The tertiary period of syphilis is not mandatory. Previously, tertiary syphilis developed in 5-40% of untreated and poorly treated patients. Recently, tertiary syphilis is rarely registered due to more effective therapy, dispensary activities, and a high percentage of detection and treatment of patients with latent syphilis.
In the typical (“classical”) course of syphilitic infection, the tertiary period of syphilis develops after the secondary period. In the overwhelming majority of patients, a latent period is observed between the secondary and tertiary periods of syphilis, and only in some cases tertiary syphilis follows directly after secondary syphilis. Most often, tertiary syphilis develops in the 3rd-5th year of the disease, later its frequency progressively and rapidly decreases. Cases of the development of clinical manifestations of tertiary syphilis have been described 50-60 years after infection.
The development of tertiary syphilitic lesions is facilitated by a decrease in the body’s reactivity, common severe diseases, and chronic intoxication. Mechanical, chemical and thermal injuries to the skin also provoke the appearance of tertiary syphilides. There are tertiary active and tertiary latent syphilis.
What is Tertiary syphilis -
Tertiary syphilis
develops in a small number of patients who were insufficiently treated for syphilis or were not treated at all. The development of tertiary syphilis is facilitated by old age and childhood, trauma (physical, mental, medication), chronic diseases and intoxication, and alcoholism. Typically, tertiary syphilis begins after 4-5 years, but in recent decades it more often appears 8-10, and sometimes decades after infection. In Ukraine, patients with tertiary syphilis are currently rare.
Unlike secondary syphilis, clinical manifestations of tertiary syphilis are predominantly local. They are accompanied by destruction of the organs and tissues in which they are localized, and leave scars after their resolution.
Morphologically, tertiary syphilides are infectious granulomas.
The main ways of contracting syphilis
There are several routes of infection:
- In 90% of cases, the disease is transmitted through any type of sexual contact.
- When receiving a blood transfusion from a donor infected with an infection.
- From an infected mother to a child during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Through saliva.
- When using one syringe.
- Through medical instruments.
The greatest threat is posed by patients with the primary form of the disease. Patients with tertiary syphilis rarely infect others. For the disease to begin to develop, it is enough for a couple of bacteria to enter a damaged area of skin or wound.
Important
In an infected patient, treponema pallidum is found in the cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, male semen, lymph, tears and breast milk.
Pathogenesis (what happens?) during Tertiary syphilis:
Photo: tertiary syphilis
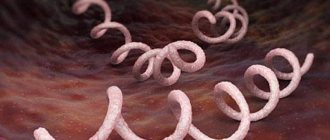
The only causative agent of the disease is Treponema pallidum, which can be detected in the patient’s lymph nodes 10 hours after infection, and 5 days later in his blood.
This is a spiral-shaped infectious microorganism that is covered with a protective membrane that provides a reliable barrier against drugs. It can also exist in the form of a cyst and L-form, which determines the various types of syphilis.
Diagnosis of syphilis using non-treponemal tests
To detect syphilis, non-treponemal tests or a complex of serological reactions (SSR) are used. Serological diagnosis is used from the 5th week from the moment of infection or from 2-3 weeks after the appearance of chancre. Antibodies are detected in almost all patients with fresh primary, secondary and recurrent syphilis. Serological reactions are positive in 70 - 80% of patients with tertiary active syphilis, in 50 - 60% of cases in patients with tertiary latent syphilis.
Serological tests using nontreponemal tests may give false-positive results.
Rice. 4. Blood sampling for testing for syphilis.
Damage to organs and systems as a sign of tertiary syphilis
Aching bones is one of the symptoms
As mentioned earlier, the tertiary period of syphilis is one of the stages of infection by the pathogen Treponema pallidum in the human body. It occurs as a result of the fact that treatment for this infection is either not carried out at all and the disease smoothly passes through all its clinical forms and manifestations on the skin, or due to the fact that the prescribed therapy was incomplete or was carried out incorrectly.
The main symptoms of tertiary syphilis:
- On the skin and mucous membranes of the patient, tubercles, which are often grouped together, and gummas, which are large nodes, appear characteristic of this period of damage to the body.
- Often gummas and tubercles with this disease appear in the area of skin injuries
- The elements are located quite deep in the skin, often reaching bone tissue
- Sometimes damage to the patient’s internal organs is also detected with the formation of these formations, for example, in the area of the liver, brain, lungs, heart
- As a rule, gummas and tubercles with a diagnosis such as tertiary syphilis develop and proceed rather slowly and resolve with scars
It is important to note that tertiary diagnosed syphilis is characterized by non-infectious elements appearing on the skin. In addition, patients are not contagious through sexual contact during this form of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease are accompanied by the most pronounced, often indelible disfigurement of the patient’s appearance, severe disorders in various organs and systems, leading to disability and often death.
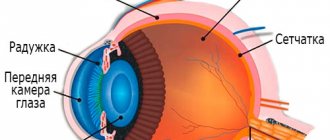
External signs of tertiary syphilis. Sometimes there is irradiation of gumma - the spread of gumma infiltrate to neighboring tissues (from the skin to the periosteum, bone, blood vessels), which can not only aggravate the disfigurement of the patient’s appearance, but also lead to death. Gummas of the mucous membranes are quite common. First of all, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity is affected, then the pharynx. Gummy lesions of the tongue, hard and soft palate, nose, pharynx, larynx lead to severe and often irreparable disorders of speech, swallowing, breathing, and change the appearance of the patient (“saddle” nose, complete destruction of the nose, perforation of the hard palate).
Etymology
Syphilis was named according to the supposed national origin - “German”, “French” disease, etc. In 1530, a work on syphilis by the professor of the University of Padua, doctor, astronomer and poet Girolamo Fracastoro (1483-1553) was published, which later became extremely widely known. ). He created the poem “Syphilis, or About the Gallic Disease
”, in fact, becoming the first popularizer of medical knowledge about this disease. Fracastoro's work was written in the form of a mythological poem in which a simple swineherd named Syphilus (ancient Greek σῦς - pig, φίλος - lover) challenges the gods themselves, arguing that the kings of the earth are more noble and rich cattle owners than the deities of Olympus. The heavenly rulers reward Syphilus for his insolence with a serious illness, the name of which is derived from his name. This is how the “multinational” disease (also called “lues” from the Latin lues - infection) acquired its modern name [4].
According to another version, the disease is named after Syphila
- the son of Niobe, who was the daughter of Tantalus and the wife of the king of Thebes Amphion, the mother of numerous children (according to one version of the myth, she had seven sons and seven daughters). Niobe, proud of her fertility, began to mock the goddess Leto, who had only a daughter, Artemis, and a son, Apollo. As a result, taking revenge for the insulted mother, Artemis destroyed the daughters, and Apollo destroyed the sons of Niobe. The father of the dead children, Amphion, committed suicide, and Niobe, out of despair and grief, turned into a rock. The Roman poet Ovid (43 BC - c. 18 AD) spoke about this in his Metamorphoses. Subsequently, doctors identified the contagious disease with the character of the myth[5].
Symptoms of late syphilis
With this form of the disease, almost all human systems and organs are affected.
The disease can take decades to develop. During this period, the patient may lose hearing, vision and even lose his mind.
Tertiary syphilis can be active or latent.
The main characteristic signs of the disease:
At this stage, almost all organs and systems of the body suffer. These are the kidneys, stomach, liver, bones, spinal cord, heart, brain, nervous system.
The disease can last for decades. During this period, deafness and blindness may occur. Such patients are usually aggressive, prone to paranoia and depression.
Characteristic signs of tertiary syphilis:
The most common form of the disease is cutaneous syphilis. It is characterized by the formation of syphilides, which lie under the skin. The following types of such formations are distinguished:
- Tuberculate.
- Gummous.
- Erythema.
Each of these formations has its own characteristics and is localized in different parts of the body. Depending on this, the symptoms of tertiary syphilis will be determined.
Tuberous syphilides
They are small nodules that are located under the skin. Their diameter does not exceed 7 mm.
The largest number of such formations is observed in the area of the limbs, lower back, face, head or back. Such syphilides have a red-brown tint.
After some syphilides heal, new ones may form in their place.
At the very beginning of the disease, tiny nodules appear, the diameter of which does not exceed 3 mm. Gradually they begin to increase in size. Over time, ulcers will appear in their place. After healing, scars remain.
Experts distinguish several types of tubercular syphilides:
The tertiary period of syphilis is characterized by infectious granulomas, large foci of inflammation that leave behind rough scars. Inside granulomas you can find single pale treponemas; outside of them, the microorganism is no longer detected during this period.
Primary syphilis begins from the moment when primary syphiloma, chancre, appears at the site of introduction of pale spirochetes. A chancre is a single, round-shaped erosion or ulcer, which has clear, smooth edges and a shiny bluish-red bottom, painless and non-inflamed.
The chancre does not increase in size, has scanty serous contents or is covered with a film or crust; a dense, painless infiltrate is felt at its base.
Hard chancre does not respond to local antiseptic therapy.
Secondary syphilis begins 2-4 months after infection and can last from 2 to 5 years. Characterized by generalization of infection.
Diagnosis and treatment
The disease is diagnosed based on the clinical picture and laboratory results:
Ultrasound of various organs and ECG are also prescribed. If necessary, consultations are carried out with an ophthalmologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, cardiologist and otolaryngologist.
The clinical picture and laboratory tests help diagnose the disease:
- PCR (polymer chain reaction. Search for bacterial DNA in the patient’s body.
- RIF (immunofluorescence reaction). The presence of Treponema pallidum is determined.
- Bacterioscopic examination. It is used to identify Treponema pallidum in human fluids.
- Examination of cerebrospinal fluid in neurosyphilis. The protein content, number of lymphocytes and monocytes are determined.
- Biopsy of syphilides.
- Serological method. Determines the presence of immunoglobulins to Treponema pallidum in the blood.
They also do ECG (electrocardiography) and ultrasound of various organs. Various specialists are consulted: ophthalmologist, neurologist, otolaryngologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist.
The diagnosis of tertiary syphilis is made on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture and serological diagnostic methods that detect antibodies to Treponema pallidum. Additionally, a biopsy of the contents of the gum is prescribed, in which treponema can be detected.
Patients with signs of tertiary syphilis are examined serologically. If the reaction is positive, a cerebrospinal fluid test, an X-ray of the brain, and an examination of the aorta are prescribed. In most patients, the serological test shows a negative result, so great importance is attached to blood tests using RIBT and RIF.
To determine the degree of damage to organs and the somatic system, an ECG and ultrasound of the heart, liver, kidneys, aortography, gastroscopy, liver tests, bone radiography, and lung radiography are performed.
Patients are also referred for additional consultations with a neurologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist, and ophthalmologist. .
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture and laboratory confirmation by any of the following methods: - Dark field examination - MR - RIF, ELISA, RPGA It must be taken into account that although in the modern classification there is no division of primary syphilis into seronegative and seropositive, within 7-14 days Serological tests may be negative.
Carry out diagnostics on time
Despite the obvious clinical signs of the disease, typical lesions of internal organs, the location of inflammatory elements on both the skin and mucous membranes, laboratory confirmation is necessary to make and confirm the diagnosis of syphilis.
Tertiary diagnosed syphilis most often implies positive serological reactions in almost 70% of patients.
It is important to remember that the tertiary period of syphilis disease is characterized by the absence of detection of the causative agent Treponema pallidum in the affected area on the skin and mucous membranes.
And, as you know, the most reliable laboratory test is considered to be a direct test, which is based on identifying a pathogenic organism from material obtained from a patient.
But with this clinical course of syphilis, the identification of the microorganism Treponema pallidum loses its decisive significance.
Diagnostic measures for syphilis include a thorough examination of the patient, taking an anamnesis and conducting clinical studies:
- Detection and identification of the causative agent of syphilis by microscopy of serous discharge from skin rashes. But in the absence of signs on the skin and mucous membranes and in the presence of a “dry” rash, the use of this method is impossible.
- Serological tests (nonspecific, specific) are performed with serum, blood plasma and cerebrospinal fluid - the most reliable method for diagnosing syphilis.
Survey
The treatment regimen is determined after a comprehensive examination. To make a diagnosis you will need:
- patient interview;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- immunofluorescence reaction;
- Wasserman reaction;
- anticardiolipin test;
- Ultrasound of the heart and abdominal organs;
cerebrospinal fluid examination;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- rhinoscopy;
- electrocardiography;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- FEGDS;
- neurological examination;
- aortography;
- CT or MRI.
It is impossible to identify the disease from one photo of patients. Diagnosis of tertiary syphilis includes serological testing. Immunoglobulins are found in the blood of patients, which are produced in response to the introduction of microbes. Treatment of tertiary syphilis is recommended after testing the sensitivity of treponemes to antibiotics.
Treatment of syphilis
Late syphilis is treated exclusively in a medical facility. Self-medication can lead to the most tragic consequences.
It is almost impossible to eliminate the disease and its symptoms during this period. Treatment is mainly aimed at preventing the development of infection and improving the patient’s quality of life.
It is mandatory to prescribe antibacterial drugs of the latest generations and different groups, as well as iodine-containing drugs.
First of all, the patient is prescribed a two-week course of erythromycin and tetracycline. Then he starts taking penicillin.
Eight courses are usually prescribed. Bismuth, mercury preparations and osarsol are taken between the sixth and seventh courses. In case of liver and kidney damage, bismuth is replaced with penicillin. In the eighth course, only bioquinol is used.
note
The number of courses, dosage and duration of therapy are prescribed by the attending physician. Basically, with tertiary syphilis, the interval between courses is one and a half months.
At the same time, therapy is carried out aimed at increasing the body's resistance to infections. Based on the degree of infection, stage of the disease, condition of systems and organs, age and physical condition, the specialist prescribes a dose of immunostimulating and enzyme preparations and vitamins.
Additional measures are being taken to heal skin lesions. If gummas and other formations are not treated promptly, the septum between the mouth and nose may fall out.
An aqueous solution of penicillin is used to treat lesions of the eyeball and neurosyphilis. If the patient is allergic to it, the drug is replaced with ceftriaxone.
Patients with damaged cartilage and joints and severe pain due to tabes dorsalis are prescribed finlepsin and analgesics.
During treatment, specialists monitor the condition of the patient’s body. Biochemical tests, urine and blood tests, ECG and ultrasound are regularly done.
After completing the course of treatment, the patient is observed for another five years. If during this period the patient has no symptoms of the disease, the person is considered to be completely healthy.
Important
Tertiary syphilis is a very advanced stage. Treatment will only help slow down the effect on the body and increase life expectancy. Full recovery at this stage is almost impossible.
Without treatment for tertiary syphilis, the life of an infected person is shortened by half and ends in painful death.
During this period, it is practically impossible to eliminate the disease and all its symptoms, so treatment is aimed at improving the patient’s life.
Antibacterial medications and other agents that affect the causative agent of the disease must be prescribed. The duration of treatment, the volume of medications chosen and the number of courses are determined by the attending doctor.
It is very important that the body is in good condition. For this purpose, they are trying to increase its resistance to infections.
The doctor, using data on the degree of infection and stage, the condition of organs and systems, age category and physical parameters of the body, calculates the required doses of vitamin, enzyme and immunostimulating drugs.
Treatment of the disease at this stage is carried out exclusively in a hospital. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Taking into account the symptoms in the tertiary period of syphilis, therapy is not aimed at completely eliminating the disease and its symptoms, but at stopping the progression of the infection and improving the patient’s quality of life. For treatment, antibiotic and antibacterial drugs of several groups and the latest generations are used, medicines containing bismuth, medicines for syphilis, including iodine. The preparatory stage consists of a two-week course of tetracycline and erythromycin. After which they begin penicillin therapy. The duration, number of courses and dosages correspond to the selected drugs. Changes in medications and breaks in treatment are strictly controlled by the doctor. When treating the tertiary form, the time between therapies is one and a half months. Extension of breaks is allowed only between the last courses. A total of up to 8 courses of treatment are recommended. The sixth and seventh include osarsol in combination with bismuth and mercury drugs. If the patient has liver or kidney damage, bismuth is contraindicated. It is replaced with penicillin. The eighth is carried out only with bioquinol. The condition of the patient’s body is of great importance, so resistance to infections should be increased. To do this, the doctor, based on data on the stage of syphilis, complications from other organs, the presence of allergies, age and body weight, calculates the doses of medications, immunomodulators, vitamins and minerals, and enzymes. It is important to adhere to the work, rest and nutrition regime, stop drinking alcohol, and adhere to the prescribed interval between courses of treatment. Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures can be performed to eliminate skin lesions. The formation of gummas does not cause severe pain, but if timely treatment is not started, this process can lead to prolapse of the septum between the oral cavity and the nose. For the prevention and treatment of eye lesions and neurosyphilis, an aqueous solution of penicillin is also used. Patients with a severe allergy to penicillin are prescribed ceftriaxone. Treatment of asymptomatic neurosyphilis is also necessary to avoid new neurological lesions. Patients with damaged articular cartilage and pain syndromes associated with tabes dorsalis take analgesics and carbamazepine.
During the treatment period, the condition of the affected organs is monitored: blood and urine tests, ECG, ultrasound, biochemical tests. If necessary, symptomatic treatment is carried out.
It is worth touching on the negative trends that are often observed in state dermatovenereal dispensaries. Doctors who have a budget salary and work in overcrowded departments do not have the opportunity to treat every patient. Often patients are not prescribed immunostimulation. This is fraught with the appearance in the patient’s body of bacteria that are not sensitive to antibiotics.
The same drugs are used to treat children as for adults: injections of mercury drugs and salvarsan. Children tolerate the one-step treatment method well: injections of miarsenol or infusion of novarsenol, and after half an hour bioquinol or mercury in one and a half dosages.
Such therapy should be carried out once a week. Children need 6 to 8 courses of treatment.
If the Wasserman reaction is still positive, an additional course of treatment is prescribed. .
Complications of syphilis
In approximately 25% of cases, due to complications, death occurs. In the third stage, almost all vital organs are destroyed.
Complications can lead to disability or appearance defects:
- Most often, death results from pneumosclerosis, bronchiectasis, aortic aneurysm and syphilitic aortritis.
- Perforation of the hard palate, dementia, osteitis, periostitis and saddle nose. These complications lead to disability.
- Serious psychoneurological disorders are caused by: late meningovascular syphilis, tabes spinal cord and progressive paralysis.
- A saddle nose and scars after purulent ulcers are cosmetic defects.
- Syphilis during pregnancy can cause premature birth and miscarriage, the death of the child or his disability.
It is worth remembering that tertiary syphilis is not a death sentence, so it is extremely important to diagnose the disease as early as possible and undergo full treatment to improve your quality of life.
Radevich Igor Tadeushevich, sex therapist-andrologist, 1st category
In approximately twenty-five percent of cases, the patient dies due to complications. In a patient with syphilis in the third stage, almost all major organs begin to collapse. A person may die, become disabled, or acquire defects in appearance.
- The most common causes of death are syphilitic aortitis, aortic aneurysm, bronchiectasis and pneumosclerosis.
- Dementia, saddle nose, perforation of the hard palate, osteitis and periostitis make a person disabled.
- Taste of the spinal cord, late meningovascular syphilis, and progressive paralysis cause serious neuropsychiatric disorders.
- Unsightly scars after purulent ulcers and a saddle nose give an obvious defect of a cosmetic nature.
- During pregnancy, syphilis can lead to miscarriage and premature birth, or death of the fetus or newborn.
Content
- 1 Etymology
- 2 History of syphilis 2.1 Theories of the origin of syphilis 2.1.1 American hypothesis
- 2.1.2 European hypothesis
- 2.1.3 African hypothesis
- 7.1 Incubation period
- 8.1 Primary syphilis
- 8.3.1 Late neurosyphilis 8.3.1.1 Asymptomatic neurosyphilis
- 10.1 Historical treatments
Prevention
Prevention of tertiary syphilis consists of timely and correct treatment of its earlier forms. There is an opinion in society that syphilis can be treated with one injection.
In fact, this is not the case, because any course of antibiotic treatment must last at least five days, and during its course it is necessary to maintain a constantly high concentration of the drug in the blood in order to completely destroy the pathogen.
Along with antibiotic therapy, it is imperative to carry out restorative treatment so that the patient’s immune system can fight the infection.
In order to avoid congenital syphilis, which very quickly turns into the tertiary form, family planning is important - if a woman has discovered signs of primary or secondary syphilis, then pregnancy should be planned after treatment and laboratory confirmation of its effectiveness.
Maternal syphilis can cause severe congenital deformities of the child, including those incompatible with life, therefore, if the fetus is syphilitically affected, the doctor may suggest terminating the pregnancy.
Antibiotics used to treat syphilis are also dangerous to the fetus, therefore, if syphilis is detected in a pregnant woman, the issue of terminating the pregnancy and undergoing a course of treatment is decided.
Post Views: 1,114