Experts call inflammation of the lacrimal duct dacryocystitis. This disease is often the result of an infection and can be acute or chronic. Due to certain anatomical features, dacryocystitis most often occurs on the left side. The infection rarely begins in the eye, more often in the nasal cavity.
Very rarely, congenital dacryocystitis can develop. This is a serious disease: since the child has a poorly formed orbital septum, there is an increased risk of infection spreading (orbital cellulitis and its complications). Inflammation of the lacrimal duct occurs more often in women, less often in men.
A little about morphology
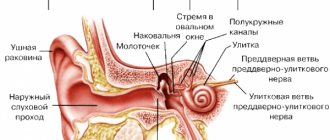
The tear duct is a system of small channels located in the inner corner of the lower eyelid, designed to drain excess secretion (tear fluid). Normally, this liquid has antibacterial properties; first it washes the eye, then it moves to the inner corner of the eyeball. Through the lacrimal canal, the fluid passes into the lacrimal sac and descends into the lower choana along the nasolacrimal canal, and it drains tears and participates in the aeration of the passages and sinuses of the nose.
The fetus has a film between the nasal cavity (canal) and the eye, which then must rupture. Sometimes this does not happen, then fluid stagnation occurs in the tear duct system. This is often observed in infants. When it stagnates, the liquid loses its antibacterial properties and an infection develops. The walls of the lacrimal sac begin to gradually stretch and sluggish chronic inflammation occurs, which is what dacryocystitis is.
The liquid changes from clear to cloudy and mucopurulent.
The purulent process develops in the lacrimal canals and lacrimal gland. In adults, such stenosis and blockage of the lacrimal canal occurs after colds of the nasopharynx or otitis media. Since lacrimal drainage is impaired, the concentration of fluid in the lacrimal sac increases, and infection and inflammation of the lacrimal sac occurs. Due to dacryocystitis, tear fluid gradually seeps into the sinuses.
Surgical treatment options for dacryocystitis
The patient is operated on if the disease is diagnosed too late or progresses.
Methodology and effectiveness of bougienage
A common method of intervention is bougienage with a probe. We budge, that is, during the procedure, a rigid probe breaks through the blockage that has gotten into the tear ducts. The tear duct, intended for the outflow of fluid, becomes slightly wider. As a result, cross-country ability improves.
Dacryocystoplasty and endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy
Balloon dacryocystoplasty is performed using a guidewire with a microscopic balloon. The entire structure is carefully inserted into the hole located in the corner of the eye. The expansion balloon is brought to the place of narrowing (blockage) of the canal.
Under pressure, it ruptures and the tear fluid contained in it presses on the walls of the lacrimal duct and pushes them apart. The structure is then removed. The surgery does not require general anesthesia.
A laser is used to perform endoscopic dacryocytorhinostomy. Using it, the doctor removes the mucous membrane of the lateral wall of the nose in the projection of the lacrimal sac, in order to then form a hole with a diameter of 5 mm in another part of the organ.
Reference! The operation is painless for the patient, does not require subsequent, long-term medical supervision, gives a good result, and does not leave a cosmetic defect.
Etiology of the phenomenon
The most common causative agents of inflammation of the lacrimal canal in adults are opportunistic microorganisms - Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus. Diseases that lead to their activation: sinusitis, otitis, ARVI, inflammation of the maxillofacial area, tonsillitis, congenital defects of the tear duct.
Tear ducts can also be clogged with your own stones (calcifications). With dacryocystitis, the causes may lie in injuries, foreign bodies and inflammation of the eye, pathologies of the nose in the form of a deviated septum, injuries and fractures of the nose, polyps, rhinitis, shell hypertrophy, the presence of lacrimal stones (dacryolite) in different parts of the lacrimal drainage system. In older people, atherosclerosis can cause dacryocystitis, when bad cholesterol is deposited on the walls of even small ducts such as the tear ducts.
In newborns, inflammation of the lacrimal sac is not uncommon; its causes are congenital stenosis of the nasolacrimal canal, the membrane of the canal, gelatinous plug in the same place, infection of the duct, which causes obstruction of the lacrimal canal. The pathology can be aggravated by allergies, diabetes, working with caustic volatile mixtures, changes in external temperatures (for example, in the cold, a spasm of the tear ducts may occur; in such cases, wearing glasses helps), long exposure to dust.
There is acute and chronic dacryocystitis.
A separate group is dacryocystitis of newborns. The acute form involves the presence of an abscess or phlegmon. According to etiology, dacryocystitis is divided into bacterial, viral, post-traumatic, parasitic, chlamydial.
Causes
The main reason for the development of dacryocystitis is a violation of the patency of the nasolacrimal duct as a result of narrowing or complete closure. Such pathological deviations lead to problems with fluid circulation. As a result, pathogenic microorganisms develop in the cavity of the blocked lacrimal canal due to stagnation of secretions.
Viral diseases, such as sinusitis, rhinitis or respiratory infections, can provoke swelling of the tissues of the nasolacrimal duct. But there are other reasons for the development of dacryocystitis:
- effects of low or high temperature on the body;
- contact with hazardous chemicals that negatively affect the functioning of the visual system;
- the body's reaction to various allergens;
- decreased immunity;
- elevated blood sugar levels;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- foreign objects entering the eye;
- benign neoplasms in the nasal cavity;
- mechanical damage to the lacrimal canals;
- nose fracture
Dacryocystitis is often diagnosed in newborns. This is due to the structural features of the tear ducts in infants in the first months after birth.
While in the womb, children's tear ducts are closed by a membrane, which under normal conditions ruptures at the time of birth or a short time after birth. In some pathologies, this membrane can persist for a long time even after birth, which leads to the accumulation of tear secretions in the eye canal and the formation of pathogenic microflora.
In adults, dacryocystitis also occurs, but much less frequently. Females are more susceptible to this disease than males. The reason here is the structural features of the tear ducts in women. One of the causes of the disease in women may be the abuse of cosmetics, many of which provoke the formation of inflammatory processes inside the tear duct.
Watch a video about the disease:
Symptomatic manifestations
For children, a chronic process with exacerbations is more common. Symptoms begin with the appearance of swelling along the tear duct, the skin over the site of inflammation becomes tense, becomes red and shiny. Since there are no connective tissue partitions in the area of the bridge of the nose, diffuse swelling appears involving the back of the nose and cheeks - a sign of acute dacryocystitis.
Inflammation often appears on one side, but if one eye is inflamed, the other side may well be involved in the process. In this case, there may be pain around the affected area, constant and severe lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids, dizziness, and loss of appetite. The aching pain when touched becomes sharp, jerking in nature, in the orbital area.
After 2-3 days, the swelling becomes soft, fluctuates, and the skin turns yellow - this is a sign of a developed abscess.
Pus discharge appears, and the slit of the eye narrows due to swelling. When the process of acute dacryocystitis transitions to chronic inflammation, the symptoms are moderate. But persistent and profuse lacrimation, redness, swelling of the eyelids and pus discharge remain. A persistent oblong swelling remains under the eye on the affected side, and when pressure is applied to it, pus and mucus are released through the lacrimal opening. The lacrimal sac is stretched (sac ectasia), enlarged, thinned. When the abscess spontaneously opens, a purulent fistula is formed. With drainage, the fistula may close after a few days. Sometimes the only symptom may be chronic watery eyes.
Newborns are required to be examined by an ophthalmologist while still in the maternity hospital. After the baby is born, Albucid is dripped into the eyes, acting as an antiseptic until the baby's eyes become stronger. Only in 5–7% of cases may probing of the eyes be necessary, and then only in cases of infection or rare pathology. In infants, symptoms may include:
- redness of the skin around the lacrimal sac;
- hyperemic conjunctiva;
- swollen and edematous eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- pus discharge;
- sticky eyelashes after waking up.
Secondary signs:
- temperature;
- cry;
- moodiness;
- child's anxiety;
- breast refusal.
If you have any of the above symptoms, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Clinical picture
Acute dacryocystitis
Signs of the disease are observed over the lacrimal sac area, but can also spread to the nose and face. Symptoms may include:
- excessive amount of tears (lacrimation) – almost always;
- pain;
- redness;
- edema.
Patients may complain of decreased visual acuity due to excess tears and their pathological composition. Upon examination, you can detect painful, tense, red swelling. Mucopurulent fluid may be released from the lacrimal openings. The patient may experience an increase in temperature and an increase in leukocytes in the general blood test.
Chronic dacryocystitis
This disease can manifest itself as constant or recurring lacrimation, redness of the inner canthus, and swelling over the lacrimal sac. If you press on this area, mucopurulent fluid may be released through the lower lacrimal punctum.
Both chronic and acute inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct can lead to its obstruction. Since tears cannot be eliminated correctly, they stagnate in the drainage system and contribute to the development of bacteria, viruses and fungi. These microorganisms lead to permanent eye infections.
Diagnostic measures
With dacryocystitis, diagnosis is not particularly difficult. At the appointment, the doctor must examine and palpate the lacrimal sac. An installation test with fluorescein, an X-ray of the duct with contrast, and a Vesta nasolacrimal test are also performed. With dacryocystitis, the eye is swollen and there is severe lacrimation. Palpation of the lacrimal openings is characterized by pain and discharge of pus.
The conductivity of the canals is determined by the West test: a cotton swab is placed in the nasal passage on the affected side, and collargol is dripped into the eye. Normally, after 2 minutes the tampon becomes stained with traces of a dark liquid—collargol. If this does not happen or the time of appearance extends to 7–12 minutes, this indicates that there is an obstruction of the lacrimal canal. And if the tampon is not colored even after 15 minutes, the result is considered negative and the canal is already completely obstructed.
To find out the extent of the lesion and its level, diagnostic probing is performed.
A passive nasolacrimal test is performed: when trying to rinse the nasolacrimal duct, the solution comes out through the lacrimal openings, and not through the nose - obstruction of the lacrimal canal. To determine the form (causative agent) of dacryocystitis, a smear is taken for microflora followed by bacterial culture, rhinoscopy is performed (determination of nasal pathologies that could affect processes in the eye), and eye diagnostics under a microscope.
Diagnostics
Dacryocystitis has characteristic symptoms, thanks to which diagnosis does not cause difficulties for doctors. Examination of the patient begins with palpation of the lacrimal sac. It is needed to detect the presence of purulent secretion.
The West test is the next step. What is its essence? The technique is carried out according to the following scheme: medical solutions (protargol, collargol) are injected into the patient’s conjunctiva.
At the same time, a turunda is inserted into the nasal sinus. The injected drug should color the tear ducts within five minutes. By the delay in the entry of the solution into the nasal cavity, doctors can easily judge the degree of narrowing of the ducts.
Diagnosis using contrast radiography shows the level of fusion of the lacrimal canals. The causative agents of the disease are identified by bacteriological culture.
In addition to the examination, the patient may be examined by a neurologist, neurosurgeon, dentist and otolaryngologist.
Possible complications
Chronic dacryocystitis in adults is considered dangerous, because it can lead to inflammation of other membranes of the eye (endophthalmitis, for example). The cornea may be involved in the process, then an ulcer appears on it, which subsequently turns into a cataract. It creates not only a cosmetic defect, but also reduces vision.
Phlegmon of the orbit may occur; its contents are not always poured out; this can also happen into the brain. When the membranes of the brain become inflamed, it can result in meningitis and sepsis. Such consequences are observed in the absence of treatment.
Complications of dacryocystitis
Complications usually involve the spread of an infectious process, which can be superficial (eg, cellulitis), deep (orbital cellulitis, orbital abscess, meningitis) or generalized (sepsis). They are rare and are mainly observed in people with poor immunity or in cases of congenital dacryocystitis.
If dacryocystitis is present, intraocular surgery (for example, cataract removal) should be postponed until it is cured, since there is a high risk of developing endophthalmitis. There are also complications associated with dacryocystorhinostomy:
- unsuccessful operation;
- formation of scars on the skin;
- nosebleeds;
- cellulite;
- discharge of cerebrospinal fluid through the nose.
Principles of treatment
If treatment for dacryocystitis in adults is started early, it can be done on an outpatient basis. In more advanced cases, when an abscess develops, treatment is carried out in surgery: the abscess is opened, washed with antiseptics (furacilin, dioxidin, hydrogen peroxide) several times a day, and if necessary, drainage is placed.
Washing is a long process, taking from half an hour to several hours. After the complete disappearance of pus, for dacryocystitis, drops with antibacterial properties are prescribed immediately: Levomycetin, Sulfacetamide, Miramistin, cephalosporin drugs, aminoglycosides, beta-lactams; antibacterial ointments - Floxal (not used during pregnancy), Dexamethasone, Ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin. Drops for dacryocystitis are combined with oral antibiotics.
The treatment complex includes NSAIDs, B vitamins, and dry heat.
To consolidate therapy, after the end of the acute period, physiotherapy is prescribed: UHF, ultraviolet irradiation, massage, warm compresses. If conservative treatment has no effect, then surgery is necessary: dacryocystorhinostomy or dacryocystoplasty. If there were symptoms of general intoxication during the abscess, then the nasolacrimal duct is opened and bougienage and antibacterial therapy are carried out. For dacryocystitis, conservative and surgical treatment go hand in hand, and they are often combined.
Bougienage is an operation to cleanse the canals of pus: a probe (bougie) is inserted into the lacrimal opening. He expands the narrowing of the canal, the procedure is quite painful, and therefore requires intravenous anesthesia.
Dacryocystomy - with this type of surgery, a valve is formed in the tear duct to prevent the formation of pus. Before this, the pus is simply squeezed out of the bag and then antibacterial drops are dripped, all this for 2 days. If there is no result and the process has become chronic, surgery is performed. For dacryocystitis in adults, surgeons carry out treatment only under intravenous anesthesia, because the procedures are painful.
Dacryocystorhinostomy - creates a connection (anastomosis) between the nasal cavity and the lacrimal duct. In this case, the pus cannot accumulate and is removed outside.
Methods of conservative treatment
Treatment of the pathology depends on the causes and form of dacryocystitis. Its goal is to restore the patency of the tear ducts and provide therapy to restore the lost function of the ducts.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
At the initial stage, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, vasoconstrictor drugs in the form of ointments or drops. To reduce the activity of bacteria, Floxal (active ingredient ofloxacin) is often used. The medication is used during the operation for two weeks. The dose of the medicine is prescribed by the doctor.
Photo 1. Sofradex eye and ear drops, 5 ml, from the manufacturer Sanofi Aventis.
To relieve inflammation and swelling of the ducts, Sofradex and Chloramphenicol drops are used. In acute forms of the pathology, they are replaced with Cefucrosime.
Elimination of infection is facilitated by sanitation (cleaning) of the conjunctiva using solutions of Neomycetin, Levomycetin, and sodium sulfacyl. The effect is enhanced by the administration of corticosteroid drugs in combination with Prednisolone and other hormonal agents.
Massage, rinsing, compresses, UHF procedures, vitamins
To consolidate therapeutic therapy, the patient is prescribed vitamins, lavage of the nasolacrimal duct, UHF, and massage.
The latter, in fact, is not a massage. The purpose of the procedure is to stimulate the tear duct and empty the lacrimal sac.
The massage is carried out with gloves and is accompanied by the introduction of medical products into the tear ducts, which are prescribed by an ophthalmologist. The massage algorithm for dacryocystitis is as follows:
- Use a finger to slightly squeeze the inner area of the eye, turn it (usually the index finger) towards the bridge of the nose, and then compress the area of the lacrimal sac to cleanse it of purulent fluid.
- After squeezing out the pus, the lacrimal canal is instilled with furatsilin.
- The purulent liquid and residues of the product are wiped off with a cotton pad.
- The area of the lacrimal canal is massaged again, while making jerking movements in the direction from the inner corner of the eye down.
- Massage actions are repeated 5 times.
- The tear duct is instilled with an antibacterial agent.
Stimulation is carried out every day, 5-6 times, for two weeks.
Attention! Rinsing the lacrimal canal is more correctly classified as a procedure aimed at diagnosing the disease. With its help, passivity of the lacrimal duct is usually established. True, sometimes through systematic washing they achieve partial expansion of the lacrimal canal.
Folk remedies
The use of traditional medicine is effective for congenital dacryocystitis or in case of early diagnosis. Most often, eyebright and Kalanchoe pinnate are used for therapy. The juice of the latter disinfects the lacrimal ducts.
Before use, the leaf of the plant is torn off, washed, wrapped in a cloth to dry and cooled in the refrigerator from several hours to a day. Next, the plant leaf is crushed and the juice is squeezed out. It cannot be used in high concentrations. Therefore, the finished juice is diluted with saline solution in a 1:1 ratio. And only after that half a pipette is dropped into each nostril.
Photo 2. Eyebright extract, 40 capsules, 0.4 g each, from .
Eyebright is used according to the instructions. This is a ready-made drug in the form of tablets and tinctures. To enhance the effect, the liquid is mixed with homemade decoctions of walnuts, fennel, and chamomile. The solid form of the drug is taken orally. The tablets can also be dissolved in water to be used as a daily eye wash as directed by your doctor.
Treatment of children
Inflammation of the lacrimal canal in children has its own specific treatment. Some parents themselves begin to drop the drops they have chosen into the child’s eyes according to their own judgment or the advice of a pharmacist; this can sometimes give an effect, but it is temporary. Only a doctor should treat a child's eyes. The only thing parents can afford at home when the eye sac is inflamed is wiping the sore spot with a napkin soaked in chamomile decoction, which has a good antibacterial effect.
In children, massage is often used for 2-3 weeks, especially if the outflow is obstructed by an existing unruptured ocular membrane.
If this does not help, bougienage is prescribed - the membrane is cut with a very thin rod.
Or balloon dacryocystoplasty is used. Then repeated therapeutic lavage of the canal is carried out, which can take 2 weeks. For purulent processes, massage is no longer prescribed.
Inflammation of the lacrimal duct: causes, symptoms, treatment, massage
Inflammation of the lacrimal canal (dacryocystitis) is a pathological condition in which fluid cannot pass through the canal of the lacrimal gland. Sometimes the duct simply becomes clogged. As a result, tears penetrate into the paranasal sinuses and stagnate there, creating ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microorganisms. Inflammation occurs in acute and chronic forms.
Reasons for appearance
Dacryocystitis occurs in the presence of physiological pathologies, namely congenital narrowing of the duct (stenosis). Sometimes doctors detect a complete blockage of the tear duct.
The main causes of the disease:
- Trauma to the eyes or paranasal sinuses.
- Inflammatory process of the nose, which provokes swelling of the tissues around the eye.
- An infectious process caused by bacteria and viruses, which leads to blockage of the duct.
- Getting foreign particles into the eye or working in dusty and smoky rooms. As a result, the channel becomes clogged.
- Allergy to exposure to an irritant.
- Reduced protective properties of the body.
- Overheating and hypothermia.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
Very often this pathology occurs in newborn babies. This is due to the structural features of the tear ducts. When the baby is in amniotic fluid, the tear duct is closed with a special membrane, which must rupture during or after childbirth. This process does not occur if pathology occurs.
Tears collect in the canal and this provokes an inflammatory process. It mainly develops in women. Men are also no exception, but this pathology is detected very rarely in them. The reason is differences in the structure of the lacrimal canal.
Women use cosmetics, most of which cause inflammation.
Symptoms of the disease
Tears are necessary for the normal functioning of the visual organs. They moisturize the cornea of the eye, protect against mechanical irritants, and perform an antibacterial function.
Sometimes tears stop flowing, this is the first sign of tear duct obstruction. Treatment is one way to cope with the problem and prevent the development of canaliculitis. Sometimes massage of the tear duct helps.
Main symptoms:
- painful and unpleasant sensations in the eye area;
- redness of the skin around the eye;
- feeling of squeezing and bursting;
- swelling of the skin;
- lacrimation;
- edema;
- vision problems;
- increased secretion of mucus, which smells bad;
- formation of pus;
- high body temperature;
- intoxication of the body.
The acute stage of dacryocystitis appears as an inflammatory process affecting one eye. In the chronic stage, the tear duct swells, the eye turns red and the number of tears increases.
If you experience such symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Blockage can occur in both acute and chronic stages. The accumulation of tear fluid increases the likelihood of infectious processes.
Ointments and drops that have an antibacterial effect:
- Phloxal . Antibacterial drug with a wide spectrum of effects. Fights the inflammatory process. The course of treatment is 10 days, two drops twice a day.
- Dexamethasone . Drops with an antibacterial effect. Effective against infectious processes. Instill 5 times a day. The required dosage and course of treatment are selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Levomycetin is a hormonal drug. Used for allergic reactions and inflammations.
- Ciprofloxacin . Prescribed for infections of the lacrimal duct. Buried every three hours.
The drugs have contraindications and side effects.
Drug therapy is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
If the treatment does not have a positive effect, bougienage is performed - cleaning the lacrimal canal from purulent contents;
You can quickly cope with the disease only if treatment is started in a timely manner. If symptoms are negative, you should visit an ophthalmologist.
Radical ways to fight
If there is no positive effect from drug treatment, or if the cause is a tumor or cyst, surgical treatment is performed.
Surgical intervention happens:
- Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy .
A device with a camera is inserted into the duct. A puncture or incision is made using an endoscope. A special valve is created, the main purpose of which is drainage. The recovery period is 7 days. In parallel, antibiotic therapy is carried out to prevent the risk of developing an inflammatory process. The main advantage is the absence of visible marks after the operation. - Balloon dacrycytoplasty is an intervention that, due to its safety, is performed even on newborns.
A conductor with a reservoir filled with liquid is inserted into the channel. Allows you to expand the area, thereby breaking through it. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia. During the rehabilitation period, special drops and antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Massage scheme:
- Press on the outer corner of the eye, turn your finger towards the bridge of the nose.
- Gently press and massage the lacrimal sac, removing purulent masses from it.
- Instill a warm solution of furatsilin and remove the discharge.
- Carry out pressing and massaging movements along the tear ducts.
- Jerky movements along the nasolacrimal sac with some force to open the canal and extract the discharge.
- Instill a solution of chloramphenicol.
In case of obstruction, the technique is carried out up to five times a day.
Folk remedies:
- Aloe. For inflammation, it is good to instill freshly prepared aloe juice, half diluted with saline solution.
- Eyebright. Cook in the same way. Use for eye drops and compresses.
- Chamomile. Has an antibacterial effect.
You need to take 1 tbsp. l. collection, boil in a glass of boiling water and leave. Use to wash eyes. - Thyme . Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, the infusion is used for dacryocystitis.
- Kalanchoe. Natural antiseptic.
Cut off the leaves and keep in the refrigerator for two days. Next, extract the juice and dilute it in a 1:1 ratio with saline solution. This remedy can be used to treat children. Adults can instill concentrated juice into the nose, 2 drops each. The person begins to sneeze, during which the tear duct is cleared of pus. - Leaves from a rose .
Only those flowers that are grown on your own plot are suitable. You will need 100 gr. collection and a glass of boiling water. Boil for five hours. Use as lotions. - Burda ivy-shaped . Brew a tablespoon of herb in a glass of boiling water, simmer for 15 minutes. Use for rinsing and compresses.
- Bell pepper . Drink a glass of sweet pepper fruit every day. adding a teaspoon of honey.
Proper massage
How and what to do to properly massage a child? Before it is carried out, hands are washed with soap and wiped with an antiseptic. The mother should be taught massage techniques by a doctor. Using a cotton swab, pre-moistened in a solution of furatsilin, first squeeze out the pus from the child’s eyes. Then a massage is performed. It should be done before feeding, at least 4 times a day. The movements should be light, circular, soft, this is how they try to squeeze out pus or other secretions. Upon completion of the procedure, the eye is wiped again with a moistened swab and antibacterial drops are instilled.
If all methods are unsuccessful, then at 2–3 years the child undergoes dacryocystorhinostomy. It can be carried out using the endoscopic or laser method. For these pathologies, even an ultrasound of the eye, any touching of the cornea, application of eye patches, or the use of contact lenses are prohibited.
Causes of pathology
Most often, the disease develops against the background of congenital narrowing of the nasolacrimal duct, when the secretion of the lacrimal gland cannot be separated from the ducts at the required speed and stagnates in them. Pathogenic microflora is formed in stagnant tear fluid. Inflammation under the eye occurs not only due to the congenital structural features of the ducts, but also due to their blockage.
Diseases that lead to blockage of tear ducts include:
- deviated nasal septum;
- diabetes;
- eye diseases that provoke inflammation (styre, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, iritis);
- oncology of the eyes and nose;
- diseases that activate the vital activity of streptococcus aureus and staphylococcus (tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis);
- atherosclerosis;
- lacrimal caruncle cyst;
- formation of stones in the tear ducts.
Inflammation of the tear ducts is often observed in newborns.
During the period of intrauterine growth, the tear duct is covered with a film; after birth, it is destroyed, which allows tears to be quietly separated. But sometimes this does not happen, and tear secretion, accumulating in the ducts, provokes an inflammatory process.
Inflammation under the eye can also be caused by:
- clogging of the tear duct with foreign objects and dust;
- hypothermia;
- eye damage;
- incomplete removal of cosmetics and poor hygiene.
Systematic hypothermia of the body leads to canal stenosis - narrowing of the lumen due to spasm.
Elderly people are also susceptible to inflammation of the lacrimal duct: with age, the lacrimal duct narrows, which provokes impaired tear production and the appearance of infection in the lacrimal sac.
Inflammation of the lacrimal caruncle
The lacrimal caruncle does not directly relate to the lacrimal organs. It is located in the inner corner of the eye, in the form of an elevation consisting of connective tissue and covered with a layer of squamous epithelium and areas of mucous membrane. It is a rudiment of the third eyelid, which in animals promotes the uniform distribution of tears over the surface of the eyeball. In humans, this is done by the eyelids.
But the caruncle and semilunar fold are involved in the function of lacrimal drainage.
The lacrimal caruncle becomes inflamed quite rarely, then the position of the lacrimal openings relative to the level of the lacrimal fluid and the level of the lacrimal lake changes. When the caruncle is inflamed, the symptoms are pronounced: pain and redness in the medial corner of the eye, headache and fever.
The eyelids and conjunctiva in the inner corner are inflamed and swollen. The meat enlarges and swells, becoming like a red currant. Then purulent heads and an abscess appear in its tissue. Its development follows the classical type with a breakthrough on days 5–6. The abscess can turn into phlegmon. Inflammation of the lacrimal caruncle can be treated without antibacterial treatment: injections, drops and ointments. UHF, diathermy and solux are also used.
Inflammation of the lacrimal duct: causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Inflammation of the lacrimal canal (the correct name is dacryocystitis) is a pathology that occurs when the canals of the lacrimal glands are obstructed.
Fluid from the lacrimal canal penetrates the nasal sinuses and stagnates. In these cavities, pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively accumulate and multiply, causing inflammatory reactions.
Dacryocystitis can occur in acute and chronic forms.
Inflammation of the lacrimal duct: causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Symptoms
This disease has its own characteristic features. Acute dacryocystitis develops with the following symptoms:
- the appearance of swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac, which responds with pain when it is squeezed;
- swelling of the eye, in which the eyelids swell and the palpebral fissure narrows, preventing a person from seeing normally;
- pronounced redness in the area of the tear duct;
- the area around the eye orbit is very painful - the pain of an aching nature can be replaced by a sharp one at the moment of touching the inflamed area;
- increased body temperature;
- intoxication of the body - weakness, fatigue, malaise.
Dacryocystitis symptoms
In the initial stage of the disease, the swelling formed in the area of the tear duct is very dense to the touch, over time it becomes soft. The redness from the sore eye subsides, and an abscess forms at the site of the swelling. The inflammation disappears with the abscess breaking through. Instead of an abscess, a fistula may form with constant release of the contents of the lacrimal canal.
Chronic dacryocystitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- continuous lacrimation, sometimes with the presence of pus;
- discharge increases when the lacrimal sac is pressed or squeezed;
- upon external examination, you can notice an oblong swelling under the sore eye;
- eyelids swollen, edematous, overflowing with blood;
- As the infection spreads further, purulent ulcers may occur.
In the advanced form of dacryocystitis, the skin under the eye becomes sluggish, flabby, thin, and is easily stretched by fingers. The danger of chronic dacryocystitis is that it causes almost no pain. A person suffering from this form of the disease does not consult a doctor immediately, when the disease has already spread widely or has caused severe complications.
Dacryocystitis in newborns
In newborns, dacryocystitis can be determined by slight purulent discharge from the tear ducts and swollen eyelids. If left untreated, after a few months the child may experience constant watery eyes, and sometimes continuous watery eyes.
Complications of dacryocystitis
When the inflammatory process worsens, phlegmon of the lacrimal canal may form. Its main symptoms are severe swelling in the lacrimal sac area, swelling and redness in the lower eyelid area. As an inflammatory process occurs in the body, body temperature rises sharply. Tests can reveal an increased number of leukocytes and ESR.
Complications of dacryocystitis
Cellulitis is a very dangerous phenomenon with dacryocystitis. It doesn't always open up. If the phlegmon is opened internally, the purulent contents will penetrate the tear ducts, through them enter the orbit, and then can spread into the cranial cavity, causing infection of the brain.
This process can lead to such serious consequences as memory impairment, partial or complete loss of vision, and disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system.
These complications can arise only when the patient delays a visit to the doctor, or when the immune system is weakened. A timely visit to the doctor, diagnosis of the disease and the correct course of treatment help to successfully cope with this unpleasant disease.
Treatment
The therapeutic approach to the treatment of dacryocystitis largely depends on the following factors:
- forms of the disease - acute or chronic;
- patient's age;
- reasons for the development of the disease.
Treatment of the disease in adults begins with active rinsing of the lacrimal canals with disinfectants.
Next, the use of special drops or ointments is prescribed that prevent the spread of infection and have an antibacterial effect - Floxal, Ciprofloxacin, Dexamethasone, Levomycetin.
In some cases, vasoconstrictor drugs may be prescribed. A special massage of the lacrimal canals can also have a good effect in this disease.
: Proper massage for blocked tear ducts
If conservative treatment does not bring any particular results, in most cases the issue of surgery is decided. Before it, the patient must undergo antibacterial therapy to prevent possible complications.
For dacryocystitis, the following types of surgical intervention are performed:
Type of surgeryDescription
| Bougienage | This operation consists of cleaning the tear ducts using a special instrument. After this operation, the tear fluid is no longer blocked and the patency of the ducts is restored. This method is usually used if the patient experiences frequent relapses of the disease. |
| Dacryocystomy | This procedure involves creating an additional connection between the nasal mucosa and the lacrimal canal. Thanks to this operation, pus stops accumulating, and the outflow of tears is normalized |
Treatment of newborns
Many parents try to cure their child of inflammation of the tear ducts on their own - they wash the child’s eyes with decoctions of various herbs, put on tea lotions, buy some drops of their choice, guided only by the opinion of the pharmacist and their intuition.
Some of these procedures can indeed have a positive effect, but only for a short time.
After stopping these treatment methods, the child’s eyes begin to water again, sometimes with the release of pus.
This is due to the fact that the cause of the disease is often physiological pathologies, expressed in obstruction of the tear ducts, and these pathologies cannot be eliminated with drops and lotions alone.
As a result of such treatment, parents only prolong the course of the disease. New pathogenic bacteria enter the child’s eyes, causing inflammation and threatening the development of complications.
That is why it is highly not recommended to take independent measures to treat the baby. When the first signs of illness appear, the child should definitely be shown to a specialist.
Be sure to show your child to a specialist
When dacryocystitis is detected in a child, the doctor usually prescribes special therapy, which consists of special massage procedures, the use of antibacterial eye drops and washing the eyes with disinfectant solutions.
Massage of the lacrimal canal is a very important part in the treatment of dacryocystitis.
The only contraindication to it is a severe stage of the disease, in which extensive inflammatory processes have already formed. In case of such phenomena, massage is prohibited, since there is a high probability of pus leaking into the tissues surrounding the lacrimal canals, and this is fraught with the formation of phlegmon.
The correct massage technique is taught by a doctor. Before starting the massage, the mother needs to wash her hands thoroughly with soap. It is recommended to massage with sterile gloves, but you can simply rinse your hands in a special antiseptic solution.
First, you need to carefully squeeze out the contents of the lacrimal sac, then remove the released pus using a tampon soaked in a furatsilin solution. Only after these procedures can you start massage. The ideal time for a massage is before feeding.
Massage of the tear duct
The massage is carried out 4-5 times a day, and you need to make squeezing movements on the lacrimal sac. An approach that is too gentle will not bring much effect, but it is also not recommended to apply excessive pressure to the affected area.
A similar procedure will help push the gelatin membrane inside the canal connecting the lacrimal sac with the sinuses. Massage is very effective for newborn babies.
For adult children, such procedures will not give much results.
After the massage, you can treat the eyes with a swab soaked in a solution of chlorhexidine or furatsilin, and then drop the same solution into the child’s eyes so that the discharged substance is removed not only from the eyelid, but also from the surface of the eyeball. Ready-made solutions can only be used within 24 hours from the moment of preparation. Instead of these medicines, you can use decoctions of herbs that have an antibacterial effect: calendula, chamomile and others.
After the massage, it is necessary to apply drops to the child’s eyes.
If a lot of pus accumulates in a child’s eyes, it is recommended to use antibacterial drops - Albucid, Floxal, Tobrex. They need to be buried three times a day.
Conservative treatment of this disease makes sense only until the baby is two months old. If massage and drops do not help, probing of the lacrimal canal is prescribed. Under local anesthesia, a special probe is inserted into the child's lacrimal canal, which pierces the membrane that caused the development of dacryocystitis. After this, the lacrimal canals are washed with antiseptics.
The effectiveness of such a procedure is very high in the first months of a child’s life. The result is visible almost immediately - the baby’s constant tearfulness and watery eyes disappear. After surgery, antibacterial drops are prescribed.
ethnoscience
Dacryocystitis can be cured using traditional methods only if its occurrence is not caused by physiological pathologies.
Aloe juice has a good effect
A good effect can be had by dropping aloe juice into the eyes, diluted in half with water, or applying compresses with this juice to the eyes. Instead of aloe, you can use eyebright juice. It is prepared and used in the same way as aloe juice.
Thyme has anti-inflammatory properties, so it can be used for dacryocystitis. This plant is steamed, then allowed to brew for several hours, after which it is filtered. This decoction is used to wash sore eyes.
Before using any folk remedies, you must consult your doctor. In some forms of the disease, many folk recipes are contraindicated, so self-medication without the approval of a specialist is strictly not recommended.
A midge bit you in the eye, what to apply on you will find the answer in the link.
Source: https://linzopedia.ru/vospalenie-sleznogo-kanala-prichiny-simptomatika-metody-lecheniya.html
Treatment for inflammation of the tear duct
What to do if the tear duct is blocked? The disease is treated with medications, massage and folk remedies. In severe cases, surgery is performed.
Medicines
For the treatment of dacryocystitis, drugs are prescribed for both oral and topical use.
Levomycetin - eye drops
| Group of drugs | Action | Examples |
| Antibiotics | Destroy pathogenic microflora in the body, fight bacteria | Ampicillin, Oxacillin |
| Eye drops | Suppress the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms | Sulfacyl sodium, Levomycetin, Gentamicin |
| Antiseptics | Disinfect, prevent suppuration and decomposition of tissues at the site of inflammation | Furacilin, Dioxidine, Chlorhexidine |
| Ointments | Have a local antibacterial effect, prevent the growth of bacteria | Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Floxal |
| Immunomodulators | Stimulate the immune system to actively protect the body | Tsitovir-3, Arbidol, Dibazol |
If there is no improvement within 3 days, the prescribed medications are not effective - inform your doctor.
Massage serves as a preventive procedure against eye diseases
Treatment of inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct only with pharmaceutical drugs has been found to be ineffective: along with taking medications, it is necessary to regularly massage in order to clear the lacrimal sac from accumulated pus as quickly as possible.
How to treat with folk remedies?
Treatment of obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct with folk recipes at home is permissible in combination with pharmaceutical drugs, provided there is no hypersensitivity to the components.
The most effective folk remedies:
- Aloe. Dilute fresh aloe juice with cold boiled water in a 1:1 ratio and drop it into your eyes 4-5 times a day.
- Kalanchoe. Squeeze out fresh Kalanchoe juice and place 2 drops in each nostril while lying down. To administer to a child, dilute the juice in equal proportions with boiled water. Kalanchoe causes sneezing, during which the tear duct is naturally cleared of pus. Do the procedure once a day.
- Chamomile. Brew 3 tbsp. l. dried chamomile flowers in 1 liter of boiling water, let it brew for 1 hour. Soak a cotton pad in the infusion and apply to the sore eye. The lotion should be warm, not hot. Keep the compress until it cools completely. It is recommended to apply chamomile lotions 2 times a day until recovery.
- Thyme. Brew 1 tsp. dry thyme in 200 ml of boiling water, strain after 30 minutes. Rinse your eyes with warm infusion of thyme 2 times a day.
- Tea. Make a very strong brew of black tea and use it to wash your eyes and remove pus from them at least 4 times a day.
- Take 30 drops of propolis aqueous extract orally 3 times a day. Propolis is a natural antibiotic, strengthens the immune system and relieves inflammation from the inside.
Propolis extract serves as a natural antibiotic against inflammation
Make compresses and rinses not only for an eye clogged with pus, but also for a healthy one - this way you can protect the healthy eye from inflammation.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is carried out when the therapeutic effect from the use of medications and massage does not occur. In adults, the process takes place under local anesthesia, in children - with general anesthesia.
Types of operations for dacryocystitis:
- Probing
– cleaning the canal using a thin rod. During the probing process, adhesions and films formed as a result of inflammation are removed. - – expansion of a canal that is narrow from birth or spasmodic.
- Dacryocystorhinostomy
is the creation of a passage for fluid from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity. During the operation, the lacrimal sac is thoroughly washed and the pus that has accumulated in it is removed. - Dacryocystectomy
- removal of the lacrimal sac through an incision in the skin.
Expansion of the tear duct
Massage for tear duct obstruction
Massage is done to remove pus from the lacrimal sac. The procedure is an integral part of the treatment of dacryocystitis in children. Massage is effective in the initial stages of the disease.
Do not massage with long fingernails - they can injure the eyes and mucous membranes.
Technique:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and treat them with antiseptic.
- Using a clean cotton swab soaked in furatsilin, clean the eye from accumulated pus.
- Feel the lacrimal sac: it is located below the inner corner of the eye. Place your finger on the lacrimal sac and massage it with slight pressure for 10 seconds, first clockwise, then counterclockwise.
- Finger on the lacrimal sac. Make 5-7 jerky upward movements with slight pressure, squeezing the pus inside upward.
- Repeat the same movements in the downward direction.
- Place your finger on the bridge of your nose at the inner corner of your eye. Using massaging movements with pressure, move your finger from the bridge of the nose to the corner of the eye, repeat 5-7 times.
- During the massage, pus will be separated from the lacrimal canal - upon completion of the massage, remove it from the eye using a cotton swab soaked in furatsilin.
Perform the massage in strict order. Frequency of execution – 5 times a day. Children are recommended to massage the lacrimal sac before feedings.
You should not massage with advanced dacryocystitis - this can lead to the development of inflammation of the orbit or eyeball.
Bougienage of the lacrimal duct in adults
In the treatment of dacryocystitis, bougienage is often performed - a gentle method of restoring the patency of the nasolacrimal canal. During this procedure, the blockage is removed using a special rigid probe (bougie). The outflow of tear fluid after surgery is no longer blocked and the patency of the ducts is quickly restored. In addition, this procedure includes washing the lacrimal canal, which is carried out with antibacterial and disinfectants. This method is used for frequent relapses of the disease.
Timely diagnosis and treatment are important
The ophthalmologist prescribes diagnostic tests:
- swab to determine the type of bacteria;
- rhinoscopy;
- examination of the eye under a microscope;
- radiography with a special contrast agent;
- computer examination.
In accordance with the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Important factors are taken into account:
- severity of the disease;
- general condition of a person;
- other chronic diseases;
- causes of inflammation;
- the age of the sick person.
Treatment of an adult patient begins with washing out the eye canaliculi with special anti-infective agents. Typically, patients are prescribed: instillation of drops, placing ointments behind the eyelid that have a pronounced antibacterial effect. These are Dexamethasone, Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin. When medications do not help, the doctor resorts to surgery.
This is done in two ways:
- bougienage – the lacrimal canaliculi are cleared of purulent accumulations;
- dacryocystomy - formation of a valve in the lacrimal canaliculus.
After these operations, tear fluid and purulent contents stop accumulating, and the patency of the ducts is restored.
In children, as can be seen in the photo, due to the peculiarity of the symptoms, inflammation of the lacrimal canal is treated differently, not in the same way as in adults. After diagnostic measures, children are prescribed special treatment, including massage of the tear ducts and lacrimal sac. Ideally, this is carried out by a specialist, but a mother can also learn.
Dacryocystitis should be treated actively and in a timely manner to avoid dangerous complications.
How often do we shed tears? When we feel bad or hurt
when the soul hurts.
In such cases, the shoulder of a close friend or a professional psychotherapist can come to the rescue. What to do if the tears come continuously? There is only one answer - go to an ENT doctor. Lacrimation
is one of the mechanisms established in our body. No matter how picturesquely poets and writers describe it, this mechanism tends to break down.
Lacrimal duct obstructions
(medically called dacryocystitis or inflammation of the lacrimal sac) is a common problem.
The infection enters
the lacrimal sac, causing its inflammation, and as a result, dacryocystitis develops. The exact cause of the obstruction of the lacrimal ducts has not yet been determined. According to experts, it is believed that one of the main factors causing inflammation is anatomical background.
If you carefully
If you study the lacrimal duct, you can identify approximately seven zones in which there may be potential narrowing. Only a specialist can determine in which zone the tear duct has narrowed.
The occurrence of inflammation
lacrimal ducts are also promoted by a disease such as chronic. That is, if another inflammatory process develops next to the lacrimal sac, it can also block the lacrimal ducts.
One of the most striking symptoms
Dacryocystitis is continuous profuse lacrimation. This symptom should cause concern; self-medication is contraindicated. You should immediately contact an ophthalmologist or ENT specialist.
For dacryocystitis, ophthalmologists
carry out the procedure of washing the lacrimal ducts, followed by drainage. The drainage procedure involves passing through the tear ducts with a special instrument, which pushes out the contents that are clogging the tear duct.
But unfortunately
, these procedures do not always bring results. And if conservative treatment methods are powerless, we have to use modern surgical techniques that will get rid of this disease once and for all. These surgical techniques are already within the competence of ENT doctors.
Methodology
is a type of surgery that is performed under general anesthesia and lasts approximately 10 minutes. It is called dacryocystorhinostomy. This operation can be performed on patients of any age, even small children.
The essence of such an operation
consists of the use of radio waves. It is their use that allows the operation to be performed in a low-traumatic manner. Thanks to this technique, the postoperative period is shortened, wounds heal quickly, and no rough scars remain on the face. After such an operation, the new canal is guaranteed to remain open and not clogged.
In order for the doctor to prescribe surgical
intervention using radio waves, the patient must have certain indications. This is incessant lacrimation, extensive purulent processes in the lacrimal sac, as well as the systematic nature of the disease.
What are the consequences of refusing treatment for inflammation
tear ducts and what can happen? Impairment of the patency of the lacrimal ducts is an unnatural process for the body; it is not normal if the processes of tear drainage and tear excretion are disrupted. If the tear stagnates, an infection process may occur and an inflammatory process will begin, which will eventually affect the lacrimal sac.
If the problem is not solved in time
, this will lead to the beginning of purulent processes in the lacrimal sac, and then it can spread to the eye itself. The most terrible consequences that can be imagined if the problem is neglected are loss of vision and removal of an eye. Whether it comes to this or not depends on the patient himself, how seriously he takes this problem and how to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Training video for checking the patency of the lacrimal canal
— Return to the table of contents of the section “
«
Inflammation of the lacrimal duct or dacryocystitis is a pathology in which the lacrimal ducts become obstructed. That is, fluid from these ducts enters the nasal sinuses and stagnates there.
How does this disease manifest itself, and how can it be dealt with?
Symptoms of inflammation of the tear duct
Signs of dacryocystitis appear gradually. You can see what inflammation of the tear duct looks like in the photo.
The first thing people notice is sudden profuse lacrimation at low air temperatures. The symptom indicates the initial stage of the disease.
Other signs of dacryocystitis:
- wet eye syndrome;
- swelling of the lower eyelid;
- blurred vision;
- itching, redness, soreness of the eyelids;
- enlarged lymph nodes behind the ears;
- uncontrollable lacrimation;
- purulent discharge from the lacrimal duct.
One of the signs of dacryocystitis is uncontrolled lacrimation
In severe cases, swelling of the lower eyelid narrows the palpebral fissure. Usually the disease is diagnosed only on one side.
The first signs of the disease in an infant are redness of the inner corner of the eye, souring, uncharacteristic restlessness and refusal to breastfeed. If you notice these signs, consult a doctor immediately.