What's happened
Soft tissues are all non-epithelial structures of the human body. The following types are usually included in this category:
- ligaments;
- tendons, nerves;
- lymphatic vessels;
- muscle, fat and connective tissue.
The origin of all these tissues is from primitive mesenchyme. Since peripheral nerves pass through all the structures described above, they are also usually combined into this group.
Tumor formations have many varieties. Among malignant growths, according to the degree of diagnosis, fibrosarcoma, neuronoma, synovioma, rhabdomyoblastoma, angiosarcoma and others are distinguished.
About 30 percent of all sarcomas are unclassified blastomas. This is explained by the fact that in most cases it is not possible to establish their histogenetic affiliation.
If we take into account statistics, then soft tissue tumors account for 0.5 to 2 percent of all cancer processes. Approximately 2/3 of them are localized in the upper and lower extremities. Of these, half are on the hips.
Favorable areas of the body for the formation of disease
Hairy areas of the human body contribute to the formation of epidermal tumors. This is due to increased secretion in these areas.
Neoplasm is possible in all areas of the body where active production of substances by the sebaceous glands occurs. The armpits and the area of the shoulder blades on the back are suitable here.
Less commonly, clinical causes of the disease can be found on the chest, palms, in the genital area (in men - on the scrotum, in women - in the ovary area), on the feet, in the neck area.
Let's look at the different forms of the disease.
Classification
All soft tissue formations are divided into four large categories.
Benign
This type of tumor is characterized by the absence of atypical cells, metastasis and rare reappearance. This group includes the following types of neoplasms.
Angiolipoma
Formation occurs on blood vessels. Localized in the deep layers of muscle tissue.
In most cases, the pathological process is diagnosed in children. In the absence of a characteristic clinical picture and concern, observation tactics are chosen.
Lipoma
The basis of the structural structure is adipose tissue. The location is those areas of the body where lipid tissue is present.
When palpating, one can detect a compaction that has a soft consistency. Does not cause pain. The growth of the tumor can take place over several years.
Fibroma and fibromatosis
As a rule, the tumor is formed from fibrous tissue. Fibroids contain cellular structures consisting of mature connective fibrous tissue.
The basis of fibroblastoma is collagen fibers. The most commonly diagnosed tumor is the soft tissue of the neck, which is called fibromitosis.
Similar neoplasms are detected in infants. In appearance they resemble dense grain. They can reach up to two centimeters in diameter.
Since this type of tumor is considered one of the most aggressive, if it is detected, removal measures must be taken.
Hemangioma
One of the most common forms that affects the vascular system. It is also more common in childhood.
If there are no manifestations, there is no need for therapeutic measures. This also includes arteriovenous angioma and racemotic hemangioma.
Neurofibroma
Formation is noted in or around the shell cavity. The basis of the structure is nervous tissue.
This disease is hereditary, has a predisposition to degenerate into cancer and can contribute to compression of the spinal cord, as a result of which neurological signs begin to appear.
Pigmented synovitis of nodular type
The tumor consists of synovial tissue. It is localized on the inner surface of the joints, and can often extend beyond its limits and affect surrounding tissues.
For this reason, surgical intervention is required when diagnosing the disease. Most often, giant cell tumors are located in the knee and hip joints. The pathological process mainly affects people over 40 years of age.
Leiomyoma
It is a benign neoplasm that affects smooth muscles. Can occur at any age. Also prone to malignancy.
Rhabdomyoma
Affects the striated muscular system in the back, lower extremities and neck. In appearance it resembles a nodular formation or infiltrate.
In general, all benign neoplasms in the initial stages of development occur without the manifestation of characteristic symptoms. Signs of the disease are observed at later stages, when the enlarged tumor begins to compress the blood vessels or nerve trunk.
Malignant
This type of neoplasm accounts for 1 percent of all cancer processes. It is most often diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50 years.
Leomyosarcoma
Affects smooth muscles. Diagnosed in relatively rare cases, it forms mainly in the uterus. As a rule, it is asymptomatic and manifests itself only in severe forms of pathology.
Rhabdomyosarcoma
The striated muscle tissues are affected. It is detected in the male half of the population over 40 years of age.
The tumor is represented by a node of dense consistency. It can be easily felt upon palpation. Formed in the head, lower extremities, pelvis and neck.
Liposarcoma
It can be localized in any part of the body where adipose tissue is present. The boundaries are blurred. A distinctive feature is slow growth and rare metastasis.
Lymphangiosarcoma
Formation occurs due to the nodes of lymphatic vessels.
Hemangiosarcoma
Neoplasms are found in the vessels of the circulatory system. The location is the deep layers of muscles. The structure is soft.
Synovial sarcoma
Can affect anyone, regardless of age. Accompanied by pain during palpation.
There is often an accumulation of blood or purulent contents in the cavity. When a cyst forms inside a tumor, the tumor has an elastic structure. In the presence of calcium salts it will be hard.
Fibrosarcoma
Connective tissue is involved in the formation. Located in the muscles of the body or lower extremities.
Has weak mobility. Presented in oval or round shape. It is more often diagnosed in the female half of the population.
Sarcoma originating from nerve tissue
The pathological condition is characterized by pain and the manifestation of neurological signs. The tumor grows slowly and is found in most cases in the thigh or lower leg area. This category includes schwannomas, sympathoblastomas, neurogenic sarcoma, and neuromas.
Place of origin
The most common localization of atheromas are:
- earlobe. In this place, the formation can reach 2 cm and is a compacted ball that becomes inflamed, festeres and hurts.
- scalp. Multiple formations are formed in this area, which have the ability to reappear after removal.
- face. Usually they are not large in size, but they become inflamed and must be removed.
- back. It is unique and especially large in size - up to 10-15 cm.
- eyelid. This can be either one or several small cysts up to about 1 cm in size. It rarely becomes inflamed, but due to the increased threat to the eye, the cyst needs to be removed as soon as possible.
- in the mammary gland. This type is much less common, but it is also necessary to remove it due to the risk of suppuration.
- on the neck. Must be removed for aesthetic reasons. It happens rarely and also inflames infrequently.
- in the groin.
- A so-called seborrheic cyst appears in the armpits.
Causes
To date, the main factors predisposing to the development of soft tissue tumors have not been established. However, experts have put forward certain reasons that contribute to the emergence of the pathological process.
These include:
- disorders at the gene level;
- injury;
- damage to the body HIV and herpes viruses;
- exposure to chemical carcinogens;
- bone diseases
- certain categories of pathologies, for example, Recklinghausen's disease.
In addition, unfavorable heredity plays an important role. Thus, tuberculous sclerosis can provoke the formation of sarcoma.
Symptoms
As a rule, the initial forms of manifestation of tumor neoplasms do not make themselves felt. The main sign of pathology in this case is the identification of a compaction, often during self-examination of the patient.
On this topic
- General
What is a cancer examination
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
The formation of such tumors, as a rule, is not accompanied by pain or disruption of tissue function. A person turns to a specialist only when he begins to experience symptoms such as ischemia, neuralgia and others that arise as a result of compression of blood vessels or nerves by a growing tumor.
As the disease progresses, signs such as:
- weight loss;
- feverish condition;
- deterioration in general health;
- hypoglycemia.
Endocrine system disorders are also possible.
Possible complications
An atheroma or epidermal cyst can transform from a benign tumor to malignancy. There is a high risk of wound infection if you try to get rid of the pathology yourself.
Suppuration of the tumor is dangerous - without disinfection, the inflammatory process can worsen. Large cysts on the head often cause vision problems and regular headaches.
For prevention purposes, you should carefully monitor your personal hygiene, use high-quality cosmetics, visit beauty salons and clean your pores, and consult a specialist in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
Since in most cases soft tissue tumors do not manifest themselves in any way, it is possible to diagnose the pathology at later stages.
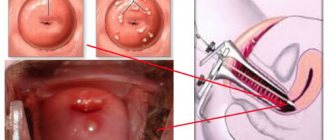
If there is a suspicion of the development of sarcoma, then first of all a biopsy is prescribed, thanks to which the nature of the neoplasm can be accurately determined.
Radiography is performed only for formations that have a dense structure.
Arterial angiography is advisable when the compaction is localized in the peritoneal cavity or lower extremities. With its help, you can identify the exact location, as well as the presence of neovessels.
On this topic
- General
Bruises on the body due to cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
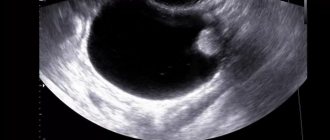
To determine the extent of the pathological process, magnetic resonance or computed tomography is performed.
Ultrasound examination is used as a primary diagnostic examination or, if there is a need to confirm existing assumptions regarding the presence of a tumor process.
Treatment
The choice of therapeutic tactics depends on the stage of the pathology, the size of the tumors, their nature, location and degree of prevalence.
As a rule, specialists use three main methods:
- operation;
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy.
To achieve the most positive result, these techniques are carried out in combination with each other.
Since almost all types of neoplasms can recur, the best option is considered to be radical intervention, which consists of complete removal of the lump and surrounding tissue.
If the tumor metastasizes or it is not possible to remove it completely, amputation of the limb is performed.
Radiation and chemotherapy are carried out when the growths are hypersensitive to these types of intervention.