What is a jaw fracture
A jaw fracture is a severe pathological condition in which the linear integrity of the bones of the lower jaw is disrupted to one degree or another.
This may be caused by one of the traumatic factors as a result of mechanical action, or a serious illness (osteomyelitis, bone syphilis, tumor). There is also a violation of the integrity of surrounding tissues - facial muscles, blood vessels, nerves. There are a number of factors that provoke jaw fractures, these are:
- Alcohol consumption. As a result, the risk of injury increases, both in an accident and due to a fall or participation in a conflict using physical force;
- Features of the anatomy of the bone, which is movably fixed at the extreme points of the jaw and forms an arch;
- Using vehicles such as a motorcycle, especially without adequate protection;
- Features of the structure of the chin. It is this most protruding part of the lower jaw that most often experiences traumatic effects;
- Some statistics. A jaw fracture occurs primarily in men aged 21 to 40 years.
Types of jaw fractures
Causes
Fractures occur as a result of various injuries due to increased physical activity or household contacts. But there are also pathological factors such as:
- lack of microelements in the body;
- cysts;
- infectious diseases;
- osteomyelitis;
- long-term treatment with potent drugs;
- metabolic disorder.
Osteomyelitis is an inflammatory process of the jaw caused by a dental infection. The pathology is difficult to treat and is extremely rare. Infection from the tooth root penetrates the bone, contributing to changes in local metabolism. As a result, partial necrosis of bone tissue is possible, and the likelihood of blockage of nearby vessels increases. Characteristic symptoms of the disease include putrid breath and loose teeth. Gradually, the bone reduces its strength, and in extremely advanced cases, even with a weak impact, it can lead to a jaw fracture.
Causes of injury
A fracture can be caused by the following reasons:
- intense stress in everyday life, falling, performing sports exercises, road accidents;
- pathologies of bones, formations and cysts;
- improper tooth extraction.
When the jaw is damaged, displacement can occur in three types:
- sagittal;
- vegital;
- transversal.
This plays a very important role in identifying the correct treatment regimen and choosing the equipment that will be used for correction. As a rule, in case of a displaced jaw fracture, treatment, symptoms, photo consequences, what to eat are special splints that are fixed on the teeth.
The doctor collects bones with his hands. The person at this moment is under local or general anesthesia.
Fragments can be fixed using nylon devices. The jaw can be attached with special metal spokes that are installed externally.
After adjustment, the patient needs peace of mind with mandatory antimicrobial actions.
We consider in detail all aspects of such a complex facial injury as a displaced jaw fracture: treatment, symptoms, consequences, photos. What to eat is a separate issue, because in the postoperative period the jaws need to be fixed, and the patient is given splints. And the consistency of the food is, for obvious reasons, extremely liquid.
Patients must be prescribed a special diet. This must be done due to the fact that the patient will not be able to fully move his jaws.
The bones heal in at least a month, so during this period the patient will have to eat only liquid meals.
The consistency of all food should be puree, so a person should consume soups, broths, fruits and vegetables, ground through a meat grinder.
Fractures of the upper jaw or its lower part are formed due to:
- Mechanical damage of any kind caused by external factors.
- Tumor diseases.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Other diseases.
Risk category: men aged 15 to 40 years.
If the jaw is damaged, self-medication is strictly prohibited, since displaced or fragmented fractures are often diagnosed, which can cause the following complications:
- bite problems;
- inability to chew food independently;
- infection of the oral cavity;
- the appearance of inflammatory processes.
In terms of the frequency of injuries, the first place is occupied by fracture of the articular process. Injuries to the middle part of the body of the lower jaw and its angle have also become frequent.
Fractures are distinguished:
- closed;
- open;
- full;
- incomplete.
Signs:
- Inability to open the mouth wide.
- The appearance of pain when talking.
- Change in bite.
- The appearance of facial numbness.
- Asymmetry of cheekbones.
- Double vision.
The full list of signs of a jaw fracture depends on its location.
Rehabilitation after injury
The rehabilitation period after treatment of a jaw fracture is accompanied by regular use of anti-inflammatory drugs. On average, its duration is 2 months, but deviations from the norm are possible. How long the healing process for a jaw fracture will take depends on the complexity of the injury. In order to accelerate the fusion of tissues and bones, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out. Fractures are treated with phosphorus and calcium electrophoresis, UV irradiation, microwave therapy and other radiological procedures. A massage of the collar area is also carried out and mud therapy is practiced. Therapy is based on the following principles:
- Exposure to ultra-high frequency magnetic field.
- Ultraviolet irradiation is practiced every three days for 20 minutes.
- Electrophoresis with calcium promotes rapid restoration of bone tissue. The general course of its implementation is 10-14 days. The procedure lasts half an hour.
- Magnetic therapy using low frequencies is carried out for 20 minutes for 10 days.
The speed of recovery depends on the following factors:
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- age and general condition of the body;
- compliance with medical recommendations;
- complexity of the fracture and the operations performed.
Symptoms and types of fractures
The following types are taken into account based on the reason:
- traumatic in nature as a result of physical impact on bone tissue. Often occurs in road accidents, violence against a person;
- pathological ones are caused by bone diseases: tumors, osteochondrosis, etc.
Based on the degree of damage:
- open fracture of the jaw, when fragments extend beyond the boundaries of the gums and, as a result, the mucous membrane ruptures;
- closed, in which the facial tissues remain intact.
The lower jaw is more prone to injury, because it is mobile. After receiving an injury, you must immediately consult a doctor for a proper examination of the lesion.
Signs of a fracture
Injuries to the upper jaw are classified according to the level of the fracture and its nature. In the latter version, a distinction is made between fractures with displaced fragments and without displacement. By level (location) they are:
- Le Fort I fracture – at the lower level. With a bilateral fracture, it is accompanied by breaking off the bottom of the maxillary sinus and a broken base of the nasal septum.
- Le Fort II fracture - at an average level. Often accompanied by separation of the upper jaw and nasal bones from the skull.
- Le Fort III fracture – at the upper level. Accompanied by complete separation of the upper jaw, nasal bones and cheekbones from the skull, as well as traumatic brain injury.
Injuries are also distinguished by their nature:
- traumatic – as a result of external influence;
- pathological – as a consequence of diseases (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, syphilis, etc.).
There may be complete or incomplete fractures:
- when complete, the injured bone is interrupted;
- incomplete - expressed by cracks, breaks.
Fractures can be open or closed. Injuries to the upper jaw are rarely closed, because rupture of the oral mucosa occurs. Fractures are also classified according to the number of injuries: single, double, multiple.
In case of jaw injury, the symptoms depend on the type of fracture: open or closed, with or without displacement, single or multiple, longitudinal or transverse. Signs of a fracture are based both on external manifestations and on the subjective sensations of the victim.
The classification of fractures is sometimes complicated by the fact that the victim is unconscious. In such cases, the diagnosis is based solely on a medical examination and data obtained as a result of hardware diagnostics.
Signs of a mandibular fracture:
- With a complete fracture, there is a displacement of the jaw and fragments, which are different in shape.
- If incomplete, there is no displacement.
- When open, damage to the epidermis and mucous membrane is visible.
- When closed, the epidermis remains intact, the fracture is noted internally.
- In case of splintered, which is very rare, surgical intervention is required. To obtain this injury, you must have powerful force.
Symptoms and main signs:
- Facial asymmetry.
- Great swelling.
- Redness of the skin.
- Temperature change towards increase.
- Formation of a frozen blood clot during a closed fracture.
- Bruise.
- Painful sensations when touching and talking.
- The presence of mobility of fragments.
- Bite problems.
- Increased sensitivity of teeth.
Based on location, fractures of the lower jaw are divided into 2 groups:
- Body fractures. More often they are open, clinically accompanied by mucosal rupture and bleeding. There are median (the fracture line runs between the central incisors), mental (violation of integrity is observed in the area between the canine and premolar or between premolars), lateral (the damage zone is localized in the area of the molars), angular (the bone is damaged in the angle area) fractures of the lower jaw.
- Fractures of the branch. This category includes violations of the integrity of the branch of the mandibular bone (the fault line has a parallel or perpendicular direction relative to the longitudinal axis) and its two processes - the articular and coronoid. In turn, a fracture of the articular process can occur at the level of the base, neck or head. Closed fractures of the mandibular ramus are more often diagnosed.
Fractures of the lower jaw are also divided into linear (one fracture line is observed), comminuted (several fragments are formed, intersecting at different angles) and combined, open and closed, unilateral and bilateral.
Types of jaw fractures
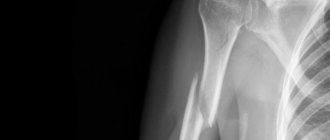
Jaw fracture on x-ray
A fracture can occur in both the lower and upper jaw. Damage is divided according to several other criteria. Based on the nature of the damage, the following fractures are distinguished:
- Pathological . A fracture occurs when there is a defect in the bone tissue. Even a small load can cause a violation of the integrity of the bone.
- Traumatic . This type of injury occurs as a result of blows, falls from a height, etc.
Depending on the presence of soft tissue damage, there are open and closed fractures of the lower jaw.
- An open fracture is accompanied by rupture of soft tissues with bone fragments. Such an injury can lead to infection in the wound.
- A closed fracture is considered less dangerous because tissue rupture does not occur during injury.
Did you know: How to treat arthritis of the jaw joint?
Another criterion by which the complexity of a fracture of the upper and lower jaw is determined is the presence of displacement. So, there are three types of damage:
- Fracture of the lower jaw with displacement . In the event of such damage, bone fragments are displaced from their usual place immediately after the impact or during transportation of the patient.
- No offset . It is logical that this type of injury is not characterized by shear during bone injury.
- Comminuted fracture . The most difficult type of injury, in which the jaw literally crumbles into pieces.
A particularly dangerous type of jaw fracture is a double mandibular fracture . With it, the central fragment of the jaw falls down, and the side parts diverge inward and upward. It turns out that such an injury combines a lateral (mental) fracture of the lower jaw and a fracture of the upper jaw.
After receiving such injuries, a person can easily suffocate, because there is a high risk of loss of consciousness and tongue retraction. This is why you need to urgently call an ambulance.
Symptoms
It is not always possible to recognize a fracture of the lower jaw at first glance, but a specialist must give an objective picture. The situation is complicated by the fact that the victim may not be conscious or may also receive a traumatic brain injury. Therefore, when it is necessary to determine a fracture in the lower jaw, the symptoms must be assessed separately - both felt by the person himself and objective.
Painful sensations
With this type of injury, pain always appears and is severe, especially in the area of injury. It intensifies with any manipulation - during conversation, eating, and other movements. This is most likely due to a rupture of the nerves or periosteum, where a large number of sensory endings are also located, which has begun with an inflammatory process.
Common signs of jaw fractures, regardless of their type, include the appearance of sharp acute pain, nausea, impaired chewing, swallowing, and speech functions, and the inability to close the mouth. Other symptoms depend on where the fracture occurred.
Fractures of the lower jaw are accompanied by:
- swelling of the soft tissues of the face;
- asymmetry;
- hemorrhage at the site of injury;
- pain during palpation, attempts to talk, open the mouth;
- malocclusion;
- tooth sensitivity;
- increased secretion of saliva mixed with blood.
In case of damage to the upper jaw, symptoms will appear:
- bleeding between the upper lip and teeth;
- swelling of the nose, cheeks, lips;
- a fracture of the upper jaw may be accompanied by a displacement of the nasal septum, a fracture of the maxillary sinus;
- hematoma under the eyes if the base of the skull is affected;
- impairment of smell and vision;
- inability to open your mouth;
- drooping eyeballs;
- facial asymmetry.
Athletes involved in traumatic sports are most susceptible to jaw fractures. Important! Fractures of the upper jaw result in death in 10% of cases. Death does not occur due to isolated trauma, but when the skull or brain stem is damaged.
Classification
The classification of mandibular fractures involves complete and incomplete fracture. In the first case, displacement of the fragments is observed. The lower facial region is more susceptible to injury, which is due to anatomical features. At the same time, fractures of the lower jaw are not so dangerous in terms of consequences. Types of fractures also include typical injuries:
- angular fracture of the mandible – known as angular violation,
- middle - the fracture site is between the central incisors,
- mental fracture - the wound is localized in the area of the mental foramen,
- coronary – diagnosed when the coronoid process is affected,
- cervical - occurs when the condyle is damaged.
In medical practice, there is a double fracture of the jaw, which can be unilateral or bilateral. The majority of injuries are closed fractures. Open wounds are not typical for non-gunshot fractures of the lower jaw.
In case of multiple injuries, comminuted fractures occur. If there is no shift, they speak of linear traumatism. Combined injuries also occur. When a bone is fractured, a displacement of the articular head of the lower jaw is observed. Then they talk about fracture-dislocation.
The classification of fractures of the upper jaw deserves special attention. In this case, the following are distinguished:
- Guerin-Lefort - in this case, part of the jaw along the bottom of the maxillary sinuses is injured. An isolated fracture of the maxillary sinus practically does not occur,
- suborbital - a characteristic fracture of the upper jaw passing through the root of the nose. In parallel, there may be damage to the posterior or anterior wall of the maxillary sinus (HPV),
- subbasal fracture - involves a separation of the upper bone. Occurs when the blow falls on the nose and eyes.
In case of a gunshot wound, the fracture lines do not fit into the traditional pattern and have unpredictable localization.
Trauma code according to ICD 10
According to the disease classifier, injuries to the facial bones are coded S02. A fracture of the upper jaw is coded S02.4. Multiple injuries are coded according to the international classification S02.7. And the fracture of the lower jaw has a code according to ICD 10 - S02.6. If the floor of the orbit is simultaneously affected, the injury is coded S02.3.
Diagnostic methods
The patient’s complaints and symptoms will help the doctor determine the presence of a fracture without obvious signs and understand what to do next, but to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the complexity of the fracture, it is necessary to use the following methods:
- initial examination and palpation;
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- orthopantomography;
- masticationography;
- gnathodynamometry;
- myography;
- thermal imaging;
- rheography;
- MRI.
X-ray
A jaw fracture can be diagnosed based on a single visual examination. However, further examination is necessary to identify the type, nature of the damage, and the presence of complications.
Important! If the victim breaks his jaw as a result of pathological bone conditions, the diagnosis must be supplemented with other laboratory and radiographic studies. This is necessary to identify the true cause of the injury.
Since fractures of the lower jaw may be accompanied by damage to other organs, consultation with a neurologist, otolaryngologist, or ophthalmologist is necessary. During the examination, blood pressure levels and heart rate are constantly monitored.
The diagnosis of a mandibular fracture is made based on the patient’s complaints, local status, and X-ray data. During a physical examination, the dentist identifies characteristic external oral signs of a mandibular fracture: swelling of the soft tissues in the area of damage, discoloration and loss of skin integrity.
There is a deviation of the midline. During palpation examination, it is possible to detect irregularities and retractions of the bone.
If the fracture line of the lower jaw passes in the area of \u200b\u200bthe angle or branch, slight pressure on the chin leads to increased pain at the site of injury. Conversely, if the patient has a mental fracture, bilateral pressure in the angular areas causes severe pain in the frontal area.
To determine the location of a mandibular fracture, dentists use a diagnostic test in which a spatula is placed along the transversal on the chewing surfaces of the lower molars. Lightly tapping on the protruding part of the spatula with the teeth closed causes pain in the patient in the place where the fracture line of the lower jaw passes.
To diagnose the integrity of the articular process, the area of skin in front of the tragus is palpated. In order to determine the trajectory of movement of the articular head, a test is used in which the dentist places his index fingers in the victim’s ear canals.
The patient slowly performs movements in the vertical and transverse planes. The absence of movement of the articular head confirms the presence of damage to the condylar process.
X-ray data are of key importance in the process of diagnosing a mandibular fracture. Often, several images are taken in different projections (anterior, lateral radiographs).
If a mental fracture of the lower jaw is suspected, a targeted radiograph is taken along with a survey radiography. To determine the integrity of the condylar process, special placements are used (according to Schuller, Parma).
An x-ray of a fracture of the lower jaw reveals a violation of the integrity of the bone in the form of a thin strip of clearing. It is necessary to differentiate a fracture of the lower jaw from other injuries to the bones of the maxillofacial area, as well as from soft tissue bruises.
A physical examination is performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Recovery after treatment
Rehabilitation measures and strict adherence to medical recommendations speed up recovery after HF fractures. Physiotherapy, medication and exercise are prescribed as shown in the table.
| Type of therapy | Target | Peculiarities |
| Medication | Relieves pain, swelling, helps replenish essential minerals and form callus | The drugs can be in the form of tablets and injection solutions |
| Physiotherapy | Accelerate tissue healing, normalize blood flow and metabolic processes | Magnetotherapy, UHF, electrophoresis |
| Gymnastics | Strengthens the muscular system, restores the functions of swallowing, chewing, speech | Loads are required 4 weeks after injury to the upper jaw. Their volume and intensity gradually increase |
| Proper nutrition | Provide the body with the necessary vitamins and energy without loading the facial muscles | Pureed, liquid dishes with a temperature of 36-50 degrees are used. Have to eat through a straw |
Only a specialist knows what to do in each specific situation with a fracture of the HF. The success of treatment depends on his experience and qualifications. It is important to remember that complex and open fractures can lead to facial deformity. Features do not change for the better, and patients often have to turn to plastic surgeons.
The classification of fractures of the upper jaw includes 3 types of traumatic injury. Let's look at each of these types separately:
- 1st – localized under the palatal vault, usually accompanied by fractures of the bottom of the maxillary sinus. It is characterized by the presence of pronounced facial deformation, bleeding from the oral cavity and its vestibule.
- 2nd – characterized by partial separation of the upper jaw and facial bones from the cranial base. This injury is accompanied by intense salivation, swelling and hematomas, nosebleeds, and impaired olfactory function.
- 3rd – represents a complete separation of the upper jaw, zygomatic and nasal bones from the cranial base. It is characterized by distortion of the shape of the face, impaired visual function, displacement of the eyeballs, and the appearance of hematomas under the eye sockets.
In addition, traumatologists distinguish the following types of this fracture:
- Complete - with concomitant displacement of jaw fragments;
- Incomplete - without accompanying displacement;
- Open - characterized by damage to soft facial tissues and skin, bleeding;
- Closed - without concomitant injury to facial tissues.
Basically, this injury is open. Often fractures of the upper jaw are accompanied by the following concomitant injuries:
- Middle ear injuries;
- Damage to the meninges;
- Ruptures of muscle tissue and facial skin;
- Pressing of the nasal bones into the anterior cranial fossa;
- Damage to the nasopharynx;
- Injury to the paranasal sinuses.
Such injuries pose a serious threat to both the health and life of the victim, so it is very important to competently provide the patient with the necessary assistance and deliver him to a medical facility!
Treatment methods
Fractures can only be treated in a hospital. Staples and plates are used to restore bone. Antibiotics and physiotherapy are prescribed. In the most severe cases, surgery is possible (for example, with a fracture of the articular process of the lower jaw). The main treatment is carried out using splinting and bypass, or, in other words, splinting.
Various types of splinting
In some cases, fixation can be done with a bandage. Before splinting the jaw, bone fragments must be carefully compared. The splint is usually installed for 1 month.
Applying a Tigerstedt splint
Serious injuries are treated with a special Tigerstedt splint. It is an aluminum structure with hooking loops and a rubber intermaxillary rod. If the rubber band breaks, you need to reinstall the tire. Self-removal of an applied splint is strictly prohibited.
Treatment of a mandibular fracture includes the following steps:
- Treatment of wounds, disinfection;
- Alignment of the nasal septum, if necessary;
- Combination of bones, fragments;
- Adjustment of the jaw using a splint; sometimes plates are used, which are fixed with screws;
- Restorative procedures.
Treatment prescribed for a jaw fracture takes on average up to one and a half months to allow the bone to heal, followed by rehabilitation. Anti-inflammatory drugs are used - antibiotics, restoratives, antifungals.
Also, high-quality treatment of fractures is impossible without proper oral hygiene at home. The splint and the teeth themselves must be thoroughly cleaned of food debris, you need to use antimicrobial rinses, antiseptics, a soda solution helps a lot.
Additionally, special gymnastics is intended to cure the patient, which must be performed immediately after removing the splint. Physiotherapy is also indicated, this is an electromagnet operating at an ultra-high frequency, low-frequency pulsed magnetic influence, ultraviolet light, calcium electrophoresis at the fracture site.
In case of a jaw fracture, the main treatment is carried out using osteosynthesis. It is indicated in the presence of multiple fragments, their displacement, pathological processes in bone tissue, and damage behind the dentition.
Treatment of mandibular fractures includes antiseptic wound treatment and pain relief. To achieve stable reposition and fixation of fragments, the edges of the bone are smoothed and interposition of soft tissues between the fragments is eliminated.
Teeth located on the fracture line must be removed. In order to prevent the addition of a secondary infection, the mucous membrane in the area of the rupture is sutured.
Primary immobilization for a fracture of the lower jaw consists of creating a fixed block consisting of the lower jaw pressed against the maxillary bones. To do this, bandage bandages or the intermaxillary ligature connection method are used.
In case of linear fractures of the jaw body without displacement, as well as in the case of angular fractures of the lower jaw without displacement, double-jaw wire splinting of the jaw is used to fix and immobilize the fragments.
Treatment
Once symptoms have been detected, treatment for mandibular fractures begins. Diagnostics only clarifies the degree of complexity of the damage. As for treatment methods, there are only two of them: splinting the jaw for a fracture and surgery. Let's take a closer look at these two methods.
Splinting
Splint for jaw fracture
This method involves fixing a broken jaw by applying splints (special plastic or metal structures). It was invented by specialists of the last century and is still used today. Although, since that time, tire manufacturing materials have changed significantly. Now specialists are working with belt and aluminum tires.
First aid
After all these measures, you should immediately consult a doctor. Having a damaged jaw is very dangerous and can cause serious complications. The best and safest option is to call an ambulance. Usually people with such injuries are admitted to the maxillofacial department.
If a fracture of the lower jaw occurs, you must urgently call an ambulance. Only outpatient treatment is possible. Before help arrives, the patient should be given first aid. It consists of:
- Stop bleeding. A clean napkin is pressed against the site of hemorrhage; it is also recommended to apply cold: ice, a wet scarf.
- The broken jaw is immobilized. A bar is placed under the upper teeth, after which it is fixed to the head with improvised materials. You can also tie the lower jaw to the upper. Immobilization is prohibited if the victim is unconscious and cannot control breathing.
- Pain relief. It is carried out to avoid painful shock. Analgin, Naproxen, Revalgin are administered intramuscularly. If only tablet preparations are available, they must be crushed, mixed with water and given to the patient to drink.
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation – if necessary. The airways are cleared of blood clots and vomit, the tongue is checked to see if the tongue is stuck, and the victim is placed on his side. If the patient is not breathing, mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration is performed; if there is no heartbeat, indirect cardiac massage is performed.
How can I help?
At the first signs characteristic of this injury, it is necessary to call doctors and competently provide first aid to the victim. First of all, the patient is placed on his side to prevent blockage of the airways. It is important to provide the person with absolute peace, since any movements in this case are strictly contraindicated!
Then you need to stop the bleeding by using tampons and applying sterile napkins. In order to immobilize and prevent possible displacement, a ruler or a special plate can be placed under the area of the patient’s upper teeth, securing it to the head with a fixing bandage. If there are no available means or the victim has damage to the dentition, the upper jaw is simply carefully aligned with the lower jaw and secured with a bandage.
It is recommended to apply an ice compress or something cold to the injured area in order to reduce swelling and pain. If the patient's tongue sinks, it needs to be fixed.
Jaw injuries in most cases are accompanied by very strong painful sensations, up to the development of painful shock. You can slightly alleviate the victim’s condition with the help of analgesic drugs; if possible, it is better to administer the painkiller by injection. After this, the patient must be taken to the clinic, always in a supine position! In this case, the victim must lie face down or on his side.
Features of the diagnostic process
Diagnosis of fractures of the upper jaw is complicated by layering of the maxillary bones. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, determine the type and severity of damage, a survey radiographic examination is performed in different projections.
In addition, studies such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may be indicated. Accurate, detailed diagnostics can reduce the duration of treatment and reduce the risk of developing characteristic complications, even several days after the injury.
Possible complications
To avoid unpleasant consequences, you need to seek professional help in time. The following complications are possible:
- tooth movement;
- the appearance of distances between teeth;
- facial deformation;
- the appearance of malocclusion.
If necessary, surgery may be necessary to restore the affected areas of the face. In case of mild fractures and timely visit to the doctor, following all his recommendations, mobility is restored within a month.