What is this?
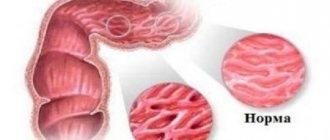
This disease, which is known as Asherman's syndrome, is characterized by the appearance of adhesions between the walls of the uterine cavity. Synechiae in the uterine cavity can lead to a wide variety of consequences - pain during the menstrual cycle, infertility and even miscarriages (if the disease occurred during pregnancy). And the later the course of treatment is started, the more difficult it will be to overcome this disease. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a specialist at the slightest suspicion of the development of Asherman's syndrome.
The staff will make every effort to ensure that the treatment of synechiae in the uterus occurs for you as quickly as possible. Our clinic has all the necessary equipment to dissect synechiae in the uterus, and high-quality medications to alleviate the symptoms of the disease in the preoperative period. You can fully count on the professionalism of our doctors and high efficiency, because our medical center has an international ISO quality certificate.
Diagnosis of synechia
- using ultrasound on the days of expected menstruation, and if there is a cycle - on days 8 - 12 and at the end of the cycle;
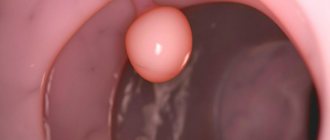
- by hysteroscopy during the menstrual phase of the cycle, when intrauterine synechiae are quite clearly visible against the background of a thin endometrium;
- using the x-ray method and introducing a contrast agent into the uterine cavity;
- by echohysterosalpingoscopy, when, as a result of filling the uterine cavity with a liquid substance, synechiae are found in the form of deforming constrictions. The diagnostic value of this method is the highest and amounts to 96%.
What types are there?
Depending on the stage of development and symptoms of synechiae in the uterus, three degrees of severity of this disease can be distinguished:
- 1st degree. At this stage of the disease, thin adhesions in the cavity occupy no more than 25% of its volume. The fallopian tubes remain free and their passage is not difficult.
- 2nd degree. The pathological process extends to 25-75% of the cavity. In this case, the patency of the fallopian tubes deteriorates significantly.
- 3rd degree. Symptoms of synechiae in the uterine cavity of this degree require immediate treatment, since pathological adhesions occupy more than 75% of the cavity, which can lead to serious complications.
Treatment of uterine synechiae in our clinic
Specialists at our gynecological center in Moscow use the most advanced and safe method for the treatment of uterine synechiae - laparoscopy. This operation is less traumatic compared to laparotomy, since to treat synechiae it is not necessary to make a large incision in the patient’s abdominal cavity. The surgeon only needs a few small punctures in the abdomen to provide access to the internal organs and effectively remove adhesions.
Treatment of uterine synechiae using laparoscopy allows you to most safely and gently overcome the disease and return the woman to a normal life!
If you want to learn more about the procedure and its stages, then make an appointment with our gynecologist. This can be done by phone or through the application form on the website.
Main causes of the disease
Asherman syndrome most often develops for three reasons:
- Inflammatory processes in the genital area. The inner layer of the uterine membranes can be destroyed due to inflammation. Ultimately, this leads to the fact that the organ begins to secrete a large amount of fibrin, which literally glues the adjacent walls together.
- Abortions and spontaneous miscarriages. In such situations, the inner layer of the organ is seriously injured, which is why the cells begin to secrete collagen fibers, from which adhesions are formed.
- Hormonal disorders. As a rule, such problems arise due to the individual physiological characteristics of the female body. In some cases, an inherited pathology may be a prerequisite.
Possible complications
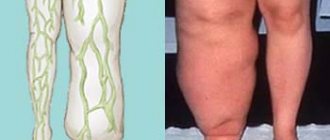
The main danger of serozometra is inflammation that occurs with suppuration. Accompanied by systems of intoxication, increasing pain, and the release of purulent secretion of a yellowish or greenish color. The infectious process can spread to adjacent organs, which only worsens the woman’s well-being. The growing uterus causes pressure on the pelvic structures and disrupts the outflow of blood from the lower vessels, which leads to swelling in the legs.
Serozometra is not an independent disease; excessive secretion formation indicates certain diseases. They must be identified in a timely manner, since serozometra can be caused by malignant tumors and inflammatory processes that require treatment at an early stage of development.
Typical symptoms of the disease
Before you begin treatment for intrauterine synechiae, you need to make a diagnosis. Symptoms of the disease usually manifest themselves in painful sensations in the lower abdomen (which intensify during the menstrual cycle). In particularly advanced cases, when the disease enters the second or third stage of its development, menstrual flow may stop altogether due to complete closure of the lumen.
In addition, infertility may be a sign of Asherman's syndrome. Synechiae in the uterus and pregnancy are incompatible things. The fact is that with this disease, the patency of the fallopian tubes, through which eggs move, worsens. If a woman has intrauterine synechiae after fertilization and the pregnancy is nearing the end, there is a high probability of miscarriage. Therefore, even if you have the slightest suspicion of the development of Asherman’s syndrome while bearing a child, you should immediately visit the clinic and be checked for the presence of synechiae of the uterine cavity using an ultrasound.
Synechia in women, in the uterus
Synechiae are adhesions between organs and can occur in the abdominal cavity, in the serous cavities of the pleura, in the pericardium, in girls between the labia, in boys between the head of the penis and the foreskin. This phenomenon can be congenital or acquired and occurs for a number of reasons.
The term “synechia”, applicable to women, means pathological fusions of the contacting surfaces inside the uterus, resulting from mechanical effects during abortion and after childbirth on the basal layer of tissue lining the uterus. Intrauterine synechiae often occur after surgical interventions, the use of an intrauterine device as a contraceptive, or the introduction of various medications into the uterus.
Infection is not the primary factor in the occurrence of intrauterine adhesions, but complications always arise when infection joins the damaged endometrium. Adhesions are most likely in women with a frozen pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that the remains of the placenta contribute to the activation of connective tissue cells (fibroblasts), resulting in the formation of collagen. The cause of the formation of synechiae inside the uterus is chronic endometritis.
Fusion of the uterine cavity causes pain in the lower abdomen and makes it difficult to discharge discharge during menstruation. Sometimes, some women may experience complete occlusion of the uterine cavity or cervical canal. In this case, menstruation stops completely.
According to histological structure there are:
- light synechiae - in the form of a film, easily dissected, composed of endometrium;
- medium synechiae - consist of endometrium, bleed when cut, fibromuscular;
- severe synechiae - connective tissue, difficult to dissect due to high density, do not bleed;
Adhesions inside the uterus are divided according to the degree of prevalence:
- I degree - thin adhesions, covering no more than 1/4 of the organ cavity, the bottom and mouth of the tubes are not affected;
- II degree - affect 1/4 to 3/4 of the uterine cavity, the walls do not stick together, only adhesions are formed, the fundus and the mouths of the tubes are not completely closed;
- III degree - more than 3/4 of the cavity of the female reproductive organ is covered.
The higher the degree of adhesions, the more serious the impact on a woman’s health; they are accompanied by menstrual dysfunction or absence of menstruation, which ultimately leads to infertility or difficulties in bearing a fetus.
If infections are observed in the lower part of the uterine cavity, then an accumulation of blood (hematometra) may be found in the upper part.
Significant infection of the uterine cavity affects the normal functioning of the internal mucous membrane (endometrium), which entails difficulty in attaching the fertilized egg. It follows from this that pregnancy in the case of intrauterine synechiae is a high risk, with possible complications during and after childbirth.
To date, the examination of women with suspected intrauterine adhesions does not have a uniform algorithm. Experts believe that diagnosis should be carried out using hysteroscopy, in which whitish strands of varying lengths and densities are usually visible, not containing vessels and significantly reducing the space of the organ. Synechiae can close the entrance to the cervical canal of the cervix, which means they make its cavity inaccessible for further development of the embryo.
If doubts arise after diagnosis by hysteroscopy, then they resort to a more effective method - hysterosalpingography. This type of study helps determine the degree of fusion and the extent of adhesions. Typically, using this diagnostic tool, it is possible to identify adhesions expressed in the form of single or multiple filling defects of irregular shape and different sizes. Multiple high-density synechiae divide the uterus into chambers that are connected by ducts. Treatment of intrauterine synechiae is limited only to dissection of the remaining endometrium with a hysteroscope. The operation takes place without injury. After this, over time, the normal menstrual cycle is restored and the female body’s ability to fertilize returns. The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the type of adhesions and the extent of spread. To prevent relapse, various hormonal drugs are introduced into the uterine cavity. Timely detection of the disease, early diagnosis and destruction of minor adhesions without injury is the key to happy motherhood. Before deciding to have a child, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination.
It is better to identify any pathologies before pregnancy. Every woman should remember the need for regular visits to a gynecologist, since advanced stages are difficult to treat, and no one can guarantee the absence of recurrences of the disease.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors
How is the disease diagnosed?
Today there are several ways to diagnose Asherman's syndrome:
- Hysteroscopy.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasound.
- Hysterosalpingography.
- Echohysterosalpingography.
The most popular and accessible among them are hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingography and ultrasound. Magnetic resonance imaging is performed on fairly expensive equipment, so diagnostic procedures are much more expensive.
Prevention of the disease Intrauterine synechiae (fusions)
It is necessary to remember about the possibility of intrauterine synechiae in patients with a complicated course of the early postpartum and post-abortion periods. If menstrual irregularities occur in such women, hysteroscopy should be performed as early as possible for early diagnosis and destruction of synechiae. In patients with suspected retention of the remnants of the ovum or placenta, it is advisable to carry out not just curettage of the uterine mucosa, but hysteroscopy to clarify the location of the pathological focus and its targeted removal without trauma to the normal endometrium.
Modern treatment methods
Only qualified specialists can be trusted to treat synechiae in the uterus - the treatment will be truly effective and will take little time. The Dad, Mom and Baby clinic practices an integrated approach to treatment for Asherman's syndrome. The entire course consists of two main stages:
- Drug treatment. With the help of special medications, you can significantly slow down the progression of the disease and prepare the body for surgery. Drug therapy is usually carried out several days before surgery.
- Surgical intervention. The operation provides an almost 100% guarantee of recovery. Its essence is that the surgeon, using special instruments, literally dissects pathological formations in the uterine cavity, thereby improving the patency of the fallopian tubes and ensuring unimpeded menstrual flow.
If you want to take care of your health and do not want to disrupt your pregnancy due to synechia of the uterine cavity, then contact “Dad, Mom and Baby”. We will definitely help you cope with any disease!
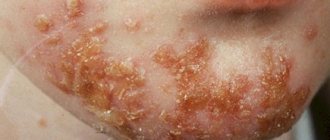
Features of the treatment of synechiae in girls using traditional methods
Most often, doctors encounter synechiae of the vagina, vulva and labia in girls. It is not surprising that for just such a case there are several remedies from the category of “traditional medicine”, which can be used in each specific case only after consultation with a doctor.
First, you need to adjust the girl’s diet. It is highly advisable to exclude from the menu foods that are likely to cause an allergic reaction - chocolate, eggs, honey, cocoa, oranges, red berries/fruits. But you need to introduce foods rich in vitamin C into your diet - persimmons, tomatoes, cabbage, broccoli, apricots and others. Even official medicine recommends eliminating or limiting the consumption of foods rich in calcium - these include milk and fermented milk products.
Important! Treatment of synechiae in girls with folk remedies should not be a priority; it is of an auxiliary nature. It is permissible only after consultation with a doctor.
Secondly, after evening hygiene procedures, you can independently separate the synechiae . To do this, you need to carefully spread the girls’ labia apart with two fingers, exposing the entrance to the vagina, and drop 2 drops of pumpkin or almond oil into the resulting space. You definitely need to remember that to treat synechiae in girls, it is not essential oil that is used, but vegetable oil! During this procedure, it is highly advisable not to come into contact with the delicate mucous membrane.
Please note: the famous and beneficial sea buckthorn oil is not suitable for treating synechiae in girls. It is in childhood that this product often provokes the development of a powerful allergic reaction.
Thirdly, you can give the girl baths with a decoction of chamomile twice a day (1 tablespoon of chamomile flowers per glass of boiling water, leave for 1 hour). And after the procedure, you need to lubricate the external genitalia and the site of synechiae with internal pork fat. It's easy to prepare fat - you just need to melt it in a frying pan and until the greaves turn golden, pour it into a vessel for further storage.
There is another option - lotions with calendula infusion . They are usually done to girls aged 2-3 years, when they can already lie down quietly for 10-15 minutes. First, prepare an infusion of 200 ml of boiling water and a tablespoon of calendula flowers (leave for 30 minutes). Then fold gauze into 2-4 layers, soak it in the infusion and apply it to the girl’s external genitalia for 15 minutes.
Synechiae is a harmless, but quite unpleasant disease, which medicine quite successfully treats not only with surgical, but also with therapeutic methods.
Konev Alexander, medical columnist
12, total, today
( 50 votes, average: 4.92 out of 5)
Prostate cyst: causes, treatment
Types and complications of medical abortion
Related Posts
Prevention of synechiae
Prevention of synechiae comes down to following the following recommendations [1]:
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- timely and adequate treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract (in particular, endometritis, vulvovaginitis, salpingoophoritis and others);
- exclusion of casual sexual contacts, as well as the use of barrier contraceptives;
- abortion prevention;
- regular visits to a gynecologist.
- Schenker JG. Etiology of and therapeutic approach to synechia uteri. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996;65(1):109-113. doi:10.1016/0028-2243(95)02315-j
Facebook Youtube Viber Telegram
Causes of the disease
There are several factors leading to the occurrence of pathology. Injury to the endometrium The source of injury can be termination of pregnancy, intrauterine contraceptives, curettage for diagnostic purposes, or surgery of the uterine cavity. The occurrence of infection may aggravate endometrial damage.
The diagnosis of genital tuberculosis is made on the basis of an endometrial biopsy or by bacteriological examination of discharge during menstruation. A previous frozen pregnancy can also provoke the formation of synechiae.
Diagnosis of synechiae
Diagnosis of synechiae involves the following procedures:
- collecting anamnesis and analyzing patient complaints;
- analysis of obstetric and gynecological history;
- analysis of menstrual function;
- gynecological examination with bimanual vaginal examination;
- hysterosalpingography is an X-ray examination of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. This research method allows you to detect adhesions, their number, as well as their location and patency of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes;
- hysteroscopy;
- laparoscopic examination.