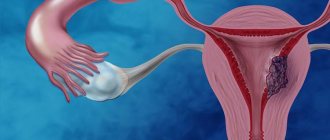
Cervical biopsy. How is it done?
When there are indications for a biopsy, the doctor prescribes it at the most convenient time for the patient.
The date will depend on the timing of the menstrual cycle. Tissue collection is performed in the gynecologist's office when there is no need for anesthesia. A cervical biopsy is performed under general anesthesia in most cases. If it is required, the procedure is performed during hospitalization for two days. The doctor must tell the patient how the biopsy will be performed. Detailed recommendations are given for proper preparation for the procedure. You will then need to see your doctor again when about a week has passed since the biopsy.
Often, the most painful thing for a woman is not the biopsy itself, but the waiting time for its results, which can last up to 10 days or more. Usually the answer is ready within 5-7 days, and the woman goes to her doctor for it. It is better not to engage in amateur activities and not to try to decipher the results yourself, since unfamiliar terms and their incorrect interpretation will lead to erroneous conclusions.
The most common processes appearing in the conclusions of pathologists based on the results of a cervical biopsy are:
- Acute or chronic cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix;
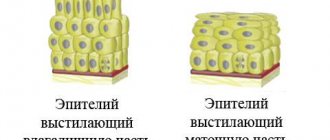
- Pseudo-erosion (endocervicosis) - simple, glandular, papillary, epidermal - ectopia of the cylindrical endocervical epithelium;
- Viral koilocytosis of stratified squamous epithelium (MSE) - indirectly indicates damage to the cervix by papillomavirus;
- Epithelial dysplasia from low to severe;
- Flat or genital warts are the result of the activity of the papillomavirus;
- Leukoplakia (keratinization) of the integumentary squamous epithelium of the cervix requires observation due to the risk of malignancy.
A much more serious problem is dysplasia - a precancerous process, but even with such a conclusion it is premature to panic. Mild and moderate degrees of dysplasia can be additionally treated conservatively if the lesions were completely removed by biopsy, otherwise they are excised during re-intervention.
In case of severe dysplasia, the doctor will suggest excision of the pathological focus to prevent malignant transformation, active antiviral treatment when diagnosing HPV, and treatment of the infection.
On which organs can a biopsy be performed?
Today, a biopsy can be done on almost all organs; a biopsy of body tissue is also often performed:
- skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- mucous membranes;
- muscle;
- bone and cartilage tissue;
- nerve tissue;
- lymphatic tissue;
- membranes (meninges, pleura, peritoneum);
- all internal organs (biopsy of the thyroid and breast glands, lungs, liver, esophagus, stomach, intestines, prostate biopsy, uterine biopsy, bladder, kidney biopsy, brain biopsy and even the heart).
Most often in oncological practice it is done in the “favorite” places of localization of malignant tumors, namely:
- liver biopsy;
- breast biopsy;
- biopsy of the lungs and bronchi;
- biopsy of the esophagus and stomach;
- intestinal biopsy;
- cervical biopsy (pipe endometrial biopsy);
- prostate biopsy;
- lymph node biopsy;
- bone marrow biopsy.
Is it painful to have a uterine biopsy?
Very often, before a biopsy, women have a question about whether the procedure is painful. This question is quite interesting, because not everything is so simple here. The cervix is one of those organs that lacks nerve endings. Consequently, when taking material that is sent for cancer research, there is no pain.
However, before the procedure, the patient is very tense and experiences some fear. As a result, all the muscles in the uterus are tense. During a biopsy, the uterus reacts in the form of spasms. Therefore, the development of painful sensations occurs. Although the pain that occurs is not so severe if you compare it with the sensations when you feel a tug in the stomach during menstruation. The more tense a woman is, the stronger the pain and uterine cramps.
In this situation, a woman’s fear and anxiety can be relieved by administering an anesthetic drug. Most often this is lidocaine, it is used as a local anesthetic, but sometimes the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Before the procedure, the woman's written consent is required that the test will take place on a voluntary basis.
Ultrasound-guided puncture biopsy
At the Kutuzovsky Children's Center, biopsies are performed under ultrasound control; this eliminates the possibility of errors when collecting material and guarantees accuracy in determining the location of the puncture.
Thanks to the experience and qualifications of our specialists, the entire procedure takes a minimum of time, is safe and virtually painless. Since all people have different degrees of sensitivity, including pain threshold, the sensations during puncture may be different for each patient. Therefore, we practice an individual approach, choosing biopsy methods: fine- or thick-needle, type of anesthesia: local or intravenous.
Monitoring the puncture with a highly sensitive ultrasound device allows you to avoid the development of various complications: trauma to surrounding tissues, obtaining false diagnostic results.
How is a uterine biopsy performed?
There are many methods for performing a uterine biopsy; the choice of a specific method is discussed with each patient individually. To perform a biopsy, the woman is seated in a gynecological chair. General anesthesia is used extremely rarely. As a rule, the operation is performed under local anesthesia, while the patient herself is conscious.
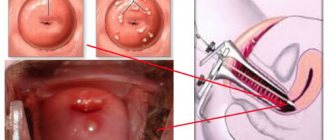
To begin, the doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina. Thanks to him, it is possible to examine the cervix. Then a bright light is directed there. Using biopsy instruments, tissue that is suspicious is removed. The resulting material is then sent for further research. All manipulations last on average half an hour. Although there are situations when the operation is delayed by 1.5 hours. After this, the woman can safely go home.
If, in the opinion of the doctor, hospitalization is required, then the patient must adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations, otherwise there is a risk of a number of complications. If necessary, the patient may be left in the hospital for a couple of days after the biopsy so that the doctor can observe her. Deciphering the analysis is a series of activities that require appropriate training from the doctor. Therefore, this should be done by a qualified specialist.
After instrumental intervention, you should not lift anything weighing more than 3 kg. You will also have to abstain from sexual intercourse for 2 weeks. And you can begin sexual activity only after the doctor has performed an examination and given his permission. As a result of the examination, he will be able to understand whether the wound has healed. To protect yourself from bleeding, you should not visit baths, saunas, or take baths. It is best to use a contrast shower.
After the procedure, you should not take aspirin. The reason is that it thins the blood and prevents fibrin from falling out. Consequently, a blood clot develops.
How to prepare
As part of the preparation, it is necessary to pass a number of tests:
- Urethral smear, analysis of biomaterial for STDs using PCR;
- Extended spermogram;
- Blood and urine tests (general and biochemistry);
- Fluorography, ECG (if general anesthesia is expected);
- Blood test for hepatitis and HIV.
Before a biopsy, a man is consulted by a urologist, andrologist, or geneticist, depending on the purpose of the study.
In order for the analysis results to be as reliable as possible, it is necessary:
- Do not drink and, if possible, do not smoke.
- Do not wear tight underwear, do not bask in the sauna.
- Avoid exposure to serious physical activity and stress.
It is advisable to follow the rules for at least a week, and if the procedure is done for the purpose of collecting sperm for further fertilization, then 3 months. For a week you need to stop taking aspirin and medications containing it. Do not ejaculate for 3-4 days. Stop taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Nurofen) 3 days before.
After 7 pm on the day before the procedure, do not consume food or carbonated drinks; in the morning you can only drink. It is necessary to remove hair from the pubis, scrotum and inner thigh. Do a cleansing enema in the morning.
Biopsy methods
Sighting
The targeted method of biopsy is quite widespread. Experts consider it the most accurate. In addition, this technique reduces the negative impact on the patient’s body. However, this procedure requires good technical support.
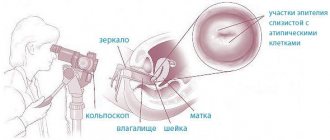
During colposcopy, the doctor uses a very thin needle. This needle is used to collect cells that cause any suspicion to the specialist. This analysis is considered the most effective for detecting cervical cancer, as well as dysplasia.
Laser biopsy of the cervix is a fairly accurate and reliable procedure. But to carry it out you will need to administer short-term anesthesia. Such analysis can be performed exclusively in stationary conditions.
A specific area of the cervix is removed using a laser. Experts recognize this operation as low-traumatic. It then takes quite a bit of time to heal. Patients should be aware that when a cervical biopsy is performed with a laser, quite unpleasant residual effects will be observed.
Many doctors recommend using radio wave sampling of tissue from the cervix. Experts say that the use of the so-called “radio knife” significantly reduces the risk of possible side effects. Here are some key benefits of the procedure.
- The cervix heals in a short time, since with such an instrument everything is done carefully, with minimal tissue damage.
- The discharge is scanty, so it will not create problems either.
- There are practically no complications of any kind after the procedure.
- Of great importance is the fact that such an analysis does not require the use of anesthesia.
Sometimes people are primarily interested in the specific cost of a cervical biopsy. However, specific prices can only be found in the appropriate clinic where you are going to take this complex test.
Wedge biopsy
This method of tissue sampling is far from the safest or most effective. Although it is used quite often, since it does not require the use of special complex equipment.
During the cervical wedge biopsy procedure, the doctor uses a scalpel. This is a full-fledged operation that can be performed exclusively in a hospital setting. A surgical scalpel is used. It is with the use of a scalpel that the specialist excises a wedge-shaped area directly on the cervix. In this case, not only diseased areas in the tissues are removed. Healthy particles are also needed: this is necessary for adequate analysis.
After the operation, stitches are required. This type of surgery takes place only under general anesthesia. The healing process takes a long time. Unfortunately, during the rehabilitation period there will be discharge, probably heavy. Pain syndrome also accompanies healing.
Loop biopsy involves the use of electrical current. A special loop is placed on a specific area on the cervix. Then an electric current is sent through the loop. It provokes cell death. This technique is used not only as part of the biopsy procedure. It is in demand in the complex treatment of cervical diseases.
Circular biopsy
The technique of circular biopsy is also known. It differs from all the methods of tissue collection that we considered earlier. During a circular biopsy, tissue is also taken from a section of the cervical canal. This is an extended biopsy. Typically, specialists use a radio knife or scalpel to remove tissue.
After the procedure
Experts note that after performing a biopsy, you need to behave correctly so that complications do not arise. Here are some important recommendations that you should definitely follow.
- Douching is prohibited.
- You can't lift weights.
- It is forbidden to take a bath or go to the sauna.
- The use of vaginal tampons is also prohibited.
- Intimacy is prohibited.
All these precautions must be taken for at least two weeks. Further, everything will depend on the specific recommendations of the attending physician and the patient’s condition.
In medicine, there are a number of types and methods of performing cervical biopsies. OXY-center specialists use the safest and most informative of them. In each case, we take into account the individual characteristics of the patient, the indicators of her tests and examination results in order to resort to a specific technique in favor of the reliability of the data obtained or painlessness for the body.
The fact is that the most informative method, which is highly accurate, is the “knife” taking of materials - this is an extended biopsy of the cervix. But in this case, a significant amount of tissue is damaged. Therefore, our specialists rarely resort to this technique.
Other methods of manipulation are less invasive and help preserve the integrity of cervical tissue:
- Conization. This technique involves taking a cone-shaped tissue sample. This leaves a pinpoint wound on the surface of the pharynx of the cervix. However, thanks to the special shape of the sample, specialists can assess the condition of both surface structures and underlying tissues. The material is taken under local, regional or general anesthesia, depending on the sensitivity of the patient.
- Scraping. When performing such a biopsy of the cervix using a special instrument - a curette, part of the mucous membrane is removed from the pharynx. The material contains a large number of epithelial cells, which makes it possible to assess their condition with a fairly large sample. Often performed under spinal anesthesia.
- Loop electrosurgical biopsy. This technique is the most painless and minimally invasive. The material is collected using a thin metal thread through which a weak electric current passes. However, due to temperature effects on the sample, this method is not very informative. Therefore, they resort to it only for special indications. To take the material, specialists numb the cervix with spinal or local anesthesia.
All types of procedures take no more than an hour. The duration depends on the chosen technique and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body structure.
Classification of biopsy types
Studies are classified according to the methods of collecting biopsies (sampling material for histo- or cytological diagnostics) and by the type of accuracy control (classical and targeted studies).
To conduct histopathological studies, the following biopsy methods are used:
- Excisional biopsies - this biopsy method is used in cases where it is necessary to examine entire pathological formations. This procedure is a full-fledged operation, since in addition to conducting a comprehensive diagnosis, it allows you to remove the affected area (that is, provide a therapeutic effect).
- Incisional biopsies - such a biopsy is performed to obtain part of the pathological biological material. In the presence of diffuse lesions of organs and tissues, samples are taken from all areas of the lesion. At least three tissue and cell samples should be taken from each pathological area at different depths of the lesion.
- Pinch biopsy methods (punch biopsy) - this study is performed using forceps. The doctor uses forceps to excise the mucous membranes of the cervix for further collection of biological material. Punch biopsy methods are used for diagnostic purposes, to identify malignant and precancerous processes in the cervical mucosa, diagnose the etiology of erosions, assess their depth, diagnose cervical dysplasia and assess the risk of malignancy of this process. To obtain the most reliable and detailed information, a punch biopsy is performed only in combination with cytological and bacteriological studies of smears.
- Trephine biopsy - this biopsy method allows you to collect specific columns of dense tissue using special needles with pointed edges - a trephine. Trephine biopsy is used to examine bone tissue, lymph nodes, breast tissue, and endocrine glands. To perform a trephine biopsy, the needle is screwed into the tissue being examined and removed with a sharp movement, after which biological material remains on the edge of the thread for examination. This method allows you to obtain larger volumes of biopsy material than with a standard study. Also, by taking material from different depths, the accuracy of the biopsy increases.
- Core biopsies (core biopsies or cutting types of biopsies) - this research method is carried out using harpoon-like trephines or biopsy guns. Core biopsy allows you to obtain a column of soft tissue. Also, such a biopsy is performed to take a biopsy sample from hard-to-reach and deep-lying areas of tissue. All core biopsies are performed under ultrasound guidance to control the depth and accuracy of trephine insertion.
- Scarification (superficial) types of biopsy - biopsy samples are taken by cutting off superficial thin layers of tissue. This type of biopsy is used to diagnose skin diseases. Also, using brushes, curettes and pliers, a scarification biopsy can be used to collect material from the cervix and uterine cavity.
- Loop biopsy methods - biological material is taken using various coagulators or radiofrequency surgical devices that dissect the tissue of the organ being examined. After this, a biopsy sample is taken using a special loop. Loop biopsies are used in ENT practice, as well as in gynecological studies. After collecting material using this method, a small scar remains on the tissue, so this study is used less frequently than other biopsy methods.
Preparatory activities
A uterine biopsy as a procedure is a surgical intervention that is allowed to be performed only if there is no infectious process in the reproductive system. To make sure of this, you need to take a smear for pathological flora. If the results are negative, then a biopsy is allowed. If the result is positive, the analysis is prohibited until the underlying factor in the development of the pathology is determined.
Biomaterial is taken from a woman immediately after her menstruation has not ended. To do this, the doctor uses a special instrument to pinch off a piece of the mucous membrane of the affected organ.
At the same time, it is important to monitor the woman so that everything heals before the next menstruation. The duration of healing of the wound reaches 2 weeks, but not longer.
Cost of biopsy abroad
| Type of procedure | Price in USD |
| Biopsy | from 279$ to 4856$ |
| Lymph node biopsy | up to $1845 |
| Brain tumor biopsy | up to $23465 |
| Bone marrow biopsy | from $8798 to $3689 |
| Prostate biopsy | from 89$ |
| Fusion biopsy of the prostate gland | from $2677 to $2972 |
| Prostate biopsy + TRUS | from 1098$ to 2897$ |
Preparation for the procedure
Preparing for a routine cervical biopsy includes a number of standard examinations that can be completed at your clinic. General and biochemical blood tests, a coagulogram, and examination for syphilis, hepatitis, and HIV are prescribed.
Before the procedure, a woman must visit a gynecologist and undergo a colposcopy with smears taken for cytology and vaginal microflora. If necessary, an ultrasound of the internal genital organs is performed.
The study is accompanied by injury to the outer layer of the organ, so it must be prescribed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (on days 5-7) so that the defect is epithelialized by the next menstruation.
Two days before the procedure, you should avoid sexual intercourse, douching, the use of vaginal suppositories, ointments, capsules, and you should also not use tampons, as all this can distort the results of the study. When planning general anesthesia, a woman should not eat or drink liquids from 6 pm the night before the test.
After undergoing examinations and preparatory measures, the patient must give her written consent to take tissue for research.
It is important to know exactly how to prepare for a biopsy. It is necessary to follow all the recommendations and advice of the doctor so that the procedure goes well and does not cause negative consequences.
The patient undergoes a certain range of tests before the biopsy. They prescribe smears for various infections, blood tests for HIV, hepatitis, and also for RW. The condition of the neck of the organ by the beginning of the critical days is also significant. That is why a biopsy is performed immediately after menstruation. Then, by the next critical days, the cervix has time to heal and is no longer damaged.
- It is important to carefully perform all hygiene procedures immediately before tissue collection.
- You should take a shower.
- Food should not be taken in the evening.
- Intimacy is prohibited two days before the biopsy.
- Do not use medications or vaginal care products.
Only with proper preparation for the test can it be carried out effectively.
Indications for cervical biopsy are determined during colposcopy. This is a gynecological examination, during which the condition of the entrance to the vagina, as well as its internal part, is examined. In particular, the pharynx of the cervix, which often shows traces of organic changes in various pathologies.
In addition, we prescribe a PAP test for patients. During the procedure, the doctor, having previously cleaned the pharynx of the cervix, takes a scraping from it using a special instrument. The manipulation is absolutely painless. The material is then sent to the laboratory for cytological studies. Using microscopy of cells and exposure to special substances, specialists detect the presence of tissue units in a precancerous state.
In most cases, the results of such an analysis are positive, and additional research is not necessary. However, if the patient shows signs of oncological changes, it is necessary to proceed to preparation for a cervical biopsy.
Factors that may indicate the risk of having benign and malignant neoplasms include:
- presence of iodine-negative areas during colposcopy;
- staining of individual areas of the epithelium in a white tint upon contact with acetic acid;
- cytological signs identified as a result of the PAP test.
In this case, we recommend undergoing a cervical biopsy at our clinic in Krasnodar. This is a quick and simple procedure that allows you to identify cancer diseases in the early stages of development, when they can be gotten rid of easily and quickly.
A cervical biopsy can be performed during pregnancy if the gynecologist suspects cancer. In other situations, the procedure is postponed until the postpartum period.
Preparation for manipulation includes a medical examination aimed at identifying concomitant diseases and infections, as well as inflammatory processes. The patient needs to submit:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram;
- tests for STIs (HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C);
- vaginal smear;
- general urine analysis.
Our center's specialists examine the test results. If the patient’s condition is good and there are no contraindications (for example, inflammatory processes), doctors move on to the legal side of preparing for a cervical biopsy.
Clients of our clinic sign consent to carry out the procedure, as well as to comply with medical prescriptions - sexual rest for 24 hours, as well as the abolition of inserting any medications into the vagina for this period.
The price of a cervical biopsy depends on the chosen method of taking biomaterial. You can check this with the administrator of our clinic.
- cervical erosion
- negative smear cytology result
- detection of atypical abnormalities that were diagnosed during colposcopy (acetowhite epithelium, iodine-negative areas)
- presence of polyps, condylomas, tumor formations
- leukopathy
A biopsy is performed on days 7-13 of the menstrual cycle.
- detection of inflammatory foci during an appointment with a gynecologist that require further examination and treatment
- the beginning of the menstrual cycle
- You must inform your doctor about pregnancy in advance.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to undergo a number of examinations and tests in order to reduce the risk of the occurrence and complications of infectious diseases.
- general blood analysis
- coagulogram (blood clotting test)
- flora smear (the ability to identify diseases of the reproductive system)
- smear for cytology
- perform a colposcopy
- tests for hidden infections (which have no external manifestations)
- tests for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis
In addition, before the procedure itself, it is recommended to avoid medications that are introduced into the vaginal cavity, the use of tampons, douching, and sexual intercourse 2 days before the procedure.
- inflammatory diseases of the cervix
- pregnancy (1st and 3rd trimester)
In these cases, the biopsy will have to be postponed.
Cases when a cervical biopsy is required during pregnancy occur when your attending physician notices suspicious changes in the cervical area and decides that it is impossible to wait until childbirth. A biopsy is performed during pregnancy. For up to 12 weeks, performing a biopsy risks increasing the likelihood miscarriage, and in the later stages increases the likelihood of premature birth, so a cervical biopsy during pregnancy is performed in the second trimester, when the risk is lower.
What is a biopsy
A biopsy is a method of intravital sampling of various cells and tissues (biopsy sampling) from the patient’s body for further laboratory testing.
The accuracy of the biopsy results depends on:
- the experience of the doctor conducting the biopsy procedure and the qualifications of the laboratory assistant examining the obtained biological material;
- the amount of biopsy taken (biological material must be taken from several areas of the tissue being examined (at least three tissue samples taken from different depths)).
At the moment, biopsy is the only diagnostic method that allows one to reliably determine the nature of various neoplasms (carrying out differential diagnosis between benign and malignant neoplasms).
Despite the fears of many patients, a biopsy is not a dangerous or harmful procedure for the body. Due to the high accuracy of the study, for many diseases a biopsy is considered the “gold standard” of diagnosis, allowing the diagnosis to be made as accurately as possible.
A biopsy allows:
- obtain the most detailed information about the depth and breadth of the pathological process;
- the nature of the neoplasm (benign or malignant tumor, eosinophilic or inflammatory infiltrate, etc.);
- confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis;
- carry out differential diagnosis;
- reliably determine the stage of the pathological process;
- eliminate neoplasms (when performing many types of biopsies, it is possible, in parallel with performing a diagnostic biopsy, to immediately remove the pathological focus);
- evaluate over time the effectiveness of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, etc.
Indications
A biopsy of the uterine cavity can be performed for certain indications. In this case, the indications include:
- When there is a pathology in the cervical area that needs confirmation at the tissue or cellular level.
- If, during a visual examination by a doctor and based on the results of smears, it was not possible to obtain the required information, and without a biopsy it is not possible to accurately establish a diagnosis.
A biopsy is performed to diagnose the following ailments:
- endocervicitis,
- ondylomas,
- leukoplakia,
- dysplasia of the cervical epithelium,
- carcinoma.
All these pathologies are very dangerous, so you need to start treating them as quickly as possible.
Any medical procedure will have certain contraindications. In this case, performing a biopsy is prohibited under the following conditions:
- bearing a child;
- inflammation affecting the vagina and cervix;
- inflammatory foci present in the pelvis;
- blood pathologies: severe anemia, hemophilia, diseases of the hemostatic system;
- sexually transmitted pathologies;
Lymph node biopsy
Enlarged lymph nodes always suggest the possibility of cancer - the presence of metastasis in the lymph nodes or their disease - lymphoma, lymphogranulomatosis. A puncture biopsy is rarely performed so as not to injure the node and not activate metastasis.
Typically, a small skin incision is made under local anesthesia and the entire node is carefully removed.
Postoperative period and possible complications
After a biopsy, almost every girl experiences discharge. Their duration and abundance depend on a number of factors, such as the sampling method, as well as the individual characteristics of the organism.
For example, during a radio wave biopsy of the cervix, a woman may experience light discharge. They may bother you for several days without causing any symptoms. But after a loop biopsy, bleeding may occur profusely, as if menstruation has occurred or bleeding has developed. Their duration is 5-7 days.
The temperature may also rise slightly, because any instrumental intervention is a huge stress for the body. There is a risk that an infection will occur after surgery. If the temperature exceeds 37.5 degrees, then you should immediately consult a doctor.
It is normal for pain in the abdomen and deep in the vagina after a biopsy. Don't worry, all symptoms will disappear on their own. To eliminate abdominal pain that occurs due to contraction of the cervix, you can use painkillers - Indomethacin or Nurofen.
During the removal of tissue from the cervical mucosa for biopsy, it is prohibited to have sexual intercourse for at least about a week.
Cervical biopsy is a very popular procedure, with which it is possible to quickly determine the presence of a malignant tumor. Consequently, the patient will be able to complete treatment in a timely manner and get rid of the pathology. Biopsies are performed today using various methods. The choice of the appropriate option is determined by the doctor after examining the patient.
In what cases is a biopsy performed in oncology?
Taking material for research is indicated in the following cases:
- if a malignant tumor is suspected;
- in the presence of cancer to identify it;
- to determine metastases in lymph nodes;
- for diagnosing blood diseases (bone marrow biopsy);
- if tumor recurrence is suspected;
- if there is a suspicion of metastasis in organs or bones.
The collected material is sent to the laboratory for pathohistological and cytological examination.
Decoding the results
When conducting such a histological analysis, specialists determine whether there are cells with changes on the surface of the uterus. Such violations are practically harmless, but they can also be drastic, characteristic of the presence of a malignant tumor or a precancerous condition. There are mild, severe and moderate dysplasia, as well as carcinoma - an early stage of cancer.
Analyzes are deciphered. All identified changes belong to one of three groups:
- background;
- precancerous;
- cervical cancer
Since the collection of material is associated with damage to the patient’s tissue, albeit to a small extent, specialists use various painkillers - anesthetics. The cervix is a part of a woman’s body in which many nerve endings are intertwined, but there are no pain receptors among them. Therefore, the duration of anesthesia for a biopsy and the selection of drugs to reduce its pain depend on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Therefore, specialists often use local anesthesia, that is, the introduction of lidocaine and other agents. Also in some cases (for example, during surgical sampling of material), spinal anesthesia is used. This is an injection into the lumbar region with which a special substance is injected that blocks pain sensitivity in the lower half of the body.
When performing a cervical biopsy, the patient needs to relax all muscles as much as possible and not experience emotional distress. This will avoid complications and pain resembling contractions.
results
The result of a diagnostic biopsy will be ready in about a week. A preparation (glass) is prepared from the resulting material and examined under a microscope for the presence of pathologically altered cells. Depending on their quantity and quality, histology can show the following types of tumors:
- Consisting of the same type of cells: seminoma, teratoma, embryonal cancer, yolk sac tumor, chorionepithelioma.
- Having a mixed composition: embryonal cancer in combination with teratoma, yolk sac tumor, seminoma.
Depending on the result obtained, the doctor chooses treatment tactics.
Testicular biopsy result sample
If a biopsy is done to extract sperm, the material is immediately transferred to reproductive specialists who study the quality of germ cells, their motility, and, if necessary, perform genetic tests.
The result depends on the reason for the absence of sperm in the ejaculate. With obstructive azoospermia (blockage of the ducts), they can almost always be removed. If the problem is a violation of their synthesis (secretory azoospermia), then with a puncture biopsy, successful extraction of high-quality sperm occurs in 2/3 of cases, with TESE this probability is 45%, with micro-TESE - 63%. The figures show the probability of sperm retrieval using different biopsy methods:
The use of microsurgical operations (PESA, MESA, TESA, TESE, Micro-TESA) for the treatment of obstructive and non-obstructive azoospermia - says urologist-andrologist Vladimir Morev
A number of genetic and endocrine factors also influence the biopsy result in patients with secretory azoospermia. Genetic include mutations in the AZF loci of the long arm of the chromosome and changes in the karyotype. With microdeletion (loss of a chromosome section) AZFa and AZFb, the probability of detecting sperm is zero, with AZFc they can be detected in 70% of cases.
See also: There is an analysis to assess the quality of the genetic material of the unborn child - karyotyping of spouses.
In the classic form of Klinefelter syndrome, sperm are obtained using micro-TESE in 56-69% of cases. In patients with the mosaic form, the probability is only 10%.
In hypogonadism, the functionality of the testicles is preliminarily stimulated through gonadotropic therapy.
Stomach biopsy, how long to wait for results
A gastric biopsy is also called a gastrobiopsy, and is most often performed when a cancerous tumor is suspected.
A biopsy sample is taken during gastroscopy. Material for research is taken from several areas of the mucosa (the most suspicious), that is, during one gastroscopy procedure, 3-4, and sometimes 6-8, biopsies are actually performed. In some cases, for example, with submucosal infiltrative growth of a neoplasm, a repeat deep biopsy is required.
A gastric biopsy is performed in order to confirm or refute a previously established diagnosis, as well as for the purpose of differential diagnosis to exclude diseases that are similar in their clinical picture.
Using a biopsy, it is possible to clarify the morphological structure of tissues and the cellular composition of a pathologically altered area of the mucosa, thereby determining the benign or malignant nature of the process, as well as clarify the activity of the inflammatory process and identify Helicobacter pylori.
Gastrobiopsy is prescribed in the following cases:
- in the presence of a stomach tumor;
- if you suspect a cancerous tumor of the stomach;
- if other studies have not made it possible to accurately formulate a diagnosis;
- with long-term non-healing stomach ulcers;
- for chronic gastritis (to clarify the stage of the process and the risk of degeneration into a gastric ulcer);
- to identify the cause of gastritis, which is difficult to treat;
- for diagnosing gastric polyps;
- in patients with Barrett's esophagus (precancerous condition);
- to control postoperative polyp removal;
- after gastric surgery to remove a cancerous tumor;
- as a screening diagnostic method for patients at risk.
Contraindications to endoscopic manipulation of the stomach
Endoscopic manipulations are considered minimally invasive, however, they sometimes have contraindications.
Contraindications for gastric biopsy can be absolute or relative.
Absolute contraindications include:
- cerebral stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- esophageal stenosis (the tube does not move from the esophagus into the stomach);
- bronchial asthma (during an attack).
Relative contraindications include:
- high body temperature;
- severe runny nose (interferes with nasal breathing; during endoscopy the patient breathes through the nose);
- inflammation in the pharynx;
- epilepsy;
- heart failure;
- mental illnesses;
- hypertensive crisis;
- hemorrhagic diathesis (high probability of bleeding).
A biopsy is performed during fibroesophagogastroscopy (FEGDS). The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. Due to the need to perform a biopsy, the manipulation is extended for a short time - only 5-10 minutes.
The patient does not need special preparation. Sometimes the manipulation is done under short-term anesthesia (for children and people with mental disorders).
You should not eat food at least 6 hours before fibrogastroscopy, and drink liquids 2 hours before the test. Patients suffering from pyloric stenosis are advised to first perform a gastric lavage, since they have a high probability of stagnation of undigested food in the stomach.
Description of the gastroscope
Fibrogastroscopy and biopsy are performed with one instrument - a fibrogastroscope. It looks like a flexible but fairly rigid probe.
The end of the probe, which is swallowed by the patient, has an optical system (lens, fiberglass light guide), in addition, at this end of the probe there is an opening for supplying water, air and instruments necessary for medical procedures. The device is controlled using a control unit located on the handle.
To take a fragment of the gastric mucosa for examination, biopsy forceps are used. If it is necessary to remove a large fragment, for example a polyp, a special electrosurgical loop is used for capture.
The patient is positioned in a lying position on the left side.
- the upper respiratory tract and esophagus (its upper third) are treated with 10% lidocaine (a local anesthetic that suppresses the gag reflex);
- then the patient takes a mouthpiece into his mouth, through which the endoscope is inserted, the tube is inserted into the throat, after which the person makes swallowing movements, pushing the probe into the stomach;
- during the examination, the image from the lens of the device is transmitted to the monitor, which is monitored by the endoscopist; he examines all visible areas of the gastrointestinal tract through which the probe passes; to improve the visibility of the folded areas, air is pumped through the endoscope;
- the required fragment of the mucous membrane, visible through the endoscope, is removed using biopsy forceps that appear from the hole at the distal end of the probe; if necessary, fragments are taken from several areas; the patient does not feel pain during this manipulation.
Chromogastroscopy
Chromogastroscopy is an additional endoscopic technique that allows you to clarify the diagnosis. This procedure makes it possible to increase the information content of FEGDS due to clearer visualization of the mucous membrane, especially its pathologically altered areas.
This examination is recommended for patients who have undergone endoscopy, but its results did not provide a basis for formulating an unambiguous diagnosis.
During chromogastroscopy, a dye is sprayed onto the gastric mucosa, which more intensely stains areas of neoplasms; the endoscopist subsequently removes fragments of the mucosa from these areas for examination.
When removing fragments of the mucous membrane for gastritis, two fragments are taken from the front wall of the stomach and two from the back (four fragments in total).
If there is a peptic ulcer or tumor, in addition to the existing four fragments, it is necessary to additionally take 5-6 fragments from the central and peripheral zones of the lesion. If necessary, take 8 additional fragments.
The greater the number of biopsies taken, the more accurate the diagnosis will be.
Removing the fragments is absolutely painless for the patient. In cases where the patient tolerates the FEGDS procedure very painfully, sedatives can be used.
Complications during FEGDS with biopsy are very rare. The procedure is minimally invasive and well tolerated by patients.
However, in rare cases, among the possible negative manifestations, the following can be identified:
- aspiration pneumonia;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- injury to the walls of the esophagus and stomach;
- endoscope entering the trachea;
- bleeding from a damaged vessel;
- allergy to lidocaine;
- infectious complications.
Before performing FEGDS, the mucous membranes are treated with a local anesthetic to eliminate discomfort. Lidocaine is usually used for this, but other drugs can also be used. People who have drug allergies should tell their doctor about this.
In rare cases, when performing FEGDS and taking bipotate from the gastric mucosa, the following may occur:
- damage to the wall of the esophagus or stomach by an endoscope;
- infectious process;
- bleeding (if a vessel is damaged);
- aspiration pneumonia (caused by vomit entering the trachea and bronchi).
Complications after a biopsy occur extremely rarely, but it is impossible to say with 100% certainty that they will not occur. Their occurrence may be due to any non-standard situations during manipulations with the endoscope, the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the patient’s digestive tract, as well as pathological changes in the esophagus and stomach.
The advancement of the endoscope, for example, may be hampered by a pronounced gag reflex or increased psycho-emotional excitability of the patient. Damage to the stomach wall most often occurs at the site of the ulcer, when the stomach wall is very thin.
During the biopsy process, small sections of the gastric mucosa are pinched off. This procedure is not accompanied by pain and patients usually tolerate it without any problems.
But in order to perform a biopsy, it is necessary to pass an endoscope through the esophagus into the stomach, so possible consequences are associated, as a rule, not with the biopsy procedure itself, but with FEGDS - esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
After the procedure, the patient may experience discomfort in the projection of the stomach; this is normal. Minor bleeding that occurs when fragments of the mucous membrane are taken usually stops on its own.
Any recommendations after the event?
The procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis, the person can go home immediately after it, but significant physical activity should be avoided for 1-2 days.
Some time after the procedure, discomfort and pain in the throat and chest may occur. These sensations usually go away on their own. If there is discomfort in the throat, it is recommended to rinse it with a soda solution or use a spray or lozenges that soften the mucous membrane.
In cases where, after a gastric biopsy, the temperature rises sharply, dizziness occurs, shortness of breath and vomiting occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If during the procedure the patient was taking sedatives, he is prohibited from driving a car, and it is also not recommended to perform work that requires concentration and is associated with danger for him and others.
Nutrition after the procedure
After a gastric biopsy, it is not recommended to drink or eat food immediately. It is recommended to wait 4 hours after the biopsy. This is due to the fact that during the FEGDS procedure the pharynx is treated with lidocaine (reduces the gag reflex). The local anesthetic partially blocks natural reflexes, which can cause choking on liquid and especially solid food.
Source: //okishechnike.com/info/biopsija-zheludka-skolko-zhdat-rezultat/
How many days will it take for a gastric biopsy analysis to be ready? | Medic Help
Diagnostic procedure aimed at examining the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
Old price from 3,500 ₽ from 2,500 ₽ promotion
Medical examination of internal organs using an endoscope
Old price from 3,000 ₽ from 2,000 ₽ promotion
Histological examination helps to accurately determine the presence of dangerous cells and neoplasms
Old price 3,500 ₽ from 2,500 ₽ promotion
Gastroscopy is one of the most objective and accurate ways to examine the gastric mucosa
Old price 3,500 ₽ from 2,500 ₽ promotion
Tests for STDs are a set of laboratory tests that help identify pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases.
Old price 2,800 ₽ from 2,000 ₽ promotion
Gastroscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy, endoscopy) is an examination of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach
Old price 3,000 ₽ 2,500 ₽ promotion
How many days does the biopsy take?
A biopsy is a study of affected tissue. It is carried out to make an accurate diagnosis. This research method is used to determine the nature of the tumor, whether it is benign or malignant. Also to confirm another disease associated with damage to organ tissue.
There are several types of biopsies
Tissue for examination is taken from the outside and inside. Internal biomaterials are collected using special instruments; a small piece is enough for examination. Samples can be taken in the following ways:
• Puncture – done using a syringe with a needle. It is used for lesions that are located not far from the surface of the skin. During the procedure, the process is monitored using ultrasound. A needle is used to pierce the skin, injected into the tumor or affected tissue, and a sample is taken. It is necessary to make several such punctures to obtain more accurate information;
For each group of organs, depending on the location and possibility of access to them, there are separate biopsy methods.
How long will it take for the result to be ready?
After the procedure, many patients ask the question how many days a biopsy is done in Moscow clinics. The study takes different times, depending on the volume of material collected and the diagnostic method.
How is the research going?
When living cells are taken from the body, they must be immediately sent to the laboratory for further research. How many days a biopsy is performed in Chertanovo depends on the amount of work.
Stomach biopsy
For diseases of the stomach, in order to clarify the origin and degree of development of the pathology, patients are often prescribed a biopsy.
A gastric biopsy, or gastrobiopsy , is a study of the cell composition of altered organ tissues to make an accurate diagnosis, involving the collection of small fragments of the mucous membrane and their subsequent microscopic analysis.
Gastric biopsy can be exploratory (blind) or targeted. A blind test is carried out using a special biopsy probe, and the contents are collected without visual control.
A visual biopsy is performed using a special device - a gastroscope. It is a long tube into which a lighting and optical system (endoscope) is mounted, equipped with a micro-instrument for taking particles of affected tissue for analysis (biopsy forceps, a special knife, loops or electromagnetic retractor devices).
The use of a gastroscope allows you to specifically collect particles of the gastric mucosa from certain areas of the gastric wall for analysis.
In what cases is a biopsy prescribed?
A biopsy examination is prescribed when other methods of examining the stomach (endoscopy and radiography) are insufficiently informative in order to differentiate diseases of different nature, but with similar examination results, and also as the most important method for identifying and diagnosing oncological diseases of the organ.
A biopsy is indicated for:
- the presence of tumor processes in the stomach (determination of oncopathology, identification of precancerous conditions); acute and chronic gastritis; ulcerative processes in the stomach (to distinguish a ulcerative defect from oncology); damage to the mucous membrane for the purpose of their removal (resection); dyspepsia (digestive disorders) to determine the presence (absence) of Helicobacter; after surgery to assess the condition of the gastric wall.
Contraindications
Contraindications to gastric biopsy are:
- states of shock; diseases of the cardiovascular system; hemorrhagic diathesis; inflammatory processes of the pharynx, larynx and upper respiratory tract; acute infectious diseases in the patient; general serious condition of the patient; narrowing of the esophagus; perforation (violation of the integrity of the walls) of the stomach; chemical burns of the stomach; mental illness.
Preparing and performing a gastric biopsy
The biopsy is performed inpatiently or in a clinic. First, the presence or absence of contraindications in the patient is determined, and an X-ray examination of the stomach is performed. To prepare for gastrobiopsy, the patient must abstain from food for 10-15 hours - the procedure is only possible on an empty stomach. The patient takes a lying position on the left side with a straight back.
If necessary, he is given a sedative (calming agent). The throat, larynx and upper part of the esophagus of the patient are treated with a local anesthetic, then an endoscope equipped with a device for separating particles of mucosal tissue is inserted into the patient's larynx through a special plastic mouthpiece.
The subject is asked to make a swallowing movement, and the device, passing through the esophagus, enters the stomach
The tube of a modern gastroscope is so thin, and the instruments for taking biopsies are miniature, that swallowing them does not cause any difficulty for most patients.
The examination is carried out by an endoscopist. Under visual control (the image is displayed on the screen), he collects material from the designated parts of the gastric wall.
The patient does not experience pain.
Often, such separation of particles of the mucous membrane is carried out in stages in several parts of the stomach to obtain more detailed information about the extent and morphology of pathological processes.
The procedure itself takes no more than 10-15 minutes.
Upon completion, the device is carefully removed and the patient is advised to lie down for a few more minutes and not eat food for another hour and a half, and then refrain from spicy, salty and hot foods.
Since hidden internal bleeding is possible as a complication after the examination, after the procedure the patient is administered drugs containing coagulants or hemostatic agents that help improve blood clotting.
If within 48 hours after the test you experience deterioration in your health, a sharp increase in temperature, or vomiting with traces of blood, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If minor bleeding occurs, the patient is prescribed bed rest for 2-3 days, taking medications to reduce bleeding, first fasting, then a gentle diet.
However, such complications occur extremely rarely; most patients do not notice any deterioration in their well-being after the procedure.
Non-targeted collection of mucous particles for analysis using a probe is carried out in a similar way, only samples of the material are taken “blindly”. This method is usually less informative and is used less often in practice.
The examination results will be ready in 2-4 days.
The resulting material is carefully removed, immersed in a preservative and sent to the laboratory for microscopic examination, which will be carried out by a morphologist or pathologist. The extracted particles are immersed in paraffin, subjected to machine cutting, and the sections are examined under a microscope.
In addition, the particles of the material are subjected to special coloring.
During the examination, under a microscope, they determine whether atypical and malignant (cancerous) cells are present among the mucosal cells and what their nature is, and draw conclusions about the degree of damage to the organ, the need and extent of surgical intervention.
Sources:
//diagnostic-md. ru/%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BA%D0%BE-%D0%B4%D0%BD%D0%B5%D0%B9-%D0 %B4%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%81%D1%8F-%D0%B1%D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1% 81%D0%B8%D1%8F
//stomachum. ru/biopsiya-zheludka
Source: //medics-spravka.ru/cherez-skolko-dnej-gotov-analiz-biopsii-zheludka/
Indications and contraindications
Most often, a breast biopsy is performed in the following cases:
- mammography and ultrasound revealed a suspicious area in the lumen of the mammary gland ducts of unknown origin;
- an x-ray in the chest area showed dark or light areas;
- upon examination and palpation, areas of compacted neoplasms were discovered;
- obvious changes in the area of the nipple and areola - changes in color, hollowness, peeling, crust formation;
- discharge from the nipples (purulent, serous, bloody);
- hyperemia (redness) or pathological pallor of the breast, ulcers.
The procedure is not prescribed to every patient indiscriminately. To carry it out, the specialist must have serious reasons. In addition, this type of diagnosis is contraindicated in the following cases:
- pregnancy;
- implanted pacemaker;
- hypersensitivity to certain drugs.
Explaining to the patient that in 85% of cases the biopsy result is negative, that is, a malignant neoplasm is not confirmed, often has a positive effect on the woman’s emotional state, and she is easier to contact and cooperate with medical personnel.
Biopsy for prostate cancer
If prostate cancer is suspected, a biopsy provides the most reliable information and, based on its results, treatment tactics are determined. TRUS (transrectal ultrasound) ultrasound device
The probe is inserted through the wall of the rectum into the prostate, the gland is scanned and, under the control of an ultrasound screen, the required number of puncture needles are “shot” into different parts of the prostate - from 10 to 30 needles. Plunging into the prostate, they collect “columns” of its tissue and are pulled back through the probe.
To prevent infection from the rectum, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. In Israel, a method of percutaneous prostate biopsy has been developed, when the introduction is performed not through the intestine, but through the skin of the perineum, and the number of samples from different parts of the prostate has been increased to 50, which increases the accuracy of the study.