The disease uterine fibroids, the symptoms and treatment of which are well known to gynecologists, is a benign tumor. It grows from muscle and connective tissues. This problem cannot be left to chance. But there is no need to panic when you hear the diagnosis - medicine makes it relatively easy to cope with.
What are uterine fibroids?
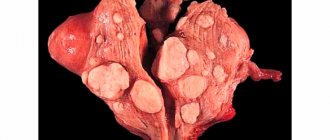
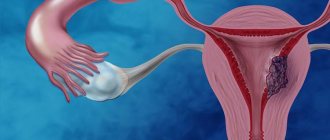
To begin with, a woman should know the most important thing: uterine fibroids, although a tumor, are benign and not at all cancerous. It develops in the walls of the uterus itself or its cervix, and ranges in size from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters. The size of fibroids is assessed by gynecologists similar to the size of the uterus during pregnancy, i.e. four, five, twelve weeks and beyond.
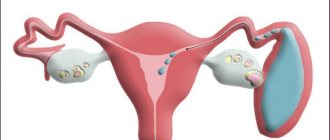
The location of uterine fibroids determines its classification:
- Subserous fibroids - the nodes are located on the outside of the uterus;
- Interstitial fibroids (intramuscular) - the tumor is located directly in the muscular walls of the uterus;
- Submucosal fibroids (submucosal) - a neoplasm grows in the uterine cavity, under its mucous membrane.
It should be noted that pedunculated fibroids are not a separate type of this disease, since fibroids can have a pedicle in both the first and third cases, only differ in width.
Prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis of the disease depends on the location of the tumor, its growth rate and the presence/absence of complications.
Possible complications:
- fibroid necrosis;
- inflammation of the node;
- life-threatening bleeding;
- dysfunction of other organs due to compression by their growing fibroids;
- circulatory disorders due to compression of large vessels.
If fibroids are not treated in the initial stages, the consequences can threaten a woman’s life.
Causes of uterine fibroids in women
There are many reasons why a woman develops uterine fibroids. But the main one is considered to be hormonal imbalance. That is why fibroids are a diagnosis for women of childbearing age, and they may well fade away with the onset of menopause.
But not only hormonal imbalance can provoke uterine fibroids; the reasons for its appearance can be different. Here are some of them:
- genetic (hereditary) predisposition;
- metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes, chronic diseases);
- adenomyosis;
- menstrual irregularities;
- intrauterine devices;
- prolonged stress;
- numerous terminations of pregnancy, that is, abortions;
- lack of orgasm during sexual intercourse.
Now let's talk in more detail about some of the causes of uterine fibroids.
Excess estrogen, lack of progesterone
Since uterine fibroids are a hormone-dependent tumor, they do not occur in girls who have not yet started menstruation and in women after menopause. The uterus feeds on female sex hormones (estrogen), and when their regulation is disrupted, i.e. their level increases, fibroids begin to grow. It is also known that it is not so much the high level of estrogen that provokes the growth of pathology, but rather their imbalance. But these changes can only be determined through a series of special hormone tests.
Number of pregnancies, births, abortions
To accurately determine a woman’s hormonal status, the doctor collects a detailed medical history. Many factors play a decisive role in the formation of hormonal levels, such as:
- at what age did menstruation begin?
- number of full-term pregnancies and abortions;
- was there lactation after childbirth, and how long did it last, etc.
If a woman has given birth to at least one child, the risk of fibroids is much reduced.
Women's nutrition
The level of estrogen in a woman’s body directly depends on how she eats. If the daily menu includes a lot of refined and fatty foods, and there is practically no fiber in it, then this can lead to an increase in estrogen. In addition, such a diet is fraught with extra pounds, which means that women who are overweight and obese have a much higher chance of getting uterine fibroids than slim women. It is also known for certain that a vegetarian diet, which mainly consists of nuts, fruits, vegetables, cereals and other low-fat foods, significantly reduces the risk of developing uterine fibroids.
Lack of orgasm during sexual intercourse
It's no secret that some women do not experience orgasm during sex, and this can have very unpleasant consequences for her health. The fact is that arousal causes a rush of blood to the genitals, and if satisfaction does not occur, then it does not go anywhere and stagnates in the pelvis. And this, in turn, provokes tension in the veins and vessels of the genital organs, and, as a result, hormonal imbalance and the growth of fibroids.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
A woman may not even know that she has uterine fibroids, since in most cases this disease occurs without any symptoms. Here everything depends on the size of the nodes: if they are small, then the woman will find out her diagnosis only during a scheduled visit to the gynecologist; if they are large, then the symptoms of uterine fibroids will definitely be present.
So what signs can tell a woman that she may be developing uterine fibroids? A consultation and examination by a gynecologist is required if a woman’s menstrual cycle is disrupted, her periods become irregular, heavy and painful, and bleeding or spotting may appear in the middle of the cycle. Heavy menstrual flow often causes anemia, and this leads to the fact that a woman begins to get tired quickly and is in a drowsy state all the time. Sharp pain appears in the groin and pelvic area.
If the fibroid is subserous, i.e. located outside the uterus, it can put pressure on neighboring organs - the bladder and intestines. In this case, the woman will experience frequent urination and constipation. With internal fibroids, infertility or spontaneous miscarriages can develop.
Relevance of the topic
Myoma ranks 2nd in the structure of gynecological diseases. Its frequency in reproductive age averages 16%-20% of cases, and in premenopausal age it reaches 30-35%. Recently, due to the increase in the number of “aggressive” gynecological and obstetric treatment methods and the improvement in the quality of diagnosis, there has been an increase in the number of women with myomatosis under 30 years of age.
In general, leiomyoma grows slowly - on average over 5 years. But sometimes rapid growth of the tumor is observed, in which within one year or less it increases by an amount corresponding to 5 weeks of pregnancy.
It can cause infertility (if localized in the area of the uterine part of the fallopian tube), spontaneous abortion, premature birth, abnormal fetal position, heavy postpartum uterine bleeding and other complications during childbirth and the immediate postpartum period.
Significant sizes of fibroids, for which surgery is indicated, correspond to 14 weeks of pregnancy. But in most other cases, radicalism in treatment (hysterectomy) is unjustified. It is based on the traditionally prevailing opinion that the uterus performs only a reproductive function, after which it can be removed without consequences for the body.
This opinion is erroneous, since the risk of transformation of leiomyoma into a malignant tumor is practically absent, but after hysterectomy, menstrual and reproductive functions are lost, and many women develop pronounced vegetative-vascular, psycho-emotional disorders and an accelerated decrease in mineral bone density.
At the same time, conservative treatment of uterine fibroids, as well as the use of non-invasive and minimally invasive treatment methods in the early stages of tumor development, make it possible to stop its growth, cause reverse development and prevent disorders of the reproductive function of the uterus. But if the indications for surgical treatment are clearly developed and defined, then the issues of using conservative methods still remain controversial.
Is it possible to treat uterine fibroids without surgery?
Naturally, if a woman discovers certain symptoms, she should consult a doctor. After examination and a thorough examination, the gynecologist will decide what treatment needs to be applied - whether it will be conservative treatment or removal of fibroids. The woman’s health status, her age, and desire to have children in the future are also taken into account. In the latter case, the most gentle therapy is selected.
If we are talking about small nodes (less than twelve weeks), which do not increase and do not give serious symptoms, then the doctor can limit the woman to regular examinations every six months and ultrasound examinations, without prescribing any medications. You should also refrain from sunbathing, visiting baths and saunas, and limit physical activity.
If the nodes grow slowly or the fibroids were already diagnosed at medium size, then the doctor prescribes treatment with hormonal drugs that inhibit the growth of estrogen and, in fact, the nodes themselves. With the proper effect, this method of treating uterine fibroids will help avoid surgery to remove it. Usually, combined oral contraceptives are prescribed for these purposes, for example, Mercilon, Novinet, or Rigevidon, Ovidon. Taking these drugs significantly reduces symptoms of uterine fibroids such as bleeding and pain. It is worth noting, however, that drugs in this group do not always help reduce the size of fibroids; they are effective only in cases where initially the nodes were no more than one and a half centimeters.
In other cases, drugs from the group of antiprogestogens - Mifeprestone - are prescribed. It is used both as a therapeutic agent for treatment and as preparation for surgery.
But the most modern, effective and gentle method of treating uterine fibroids today is considered to be FUS ablation. This is not an operation, but a non-invasive method of removing fibroid nodes, which is performed with an ultrasound beam. The doctor directs such a beam only to those places where the tumor is localized and eliminates the nodes themselves. The advantages of this method of treating uterine fibroids are quite obvious:
- with FUS ablation there is no blood loss, no anesthesia is used, and no damage is caused to the organ;
- the reproductive functions of the woman’s body are preserved, the uterus remains intact;
- high efficiency in the treatment of large nodes and multiple fibroids;
- absence of any negative side effects, i.e. no pain, fever, intoxication;
- after the use of FUS ablation, no relapses of the disease were observed;
- rehabilitation and recovery take place in the shortest possible time; the procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Basic principles of non-surgical treatment of uterine fibroids
In order to cure uterine fibroids without surgery, of course, taking hormonal drugs alone is not enough. You need to undergo a full course of conservative treatment. And it includes some additional measures.
If there is a history of sexually transmitted infections, they must be treated. A woman should reconsider her diet, and in the future adhere to a certain diet, namely: as little fatty, fried and flour foods as possible, and more vegetables, fruits, wholesome and healthy foods.
- It is worth thinking about strengthening the immune system by using special means for this.
- It is necessary to normalize metabolism.
- If there are psycho-emotional disorders, you need to undergo a course of sessions with a psychologist or psychotherapist.
- If prolonged periods cause anemia, it is imperative to treat it.
When is hysterectomy surgery indicated?
Now let's look at those cases when surgery to remove the uterus is inevitable.
- The size of the nodes is more than 12 weeks, the tumor puts pressure on nearby organs: bladder, intestines.
- Rapid growth rate of nodes - the size of the uterus increases up to six months of pregnancy in just four weeks or less.
- Due to fibroids, a woman begins to experience severe uterine bleeding.
- The tissues in the myomatous nodes die and become necrotic.
- Necrosis of the node.
- Uterine fibroids and adenomyosis at the same time.
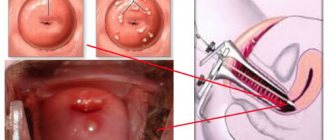
Previously, in the presence of such indications, the only option was complete removal of the uterus (hysterectomy). But the achievements of modern medicine make it possible to perform the most gentle operations, leaving women a chance for a normal life and the opportunity to have children in the future. There are several types of such operations. The most common is myomectomy. With this type of surgery, the doctor tries to directly remove only the fibroid node itself, without injuring the uterus. Myomectomy is performed in three ways, the choice of which depends on the size of the fibroid, its type and location.
Laparoscopic - several small punctures are made in the abdominal wall, through which the nodes are excised.
Hysteroscopic - done using a special instrument that is inserted into the uterus through the vagina.
These two methods of operations for removing nodes are considered the most popular and gentle today. They leave no traces, the woman’s reproductive function is preserved, and recovery after surgery does not take much time.
But when the growth of nodes cannot be stopped by any of the above methods, doctors have to resort to the most extreme and radical measure - hysterectomy, the complete removal of the uterus.
Modern medicine offers women another very delicate and gentle way to treat uterine fibroids - embolization of the uterine arteries. This method is unique in that doctors block blood flow in those vessels that feed the fibroids, the blood supply to the nodes stops and they dissolve.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of fibroids includes a mandatory initial examination, during which the doctor can immediately feel the abnormally large uterus with compacted tuberous walls.
To confirm the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is first performed. Ultrasound determines the number, location, type and size of myomatous nodes. To correctly assess the growth of fibroids, 2–3 measurements of the node are made in certain projections, repeating the ultrasound after 3–4 months. In this case, the doctor will clearly determine whether there is a tendency for the compaction to grow.
If active fibroid growth is suspected, an MRI or CT scan may be required.
Tomography (MRI) allows you to provide more information about the structure of the nodes and more objectively determine the size of the nodes, their location, changes in the structure of the uterus and its mucous layer, and detect the presence of vessels and fibrous tissue in the fibroid.
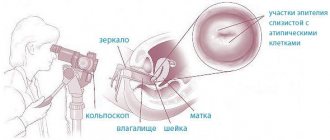
Hysteroscopy is also considered an informative diagnostic method in which the walls of the uterus are examined using an optical device - a hysteroscope. The method is used to differentiate benign structures from oncology. To do this, right during the hysteroscopy process, the doctor takes a microfragment (biopsy) of the endometrial mucosa and sends the tissue for histological examination and cytology (examination of cells under a microscope).