Why does it occur in women?
Varicose veins of the pelvis are more common in women than in men. Provoke the development of pathology:
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- lack of regular sex;
- physical inactivity;
- hard physical labor;
- frequent childbirth;
- complications during childbirth;
- anorgasmia (a woman cannot experience orgasm);
- frequent interruption of sexual intercourse;
- changes in hormonal levels caused by physiological processes (menopause, puberty, pregnancy);
- long-term treatment with hormones;
- abnormal position of the uterus (bent forward or backward).
Pelvic varicose veins in women can be a consequence of congenital weakness of the vascular wall and venous valves. But more often the disease develops due to pregnancy, hormonal disorders or sexual problems.
Risks during pregnancy
Varicose veins of the pelvis during pregnancy are provoked by the combined influence of several factors:
- changes in hormonal levels;
- compression of the veins as the fetus grows inside the uterus;
- an increase in total blood volume due to the formation of placental blood flow.
The totality of the influence of the resulting changes leads to stagnation of blood and the appearance of pelvic varicose veins.
Varicose veins in the pelvic area during pregnancy most often develop in girls who have a history of predisposition to the disease, have given birth frequently, or are obese.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing pelvic varicose veins is not easy. Previously, this disease was misdiagnosed, and therefore incorrect treatment was prescribed, leading to complications. Some doctors performed unnecessary surgery to remove the uterus, which entailed the loss of reproductive and menstrual function.
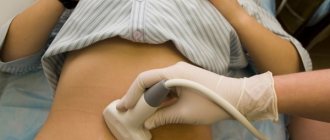
Nowadays, diagnostics have become more advanced. To identify the disease, a comprehensive comprehensive examination of the woman is carried out. The doctor, having met with a patient complaining of pain of unknown origin, finds out the factors provoking the occurrence of the pain syndrome, examines the patient’s legs to find out whether there are manifestations of varicose veins on the lower extremities. If the need arises, the patient is sent to a vascular surgeon for consultation.
Diagnostic methods:
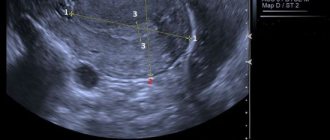
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and lower extremities, which allows you to examine the uterus, ovaries and bladder and see if there are varicose veins of the pelvic organs.
- Doppler examination to identify the characteristics of blood circulation in vascular formations that were localized in this area
- transuterine venography, which allows you to see the site of blood clot formation.
- diagnostic loparoscopy (performed in controversial cases to exclude the presence of related diseases and make an accurate diagnosis).
Thanks to these methods, the symptoms of the disease are detected with great accuracy.
Causes of appearance in men
Varicose veins of the pelvis in men are caused by:
- chronic constipation;
- lifting weights;
- intense training;
- irregular sex;
- physical inactivity;
- testicular vein valve insufficiency;
- drinking alcohol;
- poor nutrition;
- chronic inflammation of the genitourinary area;
- genetic predisposition.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases.
More often, varicose veins of the pelvic vessels in men provoke a violation of the closure of the valves of the testicular vein. Pathology can be congenital or develops under the influence of negative factors.
Intense exercise can cause varicose veins
Symptoms
Signs of varicose veins differ in girls and men. The first symptoms in women: painful discomfort in the lower abdomen. The pain radiates to the groin, sacrum or lower back.
Additionally, the girl experiences:
- painful menstruation;
- cycle disruption;
- increase in the amount of menstrual discharge.
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- premenstrual syndromes;
- difficulty conceiving.
When overwork, stress or hypothermia occurs, pain crises appear.
Painful sensations during sexual intercourse force girls to avoid intimate relationships. Lack of regular sex makes a woman irritable.
In men, the signs of the disease are different:
- pain or burning in the groin and scrotum;
- erectile dysfunction;
- discomfort during sex;
- problems with ejaculation;
- testicular atrophy.
Not all of these symptoms necessarily occur. The reason for examination should be the frequent occurrence of one of the listed symptoms.
Symptoms of varicose veins in the pelvic area
Symptoms of the disease are numerous and quite often resemble signs of other pathologies. Typical for this disease are:
- dilation of the veins of the vulva or perineal area. In addition, the woman feels incessant itching of varying intensity, heaviness and bursting pain. During the examination, the gynecologist notes swelling and swelling of the labia majora. Dilated veins are also detected in the perineal area and anal area. Very often the pathological condition is accompanied by the development of hemorrhoids;
- bleeding. There is a risk of spontaneous bleeding, which is quite difficult to stop. The reason is the thinning of the walls of the venous vessels;
- thrombophlebitis. Quite a common complication. It is diagnosed by severe pain, as well as significant swelling and redness of the skin in the perineal area. The site where the blood clot forms becomes more dense to the touch and painful. With the development of phlebitis - inflammation of the veins - the woman's general body temperature rises and signs of general intoxication appear;
- pain in the lower abdomen. The pain is felt constantly and can vary in nature and intensity. Can spread to the sacral and lumbar region, as well as the groin or perineum. The pain intensifies with prolonged stay in one position and after significant physical exertion;
- pain during and after sex;
- development of PMS. Symptoms typical for the condition are accompanied by increased pain. A woman suffers from painful menstruation, cycle disturbances occur, as well as increased vaginal discharge;
- problems with urination. Sometimes the patient experiences signs of cystitis - frequent urge to go to the toilet, accompanied by painful release of the bladder. This manifestation is due to venous congestion of the bladder.
Treatment
Treatment measures begin with eliminating the cause that provoked varicose veins of the small pelvis (correction of hormone levels, weight loss). Additionally, symptoms are assessed, then treatment is selected taking into account the nature of the pathology.
Surgical intervention (ligation of the enlarged area) is carried out for advanced pathologies, when there is no other way to eliminate congestion. For the treatment of moderate venous dilations, conservative therapy is selected.
Venotonics
For pelvic varicose veins, the use of venotonic drugs becomes the main method of treatment. Reception of funds from this group ensures:
- increasing the elasticity of the venous wall;
- reduction of discomfort and pain in the groin;
- decreased permeability of the walls of small vessels;
- antioxidant protection;
- increased lymphatic drainage;
- eliminating inflammation of the venous wall.
Venotonics are used to treat varicose veins of the pelvic organs at all stages of the disease. But medications do not cure, but only stop the progression of the pathology and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Other drugs
To improve blood circulation, reduce pain and prevent the formation of blood clots, in addition to venotonics, drugs from other groups are used for treatment:
- Anticoagulants (Aspirin Cardio, Curantil). Reduce blood viscosity, prevent the formation of blood clots in extended areas.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin, Ibuprofen). They help reduce painful discomfort in the abdomen and eliminate inflammation.
- Antioxidants (vitamins E and A). Increase the elasticity of veins, protect the vascular wall from the influence of free radicals.
In case of severe stagnation, accompanied by tissue swelling, the person is prescribed diuretics. Diuretics are taken in short courses.
Treatment in women is supplemented by the administration of vaginal suppositories that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Exercises
Exercises for pelvic varicose veins can stimulate blood circulation and prevent lymph stagnation. To prevent venous stagnation, it is recommended:
- Boat. Lying on your back, raise your legs at an angle of 15°. At the same time, raise your upper body, trying to touch your knees with your hands. Socks are pulled out. Do it 5 times.
- Bike. “Pedal” for 1 minute.
- Rider. Standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, perform a half-squat, holding the bottom position for 30 seconds. Rest and do it a couple more times.
Despite the fact that the proposed exercises are simple, you should consult a phlebologist before performing the complex. In some forms of the disease, gymnastics may be contraindicated.
Exercises to improve blood circulation in the pelvis
Treatment of varicose veins of the small pelvis
Even the best treatment does not make it possible to completely cure varicose veins of the small pelvis. But, nevertheless, adequate therapy allows you to get rid of most of the clinical manifestations and significantly improve the patient’s condition. It helps solve the following problems:
- normalizing venous tone;
- prevention of congestion in the pelvic vessels;
- improvement of tissue nutrition.
Experts advise combining drug therapy with physical therapy and wearing compression garments. The set of recommended physical exercises includes “Birch”, “Bicycle”, “Scissors”. You can also improve the outflow of blood from the venous plexuses with the help of breathing exercises, which consists of alternating slow deep inhalations and exhalations. An ascending contrast shower is recommended for the perineal area. Wearing class II compression tights is mandatory for such patients.
Read also: Retinal artery thrombosis
Due to the internal location of the veins affected by the disease, medications are prescribed orally; it is not possible to use venous gels and ointments. The following means are used:
- venotonic;
- improving blood rheology;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- hormonal;
- vitamins.
Removing venous congestion helps reduce the degree of varicose veins of the pelvic organs. For this purpose, a course of phleboprotectors such as Detralex, Venoruton, Ginkor-for is prescribed. For severe pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. This type of therapy is usually prescribed during exacerbations of the disease. As a result, the dilatation of the veins and plexuses of the pelvis decreases, venous blood flow increases, and drainage improves.
For varicose veins of the ovaries, surgical treatment is justified; it is also recommended at the 3rd stage of the disease. The goal of the intervention is to overcome pathological reflux. The optimal method is embolization of the ovarian veins, performed under angiography control. To increase the effectiveness of the intervention, an additional injection of a phlebosclerosant drug is carried out, which is in the state of fine foam. This method is called sandwich embolization.
Recently, minimally invasive methods of surgical treatment of this pathology have been introduced into practice.
What else can be done to improve the condition?
Exercising and taking medications can improve the condition of the venous vessels. But this is not enough. Let's consider what else can be done for varicose veins of the pelvis:
- Diet. It is necessary to remove “harmful goodies” from the diet (spices, smoked foods, canned food) and add porridge, fruits and vegetables, lean fish and meat to the menu. It is important to limit salt intake - sodium chloride retains moisture, increasing internal swelling.
- Compression jersey. Therapeutic linen is selected individually.
- Rejection of bad habits. Nicotine and alcohol have a negative effect on vascular tone.
For varicose veins of the pelvic veins, the use of alternative medicine recipes helps well. Before using a folk remedy, you should consult a phlebologist: contraindications are possible.
Review of reviews on the use of Detralex and Phlebodia, comparison
Detralex and Phlebodia are often prescribed for varicose veins of the pelvis. Some patients respond well to Phlebodia, while others leave positive reviews about Detralex. But they note that, compared to Detralex, Phlebodia allows you to quickly get rid of the signs of varicose veins in the pelvis.
The medications have the same active substance - diosmin, which affects vascular tone and reduces venous congestion.
Phlebodia is a single drug and contains 600 mg of active substance. And Detralex is a complex product that includes 450 mg of diosmin and 500 mg of flavonoids.
According to experts, both drugs have a similar effect on the venous wall:
- increase firmness and elasticity;
- reduce permeability.
Medications stimulate blood flow and reduce vascular inflammation.
According to reviews from patients and doctors, Phlebodia helps well with exacerbations of varicose veins, allowing you to quickly reduce the severity of symptoms. But Detralex acts more slowly and the therapeutic effect will appear after several weeks of use. Phlebologists often recommend Detralex not for treatment, but for prevention. Comparing Detralex and Venarus: which is better?
Stages of the disease
Varicose veins of the pelvis are divided into three stages:
- The first stage is characterized by veins that have increased in diameter to 5 mm; at the upper edge of the left ovary, the veins expand. Primary varicose veins in the pelvis are usually associated with acquired or congenital valvular insufficiency of the ovarian veins.
- The second stage is characterized by veins that have increased in diameter to 10 mm. They cover the left ovary. In this case, there is varicose veins of the uterine veins and the right ovary.
- The third stage is characterized by veins that have increased in diameter by more than 10 mm. At this stage, varicose veins occur in the right ovary, which approaches the diameter of the left one. The cause of tertiary varicose veins is gynecological pathologies in the form of various tumors.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the stage of the disease.
When diagnosing the first or second stage, drug therapy and therapeutic exercises are usually used. For varicose veins of the third stage, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Why is it dangerous?
Let's look at the dangers of varicose veins in women and men:
- Varicose veins of the genital organs. Varicose veins of the pelvic veins in women spread to the uterus, ovarian veins and labia, and in men, swollen veins form on the scrotum and penis.
- Sexual dysfunction. Sexual dysfunctions occur, libido decreases, and infertility develops. During conception, the pathology disrupts the normal course of pregnancy and increases the risk of miscarriage.
- Psycho-emotional disorders. Frequent abdominal pain and discomfort during sex lead to irritability and causeless mood swings. Neurasthenia may develop.
One of the rare but dangerous complications of pelvic varicose veins is vein thrombosis. When a blood clot breaks off, the clot enters the general bloodstream and can close the lumen of a smaller vessel. This will cause a heart attack, pulmonary embolism or stroke.