In the female body, estrogen plays an important role, the level of which affects the functioning of all organs and systems. Along with a decrease in indicators, representatives of the fairer sex often experience a strong increase in the hormone.
Symptoms of elevated estrogen levels in women impair physical and mental health.
This condition requires mandatory treatment, since a prolonged increase in hormone levels negatively affects the body. The balance of progesterone and estrogen ensures a woman’s reproductive function. If for some reason estrogen is elevated, this can cause problems with conception and also increase the risk of gynecological diseases. The symptoms of this condition are very unpleasant from both a physiological and mental point of view.
Causes
The following diseases can cause an increase in estrogen levels in a woman’s body:
- pituitary adenoma;
- ovarian tumors;
- any other tumors that produce estrogens;
- pathology of the adrenal glands;
- ovarian cyst.
Provoking factors are:
- poor nutrition;
- nervous tension;
- chronic diseases of the female reproductive system or other systems;
- endocrine diseases;
- obesity.
In some cases, an increase in estrogen levels is caused by a combination of these factors. In such situations, a woman needs to undergo a comprehensive examination by other highly specialized specialists who will draw up a plan for her further treatment.
Diagnosis and normal estrogen levels
Estrogen levels vary by gender and age. However, it may differ between people of the same age and gender. In women, the amount of estrogen in the body changes throughout the menstrual cycle.
Your doctor can check your estrogen levels with a blood test. There are three forms of this hormone in the blood:
- estradiol;
- estriol;
- estrone
Doctors measure the amount of estrogen in picograms per milliliter (pg/ml).
Estradiol is the main form of estrogen, and estriol and estrin are minor. Women, with the exception of those who are pregnant, have very low levels of estriol.
Women
According to the authoritative American Mayo Clinic, the normal level of estradiol in women is:
- in childhood and adolescence - up to 350 pg/ml;
- in adulthood - from 15 to 350 pg/ml;
- in postmenopause - less than 10 pg/ml.
Normal estrone levels in women are:
- in childhood and adolescence - up to 200 pg/ml;
- in adulthood - from 17 to 200 pg/ml;
- in postmenopause - from 7 to 40 pg/ml.
Men
According to the Mayo Clinic, normal estradiol levels in men are:
- in childhood and adolescence - up to 40 pg/ml;
- in adulthood - from 10 to 40 pg/ml.
Normal estrone levels in men are:
- in childhood and adolescence - up to 60 pg/ml;
- in adulthood - from 10 to 60 pg/ml.
Symptoms
A woman may suspect an increase in estrogen levels based on the following symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- engorgement of the mammary glands;
- increased sensitivity of the nipples;
- menstrual irregularities;
- the appearance of extra pounds;
- the appearance of rashes in the form of acne;
- hair loss;
- hypertension;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- digestive disorders;
- fast fatiguability;
- irritability;
- sleep changes.
The severity of symptoms when estrogen levels increase largely depends on the general health and age of the woman.
A long period of increased estrogen levels can lead to the development of the following diseases and conditions:
- increased blood clotting and blood clot formation;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- osteoporosis;
- obesity;
- the appearance of seizures;
- absence of pregnancies;
- menstrual irregularities;
- development of mastopathy and breast cancer;
- disorders of the nervous system and psyche.
To determine the reason for the increase in estrogen levels, the gynecologist draws up a plan for further examination of the woman and, if necessary, prescribes consultations with other specialized specialists (for example, an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, etc.).
Symptoms of high estrogen
Excess estrogen affects men and women differently. People with this problem can develop a range of symptoms.
Women
High estrogen levels can lead to excess weight gain, particularly around the hips and waist. In addition, excess estrogen can cause problems related to the menstrual cycle, such as:
- menstrual irregularities;
- slight bleeding from the vagina;
- heavy menstruation;
- exacerbation of symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Women with high estrogen levels may develop other symptoms, such as:
- bloating;
- cold hands and feet;
- insomnia;
- fatigue;
- hair loss;
- headache;
- decreased sexual desire;
- mood swings, depression or anxiety;
- memory problems;
- swelling and tenderness of the mammary glands;
- non-cancerous breast tumors;
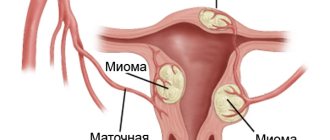
- uterine fibroids, that is, benign formations that form in the uterus.
Men
Potential symptoms of high estrogen levels in men include:
- erectile disfunction;
- enlarged breasts or gynecomastia;
- infertility.
Treatment
Mastodinon
Treatment tactics for increasing estrogen levels are drawn up depending on an analysis of the woman’s life history and data from laboratory and instrumental studies.
To reduce estrogen levels in a woman’s body, the following medications may be prescribed:
- Mastodinon and other herbal products;
- Tamoxifen;
- Aromasin, Arimidex, Femara;
- Faslodex.
If necessary, postmenopausal and premenopausal women may be prescribed drug therapy to suppress the hormonal activity of the ovaries, radiation, or surgery to remove the ovaries.
The following drugs may be prescribed for this:
- Zoladex;
- Lupron;
- Goselerin et al.
For the radiotherapy method of reducing estrogen levels, radiation exclusion of the ovaries may be recommended.
The surgical technique for suppressing the hormonal activity of the ovaries consists of performing operations such as:
- oophorectomy;
- ovarian ablation (low-traumatic endoscopic method).
All methods for suppressing excessive estrogen production are equally effective and contribute to subsequently reducing the risk of developing tumor processes in a woman’s body.
Some women are afraid to take hormonal medications and their fears are completely in vain, because a competent and experienced doctor prescribes them only in cases where his patient needs them. In such cases, the patient’s refusal to take prescribed medications can lead to serious complications.
A high level of estrogen is a condition in which a woman may experience changes in her health of varying severity, and the risk of developing fibroids, endometriosis, and mastopathy increases. At the initial stages, an increase in the level of this sex hormone can be corrected in more gentle and gentle ways. This is why gynecologists urge women to visit their doctor regularly. Remember this and be healthy!
Lack of female hormones. What to do?
Despite the fact that you can determine the lack of hormones by symptoms, it is still impossible to guess which specific hormone is missing
and how far its content is from the norm. And sometimes an increase in hormone levels can result in similar symptoms.
For this reason, it is worth talking about general recommendations for normalizing hormonal levels.
- It is necessary to eat properly, balanced and varied.
The menu must include the following products: fruits and vegetables, meat and fish, a sufficient amount of liquid, including natural juices. - You need to learn to control yourself in stressful situations
and avoid them if possible. - Sports, fitness, and dancing will help minimize the symptoms of a lack of female hormones
- If you have a lack of female hormones, it makes sense to quit smoking, alcohol, and reduce coffee consumption.
- It is necessary to allocate sufficient time for sleep and rest.
- Scrupulously. We covered this topic in detail on the sympaty.net website. It is best if a gynecologist consults you on this issue.
The lack of female hormones, as well as their excess, primarily affects the functioning of the reproductive system,
that is, on the ability to conceive and bear a child.
Therefore, do not ignore these symptoms, take care of your health.
In order for a woman to develop secondary sexual characteristics, a sufficient amount of estrogen must circulate in her body. This hormone, produced in the ovaries and partially in the adrenal glands throughout the entire period of puberty, is difficult to underestimate, its role is so great. Often it’s not just this that’s missing, but estrogen-progesterone deficiency is diagnosed.
If there is no lack of estrogen in the blood, then girls usually have a good proportional figure, the skin is clean and not spoiled by various rashes, and there is no problem of excess fat provided they have a normal diet. Starting from puberty and the next 25-30 years, approximately the same amount of the hormone should act on the body. Except for the fact that estrogens are released during pregnancy according to completely different patterns.
Lack of estrogen in women immediately makes itself felt with rather unpleasant symptoms. This occurs due to the fact that the ovaries reduce the production of the hormone for one reason or another. Low estrogen can be the result of hormonal imbalance, for example, due to improper functioning of the pituitary gland. Another possible reason may be a naturally reduced level of the hormone estrogen in relatively old age. Absolute or relative insufficiency of estrogen occurs both when production ceases completely and when there is insufficient supply of estrogen in the blood.
If estrogen deficiency is due to age-related reasons, then we are talking about menopause. The ovaries produce the hormone only until their egg supply is depleted. Each woman has her own time, genetically planned.
It happens that girls lack estrogens, female hormones, in which case the symptoms of deficiency and absence are clearly noticeable. The baby is not developing well physically and her menstruation does not come on time. But this is if the decrease or absence occurs before the onset of puberty. If estrogen deficiency occurs after this period, the doctor will find a small uterus and breasts, and a woman will come to him, most likely, with complaints of amenorrhea and infertility. And, most likely, it will be estrogen-progesterone deficiency.
Estrogen levels in women can become severely disrupted if significant attempts have been made to lose excess weight. At the same time, the euphoria from the new numbers on the scales will gradually give way to despondency from the deterioration of well-being, since there are no sudden changes.
Which doctor should I contact?
A woman should regularly visit a gynecologist. If she shows signs of hyperestrogenism, the doctor will prescribe additional examination methods and refer the patient for a consultation with a gynecologist-endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, neurosurgeon, ophthalmologist (to determine visual fields if a pituitary adenoma is suspected). Additional treatment from a psychotherapist or psychiatrist can often improve the quality of life.
Rating: (votes - 1 , average: 5.00 out of 5)
What signals does the body give when there is an excess of the hormone?
Ideally, a woman should undergo a full examination annually by a gynecologist, which includes a blood test for hormones. But most ladies visit a doctor only in extreme cases.
Therefore, it is very important for all representatives of the fair sex to know the symptoms of excess female hormones estrogen in order to promptly seek medical help.
In the early stages of hormonal changes, the body independently copes with increased estrogen levels due to internal reserves. If this is not enough, then medical intervention is necessary in order to prevent inevitable disorders and pathologies.
It is important to remember that excess estrogen in women is harmful to health, worsens appearance, spoils character, and also leads to dangerous consequences. In particular: infertility, the development of osteoporosis, endometriosis, thyroid diseases, the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, the occurrence of benign or malignant tumors in the uterus and mammary glands.
All symptoms of excess estrogen in women can be divided into two large groups: psychological and physiological.
Sometimes the causes can be easily eliminated.
Psychological manifestations
Very often, women experience the following psychological symptoms of increased estrogen:
- mood variability;
- fast fatiguability;
- general weakness;
- emotional instability, which manifests itself as short temper, tearfulness, and increased anxiety;
- panic attacks and depression;
- decreased libido (sexual desire) up to complete loss of interest in sex;
- memory impairment.
As we can see, excess estrogen in women has psychological symptoms that can lead to decreased performance. Ladies engaged in mental work experience memory loss especially acutely.
Physiological signs
What's wrong with an excess of estrogen in women's bodies?
Physiological symptoms of increased estrogen in women include:
- Periodic pain in the lower abdomen.
- Frequent headaches and dizziness.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Noise in ears.
- Feeling of heaviness in the legs.
- Premenstrual syndrome becomes more pronounced.
- Various menstrual cycle disorders. More often, bleeding becomes more abundant and lasts longer.
- The mammary glands swell and pain appears. It is possible to develop different types of mastopathy.
- Swelling of the limbs.
- Acne appears on the skin of the face.
- Hair loss is increasing.
- Nails peel and break.
- Blood pressure increases.
- The blood becomes thicker, which can lead to blood clots.
- Blood sugar levels drop.
- After eating, nausea or vomiting occurs.
- Intestinal function is disrupted, leading to frequent constipation or diarrhea.
- Various sleep disturbances appear, as a result of which the woman does not get a full rest at night.
- The lady begins to get better without changing her way of life. Moreover, more often in the lower part of the body: waist, hips, legs.
During menopause, the signs of increased estrogen levels discussed above in women include intense sweating and dryness in the intimate area. If a lady discovers manifestations from the lists proposed above, then she must immediately contact a gynecologist in order to diagnose the disease.
After all, many of the listed symptoms also occur in other diseases. Therefore, before looking for an answer to the question of how to reduce estrogen, you need to make sure that such actions are necessary. The doctor will conduct an examination, order blood tests and determine the causes of high estrogen levels. Based on the root causes of increased sex hormone levels, effective treatment will be individually selected.
The role of estrogen in the body
A group of female sex hormones that are synthesized in a woman’s body by the ovaries and regulate specific sexual functions are called estrogens.
This main type of female hormone ensures, during adolescence, the development and formation of secondary sexual characteristics in girls. At a more mature age, estrogens take an active part in the formation of the female reproductive system, preparation for pregnancy, ensure the timely release of the egg into the genital tract and fertilization after ovulation, contribute to the natural hydration of the vaginal mucous tissues and the preservation of its favorable microflora.
Estrogens in the body work in tandem with progesterone and together ensure the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy, its safety and a favorable birth.
Normal estrogen levels have a beneficial effect on skin and hair. The level of cholesterol in the blood, the strength of bone tissue, good memory, the complete absorption of calcium, magnesium, potassium and the coordinated functioning of the whole organism depend on its optimal amount.
In other words, estrogen is a hormone of youth, responsible for a woman’s emotional state, her libido, attractiveness and sexuality.
The body produces three types of estrogens:
- estriol is a minor sex hormone, present in low concentrations, produced mainly during pregnancy;
- estradiol is the most active steroid hormone common in women of childbearing age;
- Estrone is the only hormone that the body produces after the onset of menopause.
Hormones do not stand still; their levels can constantly change depending on the female cycle. In the first phase of follicle development, estrogen levels are at a fairly low level, but along with the production of a dominant follicle, there is a gradual increase in estrogen levels.
With full maturation and rupture of the follicle, during the release of the egg during ovulation, estrogen levels rise to their maximum value. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the amount of estrogen gradually decreases and drops to a minimum value.
| Cycle phase | Period of the phase | Phase duration | Hormone level, pg/ml |
| Follicular | First day of menstruation | from 7 to 22 days | from 57 to 227 pg/ml |
| Periovulatory | period before and after ovulation | 2-3 days | from 127 to 476 pg/ml |
| Corpus luteum phase (luteal) | after ovulation | 12-14 days | from 77 to 227 pg/ml |
| Menopause | from 19.7 to 82 pg/ml |
Increased estrogen in women may be a normal symptom during ovulation.
With age, the level of the hormone decreases significantly. After the onset of menopause and menopause, its amount decreases by 40 - 60%. Estrogens are naturally occurring hormones important for sexual development and other body functions. Before menopause they are produced mainly in the ovaries, after menopause they are produced in adipose tissue.
When working stable, estrogen is in balance with other hormones, but sometimes, under the influence of certain factors, its level can increase and begin to prevail over progesterone, which can lead to serious disruptions in certain body functions.
Women's hormonal levels can change significantly throughout life. Estrogen synthesis rapidly increases during a girl’s puberty, because this hormone is responsible for the menstrual cycle, affects the strength of the vaginal walls and the production of lubrication by the genitals. Moreover, under the influence of estrogens, a girl develops secondary sexual characteristics - her hips expand, her breasts become fuller, her skin becomes velvety, and her hair becomes strong and luxurious.
During menopause, the production of estrogen by the ovaries is noticeably reduced, which does not go unnoticed for a woman. Her periods disappear, vaginal dryness occurs, hot flashes attack, libido disappears, hair deteriorates, and pigment spots and wrinkles appear on the skin. And given that, together with calcium, estrogen takes part in the formation and strengthening of bones, with the onset of menopause, a woman’s bones become fragile and susceptible to disease.
Be that as it may, at puberty, estrogen in women is produced in sufficient quantities, in some cases even in excess of the norm (puberty and the time of bearing a child). The rest of the time, estrogen is in balance with another important hormone for women called progesterone.
However, under the influence of certain factors, this hormone can be produced not only by the ovaries, but also by the liver, fatty tissue, muscles, adrenal glands and even the brain. Doctors call this condition estrogen dominance, since in this case it begins to dominate over progesterone, also responsible for the menstrual cycle.
The liver is responsible for the metabolism of estrogen, and therefore this organ should be taken care of tirelessly if you do not want to encounter hormonal imbalance. And, first of all, you should stop “poisoning” him with alcohol. This will be the first step towards normalizing the level of female sex hormones. In addition, it should be remembered that drinking more than one glass of alcohol per day puts a woman at risk of breast cancer.
Inorganic food products contain a lot of “chemicals” that negatively affect the entire body, and especially the endocrine system. To improve the situation, try to buy vegetables and fruits more often at markets that sell natural products, or grow plants yourself.
Indigestible dietary fiber, which we call fiber, removes toxins and waste from the body. In the same way, they bind excess free-floating estrogen, ridding the body of excess of this substance and thereby helping to achieve the necessary hormonal balance. In this regard, try to constantly include vegetables and fruits, nuts, seeds and beans in your diet.
The development of dysbiosis threatens women not only with intestinal problems, but also with hormonal imbalance, because in this case it will be more difficult for the intestines to remove excess hormones in question from the body. To restore the level of beneficial microbes in the stomach and prevent dysbiosis, consume foods with probiotics more often, namely, fermented milk products and kvass, sauerkraut, pickles, kimchi and tofu cheese.
To avoid supplying your body with excess phytoestrogens, try to eat foods such as pears and apples, barley and oats, flaxseed and all kinds of berries.
Getting all the necessary vitamins and minerals into the body allows you to balance the production of hormones. If we talk directly about the balance of estrogen and progesterone, a woman needs to regularly receive vitamin B6, zinc and magnesium. To replenish vitamin B6 reserves, you should diversify your diet with beef liver and sea fish, nuts and beans; zinc can be found in pork and lamb, buckwheat and oatmeal, and magnesium is found in almonds, seaweed, peas and barley.
This oil is one of those rare products that helps normalize estrogen levels in the blood. Moreover, rosemary oil is excellent at reducing estradiol levels, which is considered an aggressive form of estrogen. This product also improves memory, stimulates hair growth, promotes blood flow to the brain and strengthens the immune system, i.e. combats numerous symptoms of increased estrogen.
Xenoestrogens are harmful substances with estrogen-like effects that are found in cosmetics, household chemicals, plastics and other synthetic products. Limit your exposure to these foods and your hormonal balance will be less compromised.
Stressful situations increase estrogen levels in the body and at the same time suppress the production of progesterone. To avoid this, learn to relax, not take stressful situations to heart, and under no circumstances keep negative emotions to yourself. This will allow you to avoid many health problems, including hormone imbalance.
Take care of yourself!
How to treat excess estrogen in women? In order to improve hormonal levels and eliminate high levels of estrogen in women and symptoms, you will have to seriously take care of your health. Doctors recommend getting a good night's sleep, walking a lot in the fresh air, and trying not to get nervous. A good way to prevent hormonal imbalances is to exercise. In addition, it is worth paying attention to nutrition. Estrogen production is stimulated by soy, cheeses, yogurts, legumes, coffee and cabbage.
You can make an appointment with a specialist who, after examination and tests, will prescribe effective treatment now by following the link https://45plus.rf/registration/. A qualified specialist will analyze in detail excess estrogen in women, treatment, symptoms, and prescribe a number of recommendations or medications that are most suitable for you, taking into account all the characteristics of the body.
Estrogens play a key role in a woman’s body, because they are responsible for the differentiation and development of female genitalia, the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, provide reproductive function, participate in mineral and lipid metabolism, and provide youth and beauty.
They are formed in the ovaries and in small quantities in the adrenal glands and adipose tissue. Estrogens are found not only in the female body, but also in men in low concentrations. Both deficiency and excess of estrogen have a negative effect.
Estrogens are a group of female sex hormones. By their structure, they belong to steroid physiologically active substances, i.e. they are a product synthesized from cholesterol.
Estrogens are obtained during certain chemical transformations of male sex hormones (androstenedione, testosterone), therefore the body of both sexes contains both estrogens and androgens in different proportions. In women, estrogen synthesis predominates; in men, androgens predominate.
Sometimes, due to a defect in the aromatase enzyme, which is responsible for the transition of androgens to estrogens, the level of male sex hormones in the female body increases, resulting in a condition called “hyperandrogenism.”