:
- stress (involuntary release of urine when lifting heavy objects, coughing and sneezing, during bouts of laughter);
- urgent, or uncontrollable (an urgent urge to urinate that is difficult or impossible to control);
- mixed.
Up to 40 years of age, stress incontinence worries a little more than a third of women, and they complain of an unbearable urge to urinate in 15-20% of cases. During menopause, half of women with an unruly bladder are diagnosed with mixed pathology.
With age, the muscles of the human body weaken and become flabby, and the bladder, a hollow muscular organ, is no exception. It loses elasticity and no longer holds enough urine. But in women after 40-50 years of age, due to hormonal changes, atrophic changes also affect the urethra and vagina, so they more often suffer from age-related urinary incontinence. During menopause due to lack of estrogen:
- the walls of the urethra become flabby due to a decrease in their tone and they cannot provide additional support to the bladder;
- The walls of the vagina also become thinner, and its muscles weaken and support the urethra less well.
The risk of losing control of urination during menopause is higher in obese women and mothers of many children who gave birth naturally. Due to pregnancy and childbirth, the pelvic muscles that surround and support the urethra, vagina, and rectum become stretched and less elastic. Other risk factors are:
- infections (an inflamed bladder becomes overly irritable and prone to spasmodic contractions);
- foods that irritate the bladder (spicy foods, alcohol, sweeteners) and some medications.
The second reason for urinary incontinence in women after 50 is a change in the cerebral cortex. In older people, it also occurs as a result of neurological diseases, for example, Parkinson's disease, vascular disorders that are caused by severe atherosclerosis.
What tests are there for syphilis?
If syphilis is not treated, the patient's internal organs begin to deteriorate after a few years. A person can suffer for decades, and death will be painful.
An analysis for syphilis allows you to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and prescribe treatment, primarily antibiotic therapy.
How long it will take for treatment depends on the stage of the disease and the correct treatment: at the initial stage, you can get rid of the disease in three to four months. Syphilis cannot be treated on its own.
Characteristics of the disease
Syphilis is caused by a bacterium called Treponema pallidum.
It can penetrate the body even through minor injuries, and although it is transmitted mainly through sexual contact, a person can also become infected through household items.
However, you should know that the bacterium dies after half an hour at temperatures above 48 degrees. This is why sterilization is important.
There are primary, secondary, latent and tertiary stages of syphilis. The first signs of the disease are an ulcer on the skin, which disappears after about 5 weeks .
After two months, signs of secondary syphilis appear in the form of rashes, ulcers and nodules. One of the severe complications of this form is kidney damage.
This condition is accompanied by proteinuria - an increased protein content in a urine test (above 2-3 g/l). The rash usually goes away within a few weeks without treatment.
If the disease is not treated, tertiary syphilis develops. It manifests itself after five years, when internal organs are destroyed. The nervous, cardiovascular systems, spinal cord and brain are affected. The kidneys, liver, stomach, and intestines fail.
The situation is especially dangerous if a person is sick with HIV. Like syphilis, HIV is most often transmitted through sexual contact and is difficult to treat.
At the same time, patients with syphilis are at risk of contracting HIV, and patients with HIV are at risk of contracting syphilis.
If an HIV-infected person catches syphilis, the effectiveness of treatment depends on the stage of the disease: the longer a person is sick with HIV, the greater the risk of developing severe complications of syphilis (especially if the HIV-infected person is not treated).
How is the analysis taken?
If we talk about where blood is taken from for syphilis, the answer is: just like for determining HIV, the material is taken from a vein. Sometimes your doctor may order a finger prick sample, but only for nonspecific rapid tests.
This is due to the fact that many standards are developed for venous blood: in blood taken from a finger, the indicators are different. In addition, you can get less material for study from a finger than from a vein.
If you need to take a sample for syphilis testing from a finger, the same laboratory techniques are used as for a general blood test.
If a finger prick blood test shows the likelihood of Treponema pallidum, a more detailed, extended study needs to be conducted. In this case, blood for syphilis is taken only from a vein: only in this case can a correct negative or positive result be obtained.
This type of analysis, such as a smear, is ineffective in the case of syphilis, as with HIV. The smear does not contain the pathogen at all stages of the disease.
Types of research
To determine antibodies to Treponema pallidum in the blood, the following tests are used:
- RIF or FTA (immunofluorescence reaction) - the absorption reaction of fluorescent antibodies is determined.
- RPHA or TPHA (passive hemagglutination reaction) is a test for syphilis that detects IgM and IgG antibodies.
- ELISA or ELISA - the name stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; it determines the quantitative content of IgG and IgM antibodies.
Syphilis can be detected by treponemal and non-treponemal tests. The first test for syphilis detects antibodies in the blood against Treponema pallidum antigens. The second detects antibodies against tissues that the bacterium has destroyed.
ELISA is an effective test method that is done not only to determine the presence of infection, but also to determine the stage of the disease. In addition, ELISA can answer the question of whether a given person has ever had syphilis. The sensitivity of ELISA can reach 90%.
ELISA analysis allows you to determine antibodies to Treponema pallidum: immunoglobulins - G, M, A. Their concentration allows you to trace the disease process in its dynamics.
Immediately after infection, IgA antibodies are produced to fight the bacterium, and IgM antibodies are produced two weeks later. After a month, IgG appears. When the clinical symptoms of the disease begin to appear, the blood for syphilis shows a sufficient amount of antibodies of all three types.
Research shows that syphilis-specific IgM antibodies decrease dramatically after effective treatment. The peculiarity of IgG antibodies is that the test for syphilis detects them even a long time after treatment and throughout the patient’s life.
Therefore, a positive ELISA result does not always mean the presence of the causative agent of syphilis. A positive test can determine both the stage of development of the disease and the fact that effective treatment has recently been carried out, and therefore antibodies are still circulating in the blood.
A negative ELISA result can mean either the absence of the disease or its early stage.
Passive hemagglutination reaction
RPGA refers to specific treponemal methods for identifying the causative agent of treponema pallidum. When performing an RPHA analysis, during the reaction of antibodies and red blood cells, the latter stick together and precipitate. How many precipitated red blood cells are formed during RPHA is directly proportional to the amount of treponema antibodies.
The sensitivity of RPGA is much more effective in the secondary and tertiary periods of syphilis - 99%, while in the primary the reliability of the analysis is 85%.
The specificity of RPGA allows it to be used to confirm the diagnosis of other tests, such as RPR or MRP. At the same time, RPGA is not as sensitive to the stages of syphilis as ELISA.
Therefore, RPGA and ELISA must be considered in conjunction with each other. A false positive RPHA result is possible in 2.5% of cases.
This is possible due to the similarity of immunoglobulins with other antibodies that are released in some other diseases, for example, autoimmune diseases.
Wasserman reaction
A set of serological reactions (CSR), one of which is known as the Wassermann reaction, is a valuable diagnostic method. It allows both to identify the infection and determine the stage of the disease.
A blood test for syphilis KSR must be supplemented with treponemal-specific methods of analysis (RIBD and ELISA).
To carry out the CSR test, antigens extracted from the heart muscle of cattle are used, which are similar in their properties to Treponema pallidum antigens.
The CSR is not a specific test for syphilis: a positive CSR is possible in patients with tuberculosis, malaria, autoimmune diseases, oncology, during pregnancy and other conditions. It is mandatory to take a test for syphilis during pregnancy, since the presence of this disease in a pregnant woman can lead to a miscarriage or the birth of a child with a congenital disease.
The express method is an accelerated version of the Wasserman reaction. When performing a rapid test for syphilis, a cardiolipid antigen is also used, which is mixed with serum in the recess of a special glass plate.
How long it takes to complete a test often depends on the technique used. Typically, the express method takes about half an hour.
The reaction result of the express method is evaluated in the same way as the DFR, with positive numbers from 0 to +4. The sensitivity of the express method, although superior to the CSR, may give a false positive result due to another disease.
ORS and UMSS are another variant of the Wasserman reaction or express method. The abbreviation UMSS stands for the accelerated method for latent syphilis. ORS stands for selection reaction to syphilis. When performing ORS, the same reagents are used as in the Wasserman reaction.
How to evaluate the result
To obtain accurate data, blood must be tested for syphilis on an empty stomach. The concept of fasting means that at least eight hours should pass between meals.
If the patient came to take the test on an empty stomach, but last ate food less than eight hours ago, he needs to wait. The concept of an empty stomach also means that you should not drink any drinks other than still water before the test.
Tests are taken on an empty stomach not only to diagnose syphilis: this is a general rule.
A negative test for syphilis is indicated by a “-” sign. But a negative result does not always mean that there is no pathogen in the body. More often, a false negative result occurs when decoding rapid tests based on the Wasserman reaction. Therefore, you can relax only when the data from all tests give a negative result.
The highest trust rating among syphilis patients is the PCR result . If the PCR is positive, it means it is truly positive. If the decoding is negative, then it is negative.
But PCR can show a positive result even after successful treatment, since it can determine the presence of both living and dead bacteria. Other tests may also give a false result after successful treatment.
Conservative treatment
Depending on the cause of the pathology, the doctor develops individual treatment tactics for the woman: drug therapy, exercises to strengthen muscles; laser correction or surgery. In mild cases, urinary incontinence in older women can be improved with diet and withdrawal of certain medications.
Drug therapy
The main treatment for incontinence during menopause is hormonal therapy: restoring estrogen levels helps improve the condition of the tissues of the vagina and urethra. If such pills are contraindicated for a woman, she is prescribed a hormonal cream with estrogen, which acts locally and does not penetrate the bloodstream.
Other medications affect the muscles of the bladder and sphincter: they reduce the frequency of involuntary contractions of the bladder, relax the sphincter, and improve muscle tone during atony. Sometimes a doctor prescribes drugs for women over 50 that reduce the amount of urine produced.
Urinary incontinence in menopausal women can be caused by the pills they take to treat chronic diseases. This side effect is caused by some sedatives (they are often prescribed for menopause), diuretics, antihistamines, and stimulants. After stopping the medication, painful symptoms decrease or disappear.
Bladder training and exercises
Bladder training helps teach the bladder to empty itself “on a schedule,” gradually increasing the intervals between urinations. Her technique is simple:
- in the first days of classes, visit the toilet on a schedule, every 30-60 minutes, without even feeling the urge. If it occurs at the wrong time, switch your attention, try to relax and be patient;
- after a few days (you will feel it yourself when you are ready), increase the intervals between urinations by half an hour and stick to this schedule for another week. Then increase the interval again. After a month and a half, the bladder will become accustomed to holding urine for at least four hours.
Kegel exercises strengthen the pelvic muscles, which support the bottom of the bladder. Their first results are noticeable after a month, the full course of exercises takes six months.
Laser therapy
At the initial stage of stress incontinence in menopausal women, the Incontilase erbium laser is used. By acting on the anterior wall of the vagina, it activates the growth of collagen fibers around the urethra. By becoming less mobile, the urethra stops sagging and holds urine better.
The procedure is painless, does not require prior preparation and has no contraindications. Its duration is from 20 minutes to half an hour, and after treatment the woman can go home. Laser correction of urinary incontinence during menopause gives results immediately, but to consolidate it, two treatment sessions are performed.
Reasons for the decrease and increase in the content of red blood cells in the blood
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
The designation of rbc in a blood test is erythrocytes, red blood cells. These are cells without a nucleus that carry out gas exchange between the body and the external environment. Red blood cells transport oxygen and carbon dioxide using the pigment hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein molecule that contains iron. The shape and size of red blood cells, their number are indicators of a person’s overall health.
General information
Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow from erythroid cells. To perform its main function, the red blood cell, when released into the bloodstream, loses its nucleus and remnants of nucleic acids.
A red blood cell normally remains viable for about 120 days, after which it is destroyed in the spleen. Red blood cells that have an irregular shape or are too large die faster. When foreign antigens are expressed on its surface, the red blood cell is also destroyed.
Red blood cells can be destroyed in blood clots, during sludge (clumping of formed elements) of blood, hemorrhages, or when they are damaged by the wall of implant valves. Red blood cells are elastic, as a result of which they can pass through small capillaries, and have a negative charge, so they repel each other and the endothelium of the vessel. Sometimes rbc can travel through the bloodstream in the form of coin columns, sticking together.
Red blood cells are sensitive to hemolytic poisons (acetic acid, lead) and low blood osmolarity.
The proliferation of red blood cells is influenced by sex hormones and erythropoietin. Erythropoietin is formed in the kidneys during bleeding. Stimulates the formation of more red blood cells and the lack of oxygen or thin air in the mountains.
Male sex hormones increase proliferation in the erythroid sprout of the bone marrow, while female sex hormones suppress the synthesis of red blood cells.
The rbc norm in a general blood test for men is from 4.0 to 5.1 trillion/l. In women there are fewer of them in the peripheral blood - from 3.7 to 4.7 trillion/l. In children, the normal rbc level is 3.8–4.9 trillion/l.
A decrease in the number of red blood cells (erythropenia) may occur for the following reasons:
- All types of anemia, including aplastic and posthemorrhagic, hemolytic.
- Leukemia.
- Bleeding of any nature.
- Pregnancy.
- Tumors or metastases localized in the bone marrow.
- The presence of foci of infection in which diapedesis (leakage) of formed elements (in particular, red blood cells) occurs through the vascular wall into the tissue. It is observed, for example, with pneumonia in the red hepatic stage.
- Myxedema.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Hemolytic disease of newborns.
- Poisoning with hemolytic poisons.
- Deficiency of iron and B vitamins (folate, cobalamin).
A condition such as erythrocytosis, i.e. an increase in the number of red cells in the blood, occurs under the following circumstances:
- Dehydration. At the same time, the hematocrit also decreases.
- With kidney diseases, such as polycystic disease, the production of erythropoietin increases.
- Adaptation to thin air or respiratory failure (with asthma, obstructive bronchitis).
- Vaquez disease (erythrocytosis).
- Cushingoid syndrome with adrenal hypersecretion or treatment with glucocorticoids.
- Heart defects.
- Chronic lung diseases.
- Erythremia (blood disease).
- Stress.
- Drinking poorly purified, highly carbonated, overly chlorinated water.
- Radiation therapy.
A general blood test also shows the number of young erythrocyte forms - reticulocytes. These cells also contain remnants of nucleic acids that look like a network, which is why they got their name. The number of reticulocytes in the blood is normally 30–70 billion, i.e., 0.5–1.2% of the total number of red blood cells.
Reticulocytosis, i.e., an increase in the level of reticulocytes, is caused by:
- Hypoxic conditions.
- Hemolytic, posthemorrhagic and other anemias.
- Recovery after eliminating iron deficiency and lack of cobalamin and folic acid.
Reticulopenia is observed under the following circumstances:
Why do you feed pharmacies if hypertension is afraid of the usual like fire...
Tabakov has revealed a unique remedy against hypertension! To reduce blood pressure while preserving blood vessels, add to…
- Deficiency of folates and cobalamins, iron.
- Damage to the bone marrow by metastases, radiation and the effect of drugs on it (cytostatics, chloramphenicol).
- Aplastic and hypoplastic anemia.
A comprehensive clinical blood test includes determination of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). ESR increases with a decrease in blood viscosity and albumin concentration, an increase in the content of fibrinogen and immunoglobulins, and inflammation processes. The rate of sedimentation decreases with erythrocytosis and obstructive jaundice.
The norm for men is 1–10 mm/hour, for women—2–15 mm/hour.
Erythrocyte indices: decoding
In addition to rbc, a clinical blood test also determines various erythrocyte indices.
MCH index - hemoglobin saturation of erythrocytes. This indicator is directly proportional to the CPU multiplied by 0.03.
Red blood cell index MCHC (decoding): average saturation of red blood cells with hemoglobin. A decrease in this indicator leads to the decoding of the blood picture as iron deficiency anemia.
Deciphering MCV in a clinical blood test: average red cell volume.
The RDW index shows anisocytosis, i.e. the appearance of red blood cells of different sizes in the blood.
Target organs in hypertension: disorders in hypertension
Hypertension (HD) or arterial hypertension (AH) is a very insidious and common disease.
Abnormal hypertension is the foundation for most cardiovascular problems and other diseases in the body.
Cardiovascular diseases lead among all causes of mortality in the world, in particular, such statistics are observed in developed countries. Therefore, this disease is being closely studied by scientists around the world.
The range of medications to maintain normal blood pressure and relieve all manifestations of hypertension is quite wide. Recently, new, safer and more effective drugs have appeared. A qualified cardiologist or therapist will always help you choose a treatment algorithm.
Why does GB occur?
Hypertension occurs due to a severe reboot in the emotional sphere of human activity.
Multiple unfavorable mental factors affect functionally active areas of the brain, thereby causing an imbalance in the functioning of neurons.
The nervous and humoral regulation of all processes responsible for the narrowing and relaxation of blood vessels is disrupted. The vessels are no longer able to maintain normal pressure. Thus, arterial hypertension develops.
There is no reliable data on the etiology of the disease, that is, it still remains an idiopathic disease.
Despite this, there are a number of contributing factors to the occurrence of the disease:
- Age characteristics. The older a person is, the greater the risk of blood pressure problems.
- Gender. Men get sick more often than women.
- Low physical activity.
- Consumption of large amounts of salt.
- Abuse of strong alcoholic drinks.
- Low intake of calcium from food.
- Smoking.
- Excess weight.
- Hereditary predisposition.
In addition, diseases associated with metabolic disorders, including diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis, can be factors in the occurrence of the disease.
The disease selectively affects certain organs.
The following organs are located in the area of severe damage:
- heart;
- vascular system;
- brain;
- kidneys;
- retina of the eyes.
Damage to target organs during arterial hypertension contributes to ischemia and necrotic changes in them.
What is at risk with hypertension?
on
Heart. The vital “pump” of the human body is extremely difficult to tolerate hypertension. In response to persistently high blood pressure, the left ventricle enlarges or hypertrophies. It is difficult for the myocardium to push blood into constricted vessels.
In addition, the arterial blood flow of the myocardium cannot cope with its function, the heart constantly experiences ischemia, and the cells reduce their activity. The heart is under constant tension, that is, full diastole never occurs. If there is no full diastolic pause, the contractile forces of the myocardium quickly dry up. This is how cardiac failure develops.
Vascular system. Since the pathological process is predominantly located in the vessels, they cannot remain intact. The wall of an arterial vessel consists of three walls: internal (endothelium or intima of the vessel), middle (muscular) and external (connective tissue). Thanks to the muscle wall, the vessel contracts and relaxes, and its lumen changes. With hypertension, the muscularis is constantly in the constriction phase. As a result, restructuring and sclerotization of blood vessels occurs. In the future, the affected vessels will not be able to relax on their own.
Brain. Since nervous tissue is highly active, it is permeated lengthwise and crosswise with vessels. The vessels of the brain are no less susceptible to changes than everyone else. They become sclerotized and distorted. The most dangerous manifestation of involvement of the brain in the pathological process is hemorrhagic stroke. It manifests itself as hemorrhage in the brain tissue. An ischemic stroke may occur. It occurs when the vessel narrows too much, resulting in oxygenated blood not being supplied to the tissue. Against the background of prolonged ischemia, necrosis develops.
With prolonged headache, hypertensive encephalopathy may develop. It can be acute or chronic. In acute cases, all functions and consciousness are sharply disrupted. In the case of a chronic course, impaired cognitive function and dementia come to the fore. Memory, attention, speech are impaired. Paresis and paralysis may occur. Quite often, a hypertensive crisis is the cause of most vascular accidents in the brain.
Kidneys. The nephron or renal corpuscle contains a highly active vessel. The kidney contains a huge number of nephrons, which means many vessels. If renal blood flow is impaired, filtration and purification of the blood from toxins will be impaired. If the filtration and concentration functions of the kidneys fall, renal failure will arise and begin to progress.
The first sign of chronic renal failure is the appearance of albumin in a urine test. This indicates that the integrity of the filter has already been compromised. The higher the concentration of protein in the urine, the worse the kidney function. In addition, creatinine clearance decreases. The level of creatinine in the blood determines the degree of renal failure.
Retinal damage. Since the target organs contain a developed vascular network, with arterial hypertension, the visual organ is highly susceptible to changes. The retina suffers the most. As a result, visual acuity decreases, up to complete blindness.
Symptoms of hypertension and diagnosis of damage
Hypertension is characterized by the occurrence of certain symptoms that characterize the progression of the disease.
The classic symptoms and syndromes of the disease are:
- Dizziness and loss of consciousness. This symptom complex occurs in connection with short-term cerebral ischemia.
- Severe headaches. Their occurrence is associated with impaired microcirculation of the blood vessels of the head.
- Facial hyperemia. This phenomenon occurs due to the reflex expansion of the vascular network of the face.
- Palpitations and high heart rate
- Anxiety, concern
- Chills or fever
- Throbbing sensations in the head
- Nervousness
- Swelling of the face
- Flying flies before your eyes
- Numbness of the distal extremities
Diagnosis of damage is carried out using special laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
The most informative methods of examining the body are the following:
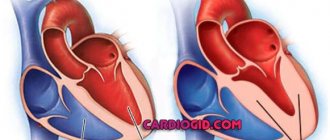
- ECG is the most accessible and acceptable way to diagnose myocardial damage; using an ECG tape, the doctor can evaluate the contractile function of the heart, rhythm, conductivity, identify the presence of hypertrophy of the left side, and even detect a heart attack;
- electrocardiographic study with stress, used to diagnose coronary artery disease.
- EchoCG - a technique that allows the attending physician to assess the condition of the cavities of the heart muscle;
- MRI, CT;
- Ultrasound of neck vessels, a method that allows you to examine the condition of neck vessels and measure the thickness of their walls;
- determining the difference between the upper and lower pressure readings;
- measurement of pulse wave speed;
- ophthalmological screening of the retina, if the organs of vision are affected, bruising, fluid accumulation and swelling of the optic nerve nipple can be detected;
- biochemical blood test with mandatory examination of the renal complex, lipid spectrum, electrolytes, etc.;
- A urine test is performed to detect hematuria, albuminuria, and impaired renal concentration function;
- Ultrasound of the obstructive system and kidneys;
- Ultrasound of head vessels;
- daily ECG monitoring;
- constant monitoring of blood pressure with entering the obtained data into a special table;
- arteriography – to assess the condition of the arteries;
- Doppler study - belongs to ultrasound diagnostic methods and is used to clarify the localization of the process and the state of blood flow
For effective treatment of hypertension, the following algorithms are used:
- Therapy will be most effective if it is started in the early stages of the disease.
- The first thing the patient should do is change his lifestyle. Establish a rest and work schedule, get rid of bad habits, rationalize your daily routine, and increase physical activity.
- A balanced diet is the key to a healthy cardiovascular system. First of all, it is necessary to reduce the amount of salt, fat, and fast carbohydrates consumed.
- Antihypertensive drug therapy. Just a few years ago there was a global presentation of the latest drugs for the treatment of hypertension. Several patient management regimens are used to treat hypertension. During therapy, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, diuretics, alpha and beta blockers and other groups of drugs are used.
Treatment of hypertension and its consequences requires therapeutic measures over a long period of time. The “target” for therapy is blood pressure.
A competent specialist always prescribes therapy in accordance with national protocols and international standards.
It is possible to determine the lesion and identify what stage it is at using ophthalmological examination methods. At an early stage of arterial hypertension, a specialist during examination can identify the Salus symptom.