The human immune system provides constant, uninterrupted protection of the body from any harmful influence from the outside. This structure is extremely heterogeneous and is represented by several types of functionally active cells. Each of them is responsible for solving one or a number of problems.
All cytological units of immunity, leukocytes, can be divided into 2 groups:
- Granulocytes. They have a clearly defined core. This category includes neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils. They make up the majority of white blood cells and are responsible for the initial immune response. That is, it is granulocytes that are the first to go into battle, eliminating the development and progression of the pathological process.
- The second type is the so-called agranulocytes. Their task is a late immune response. When the body has more or less recognized the threat, they are the ones who come into play. The task is to form stable resistance to one or another pathogenic microorganism, virus.
Agranulocytes include the so-called lymphocytes. They are produced by the bone marrow and fight tumors and dangerous viral and bacterial structures. These cytological units are less numerous.
Lymphocytosis is a laboratory condition in which the level of lymphocytes circulating in the blood, special cells that provide an immune response, steadily increases. The deviation occurs quite often, but does not always indicate a disease.
What can lead to an increase in the level of lymphocytes?
Types of lymphocytosis
Two types of pathological process can be distinguished, depending on laboratory characteristics.
Relative form. A characteristic feature is the preservation of a normal number of lymphocytes per unit of blood (for example, a milliliter) with an increase or decrease relative to other white cells: neutrophils, eosinophils and others.
This is a less noticeable type of disorder, but it is still more common. Indicates inflammatory, infectious processes, in some cases cancer.
Absolute variety. The most obvious form of the pathological condition. The number of lymphocytes increases noticeably, both per unit of blood and in the overall picture of white cells. Therefore, it is very easy to detect such a disorder.
There is another classification. By degree of aggressiveness:
- Reactive lymphocytosis: a slow, gradual increase in white blood cells, does not pose a threat to life and health, because the primary pathological process is relatively sluggish.
- Malignant lymphocytosis. Observed against the backdrop of a rapidly current state. For example, the final stages of cancer, sepsis and other similar phenomena.
Oddly enough, despite the significant difference in the essence of these forms, there is no fundamental difference in terms of origin.
Both absolute and relative lymphocytosis, and other types are caused by approximately identical factors.
Diagnostics and differential diagnostics
The diagnosis is difficult due to the diversity of clinical manifestations of the disease. Correct diagnosis is possible only taking into account blood test data.
The blood picture is characterized by leukocytosis up to 20-120 g/l with a predominance of lymphocytes in the formula - up to 60-97%, mainly meso- and microgenerations of lymphocytes. Changes are detected already at the beginning of the disease, reaching a maximum during the period of highest temperature. The hemoglobin level, the number of red blood cells, platelets are usually normal, the ESR is normal or slightly accelerated. Cases of the disease with moderate anemia and a slight decrease in the number of platelets have been described. Bone marrow hematopoiesis does not change. However, there is an increase in the number of lymphocytes due to their admixture from the blood.
A biopsy of the lymph nodes reveals overdevelopment of the reticuloendothelium, blockage of the sinuses of the nodes by lymphatic cells, and degeneration of the lymphatic follicles.
Acute infectious lymphocytosis should be differentiated from diseases characterized by an increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood with a high number of lymphocytes: infectious mononucleosis (see), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (see), whooping cough (see). It is necessary to distinguish acute infectious lymphocytosis from diseases in the clinical picture of which there are symptoms similar to those of various forms of this disease - lymphogranulomatosis (see), influenza (see), pneumonia (see), encephalitis (see), appendicitis (see). cm.). A differential diagnosis is made with various infectious diseases (measles, rubella, chicken pox, scarlet fever (see)), accompanied by leukemoid reactions (see) of the lymphoid type.
Development mechanisms
Among the mechanisms of development of the pathological process:
- Viral infections. Changes in lymphocyte counts are possible against the background of any condition of this kind, no matter what the severity.
- Bacterial, fungal phenomena.
- Autoimmune inflammation. The so-called rheumatoid pathological processes.
- Lesions of the spleen. As a result of injury, surgery or for any other reasons. Not of great clinical significance in the context of the question.
- External traumatic influences. Including direct damage, surgical interventions and other pathological influences.
- Bone marrow diseases. Congenital or acquired forms. All those diseases that potentially provoke disturbances in the synthesis and maturation of white blood cells.
- Endocrine disorders. Changes in normal hormonal levels.
It’s worth talking about provoking factors in more detail.
Causes
As for the specific culprits of the pathological process:
Autoimmune inflammation
They occur very often. They are represented by a group of diseases of various localizations.
Here are just a few possible options:
- Rheumatism. Chronic recurrent myocardial damage, affecting joint tissue. The condition is destructive.
- Arthritis. It is characterized by a persistent course and the impossibility of qualitative correction of the disorder. All that remains is to deal with the symptoms.
- Lupus erythematosus. Systemic pathological process. Potentially fatal condition.
The clinical picture depends on the specific diagnosis. The following manifestations of the disorder are always present:
- Pain syndrome at the location of the source of inflammation.
- Increased body temperature during the acute period. When everything fades away, no changes are observed.
- Weakness, drowsiness, poor general health. As a result of intoxication of the body.
Patients are treated by specialist rheumatologists. Drug therapy. The goal is to reduce the intensity of the immune response.
This issue is resolved with drugs from several groups:
- Corticosteroids. This includes Prednisolone and its more powerful analogues. They take the medication in short courses, only during exacerbations.
- Immunosuppressants. If the previous group is ineffective, they are appointed. They literally slow down the functioning of the defenses and inhibit the bone marrow. Therefore, they cannot be used for a long time. Too many side effects and dangers.
A regimen of gentle nutrition with sufficient vitamins must be prescribed. After the main treatment, it is important to restrain the further development of the pathological process. Avoid aggravations.
Viral lesions
We are talking about a variety of anomalous agents. Lymphocytosis can develop against the background of a simple cold or influenza infection. The essence of the pathological process does not matter. There is always growth. The only question is how pronounced and intense.
The clinical picture depends on the location of the disorder. To better understand, let's imagine several options:
- If it is the respiratory tract: runny nose, mucus from the nose, sore throat, voice problems, cough.
- When the lower respiratory tract is affected: chest discomfort, a feeling of heaviness, a strong wet cough.
- Fever, weakness, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting are almost always present. This is the result of severe intoxication of the body.
Therapists and infectious disease specialists treat pathological processes of this kind.
Drugs are prescribed to relieve symptoms and restore the normal state of the body, destroy viruses:
- Interferon-based products.
- Artificial ready-made antibodies.
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin.
The lesions that are caused by more dangerous viruses stand out. For example, herpes. Its strains provoke different pathological processes: the first - a simple papular rash, the fourth, fifth - generalized disorders.
Special antiherpetic agents are prescribed that enhance the functioning of the immune system, inhibit the activity of the foreign structure itself, and destroy the outer shell of the dangerous agent.
Bacterial and fungal pathological processes
A separate type of infectious lesion of the body. There are many types of disorders. Here are some common options:
- Tuberculosis. Destructive changes in pulmonary structures. Less often - other fabrics.
- Pyogenic processes. The influence of streptococci and staphylococci on the body.
- Penetration of Klebsiella, an opportunistic flora like Escherichia coli.
- Fungal disorders.
- Children's, pediatric diseases.
Exotic options are also possible, including typhoid fever, cholera, plague and many other diseases.
Symptoms depend on the specific location of the disorder. Only a few general manifestations can be clearly stated:
- Pain syndrome.
- Nausea, vomiting, weakness. Signs of intoxication. Even in relatively mild cases.
- Increased body temperature. Again, the degree of intensity of the manifestation depends on the specific pathological process.
Next you need to look for focal signs. The reason for lymphocytosis is the need to produce antibodies in response to the increased activity of bacteria and fungi; this is a protective reaction that is aimed at inhibiting foreign agents and destroying them.
Treatment is carried out by therapists and pediatricians (depending on the age of the patient).
Antibiotic medications are prescribed. It is very advisable to evaluate the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to the drugs before using drugs.
You also need a number of anti-inflammatory and immunomodulator medications (not always). The issue is resolved on an individual basis.
Disturbances of normal hormonal levels
Relative lymphocytosis is often caused by an increase in the production of thyroid compounds, as well as a change in the amount of adrenal substances, cortisol. This is the result of a partial increase in bone marrow activity.
There are three main culprits for a conditional pathological condition:
- Hyperthyroidism. When the thyroid gland begins to synthesize too many substances, T3 and T4. Oddly enough, this process itself may be secondary. For example, against the background of diseases of the pituitary gland.
- Diabetes. Changes in insulin production or decreased tissue sensitivity to it.
- Insufficient production of hormones from the adrenal cortex. Addison's disease. Occurs after surgery or as a result of inflammation or injury.
Symptoms depend on the specific pathological process:
- If there is a deviation in the functioning of the thyroid gland, this is an increase in temperature, pressure surges, and disturbances in the functional activity of the heart.
- If the adrenal glands are affected, body weight increases, problems with bones, brain and other structures are observed. You need to figure it out on the spot.
Treatment is the prerogative of the endocrinologist. Hormone-based products are used. Artificial replacement therapy is the best solution.
The diet is adjusted. If the problem is in the thyroid gland, iodine supplements are needed. In each specific case, it is necessary to develop an individual strategy.
Inflammation of the spleen
Chronic, caused by the influence of microorganisms or acute. For example, against the background of surgery or injury.
The disease is accompanied by a number of nonspecific symptoms:
- Pain in the left side of the abdomen. Just below the navel. The intensity varies. The severity of the pain depends on the degree of inflammation. The nature of the discomfort is pressing or pulling, bursting.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Weakness.
- Increased body temperature.
There are no additional signs. Basically, everything becomes clear from the laboratory picture and blood counts.
In this case, the causes of lymphocytosis in adults are the production of a large number of inflammatory mediators, which becomes a signal for the immune system and its cells to begin active actions.
The abdominal surgeon takes over the therapy. You need to try to reduce the inflammation with drugs. Most often, such a correction is of no use and surgery is prescribed.
Treatment of lymphocytosis in the case of inflammation of the spleen consists of removing part or all of the organ under anesthesia, open access.
After surgical correction, anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Also antibiotics to reduce the likelihood of a secondary infection.
Recovery takes up to several weeks and ends with complete recovery.
Internal organ injuries
First of all, we are again talking about the spleen. The most common variant of the pathological process is the rupture of its tissues. It occurs in several cases:
- Acute inflammation. Characterized by enlargement and swelling of the organ. When it gets to a certain critical point, the anatomical structures simply cannot stand it.
- Injury. Fall from a great height, traffic accident, blow to the left side. Blunt injuries, in one word. A little less often we talk about penetrating wounds at work, in a fight, in combat operations.
Symptoms are clearly visible and indicate an acute process:
- Unbearable pain in the left side of the abdomen.
- Nausea.
- Vomit. Many times, even if the person has not eaten anything for a long time.
- Weakness, drowsiness.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Possible dizziness.
- Fainting when the patient has lost a lot of blood (the spleen has an extensive network of blood vessels, this is a logical outcome if nothing is done).
It is necessary to urgently transport the victim to a hospital. An operation is performed and the organ is removed. If necessary, a blood transfusion from a donor is prescribed. The patient is being treated by an abdominal surgeon.
Postponed surgeries
A variety of interventions. It doesn't matter what kind. Be it a simple removal of the appendix or therapy for tumors.
The point is different. In such a case, infectious lymphocytosis is observed, since any operation results in tissue damage, local inflammation and increased activity of local flora and viral agents, which the immune system is forced to suppress.
Symptoms or post-operative reactions are completely natural. Therefore, they do not pose a great danger if uncontrolled inflammation is contained.
The symptoms are always essentially the same:
- Pain at the incision site.
- Increased body temperature. Because the body fights threats.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Discomfort when moving.
- Headache.
There is no need for immediate treatment. Absolute lymphocytosis against the background of surgery develops as a result of exposure to bacteria, viruses, fungi and is eliminated as soon as the inflammation goes away and the functioning of local immunity is completely restored.
Medication support is prescribed. Several types of drugs are used:
- Antibiotics. To reduce risks.
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin.
- Immunomodulators. To restore the activity of protective forces.
The surgeons who performed the operation work with the patients.
Allergic reactions
At its core, this is also an autoimmune inflammatory process. Its intensity varies. The following forms of possible disorder occur:
- Hives. Banal skin rash.
- Eczema.
- Quincke's edema.
- Bronchial asthma. Impaired functional activity of the respiratory tract.
- Anaphylactic shock.
There are different types of pathological process possible. All of them are potentially dangerous.
The clinical picture depends on the type of disorder. From a common itchy rash to breathing problems, consciousness, and other manifestations.
The treatment is specific. Several types of drugs are prescribed. You cannot take them on your own, only at the discretion of an allergist or immunologist:
- Antihistamines. Reduce the intensity of a false immune response and its consequences. Products of 1-3 generations are used. The second - in the form of ointments for local application to relieve itching and burning.
- Glucocorticoids. Prescribed as part of additional correction. To eliminate the abnormal immune response from the patient's body's defenses.
Control over the condition also falls on the shoulders of a specialist.
Malignant tumors
A topic for a separate conversation. Localization can be any. Symptoms of lymphocytosis against the background of cancer coincide with the clinical picture of oncology itself and are represented by such signs as pain, changes in body weight, weakness, drowsiness, and constantly elevated temperature.
Treatment is the job of the oncologist. Two issues need to be resolved: removing the tumor itself and eliminating residual cells.
Since cancer grows inside healthy tissue, it is not so easy to remove the tumor purely mechanically. Surgery is prescribed, plus chemotherapy is used. Radiation treatment is carried out as needed.
Consequences and complications
Lymphocytosis in adults (a comprehensive examination will help determine the causes of the pathological condition) must be treated immediately when the first disorders appear. Progressive pathological processes will lead to the occurrence of numerous pathologies and failures.
The patient will experience serious complications and consequences:
| Name | Description |
| Changes in blood composition | There is a change in the concentration of all components and elements contained in the blood. Its color also changes. The consequence of this process may be the development of a serious illness. |
| Poor blood clotting | The pathological condition is characterized by an insufficient amount of certain enzymes in the blood. Platelet production decreases. Poor blood clotting can be life-threatening. Death occurs as a result of large blood loss. |
| Development of malignant processes | Leukemia is characterized by mutations in bone marrow cells. The process of hematopoiesis is disrupted. The body's susceptibility to infections decreases, and associated clinical signs appear. |
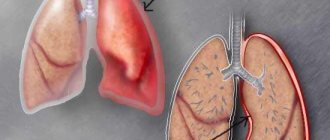
| Pneumonia | A pathological condition characterized by damage to the respiratory system. Often occurs as a result of whooping cough. A bacterial infection that is transmitted by airborne droplets. |
| Brain hemorrhages | A dangerous complication for a person’s life when the integrity of a blood vessel in the brain area is disrupted. In medicine, this pathological condition is called hemorrhagic stroke. Damage to vital centers in the brain stem will lead to respiratory and cardiac arrest. |
A high level of lymphocytes provokes blockage of blood vessels in vital internal organs. Complications arise not only against the background of an increased concentration of blood cells. The consequences are provoked by concomitant diseases or pathologies that developed against the background of lymphocytosis.
Additional examinations
Diagnostics is needed to identify the cause of lymphocytosis. The set of measures is determined by a specialized doctor.
Generally speaking, the methods could be:
- Patient interview.
- Anamnesis collection.
- Blood and urine examination.
- Biochemistry.
- Analysis of thyroid hormones, adrenal cortex, pituitary gland.
- Contrast-enhanced MRI.
- Serological tests, bacteriological culture, PCR, ELISA. That is, research on infectious processes.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- Allergy tests.
This is not a complete list, but such diagnostic measures provide basic information. Then all that remains is to clarify the details.