Steroid hormones: why are they important for the body?
Steroid hormones
- the image is rather collective. These include estrogens and androgens, corticosteroids (corticoids), produced exclusively in the adrenal cortex, are divided into glucocorticoid hormones (cortisone, corticosterone, cortisol, etc.) and mineralocorticoid hormones (aldosterone, deoxycorticosterone). Glucocorticoids affect the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acids. Their main function is weight loss by removing harmful substances in the urine. Mineralcorticoids stimulate the regulation of water-salt metabolism, salivary and sweat glands.
Female sex hormones (estrogens) are produced by the ovaries, they are responsible for the menstrual cycle, contribute to gestation and successful childbirth. Also, estrogens, like steroid hormones, form fat cells in the body, distribute them in the chest, buttocks, hips and knees, creating a female silhouette. Calcium metabolism, skin hydration and the functioning of the sebaceous glands also depend on them.
Androgens are produced in women to a lesser extent than in men. During puberty, it is androgens, like steroid hormones, that form the genital organs, affect pubic and axillary hair growth, and promote bone growth. In women, these hormones are produced throughout life and support the normal functioning of the uterus and ovaries.
Steroid hormones: what is the danger of excess or deficiency?
With an increased content of corticosteroids, increased appetite is manifested, as a result - obesity, diseases such as hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, myopathy, arrhythmia, vasculitis, and gastric ulcers. Acne, urolithiasis, swelling and menstrual irregularities may also appear. When there is a lack of corticosteroids in the body, the functioning of the adrenal glands is disrupted, which can lead to adrenal insufficiency.
Estrogens, female sex hormones, can also be produced incorrectly. If the level of estrogen exceeds the norm, women may experience disruptions to their menstrual cycle, pain and lumps in the mammary glands, frequent mood changes and sudden weight jumps.
When a woman lacks estrogen, the water exchange process in the body is disrupted. As a result, the skin becomes dry and lifeless, acne, wrinkles and cellulite appear. Also, a lack of estrogen leads to urinary incontinence and vaginal dryness. Bones also suffer from this - they become weak and fragile.
The female body is especially sensitive to steroid hormones such as androgens. The body responds to an excess of these hormones by suppressing female sex hormones, slowing down the development of the egg and uterus. Also, women begin to develop pronounced “male” signs - hair growth, deepening of the voice, and menstruation may stop. When there is not enough androgens, this leads to frequent depression, decreased libido, excessive emotionality, and sudden hot flashes.
Steroid hormones are mainly used by athletes to increase muscle mass and endurance. Most often, this applies specifically to male sex hormones - androgens. Therefore, female athletes have a “male” figure, an almost complete absence of breasts and a low voice. The use of steroid hormones in our time is equivalent to doping. However, they are actively used by athletes, but only under medical supervision. After all, in case of an overdose, hormones can destroy not only a sports career, but also ruin your health in general.
Drugs such as steroid hormones, or as they are popularly called steroids, are elements that control vital processes in the human body. It is especially important for people who monitor their health to learn the specifics of these drugs.
Why are steroid hormones needed?
The range of application points for steroid hormones is large. They have the following effects:
- anti-shock;
- anti-stress;
- regulate immune reactions;
- reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process;
- regulate water-salt balance;
- participate in the regulation of blood pressure and blood volume;
- demonstrate anabolic effects;
- determine the formation of secondary sexual characteristics;
- control the function of the reproductive system.
A simplified version of steroidogenesis.
The main groups of steroid hormones are shown Photo: ru.wikipedia.org The abundance of functions important for the body makes steroid hormones necessary for full life, and their ability to influence the cardiovascular system is vital. This determined the need to produce synthetic analogues of steroid hormones.
In medical practice, there are many situations where the timely use of such medications significantly improves the patient’s condition. In many cases, they are also used as first aid to save the life of a victim.
Photo: Depositphotos
Common indications for the use of synthetic steroids are:
- insufficiency of adrenal cortex function of primary or secondary origin;
- subacute thyroiditis;
- congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex;
- shock state of toxic, traumatic, burn, postoperative origin; in this case, analogues of steroid hormones are used when vasoconstrictor drugs and plasma replacement solutions, as well as other symptomatic therapy, are ineffective;
- cerebral edema due to cancer, traumatic brain injury, neurosurgical operations, hemorrhage, encephalitis, meningitis, radiation injury;
- severe bronchospasm and status asthmaticus with exacerbation of asthma or obstructive chronic bronchitis;
- severe allergic reactions, anaphylactic shock;
- rheumatic diseases;
- connective tissue diseases of a systemic nature;
- dermatoses with severe course;
- palliative therapy for malignant diseases: leukemia, lymphoma, leukemia in children;
- hypercalcemia, whose origin is associated with cancer (if oral administration is not possible);
- blood diseases, including hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenic purpura and agranulocytosis in adults;
- in combination with antibacterial drugs for severe infectious diseases;
- in ophthalmology, these drugs are used for conjunctivitis, keratitis, iridocyclitis, blepharitis, and the consequences of trauma to the eyeball (the drug is used in the form of retrobulbar, parabulbar or subconjunctival administration).
Another indication from the field of ophthalmology is the need for immunosuppression during corneal transplantation.
Analogs of steroid hormones are used when vasoconstrictor drugs and plasma replacement solutions are ineffective Photo: Depositphotos
If it is impossible to take the drug orally, it is administered parenterally.
Local use of steroid solutions is indicated for discoid lupus erythematosus and annular erythema. The injection is made into the area where the pathological formation is localized.
Being substances that actively affect the functioning of all organs and systems, steroids require extremely careful attention to themselves. Their use requires medical personnel to have certain qualifications and careful systematic monitoring of the patient’s condition throughout the entire course of treatment.
Tags: drugs, steroid hormones, hormones
Where are they used?
Steroids are a very important link in the body of any person. The more competently the chain of their work is built, the healthier the human body. This change in the body is due to their strong effects.
You can hear about steroid drugs in sports circles, and most often they are used there. Anabolic steroids are especially popular in the following strength sports:
- powerlifting;
- Weightlifting;
- crossfit.
Such drugs help achieve various goals, from gaining muscle mass to losing excess weight.
Adrenal steroids
The modern market is oversaturated with drugs and sports nutrition, and it is sometimes difficult to understand this wealth. The list of steroids can include several groups.
Adrenal steroids are a type of steroid that is generated by the body in the adrenal glands. These organs perform irreplaceable work and produce the following:
- Hydrocortisone, or as it is more often called -. Also called glucocorticoid. Performs one of the key roles in metabolism - metabolism and blood pressure regulation. This hormone has many names, a popular one is “”. Cortisol is produced in the body during stressful situations (anxiety, anxiety, fasting, lack of sleep). Due to the production of cortisol, muscle fibers break down and immunity deteriorates. Therefore, this substance is considered negative due to its effect on the body; its production should be controlled.
- Corticosterone is a substance responsible for the degradation of proteins. It also promotes the processing of amino acids into complex carbohydrates, which serve as fuel for the body and give it energy. It also helps the liver produce glycogen, which is found in muscles and is also used as a source of energy.
- – this hormone is involved in blood pressure. This steroid also controls the value of potassium and sodium in the human body. It encourages the kidneys to absorb sodium and eliminate potassium from the urine if necessary.
Sex steroids
No less popular are sexual substances:
- (androgen – male sex hormone) – the main androgen among the male genital organs is testosterone. Testosterone is produced by the male body in the testicles and performs important functions in the body. Testosterone is directly responsible for a man’s sexual characteristics, such as hair on the face, chest and other parts of the body, unlike women. This androgen makes the voice rough and gives it a baritone tone. Testosterone is also responsible for muscle development and sexual desire. All these functions are carried out by androgen.
- Estrogens (female sex hormones) - these substances are produced by women by the follicular apparatus of the ovaries. The estrogen class includes three types of hormones: estradiol, estriol and estrone. Estrogens promote the development of the uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, pigmentation in the area of the nipples and genitals. They increase the concentration of thyroxine, iron and copper in the blood. If there is a lack of estrogen in a woman’s body, there is a possibility of developing osteoporosis.
Anabolic steroids are steroids that cause androgenic activity in the human body and are similar in action to the male hormone testosterone.
Such drugs are often found in strength sports. Athletes use anabolic drugs to improve physical condition and athletic performance. This type of drug has an effect on muscle tissue and increases its volume due to increased metabolism and protein synthesis. Anabolic agents can also be prescribed to people suffering from dystrophy.
7
Steroid hormones.
Steroid hormones are derivatives of a number of hydrocarbons, mainly pregnane, antrostane, estran:
They are similar to each other in chemical structure. The difference from androstane is that pregnane has an ethyl radical in its structure, while estrane has an aromatic ring and lacks one methyl group.
The basis of the structure is cyclopentaneperhydrophenanthrene:
Methyl groups attached to the steroid ring at positions 10 and 13 are called angular. The R radical and the hydrogen atoms (at positions 8, 9, 14) are oriented in space in a cis or trans position. It is conventionally accepted that angular methyl groups are located above the plane of the drawing (this is indicated by a solid line). If other substituents are in the cis position, i.e., in the same plane with the angular groups (β-configuration), then they are also designated by a solid line, and if in the trans position (α-configuration), then by a dotted line.
Pregnane derivatives include corticosteroids and progestin hormones, androstane derivatives are androgenic hormones, and estran derivatives are estrogenic hormones.
Estrogens.
Estrogenic sex hormones regulate the sexual function of the female body. They are produced in the female gonads (ovaries) in the form of two types of hormones: follicular, or estrogenic, hormones (in maturing follicles) and progestational, or lutoid, hormones (corpus luteum hormone). These hormones differ from each other both in their physiological action and in their chemical structure, but both are equally necessary for the normal development of the female body. Estrogenic hormones are derivatives of the hydrocarbon estrane.
The main source of their biosynthesis is cholesterol.
Estrogenic hormones are contained (in the form of esters) in the flowers and fruits of higher plants (willow, wheat), in the urine of pregnant women, in the urine of stallions and pregnant mares. The estrone content in the urine of stallions and pregnant mares is 10-25 mg per 1 liter. This allows urine to be used as a source of estrogenic hormones. Estrogen esters contained in urine are hydrolyzed with hydrochloric acid, and then free estrogens are extracted with organic solvents. During further purification, the ability of estrogens to dissolve in alkalis to form phenolates (phenoxides) is used.
For a long time, the natural hormone estrone (folliculin) in the form of oil solutions was used in medicine. Estradiol has twice the activity, but due to rapid inactivation it was not used. Subsequently, it was shown that estradiol esters are more stable substances than estrone. In addition, they have a prolonged effect.
The synthesis of estrone was carried out by V. Johnson. the method he proposed is the simplest, stereospecific and elegant:
Since estrogenic hormones are unstable, almost exclusively their semisynthetic derivatives are used as drugs. ethinyl-estradiol, mestranol and estradiol dipropionate are used as medicinal substances
Ethinyl estradiol – Aethinyloestradiolum
17-α-ethinidestratriene-1,3,5(10)-diol-3,17β
Properties . From white with a creamy tint to light cream color, finely crystalline powder. T.pl. 181-186 °C. Specific rotation from –27 to -31° (0.4% solution in pyridine). Practically insoluble in water, moderately soluble in chloroform, slowly soluble in vegetable oils.
Receipt . The synthesis of ethinyl estradiol is carried out by the action of acetylene on estrone:
Authenticity . 1.IR spectrum in the region from 4000 to 200 cm-1 in petrolatum oil. 2. The UV spectrum in a mixture of ethanol and sodium hydroxide 0.005% solution has absorption maxima at 241 and 299 nm and minima at 226 and 271 nm. 3.HPLC. 4.TLC.
Chemical methods:
5. Color reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid. In the presence of ethinyl estradiol, the solution acquires an orange-red color with yellow-green fluorescence. After adding water to the solution, the color changes to purple and a purple precipitate forms. 6. The presence of phenolic hydroxyl makes it possible to obtain esters, for example with benzoyl chloride, which have a clear melting point of 199-202 °C.
Impurities . Impurities are determined by TLC. According to the current FS, only the total amount of impurities is determined - no more than 1%.
quantitation.
1.The property of acetylene derivatives to form salts with silver is used. Ethinyl estradiol is quantified by indirect neutralization in the same way as norethisterone. Tetrahydrofuran purified from peroxide compounds is used as a solvent. The nitric acid released after adding silver nitrate is titrated with a 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution using the potentiometric method with a glass indicator electrode. Ethinyl estradiol forms a double salt with silver nitrate, which consists of the silver salt of ethinyl estradiol and six molecules of silver nitrate:
2. According to MF, ethinyl estradiol is determined spectrophotometrically in anhydrous ethanol at 281 nm.
3. The photocolorimetric method for determining ethinyl estradiol is based on the use of a diazo reagent (a mixture of sulfanilic acid, sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid). In an alkaline environment, a colored bisazo compound is formed:
4.HPLC.
Release form . Tablets 0.00001 and 0.00005 g; forte tablets 0.05 g each. Included in the contraceptives Nonovlon, Ovidone, etc. Injectable forms are known.
Application . Oncological diseases, endocrine infertility, etc.
Storage .List B.
Mestranol – Mestranolum
17-α-ethynylestrateriene-1,3,5(10)-diol-3,17β-3 methyl ester
Properties . White or off-white crystalline powder. Melting point 149-154°C. Specific rotation from +2 to + 8° (2% solution in chloroform).
Receipt . Methylation of estrone with various methylating agents (diazomethane, methanol with sulfuric acid) and subsequent acetylation with ammonia.
Authenticity . 1.IR spectrum in petroleum jelly in the range from 4000 to 200 cm-1. 2.UV spectrum of a 0.005% solution in ethanol or methanol has a maximum at 279 nm and an absorption index from 59 to 64. 3.TLC. 4.HPLC.
Chemical reactions. 5. Interaction with concentrated sulfuric acid produces a blood-red color with yellow-green fluorescence.
Impurities . Impurities are determined by TLC method in total no more than 2% without identification of individual impurities.
quantitation.
Produced similarly to ethinyl estradiol.
Release forms . Tablets of 0.05 and 0.08 g. Included in the contraceptive drug infekundin . Application . Hormonal therapy. Storage . List B.
Estradiol dipropionate – Oestradiolum dipropionicum
Estratriene-1.3,5(10)-diol-3,17β dipropionate
Properties . White crystalline powder, odorless. T.pl. 104-108°C. Specific rotation from +37 to +41° (1% solution in dioxane). Moderately soluble in oils.
Receipt.
The synthesis of estradiol dipropionate is carried out from estrone by hydrogenation of the 17 keto group to estradiol, followed by acylation of the 3- and 17β-hydroxy groups:
Authenticity . 1.IR spectrum in Vaseline oil. 2. The UV spectrum of a 0.01% solution in ethanol has maxima of 269 and 276 nm. 3.TLC. 4.HPLC.
Chemical methods. 5. When concentrated sulfuric acid is added to the preparation upon heating, a brown color with a characteristic greenish fluorescence appears. If this mixture is diluted with water, a pink color appears. 6. Under the influence of concentrated acids, two molecules of propionic acid are split off when heated. Heating the mixture with the addition of ethyl alcohol produces an ether with a characteristic odor.
Impurities . TLC no more than 2%.
quantitation.
1.HPLC. 2. Alkaline hydrolysis reaction with a precisely measured amount of 0.1 M alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide. The excess is titrated with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid solution, phenolphthalein indicator.
Release forms . 0.1% solution in oil. Application: Intramuscular. the drug has a prolonged effect. Storage . List B.
Synthetic analogues of estrogens of non-steroidal structure.
Substances with estrogenic activity were found not only among steroids, but also among aromatic compounds, in particular, phenanthrene derivatives, diphenyl derivatives and others. It is assumed that the estrogenic effect depends on the presence of aromatic nuclei in the molecule. An important role is played by hydroxyl and ketone groups, which are capable of forming hydrogen bonds and interacting with proteins in the body.
The great advantage of synthetic estrogens is the availability of their synthesis due to the simplicity of the chemical structure. In medical practice, diphenylethane derivatives and stilbene derivatives are used:
Diphenylethane derivatives include hexestrol (sinestrol), and stilbene derivatives include diethylstilbestrol. The molecules of synthetic estrogens contain oxyphenyl radicals, which are attached in the p-position to a chain of six carbon atoms. Therefore, they can be considered as derivatives of hexane (hexestrol) and hexene-3 (diethyl-stilbestrol).
For the manifestation of estrogenic action, the distance between the functional groups in the molecule is important. It was found that the distance between the hydroxyl groups (at positions 3 and 17) in estradiol is 1.1 nm, in the meso form of hexestrol it is 1.2 nm, in the trans isomer of diethylstilbestrol it is 1.22 nm. At the same time, the cis-isomer of diethylstilbestrol, in which the distance between hydroxyls is 0.75 nm, is physiologically inactive. The formation of ethers and esters does not reduce the activity of estrogens, but increases the duration of action.
Sinestrol – Hexestrol – Synoestrolum
meso -3.4-bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-hexane
Properties. White or white with a slight yellowish tint, odorless powder. T.pl. 184-187°C. Practically insoluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether, slightly soluble in chloroform.
Receipt . The synthesis of hexestrol (synestrol) was first carried out in 1937 by O. Yu. Magidson et al. (VNIHFI) from anethole contained in anise essential oil. Anethole is exposed to hydrogen bromide:
Then, by reacting anethol hydrobromide and phenylmagnesium bromide, hexestrol dimethyl ether is obtained, which is demethylated:
Due to the presence of two asymmetric carbon atoms, hexestrol can exist in the form of two optically active d- and l-isomers and a meso-isomer. It is characteristic that the d-isomer has 500 times, and the l-isomer 5000 times less activity than the meso-isomer. The latter is used in medical practice.
Authenticity.
- IR spectroscopy in a tablet with Kvg.
- UV spectroscopy. A solution in ethanol 0.005% has an absorption maximum at 280 nm.
- HPLC
- TLC.
Chemical reactions.
5. When concentrated sulfuric acid acts on a chloroform solution of hexestrol (in the presence of formalin), the chloroform layer turns cherry-red.
6. Hexestrol can be detected by the formation of bromine derivatives. When bromine water acts on its solution in glacial acetic acid, a yellow precipitate of tetrabromohexestrol is released:
7. The presence of unsubstituted phenolic hydroxyls can be detected using ferric chloride (green color turning to yellow).
8. Hexestrol can be identified using the nitration reaction. After adding nitric acid and heating in a water bath, a yellow color gradually appears:
Foreign matter . TLC method.
Quantitation . 1.HPLC. 2.UV spectrophotometry. 3. Quantitative determination of hexestrol is based on the preparation of esters (diacetyl derivatives) by heating with a precisely measured amount of acetic anhydride (in the presence of pyridine). Excess acetic anhydride, converted to acetic acid, is titrated with 0.5 M sodium hydroxide solution (phenolphthalein indicator). In parallel, a control experiment is performed with the same amount of acetic anhydride.
The chemistry of this process in determining hexestrol:
4. Hexestrol can be identified and photometered by azo coupling with diazotized sulfanilic acid. An azo dye is formed due to the presence of phenolic hydroxyls in the molecules:
Release forms . Tablets 1 mg, oil solutions intramuscularly 0.1% and 2-3%.
Application . Hormone therapy and oncology.
Storage . List B.
Diethylstilboestrol – Diaethylstilboestrolum
trans- 3.4-bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-hexene-3
Properties . White crystalline powder, odorless. T.pl. 168-174°C. Practically insoluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether. Slightly soluble in oil.
Receipt . Obtained by three methods: from anethole, deoxyanisoin and p-hydroxypropiophenone:
Authenticity . 1.IR spectrum of diethylstilbestrol in tablets with KBr. 2.UV spectrophotometry of a 0.001% solution in ethanol has an absorption maximum at 242 nm and a shoulder from 276 to 280 nm. In an alkaline medium in a 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution, a 0.0006% solution of diethylstilbestrol has a maximum at 262 nm. 3.TLC. 4.HPLC.
Chemical reactions. 5. A solution of diethylstilbestrol in concentrated sulfuric acid has a bright orange color, which gradually disappears when diluted with water. 6. Heating diethylstilbestrol with acetic acid and vanillin, followed by the addition of hydrochloric acid, boiling and the addition of chloramine (after cooling) leads to the appearance of a blue color. 7. Diethylstilbestrol, when exposed to bromine water in glacial acetic acid, gives an emerald green color when heated. 8. A solution of diethylstilbestrol in glacial acetic acid, after adding phosphoric acid and heating in a water bath, acquires an intense yellow color, which almost disappears when diluted with glacial acetic acid.
Foreign impurities are determined by TLC.
Quantitation . 1.HPLC. 2.UV spectrophotometry. 3. Similar to hexestrol with acetic anhydride. 4. photometric determination of azo dye is similar to hexestrol, including in tablets according to V.G. Belikov.
Release form . Tablets 0.025 g. Application . Oncological diseases.
Synthetic antiestrogenic agents.
Stilbene derivatives include p-diphenyl-1-butenyl derivatives, a representative of which is tamoxifen citrate, one of the main modern antiestrogens. The antiestrogenic effect is due to the competitive antagonism of such compounds with estrogens. Antiestrogens have become widespread as antitumor agents.
The basis of the chemical structure of tamoxifen is (like synthetic estrogens) stilbene, to which an ethyl radical and phenoxydimethylethylamine are attached:
The drug binds to estradiol protein receptors, reducing their concentration in the cytoplasm, inhibiting the division of tumor cells:
Tamoxifen citrate _
Properties . White or almost white crystalline powder. T.dec. 142-145°C. Practically insoluble in water (easily in hot water), soluble in methanol and very slightly in ethanol, chloroform, and acetone.
Receipt . Obtained through organomagnesium compounds according to Grignard.
Further interaction with dimethylaminoethyl chloride gives a mixture of cis- and trans-isomers of tamoxifen, which are separated by recrystallization from petroleum ether.
The second synthesis method involves the interaction of phenolic derivatives with organomagnesium compounds.
Tamoxifen citrate can exist as a pharmacologically active Z-isomer and an inactive E-isomer. They are contained in tamoxifen in different proportions, have different peak areas on HPLC and different specific absorption values.
Authenticity . 1.IR spectrum. The authenticity of tamoxifen citrate is determined by two IR spectra, which are recorded in the region from 4000 to 1600 cm-1 and from 1600 to 400 cm-1. The absorption bands in both regions must completely coincide with the absorption and intensity spectra drawings attached to the FS. 2.UV spectrophotolmetry. The UV spectrum of a solution of tamoxifen citrate in ethanol containing hydrochloric acid should have absorption maxima at 237 and 277 nm. 3.TLC.
Chemical reactions. 4. To test for authenticity, use a reaction with pyridine and acetic anhydride; The yellow color that appears after heating in a water bath turns red.
Foreign matter . The HPLC method is used to determine the presence of the E-isomer (no more than 1%). TLC determines other impurities.
Quantitation . 1. HPLC 2. Quantitative determination of tamoxifen citrate is performed by non-aqueous titration in glacial acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid solution (crystal violet indicator). Under the same conditions, but using the indicator 1-naphtholbenzein, the quantitative content is determined by MF. There is also a known method for determining the equivalence point by the potentiometric method using a glass indicator electrode. 3. For the quantitative determination of tamoxifen citrate by the spectrophotometric method, a color reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid was used, which resulted in the formation of a yellow complex compound with an absorption maximum at 440 nm.
Release form . Tablets 0.01 g; 0.02 g; Nolvadex and Nolvadex-forte tablets. Application . Antiestrogenic and anticancer effects. Kidney cancer, melanoma, breast. Storage . List B.
Known drugs
Drugs proven in sports circles are:
- Hydrocortisone;
- Dexamethasone;
- Prednisone;
- Estriol;
- Prednisolone.
Before using these medications, you should consult your doctor.
Side effects
Steroid hormones (especially androgen) can also have negative effects on the body:
- suppression of the production of your own testosterone;
- liver tissue damage;
- development ;
- acne (blackheads);
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- increased blood pressure;
- kidney problems;
- mental disorders;
- growth arrest;
- prostate hypertrophy;
- infertility;
- blood clot formation.
The use of steroids requires utmost attention and scrupulousness from the individual. Steroid hormones have a comprehensive effect on the human body. You should not use untested hormonal drugs without consulting a specialist.
STEROID HORMONES STEROID HORMONES
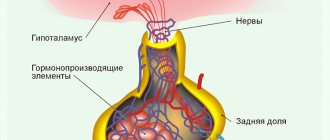
a group of physiologically active substances of a steroid nature (sex hormones, progestins, corticosteroids, ecdysones) that regulate vital processes in animals and humans. In vertebrates, cholesterol is synthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal cortex, Leydig cells of the testes, in the follicles and corpus luteum of the ovaries, and also in the placenta. The hormonal form of vitamin D3 is completed from the exogenous vitamin in the liver and kidneys. A characteristic feature of S. g.'s synthesis is a series of sequential processes of hydroxylation of steroid molecules occurring in mitochondria and microsomes. These processes are carried out by special cell enzymes from the class of hydrolases or mixed-type oxidases. S. g. are contained in lipid droplets in the cytoplasm in free form. Due to the high lipophilicity of steroids, S. g. diffuse relatively freely through the plasmatic. membranes into the blood (without accumulating in producing cells), and then penetrate into target cells. About the mechanism of action of S. g. (see HORMONES).
.(Source: “Biological Encyclopedic Dictionary.” Editor-in-chief M. S. Gilyarov; Editorial Board: A. A. Babaev, G. G. Vinberg, G. A. Zavarzin and others - 2nd ed., corrected - M.: Sov. Encyclopedia, 1986.)
See what “STEROID HORMONES” are in other dictionaries:
- Steroid hormones are a group of physiologically active substances (sex hormones, corticosteroids, etc.) that regulate vital processes in animals and humans. In vertebrates, steroid hormones are synthesized from cholesterol in the cortex... ... Wikipedia
A group of physiologically active steroids. According to chemistry structure and biol. action are divided into C 21 steroids with a pregnane skeleton (gestagens and corticoids), C 19 steroids with an androstane skeleton (androgeps) and C 18 steroids with ... ... Chemical Encyclopedia
Steroid hormones
- a group of physiologically active substances (sex hormones, corticosteroids, etc.) that regulate vital processes in animals and humans. In vertebrates S.g. synthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal cortex, Leydig cells of the testes, in... ... Dictionary of psychogenetics
- (ancient Greek ὁρμάω excite, induce) biologically active substances of organic nature, produced in specialized cells of the endocrine glands, entering the blood and exerting a regulatory effect on metabolism... ... Wikipedia
Ov; pl. (unit hormone, a; m.). [from Greek hormaō I move, I excite]. 1. Physiol. Biologically active substances produced in the body and affecting all vital processes. G. pituitary gland. Sexual g. 2. Synthetic drugs that provide ... ... Encyclopedic Dictionary
They are represented by two different classes of biologically active substances: iodothyronines and the polypeptide hormone calcitonin. These classes of substances perform different physiological functions: iodothyronines regulate the state of basal metabolism, and ... ... Wikipedia
G. is a chemical. substances synthesized and secreted by endocrine glands. G. are delivered to the target organs, the activity of which they regulate, along the bloodstream along with the blood. They perform the function of transmitting information. inside the body, ... ... Psychological Encyclopedia
- (from the Greek hormao I set in motion, encourage), biologically active substances secreted by the internal glands. secretion or accumulations of special lysir. cells of the body and have a targeted effect on other organs and tissues. The term “G.” ... ... Biological encyclopedic dictionary
hormones
— * hormones * hormones are highly specific biologically active organic substances that are regulators of the most important life processes. G. are produced in the body by highly specialized cells or organs (endocrine glands, or ... ... Genetics. Encyclopedic Dictionary
Animals (from the Greek hormao I set in motion, motivate), in va, produced by specialists. cells and glands internal secretions and regulating metabolism in individual organs and the entire organism as a whole. All G. are characterized by great specificity... ... Chemical Encyclopedia
Books
- Pharmaceutical biotechnology. Guide to practical classes, Orekhov S.N.. The training manual provides information about modern methods of obtaining medications in the conditions of industrial biopharmaceutical production. The greatest attention is paid...
The biosynthesis of steroid hormones comes from cholesterol. Cholesterol is synthesized from acetyl-CoA.
Most of the cholesterol in endocrine cells is contained in lipid droplets localized in the cytoplasm, in the form of esters with fatty acids.
Stages of synthesis of steroid hormones.
- First, cholesterol is released from lipid droplets and transferred to mitochondria, where non-esterified cholesterol forms complexes with proteins of the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- Formation of a key hormone precursor, pregnenolone, leaving the mitochondria.
- Progesterone formation. The process takes place in the microsomes of the cell.
Progesterone produces two branches: corticosteroids and androgens. Corticosteroids give rise to mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, and androgens give rise to estrogens.
Transport of hormones.
Hormones circulate in the blood in several forms:
- Free (as an aqueous solution)
- In the form of complexes with specific plasma proteins
- In the form of nonspecific complexes with plasma proteins
- In the form of nonspecific complexes with formed elements of blood.
This hormone binding mechanism ensures stable hormone levels and a hormone storage mechanism that limits the flow of hormones from the blood into the tissues.
Specific transport proteins of blood plasma.
- Transcortin, or corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG).
- Sex-steroid binding globulin (SSB).
- Thyroxine binding globulin (TBG).
- Insulin binding protein.
Nonspecific proteins.
- Orosomucoid – binds various steroid hormones.
- Serum albumin – various hormones.
- Transferin
- Trypsin
- -globulins
The physiological role of hormone binding in the blood.
The complexation of hormones with blood proteins, and especially specific proteins, plays a buffer-reserving role in relation to hormones, regulating their flow from the blood into the tissues.
The specific binding of hormones becomes especially important during pregnancy, when the concentration of hormones increases several times. Under these conditions, hormone binding performs a protective function, protecting the mother and fetus from excess hormones and maintaining optimal hormonal balance in the mother-fetus system. Hormone binding proteins limit the movement of hormones across the placenta.
It is assumed that some forms of pathology of the endocrine system may be primarily caused by disturbances in the binding of hormones by specific transport proteins. Some forms of hypercorticism (excess of free glucocorticoids due to decreased concentration of transcortin), diabetes (increased binding of insulin to specific proteins).
Peripheral hormone metabolism.
| Activation |
| Tetraiodothyronine triiodothyronine |
Examples of activation: Conversion of estrone to estradiol
Thyroxine to triiodothyronine,
Angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
Examples of reactivation: Transition of cortisone to cortisol,
Restoring the structure of testosterone into estradiol.
Types of metabolism:
- Catabolism of hormones and their inactivation are possible.
- Reactivation - The thyroid gland produces tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine), which, losing iodine, is converted into triiodothyronine, the concentration of which in the bloodstream is lower, but its biological activity is greater.
- The emergence of molecules with different hormonal activity. Androgens can be converted into estrogens.
- Activation – angiotensin I to angiotensin II
Metabolism of steroid hormones.
It occurs without cleavage of the steroid skeleton and comes down to the restoration of the double bond in ring A; oxidation – reduction of oxygen groups; hydroxylation of carbon atoms.
Androgen metabolism.
The metabolism of secreted androgens is characterized by a series of activation reactions in the periphery. Activation is based on reduction and hydroxylation reactions.
Metabolism of estrogen.
Metabolism comes down to the reactions of hydroxylation, methylation of carbon atoms, oxidation and restoration of the oxygen function of 17C.
Pathways for excretion of hormones and their metabolites.
A small proportion of hormones are excreted unchanged. Metabolites of steroid hormones that are poorly soluble in water are excreted in the form of glucuronides, sulfates and other esters that have high water solubility.
Metabolites of amino acid hormones are highly soluble in water and are excreted mainly in free form, and only a small part is released as part of paired compounds with acids.
Metabolites of protein-peptide hormones are excreted mainly in the form of free amino acids, their salts and small peptides.
Hormonal metabolites are excreted in urine and bile. Some of the metabolites are excreted from the body through sweat and saliva.
Most hormones and their metabolites are eliminated from the body almost completely after 48-72 hours, and 80-90% of the hormones that enter the blood are eliminated in the first day. The exception is thyroid hormones, which accumulate in the body over a period of days in the form of thyroxine.
Man belongs to a biological species, therefore he is subject to the same laws as other representatives of the animal kingdom. This is true not only of the processes occurring in our cells, tissues and organs, but also of our behavior - both individual and social. It is studied not only by biologists and doctors, but also by sociologists, psychologists, and representatives of other humanities disciplines. Using extensive material, supporting it with examples from medicine, history, literature and painting, the author analyzes issues at the intersection of biology, endocrinology and psychology, and shows that human behavior is based on biological mechanisms, including hormonal ones. The book examines topics such as stress, depression, rhythms of life, psychological types and sex differences, hormones and the sense of smell in social behavior, nutrition and the psyche, homosexuality, types of parental behavior, etc. Thanks to the rich illustrative material, the author’s ability to speak simply about complex things and his humor, the book is read with unflagging interest.
The book “Wait, who’s leading? Biology of human and other animal behavior” was awarded the “Enlightener” prize in the “Natural and Exact Sciences” category.
What are steroids
Steroids have different origins: natural (animal, plant) and artificial. Used in medicine and sports.
1
The classification of steroids is based on their structure and origin:
- sterols are steroid alcohols, which include cholesterol, ergosterol, stigmasterol;
- steroid hormones;
- bile acids are formed in the liver during the processing of cholesterol, they ensure the digestion of lipids;
- alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, saponins, etc.
2
Steroid hormones can cause genetic changes in a cell. Due to this, they regulate metabolism, growth and reproduction functions of animals and humans. Steroid hormones are of natural origin and are synthesized from cholesterol. Steroid hormones include cortisol, progesterone, testosterone, calcitriol, aldosterone, estradiol.
3
Among athletes and doctors, steroids are synthetic hormones. Steroids are derivatives of steroid hormones. They are created artificially, but have a structure as close as possible to the natural one. Steroids are based on one of the steroid hormones and changes are made to the structure of its molecule. A more detailed name is anabolic androgenic steroids. Their main purpose is to accelerate processes associated with the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, for example, nucleic acids, which is associated with the accumulation of energy.
4
Steroids have a great effect on the body, so they are used in medicine to restore the body after serious illnesses and in sports as doping to:
- increase appetite;
- accelerate the regeneration of the body;
- promote weight gain, thereby reducing the level of body fat in relation to total body weight;
- calcium and phosphorus accumulate better in bones and teeth;
- increase performance and endurance;
- blood vessel filling and brain activity improves;
- the feeling of fear decreases, self-confidence and communication abilities increase.
5
Steroids are prohibited for use in sports competitions and in preparation for them; they are often used in bodybuilding by increasing the building abilities of the body. In addition to the positive effect, the use of steroids also leads to undesirable consequences, for example:
- the occurrence of acne;
- increased irritability and frequent mood swings, depression;
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis due to increased cholesterol levels;
- negative effect on the liver, myocardium;
- impotence, decreased sperm production, infertility, testicular atrophy;
- accumulation of excess fluid;
- enlargement of the mammary glands in men, etc.
Side effects occur if there is a violation of the dosage of the drug. If you prevent abuse, you can reverse the negative consequences. Before starting the course, consult your doctor and carefully study the instructions.