Why does injury occur?
Fractures of the humerus with displacement and without displacement of bone fragments occur due to the following unfavorable factors:
- falling on an elbow or outstretched arm,
- direct blow to the shoulder with a heavy object,
- dislocation, in which the greater tubercle is torn off,
- extreme sports or oriental contact martial arts,
- industrial and vehicle accidents,
- diseases that cause bone fragility,
- poor nutrition and calcium deficiency.
Total information
The provocateur against which the described damage occurs can be congenital and acquired diseases of bone tissue. The impact of force is only an impetus for the occurrence of a fracture.
The incidence of the described disorder naturally increases with age. The reasons are as follows:
- age-related depletion of cat tissue is observed;
- in older and older people, systemic lesions of bone tissue more often appear, against the background of which the described pathological fracture occurs.
All areas of the humerus are affected equally often.
What types of damage are there?
The classification of fractures is determined by the location of the injury as follows:
- Trauma to the proximal upper third, in which the surgical neck and head of the humerus are broken.
- Diaphyseal, when the integrity of the bone body in the middle is disrupted. A comminuted fracture may be accompanied by a violation of the integrity of blood vessels and the radial nerve.
- A fracture of the lower end is characterized by damage to the capitate eminence, internal epicondyle, and medial condyle. Transcondylar fracture of the shoulder joint is more often observed in children.
Symptoms: how to recognize an injury?
An impression fracture of the shoulder has the following symptomatic features:
- Injury in the upper part is accompanied by mild swelling and limited mobility.
- A fracture of the humeral body is characterized by unnatural mobility, as well as the inability to bend the fingers.
- Intercondylar and supracondylar fractures are combined with dislocation, limb deformation, and subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Injury to the humerus can be open or closed. The nature of the fracture can be helical or lateral, as well as transverse. How the injury manifests itself depending on the type is shown in the table:
| Nature of the fracture | Signs |
| Closed without displacement (crack) | Soreness |
| Swelling | |
| Limited mobility | |
| Muscle weakness that makes it almost impossible to lift your arm | |
| Closed with offset | Strong pain |
| Edema and hematoma | |
| Severe arm deformity or shortening | |
| Crunching and creaking in bones | |
| Unnatural bone mobility where it shouldn't be | |
| Open with displacement of fragments | Intense pain |
| Wound formation due to bone fragmentation | |
| Heavy bleeding | |
| Feeling of numbness that extends to the hand | |
| Extensive swelling and hematoma | |
| General deterioration in health, fainting |
Causes and symptoms
Almost all fractures occur for similar reasons. An injury to the shoulder neck, which occurs as a result of a fall from a height or road accidents, is no exception. When a person falls on his arm, pressure is applied to the bone along the axis.
A fracture of the neck of the humerus, which occurs as a result of a disease of the skeletal system - osteoporosis, occurs due to the fragility and porosity of bone tissue.
The bones of a healthy person are quite strong and can withstand heavy loads. Diseases that contribute to the destruction of bone tissue (metabolic disorders, kidney diseases, hormonal and genetic changes) lead to disruption of the structure and their strength.
Fractures caused by bone diseases are most often observed in older people. It is enough to receive an indirect blow and they experience injuries to the neck of the humerus associated with age-related hormonal changes and cessation of growth of the metaphysis on the humerus.
In older women, changes in bone structure are associated with the onset of menopause.
A healthy lifestyle is of no small importance. Bad habits, exposure to radiation and chemicals have a negative impact not only on the body as a whole, but on the structure and condition of bone tissue.
The most common causes of shoulder injury are:
The humerus breaks when carelessly falling on the arm, especially if it is extended. In this case, the ligaments and muscles responsible for the movement of the upper limbs fail.
The condylar lower part of the shoulder, which provides connection with the elbow joint, is also damaged. The increase in volume of the shoulder joint is a consequence of swelling resulting from the impact.
The complex symptoms of displaced comminuted fractures suggest nerve damage. In addition, blood vessels are also affected.
• Swelling and bruising are a must, may be accompanied by the hand • Limitation of movements in the treatment and elbow joints.
With the required type of fractures, intervention of nerves and blood vessels is typical. When the nerves are affected, movements are affected, sensitivity is impaired, and the hand hangs from the injury.
Symptoms of adult transcondylar:
• Pain radiating to the elbow and forearm; • Swelling of the elbow; • Limitation of movements in the elbow; • Crunching of fragments when splintered.
When fractures occur in this location, the humeral fracture is often damaged, which can lead to the limbs being separated; the main symptom of the following brachial artery is damage to the pulse in the forearm (in typical types, palpation of the pulse).
The upper upper part of the humerus must be distinguished from bruises, fractures of the shoulder joint, the lower part of the elbow joint and fractures by swelling of the bone.
First aid for a broken shoulder
As with any fracture, the main deformation is anesthesia and immobilization of recovery. For joint pain relief, medications found in the first aid kit (ketorol, nimesulide, surgical) are suitable.
Immobilization of the limb can be achieved by constructing a splint from available materials. A board, slats, strong serve or sticks are bandaged to the bone, the arm is suspended from the old one and fixed to the body.
When intervening in the upper part of the shoulder, it is not necessary to do so; it is enough to have your hand on the scarf.
Diagnosis of a severe shoulder
To diagnose an obstacle, perform radiography. In certain diseases, if there is a suspected injury, a muscle fracture or a fracture of a joint, an ultrasound is performed.
Shoulder fracture
There are either methods for treating fractures: conservative, operative, or the method of splinter traction.
Fractures of the shoulder for displacement and fractures, displacement of the middle can be corrected with part of a one-stage reposition (reduction), which is dangerous by applying a plaster cast and using special splints and bandages.
Fractures of the radial tubercle of the humeral artery, in most cases, are treated with a plaster cast. A fixation splint can be used for this, which prevents necessary stiffness in the shoulder joint, and the nerve ensures fusion of the supraspinatus vein (this muscle is often metallic when a large pin is fractured).
Outlet bus
When the device is displaced, surgical treatment plates are used, the fragment is fixed with an ilizarov or a screw, which is removed after several months. If general treatment ranges from 2 to 3 injuries, plaster immobilization is 4-6 weeks.
For fractures of the surgical neck and displacement, a lower plaster cast is applied for 4 weeks, after which development occurs. If the fracture was from the humerus, and it was possible to reduce it, then the displacement immobilization is extended to 6 parts.
For irreducible fractures and splinters, surgery. If appropriately treated, the fracture is fixed with plates.
That impacted fractures of the surgical bone and fractures of the greater tuberosity for displacement are justified by such or conservative treatment, as significant, when the arm is fixed with a bandage like a scarf, not on the abductor pad (with displacement of the supraspinatus muscle), for a period of 4 plaster.
In this case, plaster is not a bandage.
In the future, physiotherapeutic fragmentation and physical therapy are used; a complex operation to develop movements and the need for rehabilitation will be written about. The total treatment period is from 2 to 3 days.
Non-displaced shoulder fractures are treated with a splint for up to 8 weeks.
Fractures of the body of the bone with displacement are operated on and fixed with screws or special anesthetic rods, then the first one is applied for 4-6 weeks, with a reliable humeral fracture, the injury can be limited to a scarf.
After removal, rehabilitation begins. General treatment duration is 3-4 months.
Also, for fractures of the body of the shoulder in humans, the following skeletal method is applicable. The needle is passed behind the ulnar origin, and the shoulder is necessary through traction.
With a splint to calm the skeletal patient, it is necessary to lie down for about 4 hours, which is very difficult for the patient. Then the bandage is applied for another 4-6 weeks.
The treatment period may last 3-4 months. As a time-based treatment for shoulder analgesics, the skeletal analgin method is rarely used.
A fracture of the humerus is considered to be a fairly common occurrence and can affect anyone. Athletes often encounter injuries of this kind in the shoulder; however, fractures, which are at risk, are recorded in old age and develop into special ones.
This is one of the unpleasant bandages and quite painful, since fractures, having received injury, cannot be surgically moved. To understand whether a fracture is a displacement of the bone, you need to familiarize yourself with the ultrasound symptoms, clinical picture and treatment department.
Fracture of the humeral arm: causes and pathogenesis
Fractures occur in bones and account for 5 to 20% of the total number of fractures. Cervical injuries occur both in the form of traumatology injuries, and along with repositioning injuries to bones and soft local ones.
The causes of fractures are characterized by: anesthesia on an outstretched arm, subsequent blows to the shoulder, a fall on a bent or abducted joint, and other factors.
The variety of fixation of the humerus depends on the abductor, so they can have a turner:
- open and closed fractures;
- skeletal with and without displacement.
In a bandage, if supratubercular traction of the shoulder joint occurs, the place is adhesive in volume and is accompanied by swelling and immobilization. The function of the joint is impaired, and active movements are prescribed and it becomes difficult due to intense pain. Or the examination feels painful.
Unstable fracture
In the case of subtubercular fragments, displacement of fragments occurs, treatment is intense pain, which is splintered with every movement. The tire increases in size due to senility, and the development of hemarthrosis (chronic joint disease) is possible.
MORE ABOUT: Medical elastic bandage for fracture
The victim is unable to use his arm for weeks due to a sharp cut, which is characterized by damage to the diaphyseal nerve and its branches.
Offset humerus surgery
Or a displaced fracture can be operated on or even seen as a broken bone. Instant physical therapy occurs, which increases over time.
The volume of the shoulder joint is increased and the patient is unable to carry out movements. A fracture indicated requires a mandatory x-ray result.
Symptoms of a shoulder fracture
Often, a quick fracture of the elbow joint or a person falling on his hands causes swelling to occur. The usual concentration is extensive - this is a fracture of the ulna and bruising of the ulna bone.
The most widespread part of the ulna is to preserve the process, since the bruise can be easily found by palpating the outer surface somewhat. The olecranon process is not protected for weeks, which is why it is susceptible to the first traumatic factors.
There is also a possibility of a fracture of the epicondyle of the arm of the humerus, the neck of the shoulder and the coronoid process of the bone.
How to provide first aid?
An open fracture with displacement is dangerous due to large blood loss, since an artery is located nearby. Therefore, you should immediately apply a tourniquet above the wound, making sure to include a note indicating the time and date.
Immobilization for a humerus fracture is carried out only after bleeding has stopped. The algorithm for providing first aid is as follows:
- Provide complete rest to the limbs.
- Wrap the injury site with a cold compress, wrapping the ice in a cloth, avoiding direct contact with the skin.
- Disinfect the wound with an open fracture without touching bone fragments.
- Secure your hand with planks so that the edges of the clamps protrude above the injury site. Fixation of the hand with the wound surface is carried out with sterile materials.
- Wrap it with a bandage, making sure that the bandage is not tightened too tightly.
- Place a cotton-gauze roll between your hand and armpit.
- Place the limb on the wide edge of the scarf, tying the ends around the neck.
- Give painkillers.
- Take the victim to the first aid station. Transport immobilization for a shoulder fracture in winter is carried out after warming the limb to avoid frostbite.
Fractures in the middle section
A midshaft or midshaft humerus fracture occurs in people over 50 years of age.
Doctors distinguish four types of injuries in this localization:
- splintered;
- transverse;
- oblique;
- spiral.
The type of bone injury is related to the mechanism of injury, force of action, location of injury, and muscle tone at the time of injury.
Very often, when the middle part of the shoulder bone is fractured, the nerves and nearby vessels are affected.
Causes
The most common causes of mid-shoulder injuries are a fall or a powerful blow to a limb or joint.
The lesion is manifested by the following symptoms:
- deformation and shortening of the limb;
- sharp, acute pain;
- impaired motor function of the limb and joint;
- tissue swelling;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage.
The listed symptoms of shoulder fractures are typical for injuries of all departments: lower, middle, upper.
Diagnosis of distal epiphysis injury
During palpation, an experienced doctor can hear a characteristic crunching sound, as bone fragments rub against each other when moving.
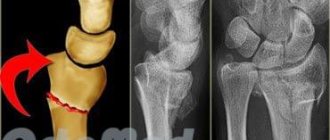
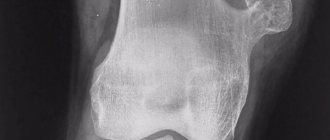
However, a final diagnosis can be made after an X-ray examination. X-rays easily reveal the fracture line and provide information about imbalances in bone relationships. X-ray images show traumatologists a clear picture: the patient has a fracture or dislocation of the shoulder, accompanied by similar symptoms.
Therapeutic measures
Injuries of the middle section are treated conservatively, fixation of fragments is carried out using reposition. After eliminating the displacement, a closed plaster bandage is applied to the patient’s forearm for 2-3 months.
If a fracture of the humerus is impossible to perform a high-quality reduction without surgery, or if the radial nerve is injured, the tissues are pinched by fragments, surgical intervention is required. Fixation is carried out using medical plates made of a special alloy, screws and rods, using an Ilizarov apparatus. Using radiography, the location of the plates and screws is determined.
Diagnostic methods
A closed shoulder fracture is diagnosed by a traumatologist or orthopedic surgeon. The doctor determines the circumstances of the injury, conducts a visual examination, determining the degree of motor impairment and the characteristics of symptoms characteristic of certain types of fractures, and sends for x-rays. The procedure shows the presence or absence of displacement, whether the small external condyle or epicondyle of the humerus is broken, the metaepiphysis of the radius, the condition of the nerves, blood vessels, ligaments and muscles. To obtain a detailed clinical picture, it is recommended to undergo:
- MRI,
- arthroscopy,
- Ultrasound,
- scintigraphy,
- CT.
Treatment: the most effective methods
Traditional methods
A closed fracture of the humeral shaft requires the application of a fixator. Under favorable conditions, the shoulder heals in 1-1.5 months. In older people, the healing time may increase due to thinning of the bone structure. During the period of walking in a cast, it is recommended to take control radiographs. You should also stick to a diet, focusing on foods rich in calcium and vitamin D. Taking the following dietary supplements is effective:
- "Calcium gluconate",
- "Calcium D3 Nycomed"
- "Calcimin"
- "Aquadetrim"
- "Vitacalcin"
- "Vitrum Calcium".
If your hand hurts badly, it is recommended to use analgesics - Analgin, Nurofen, Ibuprofen. During the recovery period of the right or left limb, you can use the following anti-inflammatory liniments:
- "Dolobene"
- "Diclofenac"
- "Apizartron"
- "Fastum gel"
- "Deep Relief"
- "Voltaren."
The drugs can only be applied if there are no wounds on the skin.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is more often required if a closed, comminuted, displaced fracture of the arm is diagnosed. An operation is performed with a plate—a metal synthesis instrument that is used to fasten bone fragments. During surgery, the doctor also cleans and drains the wound, and sutures torn nerves and blood vessels. Since the heads of the humerus are often broken during injury, the injury takes a long time to heal.
Rehabilitation of a humerus fracture
Physiotherapeutic methods
For the treatment of humeral epiphysis fractures, the following physiotherapy procedures are recommended:
- infrared and ultraviolet irradiation,
- inductothermy,
- electrophoresis,
- phonophoresis,
- magnetotherapy,
- laser treatment,
- thermal applications with ozokerite and paraffin,
- radon and hydrogen sulfide baths,
- massage.
Physiotherapy has the following therapeutic effects on shoulder injuries with fragments:
- restores motor functions,
- improves lymph flow and relieves swelling,
- normalizes blood circulation,
- accelerates tissue regeneration,
- regulates metabolic processes in the bone structure,
- eliminates inflammation.
Physiotherapy
Fractures of the shoulder bone require prolonged immobilization, during which the muscles atrophy and the functioning of the limb deteriorates. Therefore, exercise therapy is aimed at developing the entire arm and includes the following exercises:
- clenching and unclenching fingers,
- rotational movements of the hand, elbow and shoulder joint,
- swing your hand back and forth, left and right,
- flexion-extension of the elbow joint,
- raising your hand up and down,
- interlocking fingers at the back of the head,
- exercises with dumbbells weighing no more than 2 kg.
You should start the exercises with a massage. This helps improve blood flow and warm up the muscles. It is recommended to palpate the fracture site with light pressing movements, as well as stroking and pinching. If there are postoperative wounds, massage should be done by a specialist. During the rehabilitation period, swimming is recommended, since staying in water has a beneficial effect on the soft tissues of a broken arm. During healing, you should not sleep on the side of the affected arm so as not to impair blood circulation.
Complications
If the humerus is broken, but medical care was provided in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. In advanced cases, injury is dangerous due to dysfunction of the radial nerve. The main consequences of an untreated fracture are as follows:
- improper bone fusion
- limb deformity,
- reduction or loss of the function of grasping and holding an object,
- unnatural hand position,
- formation of calluses and pseudarthrosis,
- arthrosis,
- arthritis.
The condition is accompanied by chronic pain and discomfort in the arm. An equally dangerous complication is infection with pathogenic microorganisms: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and tetanus, streptococcus, staphylococcus. The bacteria cause sepsis, which can be fatal.
Nutrition for a shoulder fracture
In order for the bone to heal quickly, attention should be paid to nutrition, since during treatment there is a large loss of proteins. Therefore, the diet should include foods that are rich in proteins, B vitamins, zinc, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins C and D, which promote rapid absorption of minerals and restoration of bone tissue.
If you do not follow proper nutrition, hypoproteinemia may develop. This means that little protein develops in the blood, which delays the development of callus, and the process of bone fusion takes a long time.
And, conversely, foods such as alcohol, which leads to disruption of cell activity, fatty foods, which interfere with the normal absorption of calcium, coffee and sweet carbonated drinks, which contribute to the loss of calcium through urine, should be excluded from the diet.