What is a thyroid adenoma
Thyroid adenoma is a benign neoplasm that appears in the tissues of the organ. Most often, this tumor is round, small in size, with clear edges, but there are exceptions. It is not attached to healthy tissue; inside it there is a capsule of fibrous material.
Thyroid adenoma is usually noticeable even to the naked eye, it is painless, but can cause various kinds of complications that significantly reduce a person’s quality of life.
Although the tumor is noticeable, without a diagnostic examination it is impossible to determine its origin.
Against the background of the disease, a hormonal imbalance occurs, which causes a variety of symptoms. The main danger of an adenoma is that it can degenerate into cancer.
Prevention
Prevention of thyroid adenoma consists of following a few simple rules.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Have an annual medical examination with an endocrinologist. This primarily concerns women.
- Check hormone levels in the blood.
- Donate blood (at least once every 12 months) for biochemical analysis.
This will help you avoid relapses and immediately take adequate measures if any complications occur.
Tavaluk Natalya, medical columnist
8, total, today
( 180 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
How to reduce blood cholesterol: recommendations from specialists and traditional medicine
Endocrine obesity: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Related Posts
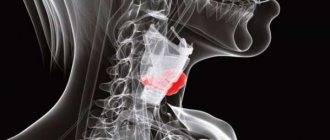
Morbidity
The thyroid gland consists of a left and right lobe, and there is also an isthmus. Normally, the right side of the organ may be larger than the left.
Practice shows that in most cases a neoplasm develops only in one of the lobes, less often it affects the entire gland. At the same time, the left lobe is affected less frequently than the right. However, the most dangerous disease is considered to be isthmus adenoma, as it often turns into a malignant form.
Thyroid adenoma is diagnosed in patients of all age groups, but is more often detected in middle-aged and elderly adults. Women suffer from this disease 4-5 times more often than men.
According to statistics, increased incidence is observed in areas with iodine deficiency. The longer a person lives in such an area, the higher the risk of developing adenoma.
The most common form of the disease is benign follicular formation. Thyrotoxic adenoma is detected in every second case of diagnosing the disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
Preliminary diagnosis is carried out during a preventive examination, which is carried out annually. To ensure that an adenoma formed on the thyroid gland is detected on time, the physician resorts to the following measures:
- The doctor listens to the patient’s story about how he is feeling, asks clarifying questions, finds out the presence of symptoms, and tries to determine the causes of the problem. Toxic thyroid adenoma is detected already at this stage, since it has characteristic manifestations.
- The doctor conducts a visual examination of the neck, noting any deformities. At an advanced stage, an adenoma of the right lobe of the thyroid gland, like the left, can be noticed externally. The doctor monitors contour changes and performs palpation.
Although measures can detect compactions, a final diagnosis is not made at the examination stage. To clarify what type the neoplasm is, the following options are used:
- An ultrasound examination makes it possible to determine whether the patient has developed a follicular adenoma of the thyroid gland or is dealing with an atypical variant. The size and location of the tumor and its shape are also assessed.
- Radioisotope scanning allows you to diagnose the disease based on the level of iodine absorption.
- To make a final diagnosis, a puncture biopsy is performed. Thanks to it, it is possible to determine the risk of degeneration into a malignant formation.
- If a toxic type is suspected, a blood test from a vein is performed. Indeed, during illness, the level of hormone secretion by the pituitary gland changes, which affects the functioning of the thyroid organ. For other types, the analysis is not effective.
Parathyroid adenoma has a special feature in diagnosis, because it is mostly carried out in the laboratory. After identifying specific signs, the physician begins to establish the localization of the tumor, since in the future it will be necessary to resort to surgical removal. With this type, the location varies greatly, so the doctor combines ultrasound with scintigraphy.
When different types of examination give the same result, surgery can be planned. If there are any doubts, computed tomography comes to the rescue.
Classification
An adenoma can be detected by a small nodule or a formed capsule in the gland. More often, one compaction appears in the tissues, and much less often several at once.
Depending on the type of cells that participate in the formation of the structure and functions of the tumor, several types of adenoma are distinguished.
Toxic adenoma (Plummer syndrome)
This is a benign tumor formation that autonomously produces thyroid hormones.
Papillary adenoma
The tumor has a pronounced cystic structure; inside the cyst there are papillary growths that are located in a brownish liquid.
Hurthle cell adenoma
Other names: Hürthle adenoma, oncocintic adenoma of B-lymphocytes is a formation that provokes an increase in the level of thyroid hormones in the blood; It is more often diagnosed in women under 40 years of age.
Follicular adenoma
Tumors arise in the follicles of the gland; the adenomatous node is small in size, can move and does not cause discomfort, and is often detected only at the last stage. There are several types of follicular adenoma:
- microfollicular - there are no colloid cells in the cavity;
- macrofollicular - large formation with colloid in the cavity;
- embryonic (trabicular) - strands of thyroid cells are formed, which are similar to the gland of the embryo at the initial stage of development;
- fetal (tubular) - the composition contains tubules, but there are no colloids, or there is a small amount of them;
- atypical - the node may consist of Hürthle cells or have a papillary composition, an irregularly shaped formation, with a bumpy surface, filled with hemorrhagic or serous exudate.
Oxyphilic adenoma
It is distinguished by aggressive development, its malignancy occurs very quickly.
Types of pathology
The pathology can be located in different parts of the organ:
- Damage to the right lobe of the thyroid gland by adenoma is diagnosed more often. It is distinguished by the large size of the nodular tumor. The main symptom is pain when swallowing.
- In the left lobe of the organ, the neoplasm is usually small in size. Easily felt by palpation.
- The isthmus of the thyroid gland affects a node that can gradually degenerate into cancer.
According to the structural composition, the following types of adenoma are distinguished:
- The follicular form may consist of many enlarged follicles. Outwardly it resembles a capsule in the form of a ball with a smooth surface and dense structure. It also likely contains other types of cells that give a separate name to the pathology - fetal, trabecular, simple or colloidal form. Cells can transform into cancer cells. During motor functions of the larynx, the tumor moves. The first symptoms appear in the later stages of the pathology.
- Papillary adenoma is a cystic accumulation containing brown liquid inside. It is formed on the inside of the walls of the organ, resembling small papillae.
Papillary thyroid adenoma
- The toxic form, or Plummer's disease, occurs due to hormonal imbalance. One or several thyroid-producing nodes may form. The seal is formed in the form of a ball or oval with small dimensions. Can be detected by palpation. When consuming foods high in iodine, the tumor rapidly increases, and the level of thyroid in the blood increases. In the early stages, it is treated with drug therapy. If the volume of the node exceeds 20 mm, it must be urgently removed by surgery.
- The oncocytic form consists of Hürthle pathogens. Diagnosed in young people aged 20-30 years. The neoplasm is distinguished by a yellowish-brown tint and short-term bleeding. It is considered a benign neoplasm, but is often confused with malignant types.
- Atypical or pathological adenoma consists of follicular and proliferating pathogens. It can take on various shapes - oval, ball, spindle or elongated knot. The cells can transform into a malignant type and urgent removal is required.
- Oxyphilic adenoma often degenerates into cancer, therefore it is considered the most dangerous for humans. It is formed in Hürthle cells and is distinguished by the presence of eosinophilic cytoplasm with large nuclei without colloid.
Causes
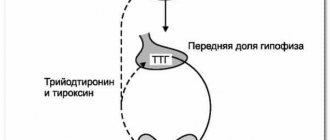
Medicine has not yet been able to fully study the disease and find out what causes the development of thyroid adenoma. But the growth of cells of benign formations is associated with an increase in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone, which is synthesized by the pituitary gland.
In addition, an adenoma is formed when the functionality of the ganglionic nervous system is disrupted - this is a prerequisite for the development of pathology.
Experts identify several factors that increase the risk of tumor formation in glandular tissues: hereditary predisposition, exposure to toxins, diseases of the vegetative-vascular system, work in hazardous industries.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
How are the lymph nodes connected to the thyroid gland?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2020
Toxic thyroid adenoma often acts as a concomitant pathology that occurs against the background of a solitary or multinodular goiter.
Injuries to the cervical vertebrae and thyroid gland can also lead to the development of adenoma, as can iodine deficiency in the body.
Causes and mechanism of development
Like other endocrine glands, the thyroid gland produces hormones. The most important are triiodothyronine and thyroxine. They help activate metabolic processes, regulate brain activity, and heart rate. Therefore, the thyroid gland is a multifunctional organ. The thyroid gland consists of A-, B- and C-cells. Each of them has its own functions. A cells are responsible for the synthesis of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. B cells (Hurthle cells) produce substances that affect certain body functions. C cells regulate calcium levels.
Scientists have not yet fully studied what becomes the direct cause of the tumor and what is the mechanism of its development. Thyroid adenoma may be a consequence of hyperfunction of the pituitary gland in response to a deficiency of thyroid hormones, a gene mutation that encodes the pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors.
A functioning adenoma can develop against the background of a non-toxic node. As a rule, formations grow in the form of single nodes and develop slowly over several years. At first, the adenoma does not affect thyroid function, hormonal levels remain normal. The formation can be detected using scintigraphy.
READ ALSO: How thyroid surgery to remove nodes is performed: rules of preparation and the result of the intervention, features of HRT
As the node grows and its functional activity increases, TSH synthesis begins to decrease. The intact part of the thyroid tissue gradually becomes atrophied and loses its functionality. In the area of the adenoma, an accumulation of radioactive iodine is detected. The disease begins to manifest itself in the form of thyrotoxicosis.
Risk factors for thyroid adenoma:
- iodine deficiency;
- heredity;
- neck injuries;
- autoimmune diseases;
- work in hazardous production;
- living in an environmentally polluted region.
Symptoms
The manifestations of the disease largely depend on whether the pathological process is accompanied by increased production of hormones. With a toxic form of benign formation, the clinical picture is more vivid. In other forms of adenoma, vague symptoms are present or absent altogether.
General signs of thyroid adenoma are as follows:
- loss ;
- nervousness, anxiety;
- increased sweating, regardless of the time of day;
- increased fatigue, tiredness, decreased performance;
- periodic increase in heart rate .
As the tumor grows, other signs of pathology appear: pain in the area of the node, discomfort, sore throat, difficulty swallowing. Large neoplasms of grade 4 lead to deformation of the neck, the patient suffers from a dry cough, the timbre of the voice changes, and it becomes difficult to breathe.
In some people, adenoma negatively affects the functioning of the digestive tract, causing an increase or decrease in blood pressure, and a rise in low-grade body temperature.
Clinical picture
The formations develop slowly and initially do not affect the hormonal balance. The disease is often diagnosed accidentally during a medical examination. As the nodes enlarge, deformation of the neck is noticeable, shortness of breath and dysphagia (impaired swallowing) appear. During exercise and at rest, tachycardia and weakness bother me.
All forms of adenoma have common symptoms:
- spontaneous weight loss;
- drowsiness;
- heat intolerance;
- unmotivated irritability;
- lump in throat;
- sweating
Important! When the first symptoms appear, you should be examined by an endocrinologist. With a long course of adenoma, the risk of malignancy, development of toxic goiter, fibrosis, and compression of the larynx and nerves increases.
Excessive secretion of thyroid hormones provokes dysfunction of many organs.
Symptoms by group
| Organ | Manifestations of violations |
| Nervous system | Temper, hand tremors, anxiety, hyperactivity, rapid speech |
| Organs of vision | Double objects, dry eyes, blurred vision |
| Heart and blood vessels | Tachycardia, increased blood pressure, high pulse, decreased myocardial tone |
| Digestive system | Appetite disorders, diarrhea, attacks of abdominal pain |
| Bones, muscles | Fatigue and loss of muscle mass, mild incoordination |
| Reproductive system | Infertility, weak potency, gynecomastia in men. Menstrual irregularities, infertility, high risk of mastopathy in women |
Diagnostics
Diseases related to the thyroid gland are treated by an endocrinologist. It is he who should be consulted if alarming symptoms appear.
To confirm the diagnosis and classify the disease, the doctor prescribes a set of laboratory and instrumental tests.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
One of the important studies of this organ, which allows us to identify its size and structure. Using ultrasound, a specialist can detect nodes, determine their orientation, shape, thickness of the capsular membrane and contours.
Radioisotope scanning
The examination helps to determine how functionally active the adenoma is, which depends on the uptake of radioiodine by the tumor—whether it is a “cold”, “warm” or “hot” tumor.
Thyroid hormone testing
The patient takes a blood test showing the level of thyroid hormones - thyroxine, triiodothyronine, as well as thyroid-stimulating hormone - TSH. Against the background of a toxic adenoma, the amount of TSH in the serum part of the blood decreases, T3 and T4 are higher than normal or increased. If the adenoma is non-functioning, then the hormone level remains within the normal range.
Blood biochemistry
The analysis determines hyperlipoproteinemia - a significant increase in the level of lipids and/or lipoproteins in the blood. Also, as a result, it is possible to detect a prediabetic state or latent diabetes mellitus - impaired glucose tolerance.
Tissue biopsy of a thyroid nodule
Carry out to finally confirm the diagnosis and determine the morphological form of the formation. A fine-needle aspiration method and examination of adenoma cells are used. In 4 out of 5 cases it is possible to differentiate benign from malignant.
X-ray of the esophagus with barium
An examination with a contrast agent—thick barium—allows for a detailed examination of the esophagus. The mixture begins to flow down the mucous surfaces, highlighting the pathological areas with color.
If there is a persistent increase in thyroid hormones, a heart examination is prescribed - electrocardiography, echocardiography, ultrasound of the kidneys, liver, blood biochemistry.
Treatment of the disease
After determining the type of adenoma, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. In some situations it is possible to do without surgery, but more often surgery to remove the node is used.
Drug treatment is used in the presence of pathology in pregnant women, elderly people and the presence of incurable types of disease. The dosage of drugs is calculated individually for each patient. A tumor without visible signs of growth does not require active therapy; it is mainly monitored with regular examinations.
For drug therapy, suppressive drugs are used, for example, Levothyroxine. The substance reduces the production of the hormone and allows thyroid levels to return to normal. But such treatment does not always help get rid of the tumor, so surgical excision is used.
Toxic adenoma is treated with radioactive iodine or surgery. Radioactive iodine is introduced into the body in the required volume, which accumulates in diseased cells. When the required amount is reached, iodine begins to actively destroy atypical pathogens. If the outcome of therapy is positive, the patient recovers completely and an annual examination by an endocrinologist is required.
For larger nodes, surgical resection, partial or complete, is used. Large sizes are removed in small parts with short time intervals between operations. The patient is discharged from the hospital on the 5th day after tumor removal.
After taking the necessary measures to treat the adenoma, the patient is prescribed a course of L-Thyroxine. You will have to take the drug constantly. Following all the doctor’s recommendations allows you to recover in 1-2 months and begin a full life.
Treatment
Therapy is prescribed based on the results obtained; only the endocrinologist decides whether the patient needs surgery or whether medication is sufficient.
Drug therapy
If the form and stage of the disease allow, specialists prescribe conservative treatment. This is the best way to cure follicular disease.
First of all, the doctor prescribes drugs that suppress thyroid synthesis: Thyroxine, Levothyroxine, Carbimazole, Propicil. This suppressive therapy is considered very serious and is therefore carried out only under medical supervision.
The therapeutic course also includes medications with anti-inflammatory effects, immunomodulators and vitamin-mineral complexes.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
How to avoid calcifications in the thyroid gland
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
For Plummer's disease, radioiodine therapy is sometimes recommended, in which the patient takes capsules of radioiodine. This leads to inhibition of the hormone-forming activity of the organ.
Drug treatment is also carried out as a preparatory measure before surgery for the thyrotoxic form of the tumor.
Preparation for surgery for thyrotoxic adenoma
Therapy for destructive processes in the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis, in which the cells of the gland are destroyed and an increased amount of hormones enter the blood) involves taking glucocorticosteroid hormones - the drug Prednisolone.
The active ingredients of the drug reduce the process of cell destruction. The duration of treatment and dosage of the drug are selected individually.
Surgery for thyrotoxicosis is performed only when the level of thyroid hormones returns to normal.
Surgical treatment of thyroid adenoma
Surgery remains the main treatment for thyroid adenoma. Doctors use various techniques, based on the degree of damage to organ tissue, the presence or absence of malignant cells.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
Normal thyroglobulin levels
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
If there are no signs of degeneration of benign tissues and the remaining areas of the gland do not have pathologies, enucleation of the node is performed. During surgery, the tumor is removed along with the capsule, while healthy tissue remains intact.
If the biopsy shows signs of malignancy of the tumor cells or the lesion affects most of the gland, one of the following operations is recommended:
- hemistrumectomy - removal of half the gland along with the isthmus;
- subtotal resection - most of the organ is removed, leaving a little of the left and right lobes; after the operation, the patient is prescribed hormonal therapy;
- thyroidectomy - complete removal of the gland, performed when there are obvious symptoms of cancer; the patient requires lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
Any surgical procedure involves risks, and the patient is warned about possible complications.
Other methods if surgical treatment is not possible
In some cases, the operation cannot be performed and specialists resort to using alternative techniques. You can reduce the size of the tumor and stop hormonal activity using ethanol sclerotherapy.
The procedure consists of introducing 95% alcohol into the tissue of the node and monitoring the ongoing processes using ultrasound.
The second technique is radioiodine therapy, the patient takes a radioactive iodine drug while staying in an isolated room for about a week.
Phytotherapy
It is impossible to get rid of thyroid adenoma using traditional recipes. But often specialists prescribe herbal medicine in preparation for surgery or conservative treatment.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
Why do antibodies to thyroglobulin increase?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
To suppress the functioning of the gland, infusions and decoctions of watercress, Icelandic cetraria, and gorse are used.
In addition, there are a number of plants that contain a thyroid hormone analogue. Once in the body, it acts locally on the pituitary gland, inhibiting its functionality. This group includes the following plants: comfrey, common blackroot, red-rooted sparrow.
Herbal formulations should be prescribed only by the attending physician; self-medication is not recommended.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of thyroid adenoma in most cases do not manifest themselves at all. However, by listening to your body, you can still detect some of them.
- The neoplasm is most often associated with cell proliferation and increased synthesis of hormones that enhance metabolic processes in the body. Therefore, the very first sign of its presence is a sharp weight loss, provided that the usual diet is maintained.
- Unreasonable irritability and aggressiveness can also be symptoms of parathyroid adenoma.
- Increased metabolism leads to increased sweating and intolerance to high temperatures.
- The presence of a neoplasm may be indicated by accelerated pulsation even at complete rest.
- One of the symptoms of a tumor in the thyroid gland is a feeling of fatigue that does not go away even after a long rest. Moreover, the most pronounced symptoms are toxic thyroid adenoma.
As the tumor grows, the sick person's digestive system becomes impaired. Accelerating metabolism enhances intestinal function. This factor leads to the fact that food does not have time to digest and assimilate. As a result, patients suffer from diarrhea and nutritional deficiencies.
Another sign of a tumor, both in the thyroid and parathyroid glands, is characterized by disruptions in the functioning of the heart. In sick people, blood pressure increases, which has not previously been observed. In some conditions, a persistent increase in temperature is possible.
The only signs of a hidden disease are drowsiness and increased heart rate. If the disease is not treated, its manifestations become more pronounced.
Parathyroid adenoma leads to increased cholesterol levels in the blood, and then to the development of atherosclerosis and heart failure.
Possible complications
Even minor surgery can cause negative consequences. During removal of the thyroid gland, the parathyroid glands, which regulate calcium levels in the body, may be damaged or excised.
In this case, the amount of the microelement steadily decreases, and a number of symptoms occur, including seizures, muscle weakness, and numbness of the limbs.
Another pathological condition that can occur during surgery is damage to the laryngeal nerves. The consequences of the violation are hoarseness of the voice and even its complete loss.
In case of illiterate, untimely therapy or its absence, complications will affect the heart muscle and central nervous system. Severe consequences are thyrotoxic psychosis, crisis, jaundice and, as a consequence, acute renal and cardiovascular failure. Such dangerous violations result in death in 50% of cases.
Signs of the disease
The first symptom appears when the tumor increases in size up to 30 mm. At the initial stage, the disease develops secretly. Signs of pathology are expressed equally in people of mature age and in adolescents. Women often attribute the symptoms to instability of the emotional background, depression, menstrual cycle, menopause or nervous fatigue.
Patients present with the following signs during the formation of a neoplasm:
- the person becomes irritable, nervous with signs of aggression;
- excessive fatigue with little physical activity;
- heart rate increases to 100 beats per minute;
- increased shortness of breath develops;
- increased sweating;
- muscle mass decreases sharply;
- Insomnia or, conversely, increased drowsiness may occur;
- discomfort from heat with stuffiness.
In the absence of treatment, the patient develops disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract, body temperature rises to 39 degrees against the background of high blood pressure. A chest cough develops with signs of discomfort when swallowing and inhaling air. There is pain in the area of the thyroid gland. A change in voice timbre may be observed. In the later stages of the disease, pathologies of the cardiovascular system are diagnosed.
Lifestyle recommendations
Thyroid adenoma, even after surgery to remove it, obliges the patient to change his lifestyle. He is recommended to regularly visit an endocrinologist - at least once a year, periodically undergo tests to determine hormone levels, and take care of proper nutrition.
It is advisable to give up bad habits, especially drinking alcohol and smoking, and avoid prolonged sunbathing.
The change also applies to diet. The menu should include fermented milk products, seaweed, fish, nuts, dried fruits, citrus fruits, fresh herbs, and vegetables. The best drinks are pure water and green tea.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for life when the thyroid gland is damaged by an adenoma is predominantly favorable. For small node volumes, doctors prefer to monitor the patient’s condition and monitor the growth process. Surgery is required when the pathology progresses to prevent negative consequences.
Treatment in the early stages of the disease avoids removal surgery. The disease can be cured with medications. All you need to do is take the pills correctly and follow your doctor's recommendations.
After medical or surgical intervention, the patient usually recovers quickly. The patient returns to the usual rhythm of life. But after treatment, you need to regularly see an endocrinologist and take blood and urine tests. Controlling hormonal balance allows you to prevent relapse and begin timely treatment.
Thyroid pathology is a benign formation, but lack of therapy is dangerous for the development of cancer. Therefore, timely and correct treatment allows you to live a long, normal life.