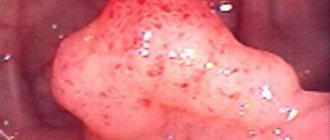
What do polyps look like?
Polyps have different shades - from gray and almost white to bright red and purple. They can be of different sizes, and in appearance they usually resemble a ball growing on a stem.
Cervical polyps can be of two types:
- Ectocervical polyps. Such polyps most often develop in women who have gone through menopause. Ectocervical polyps form from cells that form the outer surface layer of the cervix.
- Endocervical polyps. Such polyps are more common and form from glands located inside the cervical canal. Endocervical polyps are more likely to affect women who are in their reproductive years.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is determined by the size of the polyps and accompanying conditions. When the formation is small in size and single in nature, it, as a rule, does not manifest itself in any way. A woman can learn about the diagnosis based on the results of the next preventive examination. But if inflammation occurs or trauma occurs (sexual intercourse, physical stress), then obvious symptoms are observed:
- Pain in the lower abdomen (pulling, intensifies before menstruation).
- Leucorrhoea becomes profuse and can change appearance, consistency and smell.
- Scanty bloody or brown vaginal discharge (between periods).
In women of reproductive age, cervical canal polyps are associated with menstrual irregularities (prolonged periods, uterine bleeding) and infertility. If you do manage to get pregnant, then while carrying a child, complications are likely in the form of isthmic-cervical insufficiency and spontaneous abortions.
The doctor will suspect a tumor in the cervical canal based on the barrel-shaped shape of the neck, its hypertrophy and the asymmetry of the external pharynx. A bright pink polypous formation may protrude from it. It has a round or grape-shaped shape and a soft-elastic consistency. If the polyp suddenly turns blue, then most likely its blood circulation is impaired. In the future, this can cause necrosis of the node.
What are the causes of polyps?
It is not known exactly why some women develop polyps, although it is believed that one of the reasons for their formation is the body's abnormal response to estrogen.
Other possible causes include the following:
- a sharp increase or persistently high levels of estrogen;
- clogged blood vessels;
- inflammatory processes in the cervix, vagina or uterus.
Estrogen is a female sex hormone. During a woman’s life, its level constantly changes. During the reproductive years, the content of estrogen in the body is highest, so cervical polyps are highly likely to appear at this time.
The amount of estrogen can also increase sharply during pregnancy.
The level of this hormone can also be affected by chemical estrogens, which are found in various products, such as air fresheners.
Inflammation of the cervix can occur for several reasons, including the following:
- yeast infections;
- sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as herpes or human papillomavirus;
- bacterial infections;
- pregnancy;
- miscarriages;
- abortions;
- changes in hormonal levels.
In very rare cases, polyps develop in girls who have not yet experienced menstruation.
How to prepare for surgery
So, how is a cervical canal polyp removed? When preparing for surgery, it is necessary to have accurate information about the polyp being removed.
- By examining a vaginal smear, the presence of pathogenic microflora is checked; in particular, ureaplasma, mycoplasma and chlamydia can be detected.
- PCR analysis checks for the presence of viruses. These can be a variety of viruses, even HIV.
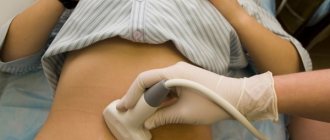
- Ultrasound reveals the location, shape and size of polyps.
- X-ray – to identify pathologies of the respiratory system.
- ECG - to detect heart pathologies.
- An examination by a phlebologist is required for patients with varicose veins of the legs.
- Hysteroscopy with an endoscope - the uterus and cervical canal are examined.
For two weeks before the operation, the patient is prohibited from smoking (at least reducing the number of cigarettes smoked) and drinking alcohol. On the eve of the operation, the patient undergoes a cleansing enema and removes hair near the genitals. On the day on which the operation is scheduled, you cannot eat or even drink water.
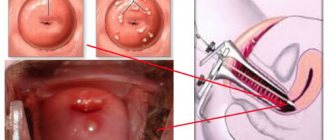
Curettage operation
The patient is placed on a gynecological chair. The gynecologist inserts a hysteroscope into the cervical canal, through which the polyp can be seen. In other cases, a hysteroresoscope is used (this is a device with a cutting attachment).
The polyp is removed by twisting it and excising the stalk (the base of the polyp is visible on the ultrasound machine screen). Curettage completely cleanses the mucous membrane of the canal and cervix.
Curettage has the advantage of reducing the risk of recurrent polyps
. Disadvantage of the technology: trauma and the need for pain relief with general anesthesia. For small polyp sizes, more modern surgical technologies are indicated.
After the operation, a wound remains in the tissue of the canal mucosa; it is necessary to prevent its infection. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
Operation with radio waves
The Surgitron device delivers high-frequency radio waves to an electrode used as a surgical scalpel. Polyp cells evaporate when heated by high-frequency vibrations
. The polyp cells themselves release thermal energy, which destroys them. In this case, the electrode does not heat up, due to this the mucous membrane of the canal is not at risk of getting burned.
After removing the pathological formation with radio waves, no scars are formed, the surface of the mucous membrane is smooth. There is no pain after the operation, so there is no need to take painkillers.
Liquid nitrogen operation
Cryodestruction method. Liquid nitrogen has a very low temperature - minus 195.7 degrees Celsius. At this temperature, the polyp cells are destroyed, being frozen
. This method has significant disadvantages: it is painful and is used under anesthesia. It is necessary to carefully calculate the depth of exposure to cold so as not to involve healthy canal tissues in freezing. The operation leaves behind a small bleeding wound.
Laser surgery
Laser removal is a gentle method. The good thing about the laser is that it hits the polyp precisely. Only pathological tissues are exposed to the laser beam; the rest of the canal surface is not affected. Polyp cells are removed layer by layer, while the doctor changes the intensity of irradiation
. Vessels damaged by the destruction of the polyp are sealed with the same laser beam, so there is no bleeding. It is preferable to remove a polyp with a laser: there is no need to insert mechanical instruments into the canal. The operation is carried out with maximum supervision from the doctor. Laser equipment allows you to calculate the intensity of radiation, its duration and the depth of penetration of the beam into tissue. A scar does not form at the site of the removed polyp. After laser surgery, the rehabilitation period is reduced to two weeks.
High frequency electric current surgery
Diathermocoagulation method. The base of the polyp stalk is cauterized with high frequency electric current. The cauterization process is painful and requires anesthesia. Unfortunately, this method has not worked well: complications arise after the operation. Therefore, modern medicine refuses this method.
Fortunately, it is not always necessary to resort to surgery: there are cases of spontaneous disappearance of polyps. On the recommendation of a doctor, you should undergo a gynecological examination again after your next menstruation.
Surgery to remove polyps has contraindications:
- Inflammatory processes in the genitals;
- Pregnancy;
- Period;
- Oncological processes;
- Uterine bleeding.
It is not prohibited, but the removal of polyps in chronic diseases is strictly limited: diabetes, cirrhosis of the liver, hemophilia, renal failure. The gynecologist is obliged to consult with a specialized specialist.
Symptoms of polyps
Bleeding after sex may indicate the presence of polyps
For some women, polyps do not cause any obvious symptoms. Others may observe the following signs of formations on or inside the cervix:
- vaginal discharge, which may have a strong odor if there is an infection;
- heavy menstrual bleeding;
- bleeding between periods;
- bleeding after sexual activity;
- bleeding after douching;
- bleeding after menopause.
When should you see a doctor?
If a woman experiences one of these symptoms, she needs to go to the hospital as soon as possible, since symptoms characteristic of cervical polyps may also indicate cancer.
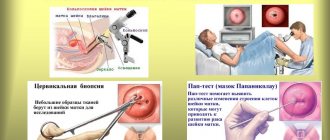
Diagnosis of polyps is carried out during a routine gynecological examination or Pap test.
If a polyp is found, your doctor may recommend removing it or having a polypectomy. He will also suggest taking a sample of polyp tissue for analysis, that is, performing a biopsy, which will help determine the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment methods for polyps
Your doctor may recommend surgical removal of the cervical polyp.
In most cases, cervical polyps are benign formations and therefore can be removed surgically.
Treatment may not be required in cases where the polyps do not cause symptoms or discomfort. However, patients with asymptomatic polyps still have to regularly visit a doctor to monitor the condition of the formations.
There are various techniques for surgical removal of polyps.
Specifically, your doctor may do the following:
- use special forceps to grab the polyp and carefully remove it;
- tie the polyp with a surgical loop and then cut it off;
- twist the polyp at its base and then remove it.
After each of these procedures, the doctor will use liquid nitrogen, laser, or electrocautery to destroy the base of the polyp.
When patients develop very large polyps, the removal procedure is performed in special hospital operating rooms. During such operations, local, regional or general anesthesia is used.
After the polyp is removed, a woman may experience cramping and bleeding for some time. Over-the-counter pain relievers usually help relieve discomfort.
The polyp or polyps should be tested for cancer. If the polyp is cancerous, the patient will need further diagnosis and treatment, which will depend on the type of cancer and its extent.
In some cases, cervical polyps disappear on their own without any therapy. They may leave the body with menstrual bleeding or during sexual activity.
Polyp during early and late pregnancy on the cervix: what to do, why is it dangerous?
Hormonal disorders during pregnancy affect the general condition of a woman. In this case, the uterine lining (the lining that lines the uterine cavity) may not grow evenly and form polyps.
Is this condition dangerous for the fetus and does it threaten the normal course of pregnancy? These questions worry any expectant mother who has been diagnosed with uterine polyps or cervical canal growth.
What are polyps, what types are there?
Hormonal imbalances in a woman's body, especially progesterone and estrogen, can cause hyperplasia.
Proliferation of endometrial cells forms polyps - mushroom-like growths. The new growth has a thin base (stem) and a wide cap. Polyps can occur individually or in groups.
Pregnant women are often diagnosed with extra cervical canal polyps.
The size of the growth varies from 1 mm to 2 cm, but in some cases it is larger. Polyps can appear according to the structure:
- black;
- fibrous;
- mixed.
Why do polyps grow?
Experts cannot name the cause of this pathology. In their opinion, the factors that provoke the appearance of polyps are
- 8 medical abortion;
- bacterial infections;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- elevated blood sugar levels;
- metabolic disease;
- inflammation of the genitals;
- autoimmune diseases;
- venereal diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- hormonal disorders.
The main symptoms of growths
In most cases, the pathology does not manifest itself or cause symptoms. Often the presence of such tumors can be detected during a gynecological examination of a woman. If the growth is large enough, there may be characteristic signs:
- discharge interspersed with blood;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- pulling pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- stench.
Diagnostic methods
It is impossible to diagnose polyps during pregnancy itself. The diagnosis is made by a specialist using various methods:
- examination on a gynecological chair. The gynecologist uses speculums to examine the cervix and vagina. With this method, only large excrement can be detected in the cervical canal or vaginal tissue. Polyps growing in the uterine cavity cannot be diagnosed by visual examination.
- Ultrasound. This method is used when a woman has unusual vaginal discharge. An ultrasound is needed to determine the cause of the bleeding. In some cases, this is a contact discharge associated with damage to the nodes, but there may also be a risk of spontaneous abortion.
- Colposcopy is performed with a special device (colposcope) to examine the cervix. Colposcopy is performed at any time during pregnancy, since the procedure does not pose a danger to either the child or the expectant mother. An examination of the cervix is performed under a microscope, and the doctor removes part of the changed tissue for cytological examination. The diagnostic results make it possible to determine the type of formation and its effect on the course of pregnancy.
- Histological examination. Histology is usually performed after surgical removal of the polyp. As a result of this study, the type of polyp can be determined.
You might be interested in: Papillomas on the neck and armpits - what does this mean?
How to treat during pregnancy?
At the same time, a woman should systematically consult a gynecologist to check her condition. Sometimes a pregnant mother is prescribed medications, such as Duphaston, to restore progesterone levels. Doctors recommend abstaining from sexual activity and reducing physical activity.
Uterine polyp
Found uterine polyps require constant monitoring during pregnancy. Therapy is not required if the tumor does not increase and inflammation does not occur. Otherwise, the specialist will select individual treatment, which may consist of the following elements:
- antibacterial therapy;
- use of antiseptics and antimicrobes;
- taking hormones.
A polyp formed in the cervical canal can constantly bleed, threatening the normal course of pregnancy. In this case, it is necessary to use radical methods. The polyp is usually removed by laser, endoscopy, or polypectomy.
Cervical polyp
Polyps in the cervix occur in 25% of pregnant women and in most cases are deciduous. Such tumors can dissolve at different stages of pregnancy or immediately after childbirth. Indications for polyp removal may be as follows:
- frequent bleeding;
- growth size more than 12 mm;
- malignant tumor (fibrosis);
- inflammation of the cervix;
- risk of fetal infection.
Could there be complications?
The formation of polyps in endometrial tissues during pregnancy can cause a number of complications. They protrude from below:
- separation of the placenta;
- miscarriage;
- heavy bleeding;
- fetal death;
- formation of cancer cells;
- ovarian failure;
- early birth;
- inflammatory processes;
- uterine rupture;
- fetal malformations;
- difficult childbirth;
- sepsis.
Preventive measures
A healthy endometrium is essential for a normal pregnancy, so it is important to follow some recommendations:
- for careful monitoring of personal hygiene;
- for maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- for the treatment of existing diseases of the genital organs before conception;
- for regular visits to the gynecologist;
- to eliminate anxiety and stress;
- to monitor hormone levels;
- to refuse an abortion.
How is recovery after surgery?
During polyp removal, patients may feel pain and discomfort. However, once the procedure is over, they usually go home, where they continue to take over-the-counter pain medications for several days.
Even if the operation is performed in a hospital under anesthesia, the woman is also discharged on the day the polyp is removed.
Doctors recommend abstaining from sexual activity for at least three days after surgery.
The outlook for women who have had polyp removal surgery is good. Polyps usually do not grow back.
However, in some cases, patients who have had cervical polyps in the past have an increased risk of their recurrence. Such women have to regularly visit the doctor for gynecological examinations, during which the specialist checks for the possible formation of new formations.
Diagnostics
Detection of polyps is possible during a gynecological examination if the neoplasms are not localized in the upper parts of the cervix. However, if cervical polyposis is detected, it is necessary to conduct a full gynecological examination, since often the growths can be located in the uterine cavity.
Diagnosis of polyposis includes the following research methods.
- Gynecological examination. The cervix is examined using a mirror. The doctor evaluates the homogeneity of the epithelium and the uniformity of its color. Specialists pay special attention to the presence of discharge, which may indicate an infection.
- Colposcopy. This study is carried out using a colposcope. This is a gynecological device that allows you to examine in detail the mucous membrane of the cervix under multiple magnification. If necessary, an extended version of colposcopy is performed. The neck is treated with a solution of acetic acid. In case of HPV infection, some areas become light in color. After treatment with Lugol's solution, atypical areas are not stained.
- Biopsy. Sampling of material for subsequent histological analysis is recommended when areas with signs of atypia are identified.
- Hysteroscopy. Manipulation is recommended for localization of polyps in the upper parts of the cervix and in the uterine cavity. The procedure allows not only to diagnose the location and number of polyps, but also to remove them. After the biopsy, the resulting material is also subject to histological examination.
Diagnostics is complemented by examination for sexually transmitted infections and hormone levels, including the thyroid gland.
Prevention of cervical polyps
In most cases, it is impossible to prevent the development of cervical polyps.
However, regular gynecological examinations and Pap tests help doctors identify polyps at an early stage of development and quickly begin treating them.
It is possible that some types of infection lead to the development of polyps. Therefore, protected sex and proper hygiene are measures that can help prevent polyps.
Women can also wear cotton underwear to increase air flow to the genital area. This can prevent the intimate area from creating a warm, moist environment that is ideal for the growth of bacteria that cause infections.