Main symptoms:
- Painful purulent blisters on the skin
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Burning skin
- Itchy skin
- Formation of crusts on the skin
Impetigo is a contagious infectious disease caused by staphylococci and streptococci. The disease is characterized by such a symptom as damage to the upper layers of the epidermis, which as a result leads to the appearance of multiple pustules, gradually turning into scabs with crusts.
Online consultation on the disease “Impetigo”.
Ask a question to the experts for free: Dermatologist.
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Kinds
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Traditional methods
- Prevention
Impetigo is a dangerous disease that is transmitted through household contact. Children are often susceptible to this disease, but in rare cases it can occur in adults if personal hygiene rules are not followed. Infection with impetigo in children occurs as a result of microtraumas received (scratches, bites, cuts and abrasions). Mycobacterium, as a result of penetration into the skin, begins to multiply rapidly, causing an inflammatory process.
Streptococci and staphylococci are constantly on the skin, but thanks to daily hygiene procedures their number is reduced without causing skin diseases. People suffering from the following ailments fall under this category:
- eczema;
- psoriasis;
- exudative diathesis.
If this disease is not treated, internal organs may be damaged. That is why it is so important to carry out timely diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment for impetigo.
Causes
Most patients suffering from a dangerous pustular disease are preschool children. In kindergartens, high crowding leads to the immediate spread of infection. Shared toys, household items, and joint games are the reasons for the transmission of pathogenic microorganisms by contact.
Other factors contributing to the spread of infection:
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- wounds, cuts, bites through which pathogens enter the body;
- skin diseases. Inflamed areas of the epidermis, ulcers, cracks in eczema, psoriasis, and other pathologies are fertile ground for pathogenic microorganisms; (you can find out about other skin diseases on our website. Streptoderma is written about here, and about the treatment of neurodermatitis in this article);
- heat, high humidity;
- weakened immunity. This factor often leads to the development of impetigo in children;
- long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Group A staphylococci and streptococci affect people suffering from:
- diabetes;
- itchy dermatoses;
- damage to the arteries of the lower extremities.
How do other types of disease manifest themselves?
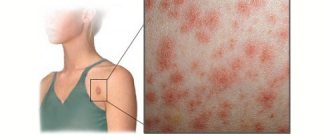
Streptococcal impetigo is the formation of painful, red blisters with pus inside. After maturation, the blisters open and ulcers appear in their place.
Staphylococcal impetigo (photo available) is accompanied by small rashes. The degree of complications depends on how deeply the skin is affected.
Strepto-staphylococcal skin lesions are expressed in multiple purulent conflicts on the skin. The peculiarity of this form is the increase in the process - the capture of new areas of healthy skin.
In the case of simultaneous infection with both staphylococcal and streptococcal infections, the contents of the blisters become purulent, and after opening, massive crusts appear. Most often it forms on the skin of the face, and the process spreads very quickly due to the fact that Staphylococcus aureus is carried by hands. We looked at the symptoms in adults.
Types and forms of impetigo
Modern dermatology identifies several types of pustular disease. Each form has characteristic features.
Osteofolliculitis or staphylococcal form Inflammation of the hair follicle is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Small pustules filled with pus are located on the face, neck, and in rare cases, on the thighs.
The ulcers dry out and become covered with a dirty yellow crust. After a few days, the crust falls off, the skin peels off, and the marks gradually disappear.
Streptococcal form The second name is contagious impetigo. The main category of patients are children and women with delicate skin. The disease spreads quickly in communities.
Small red spots appear on the face and sides; after a few hours, conflicts (bubbles) with an inflamed rim appear in these places. Inside there is pus, due to which the formations are released above the skin. Pustules can be grouped or single.
With timely treatment, you can get rid of the infectious disease in a month. There are no serious complications, no marks remain on the skin.
Ring-shaped impetigo One of the subtypes of the streptococcal form. Conflicts grow, increase, and group. In the central part, the abscess dries out and a dense crust forms. The process develops further - ring-shaped conflicts are formed along the edges.
Locations: feet, legs, area around the nail plates. Abscesses near the nail plates appear due to microtraumas and hangnails. Microbes quickly penetrate inside through wounds, and suppuration develops. Sometimes the help of a surgeon is required. The disease is accompanied by weakness, poor health, chills, and fever.
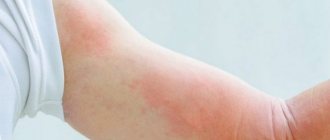
Bullous impetigo One of the dangerous types of pathology. The blisters, filled with pus mixed with blood, reach a diameter of 2 cm and rarely burst. The top of the conflicts is covered with a dense crust. Bubbles form on the shins and the back of the hands.
The course of the disease is severe - the skin swells, the patient feels unwell, the temperature rises, and the level of ESR in the blood rises. There are frequent headaches. The cause of complications is the presence of dermatitis, for example, psoriasis, eczema, neurodermatitis.
The disease does not have a chronic form. Heredity does not play a role in the development of pathology.
Vulgar impetigo This type manifests itself in girls, women, patients suffering from diseases of the liver, kidneys, and cardiovascular system. People with weakened immune systems are at risk. Often the cause of the vulgar variety is frequent stress and mental disorders.
Ulcers appear on the back of the head, in the neck, on the bends of the arms and legs. The disease lasts 8–15 days. The bubbles gradually dry out and become covered with dense crusts. After cleansing the epidermis, the spots at the locations of the pustules disappear.
Slit-like impetigo This form of infectious disease has another name - angular stomatitis. Seizures appear in the corners of the mouth, conflicts grow near the wings of the nose, and sometimes near the eyes.
The patient suffers, the pustules itch, the spots crack when talking and eating. Patients with carious cavities in the teeth, inflammatory eye diseases, and vitamin B deficiency tolerate the disease worse, and treatment lasts longer. The ways of spreading the infection are through kissing, when using shared utensils, and personal hygiene items.
Do you know what a Mongolian body spot is? We have the answer!
Read all about the prevention and treatment of bedsores in this article.
Prevention
It is easier for people with strong immunity to avoid infection by harmful bacteria.
The risk of contracting impetigo is significantly reduced in those who observe basic personal hygiene, maintain physical fitness, eat a balanced diet and monitor their health.
Those who have reduced body defenses and young children are at greater risk of infection. They need to take special care of hygiene and protect themselves from skin injuries.
What other preventative measures should be taken:
Impetigo is a contagious disease, but with timely treatment the prognosis is favorable in most cases.
A timely diagnosis and appropriate therapy will help to avoid complications and speed up the recovery process.
An important factor in this case is strengthening the body’s defenses, which protect against the action of harmful microorganisms.
Impetigo is an infectious dermatological disease. Children who attend kindergarten, school or creative electives are at risk of infection. One child with impetigo can infect an entire group or class, so parents should know a few simple rules on how to help their child protect themselves from this disease. If the baby does get impetigo, the mother needs to urgently consult a doctor to prescribe effective treatment. The disease has a positive prognosis and does not cause complications with timely treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Despite the large number of varieties, the infectious disease has a number of specific symptoms. What unites different forms is the presence of pathogenic microflora.
How the disease develops:
- in the initial stage, the skin becomes inflamed, reddens, and the general condition worsens;
- bubbles (phlycten) appear, filled with serous or purulent contents;
- many forms of pathology are accompanied by itching;
- sometimes the lymph nodes become inflamed;
- After a while, the ulcers burst, forming ulcers covered with yellow-brown crusts;
- gradually the affected areas cleanse, peel off, and traces of ulcers disappear.
Symptoms
The main external symptom of the disease is spotty purulent rashes, which are very painful and cause discomfort. An infiltrate appears at the site where the pathogen enters the hair follicle due to microtrauma. After some time, the formation bursts, after which the purulent infiltrate dries out, and yellow-brown crusts form in its place. Further, the symptoms become less painful, the crusts gradually disappear. The skin area is easily injured and bleeds. The infiltrate originates mainly in the place where there was microtrauma. This is where it is easiest for bacteria to penetrate.
Most often, the rash has the following localization:
- in the nasolabial triangle;
- chin;
- mouth.
Symptoms of impetigo
The following symptoms appear:
- itching;
- burning;
- pain;
- scratching the blisters, which causes the infection to spread;
- exacerbation of lymph nodes.
Medications
The therapy is not difficult for the patient. Effective medications and procedures quickly lead to improvement. Most drugs for the treatment of this pustular disease are affordable.
Treatment methods:
- wipe the areas around the ulcers with 2% salicylic alcohol;
- treat rashes with 5% biomycin ointment, brilliant green solution, pyoctanin;
- for streptococcal form, take sulfonamides;
- penicillin intramuscularly is indicated;
- lubricate phlyctenas in case of bullous type of pathology with ointments with antibiotics (Synthomycin emulsion, Tetracycline ointment) 3 times a day;
- Aniline dyes dry out opened ulcers well;
- for angular stomatitis, lubricate cracks and ulcers with 2% mercury ointment. Take riboflavin 0.03 g daily;
- treat inflamed areas with an alcohol solution; healthy skin near cracks and conflicts;
- take vitamin complexes to strengthen your immune system.
Treatment
Patients with widespread rashes and general symptoms of intoxication are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics (oletethrin, albomycin, rondomycin, etc. are especially effective). The conflicts (bubbles) are opened, the erosions are treated with 1-2% solution of aniline dyes (brilliant green, gentian violet or 5-10% anthocyanin solution). To remove purulent crusts and have an anti-inflammatory effect, use 5% colymicin, dibiomycin, 0.5-1.5% erythromycin or 5% polymyxin ointments, 2-3% white mercury ointment, as well as creams and ointments containing corticosteroid hormones along with antibiotics: oxycort, geocortone, locacorten, dermosolone.
The duration of antibiotic use depends on the form of I. and its course. Sulfonamides are used less frequently. Etazol, norsulfazole and long-acting agents - sulfapyridazine and sulfadimethoxine (Madribon) - are prescribed. For long-term cases, specific and nonspecific immunotherapy is widely used: staphylococcal toxoid, staphylococcal antiphagin, staphylofiltrate, staphylococcal bacteriophage, strepto- and staphylovaccine, streptofibroantigen, gamma globulin, native plasma, autohemotherapy and blood transfusions. Among the general strengthening agents used are iron, phytin, rutin, ascorbic acid, vitamins A, B. The food of patients should contain an increased amount of proteins and vitamins; carbohydrates are limited, salty foods are excluded; The diet should include mainly dairy and plant products.
Forecast
in uncomplicated cases, it is usually favorable; with proper treatment and careful care of the child, complications are rarely observed. Timely treatment of complications also leads to recovery.
Traditional methods
Check with your dermatologist about the use of traditional medicine. Do not prescribe treatment on your own. For example, baths and lotions are not suitable.
Helpful Tips:
- treat ulcers with alcohol tincture of calendula. The product perfectly disinfects and quickly dries the skin;
- Brew medicinal herbs - chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort. Take 1 tsp. each of the herbs, pour a liter of boiling water, keep on fire for 2 minutes. After half an hour, strain. Drink a healthy decoction 3 times a day, 0.5 cups.
Reviews of boric acid for acne can be read in a separate article.
Everything about the treatment of hand dyshidrosis is written at this address.
After clicking on the link, you can find information about boils on the eye.
Types of ostiofolliculitis
The disease can occur in different parts of the human body. The classification of the disease depends on the location:
- Cervicofacial ostiofolliculitis. It often causes unpleasant painful sensations and is more severe than in other places. Affects the neck and face area.
- Pathology covering the area of the upper and lower extremities. The formation appears on the thighs, calves, arms, and buttocks.
- Ostiofolliculitis of the scalp. Occurs extremely rarely.
In men, the disease often occurs in the beard and mustache area.
Important Tips
Follow the rules:
- provide the patient with separate dishes, personal bed linen, and hygiene products;
- Carry out wet cleaning with disinfectants every day;
- frequently wipe surfaces touched by the patient with soap and soda solution;
- limit the contact of a sick person with other people;
- leave the sick child at home;
- cover wounds with bandages;
- do not wash pustular rashes with water;
- do not use questionable treatment methods;
- exclude sweets, baked goods, spicy and sour dishes from the menu.
Impetigo in children
Most young patients who have suffered streptococcal and staphylococcal infections attend preschool institutions. In a group, the infection quickly spreads through contact between sick and healthy children.
Causes of impetigo in children:
- weak immunity;
- poor hygiene;
- habit of putting fingers in mouth;
- skin wounds;
- insect bites;
- malnutrition.
Symptoms:
- red spots appear in the mouth area, behind the ears, under the nose, on the backs of the hands;
- Many babies have cracks in the corners of their mouths (popularly called jams);
- sometimes, due to dirty hands, an infection appears on the gums;
- pustules covered with thin skin form on the reddened areas;
- After a while, the bubbles burst and erosion occurs;
- Gradually the wound dries up and the crust disappears.
The duration and nature of the disease depends on:
- time to see a doctor;
- state of the immune system;
- compliance by the child and adults with the doctor’s recommendations.
Important! Regularly lubricate the wounds with mercury ointment, ask your son or daughter not to lick the wounds. Then recovery will come faster.
Diagnostics
With these kinds of problems you need to contact a dermatologist. Typically, a specialist makes the correct diagnosis already at the stage of examination and collection of subjective complaints. Based on the location and nature of the rash, the type of impetigo can be determined even before laboratory and instrumental studies. The latter are carried out to confirm the initial diagnosis and select antibiotics:
- dermatoscopy;
- bacterial sowing;
- antibiogram;
- Gram staining of exudate smears.
Based on the information received, local antibiotic therapy is prescribed. If necessary, the system option is used.