Hepatic cytolysis is the destruction of gland cells under the influence of endogenous and exogenous factors.
Damage to cell membranes leads to the death of hepatocytes, necrosis and degeneration of the parenchyma, and in general to dysfunction of the organ. If not treated in a timely manner, the destructive process becomes irreversible and leads to severe complications such as cirrhosis, internal hemorrhages, and coma. In some cases, cytolysis provokes the death of the patient.
General information
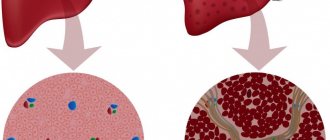
Cytolytic syndrome is a phenomenon in which liver cells are adversely affected by conditions that destroy its protective membrane. Then active enzymes penetrate outside and disrupt the structure of the entire organ, thus provoking dystrophic changes and necrotization.
Due to various conditions, the disease appears at any time in life. For example, the autoimmune type can occur in infancy, and fatty degeneration can occur in people over 50 years of age. Cytolytic syndrome is the main indicator of liver damage, its structure and functionality.
What can cause destruction: alcohol, drugs, viruses
As a result of the activity of various factors, the cellular structure of the liver is destroyed, which leads to the onset of necrosis and tissue degeneration, as well as increased permeability of cell membranes. The result of this is a disruption in the functioning of hepatocytes and, accordingly, a loss of the functional qualities of the liver itself. With timely initiation of treatment, cellular damage in a mild form (at the necrobiotic stage) can be reversible; later (with the onset of the necrotic stage) they become irreversible.
The list of reasons that provoke liver cytolysis is quite extensive:
- toxic breakdown products of ethanol, which is part of alcohol, which accumulates in the body due to alcohol abuse;
- medications with hepatotoxic properties;
- direct attack on liver cells carried out by hepatitis A, B and C viruses;
- toxic effect of lipids (including in liver diseases not associated with alcohol dependence);
- parasitic liver lesions;
- autoimmune processes in which liver cells are attacked by a person’s own immune system.
Most often, the factor leading to problems with damage and destruction of hepatocytes is excessive alcohol consumption: ethanol, which is the main component of alcoholic beverages, is a hepatotropic poison, the effect of which, with prolonged abuse and accumulation in the body, leads to alcoholic liver disease. It is enough to drink 40-80 grams per day. ethanol (100-200 grams of vodka), so that over the course of several years the liver begins to clearly demonstrate to its “owner” the consequences of his intemperance. Liver cytolysis syndrome in alcoholic illness can occur in different ways, depending on the daily dosage of booze, its quality and strength, the “experience” of alcoholism, the gender of the patient and the characteristics of his body. In the early stages, pathological changes in liver cells and tissues are reversible if the patient undergoes a course of restorative treatment and completely abstains from alcohol.
A fairly large number of medications have such a side effect as hepatotoxicity, that is, the ability to poison the liver with toxic products of their processing in the body. This complication of treatment can be corrected in only one way - by replacing the prescribed medication with a safe analogue. Drug toxicity is one of the main factors leading to cytolysis and liver failure with subsequent need for organ transplantation, which is observed in many countries around the world. Experts try to remove drugs with detected hepatotoxic effects from circulation - there is, and is updated from time to time, a list of drugs that cause liver damage in more than 45% of cases. These include:
- certain types of antibiotics (in particular tetracycline);
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- antifungal drugs;
- laxatives;
- some antiarrhythmic drugs (Amiodarone);
- neuroleptic, psychotropic drugs, antidepressants;
- some types of hormones (anabolic steroids, glucocorticoids, estrogens and androgens);
- drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis;
- anticonvulsant medications.
The list also includes the following drugs: Tamoxifen (prescribed to combat cancer, has a non-steroidal anti-estrogenic effect), Methotrexate and Ftorafur (both antimetabolites used in antitumor therapy to prevent the proliferation of cancer cells), as well as combined oral contraceptives (for long-term reception).
Naturally, taking certain medications alone cannot cause liver cytolysis syndrome - the medicinal components only create favorable soil on which the disease can develop if additional conditions coincide. In particular, health problems should be expected if:
- concomitant liver problems, supplemented by an abnormally low number of liver cells and impaired blood supply to the organ;
- sudden weight loss caused by transition to vegetarianism, forced prolonged parenteral nutrition, unbalanced diet;
- polypharmacy (taking several - more than 3 - hepatotoxic drugs at once);
- contact with environmental factors such as air polluted with heavy metals, the need to breathe insecticides and toxic chemical compounds, including household chemicals.
- pregnancy;
- reaching old age.
In most cases, if the syndrome is not advanced, stopping the use of dangerous medications is enough to reverse the damage to hepatocytes.
Cytolysis during a viral infection most often develops against the background of hepatitis, caused by viruses of one of five main types - A, B, C, D or E. Hepatitis A and E are usually transmitted through drinking contaminated water and eating unwashed food. Varieties B, C and D are infected parenterally, through contact with the body fluids of an infected person (usually the source of infection is blood). In any case, if cytolysis is suspected, it is recommended to be tested for hepatitis in order to identify the specific type of disease and prescribe precise treatment, usually with antiviral therapy.
Signs of pathology
Depending on the degree of tissue damage and the stage of the disease, hepatic cytolytic syndrome may not manifest itself in any way and show absolutely no symptoms for a long time. Total or partial destructive changes usually manifest themselves in the form of yellowing of the skin and eye whites. This phenomenon is explained by the release of bilirubin into the systemic circulation. That is why jaundice is considered an informative symptom of metabolic disorders.
Cytolytic liver syndrome is also characterized by digestive disorders: increased acidity of the gastric environment, frequent belching, discomfort after eating, a bitter taste in the mouth after eating or in the morning on an empty stomach. In the later stages of the pathology, signs of cytolytic syndrome appear in the form of organ enlargement and pain in the right hypochondrium. To obtain a complete clinical picture, diagnostics are necessary to help determine the extent of liver damage.
Treatment of cytolysis syndrome
Therapy is selected depending on the degree of parenchymal damage, symptoms and the presence of concomitant diseases. First of all, the factors that provoke cell destruction are eliminated. For this purpose, detoxification agents and hepatoprotectors are prescribed, which help restore hepatocytes and support the functions of the organ.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
Treatment of cytolysis is aimed at eliminating the provoking factors of the disease:
- If the cells are destroyed by taking medications, they need to be stopped, and if this is not possible, replaced with others or the dose adjusted.
- With alcoholic cytolysis, complete abstinence from alcohol is required. If necessary, a rehabilitation course for drug addiction is prescribed.
- If there are signs of autoimmune processes, immunosuppressive therapy is prescribed, which is aimed at reducing the production of antibodies.
For cytolysis, the following drugs can be prescribed:
- For viral infections, Ribavirin, Viferon, Interferon, which stimulate the production of antibodies, will be effective.
- For helminthic and protozoal infestations, Metronidazole, Furazolidone, Albendazole, Mebendazole and other drugs with antiparasitic effects are prescribed. For echinococcosis, surgical treatment is indicated.
- To regenerate liver tissue, remove toxins and strengthen cell membranes, natural and synthetic hepatoprotectors “Karsil”, “Sirepar”, “Phosphogliv”, “Hepa-merz” are prescribed.
- To remove toxins, Enterosgel and Polyphepan sorbents are used.
- Choleretic drugs are used if there are no stones in the bladder, “Allohol”, “Hofitol”.
- B vitamins and ascorbic acid are prescribed to restore protein synthesis and hematopoietic functions, improve metabolism and bile flow.
Complex therapy also involves following a diet. Nutrition should be complete, balanced, but easy on the liver.
Basic rules of diet for cytolysis:
- fried, smoked, spicy foods should be excluded,
- salt, sugar, chocolate must be limited,
- Avoid coffee, tea, fresh pastries and citrus fruits that increase acidity.
- It is useful to drink compotes, fruit drinks, herbal teas,
- you must drink at least 2 liters of water, including still mineral water, per day,
- meals are divided, with intervals between meals of no more than 3 hours.
Organ examinations
If a clinical picture characteristic of cytolysis occurs, specialists carry out a comprehensive biochemical examination.
- The main laboratory criteria for cytolytic syndrome are special hepatocyte markers asta, alta and LDH. Also, with this examination technique, the patient’s levels of iron and bilirubin in the blood are checked. Normal marker values for women are 31 g/l, for men - 41 g/l, LDH - up to 260 units/l. An elevated level indicates a disorder in protein metabolism, as well as the onset of necrotization of the liver. To determine these data, a general blood test is performed.
- Histological examination. During a biopsy, a piece of the patient's liver is removed. During diagnosis, cellular material is selected and the content of helminths, the degree of cell injury and the presence of necrosis are determined.
- Ultrasound and MRI. With this technique, a specialist can examine the damaged organ in various projections. Detailing of the picture is also acceptable. These techniques make it possible to identify changes in the parameters and structure of the organ, as well as the presence of helminths and tumors.
Causes
Various conditions lead to liver injury and the onset of cytolytic syndrome. As a rule, the functions and structure of the organ suffer due to:
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and exceeding the permissible dose of ethyl alcohol - the norm is 40-80 ml, depending on the characteristics of the person and the speed of his metabolism;
- improperly selected drug therapy, a combination of several drugs with hepatotoxic potential;
- penetration of the hepatitis virus;
- helminths entering the liver;
- disorders in humoral and cellular immunity.
The real cause of cytolytic syndrome can be determined solely by determining the number of enzymes, viruses in the bloodstream, histological examination of tissues and an etiological interview with the patient.
The acute and chronic form of the disease has certain symptoms: jaundice, enlarged liver, pain in the damaged area, enlarged spleen, disruption of the digestive tract.
Symptoms of liver damage due to cytolysis
It is not entirely correct to talk about liver cytolysis as a disease - this condition is a syndrome, that is, a complex of biochemical and clinical symptoms that have a common etiology (cause of occurrence) and pathogenesis (process of origin and development). Cytolysis syndrome is part of the picture of liver disease, which is why it is often so difficult to separate its manifestations from the symptoms of the disease as a whole. And for the same reason, when examining a patient, doctors pay less attention to clinical signs (they may be similar to the picture of hepatitis, body intoxication or cholestasis), placing more trust in morphological studies.
However, you should consult a doctor to clarify whether the patient is suffering from cytolysis (reversible in the early stages) or more serious liver damage if the following symptoms occur:
- jaundice;
- fever (with rapid flow);
- asthenia;
- nausea to vomiting;
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- hepatomegaly combined with splenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen).
When contacting a specialist with these symptoms, the patient can count on identifying hepatic liver disease and the severity of cytolysis (if it occurs).
A significantly larger amount of information is provided to doctors by examining the blood of a sick person. Morphological signs of cytolysis consist in the manifestation in a blood sample of an increased content of substances produced and stored specifically in hepatocytes. In a healthy state of the body (or in the presence of other liver diseases), the level of these substances in the liver cells is higher than in other biological fluids (blood and bile). During cytolysis, when the membranes of hepatocytes become thinner, all substances enter the bloodstream, where they are detected during the study.
In particular, the analysis notes:
We recommend reading:
Alcoholic liver disease
- increased content of indicator enzymes (special substances that are indicators of this particular syndrome);
- the ratio of indicator enzymes to each other;
- a large amount of free and bound bilirubin.
Ribavirin is included in the list of drugs used in the treatment of liver cytolysis
After obtaining the necessary information and differentiating liver cytolysis syndrome from other problems with this organ, the attending physician prescribes the patient the optimal course of therapy to reverse the process of necrosis of cells and then liver tissue.
Alcohol pathology
Often the causative agent of cytolytic syndrome is alcohol. With daily consumption of alcoholic beverages, a low-quality product or a surrogate, a pathological reaction appears: the activity of organ enzymes increases, the density of hepatocytes decreases. Already at this stage, the lysis mechanism is launched. Only 40-80 ml of undiluted ethyl alcohol has a toxic effect on the liver structure.
Cytolytic syndrome may not manifest itself in any way when abusing alcoholic beverages for a long time. However, gradually bitterness in the mouth and other digestive disorders will tell the patient about the pathological processes developing in his body. Cytolysis of this type is easily corrected with the help of certain medications. Hepatocytes have high elasticity and ability to recover. Thanks to this, by completely abstaining from alcohol and following the treatment regimen, the patient can very quickly notice the positive effect of therapy, at any stage of the disease.
Causes
Damage to the cell membranes of hepatocytes develops under the influence of provoking factors. Most often, the permeability of the liver cell membrane is affected due to:
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- viral infection;
- poor nutrition;
- insulin resistance;
- parasitic infestation;
- immunity disorders;
- tumor formation.
In the early stages, the disease can be treated, destructive processes can be stopped, and damaged cells can be restored. In advanced cases, with the development of tissue necrosis, the disease cannot be completely cured.
Alcohol addiction
Ethanol is the basis of all alcoholic beverages. It is a toxic substance for the liver, since alcohol is broken down into water and carbon in the gland. But with excessive alcohol consumption, the organ cannot cope with its assigned task, metabolic processes are disrupted, the structural elements of the cells are deformed and destroyed over time, which leads to lysis of the parenchyma.
The degree of liver damage is determined by the regular dosage and type of alcohol, as well as the individual characteristics of the activity of enzymes that process alcohol. The quality of the product also plays an important role; surrogates have a toxic effect, additionally poisoning the body with decay products.
In people with alcohol dependence, when diagnosing the disease, viruses are not detected, but symptoms of alcohol intoxication are detected. An increase in total bilirubin is detected in the blood; when examining a biopsy, Mallory bodies, a fibrillar protein synthesized under the influence of ethanol, are present.
Hepatocytes have a high ability to regenerate, so pathological changes disappear with abstinence from alcohol and concomitant treatment. Particularly successful and rapid results are observed in the initial stage of changes in liver cells.
Medicines
The danger of developing cytolysis comes from uncontrolled use of medications in violation of the dosage and without taking into account the contraindications specified in the instructions. The only way to avoid side effects of medications is to stop taking them, but this is not always possible, so you should know which medications can cause liver damage and carefully follow the instructions for use:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antimycotics;
- antibiotics;
- antimetabolites – antitumor chemotherapeutic agents;
- antidepressants;
- anticonvulsants;
- glucosteroid hormones.
Long-term use of hormonal contraception increases the risk of developing thrombosis by thickening the blood, disrupting blood flow in the gland and slowing down the elimination of toxins.
The hepatotoxic effects of drugs are enhanced by risk factors. These include the simultaneous use of more than three drugs, the presence of liver pathologies with impaired blood flow and insufficiency of hepatocytes, unbalanced nutrition, pregnancy, and old age. The condition of the organ is worsened by unfavorable ecology and excessive use of household chemicals.
It is important for pregnant women to remember that many medications cross the placenta and enter the fetal liver, damaging the organ and causing congenital anomalies.
Therefore, when carrying a child, taking medications is not recommended; only in exceptional cases are they prescribed by a doctor, taking into account contraindications and possible risks for the developing organism.
Autoimmune disease
Congenital abnormalities of immunity in some cases lead to the development of cytolytic syndrome. In autoimmune hepatitis, the liver lining is damaged by the body's humoral or cellular defenses for unknown reasons. Young children most often suffer from this type of disease. Severe signs of organ dysfunction can occur even in the first days after the birth of the baby.
Cytolytic syndrome in autoimmune hepatitis develops very rapidly. Only a donor liver transplant can save a small patient’s health and life.
This pathology is characterized by the absence of injuries to the bile ducts. In this case, the bubble does not change its shape and does not undergo anomalous changes.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical picture of cytolysis syndrome.
The clinical picture of this disease is characteristic of liver pathologies, so the cause of its manifestation can be determined only after appropriate diagnostics. It should also be noted that the initial development of the pathological process is practically asymptomatic.
In general, the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- yellowness of the skin, sclera;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- the tongue may be covered with a white coating;
- heaviness and feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies after eating;
- nausea and vomiting, while the release of vomit does not bring relief;
- increased flatulence, rumbling in the stomach;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- discoloration of stool;
- darkening of urine;
- itching on the skin, sometimes even on the mucous membranes;
- pain in the liver area, which intensifies after eating.
In addition, the affected epithelium of the organ can lead to exacerbation of existing chronic diseases. Enzymes are also produced incorrectly, which leads to additional symptoms. A person almost constantly feels weak and unwell, even if he does not perform any physical or mental activities, while his performance decreases, and apathy is present.
The presence of such clinical signs requires immediate medical attention, since delay can lead to extremely negative, including irreversible, complications.
Drug effects
Uncontrolled and prolonged use of pharmaceutical drugs most often causes cytolysis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are used by the patient without first undergoing tests and consulting a specialist, are considered especially dangerous.
Powerful antibiotics and antifungal medications also pose a threat. In case of violation of the treatment regimen or self-prescription, the medication may not lead to improvement, but to the development of liver failure. The dosage of the drug also plays an important role. The insert for any medicine indicates the maximum permissible daily amount of the drug, exceeding which entails the destruction of organ cells.
Representatives of the fairer sex expose themselves to the risk of cytolytic syndrome when taking hormonal contraceptives in any form. Such drugs lead to disruption of blood flow in the gallbladder and liver. The blood itself becomes more viscous, toxins are increasingly difficult to remove from it, and the size of the organ increases. All kinds of hormonal medications have a toxic effect on the liver. And at the same time, it does not matter at all for what purpose the drug is taken: therapeutic or contraceptive.
During pregnancy, cytolytic syndrome can significantly harm not only the expectant mother, but also the fetus. That is why pregnant women should be especially careful about drug therapy. The placenta collects incoming drugs and transfers them to the fetus. As a result, the child may develop congenital liver abnormalities. To prevent this phenomenon in the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman should give up pharmaceutical drugs. If this is not possible, the doctor must select the most gentle medications for the patient.
The most common syndromes in patients with hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease characterized by diffuse (extensive) liver damage. It is provoked by the RNA-containing HCV virus, the activity of which determines the clinical picture and the likelihood of complications. Most syndromes occur when the disease passes into a sluggish form. Inflammatory-dystrophic changes in the liver lead to disruption of the functions of many other organs, which becomes the cause of various symptom complexes.
Cytolytic
In patients with chronic hepatitis C, necrosis of the liver tissue (parenchyma) is observed, which is characterized by the destruction of its functional cells. During cytolysis of hepatocytes, various bioactive substances penetrate into the bloodstream, so analyzes reveal an increase in concentration:
- alkaline phosphatase;
- sorbitol dehydrogenase;
- liver enzymes (ALT, AST);
- bound bilirubin;
- gland;
- cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12).
Cytolytic syndrome (minor liver failure) is a consequence of active inflammation of hepatocytes, increased permeability or destruction of their membranes.
Due to cytolysis, liver functions are impaired, as indicated by:
- liver odor from the mouth;
- white coating on the tongue;
- weight loss.
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) triggers the production of antibodies that attack infected hepatocytes. Therefore, the more active the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms of cytolytic syndrome.
Cholestatic
Cholestatic hepatitis is a disease associated with difficulty in the outflow of bile into the duodenum. With intrahepatic cholestasis, the excretory function of hepatocytes is disrupted and the hepatic ducts are damaged. Stagnation of bile leads to the absorption of its components into the blood. They have a toxic effect on the body, provoking:
- skin itching;
- jaundice;
- darkening of urine;
- stool discoloration;
- xanthomas;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- liver enlargement;
- frequent constipation.
Cholestatic syndrome is diagnosed in 2/3 of patients with chronic hepatitis. Laboratoryly, it is determined by an increase in bilirubin concentration over 20 µmol/l. Constant itching and stool disorders worsen the psycho-emotional state, causing irritability and depression.
Hemorrhagic
In 50% of cases with sluggish hepatitis C, hemorrhagic syndrome is observed - a tendency to bleeding mucous membranes, skin rashes (petechiae), and nosebleeds. Due to inflammation of the liver, its secretory function is disrupted, the biosynthesis of clotting factors, and the content of platelets in the blood decreases (thrombocytopenia).
With chronic hepatitis, half of the patients exhibit 2 forms of hemorrhagic syndrome - bruise and hematoma. Both are caused by a decrease in blood clotting factors.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic syndrome:
- capillaritis (dilation of the smallest arteries and veins);
- large hematomas on the body;
- nosebleeds;
- spider veins on the face;
- pinpoint hemorrhages on the oral mucosa;
- bleeding gums.
A change in blood composition is fraught with not only superficial, but also internal bleeding. Their likelihood increases with hepatitis complicated by portal hypertension.
Dyspeptic
Dyspepsia is a digestive problem that is often accompanied by stool upset. In patients with viral hepatitis, it occurs due to impaired bile drainage and liver dysfunction. Dyspepsia is indicated by:
- discomfort in the epigastric region;
- early saturation;
- pain in the intestines;
- problems with stool;
- nausea;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- belching;
- bloating;
- poor appetite.
Dyspeptic syndrome is one of the first manifestations of viral hepatitis. At the initial stage, its symptoms are mild, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor. Over time, the outflow of bile into the duodenum almost stops, which causes flatulence, constipation, and abdominal pain.
If symptoms do not improve after defecation, this indicates irritable bowel syndrome.
Hydropic
Edema syndrome is observed in an advanced stage of sluggish hepatitis. Most often it becomes a consequence of liver failure, cirrhosis and liver cancer. The accumulation of intercellular fluid in tissues is associated with a decrease in albumin levels in the blood. Due to an imbalance in the acid-base balance, the density of the blood serum decreases, so it easily leaks through the walls of the capillaries.
If hepatitis is complicated by cirrhosis, effusions accumulate in the abdominal cavity - this is called abdominal hydrops, or ascites. An increase in intra-abdominal pressure causes pain and increases the risk of peritonitis.
Manifestations of edema syndrome:
- abdominal enlargement;
- hydrothorax (fluid in the chest);
- wheezing when breathing;
- swelling of the limbs;
- puffiness of the face.
Swelling due to liver cirrhosis is combined with redness of the skin on the palms, telangiectasia, and enlargement of the parotid salivary glands.
Hepatocellular failure
The syndrome is caused by a violation of the detoxification function of the liver due to damage to the parenchyma. It appears in people with long-term viral hepatitis. As a result of the accumulation of metabolic products and toxins, the functions of various systems are disrupted:
- nervous;
- immune;
- cardiovascular;
- endocrine.
Characteristic signs of hepatic cell failure:
- decreased ability to work;
- emotional disorders;
- perversion of taste;
- fast fatiguability;
- profound metabolic disorders;
- exhaustion of the body (cachexia);
- unmotivated weakness;
- aversion to food;
- loss of consciousness.
Liver failure due to hepatitis is dangerous due to encephalopathy - degenerative changes in brain tissue. The pathology is manifested by headaches, memory disorders, depression, mental disorders, and the desire to die.
Portal hypertension
Portal hypertension or hypertension is an increase in pressure in the portal vein. Diagnosed with hepatitis C complicated by cirrhosis. Fibrotic changes in the parenchyma lead to scarring of the liver vessels. A decrease in their patency leads to an increase in pressure in the portal vein.
Signs of portal hypertension:
- enlarged spleen;
- isolated abdominal dropsy;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- hemorrhoidal bleeding;
- bloody vomiting.
The syndrome is accompanied by changes in the composition of the blood - leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
An increase in blood pressure with a decrease in the density of the vascular walls increases the risk of internal bleeding. Many patients die due to gastrointestinal bleeding, which does not manifest significant symptoms.
Other syndromes associated with hepatitis
With hepatitis C, the functioning of the hepatobiliary system - the liver, gallbladder and tract - is impaired. Due to the deterioration of bile drainage, the gastrointestinal tract functions incorrectly, the absorption of nutrients from the intestine decreases, which leads to hypo- and vitamin deficiency. In the later stages of hepatitis, the following syndromes appear:
- Pain is a consequence of stretching of the Glissonian capsule of the liver, damage to the bile ducts and bladder. It manifests itself as discomfort in the right side, cutting pain in the epigastric region.
- Asthenovegetative – a pathology of the autonomic nervous system associated with a violation of the conduction and processing of impulses entering the corresponding parts of the brain. With asthenovegetative syndrome, patients complain of emotional disorders, insomnia, nervousness, and fatigue.
- Hypersplenic - an increase in the volume of the spleen in combination with a decrease in the number of blood cells - red blood cells, leukocytes. Accompanied by anemia, discomfort in the left side, thrombocytopenia.
Extrahepatic signs of advanced hepatitis C include eye damage, gynecomastia in men, diabetes mellitus, and amenorrhea in women.
Cytolytic syndrome in chronic hepatitis
Pathology is transmitted by viruses of types D, E, A, B, C. Some of them enter the body in case of violation of personal hygiene rules, others - in the absence of contraception during sexual intercourse or when using non-sterile cosmetic and medical devices. If there are symptoms of cytolysis, then a biopsy will accurately determine the type of virus.
Antiviral treatment with modern drugs can stop the progression of the disease and activate the restoration of injured organ structures. Viral cytolysis in the initial stages is much more quickly treatable.
Lipids
The body is capable of independently provoking the development of the disease when fat metabolism is disturbed. This can happen for several reasons. For example, with diabetes and obesity, metabolic disorders occur. Instead of hepatocytes, fatty deposits form in the liver. Over time, the acids and glycerol that make up the lipids interfere with the work of enzymes, destroying the protective membrane of the liver.
Presence of parasites
Increased blood flow, glucose and glycogen content make the liver one of the most attractive places for helminths. Various parasites can injure the structure of the organ.
- Amoebas. Capable of forming abscesses and accumulations. The pathological process with the participation of helminths injures the structure of the liver and leads to the development of choleostasis in both adults and children.
- Echinococcus. They can block the bile ducts, causing cytolysis. The pathological process requires not only drug therapy, but also surgical intervention.
- Giardia. Toxic products of its vital activity provoke the pathogenesis of cytolysis. A decrease in local immunity creates favorable flora for viruses and microbes to enter the liver.
- Ascariasis. Leads to cell destruction and necrotization of the organ. This phenomenon is almost always accompanied by choleostatic syndrome. Treatment in this case involves medication and the use of folk recipes.
Viruses that cause hepatitis
The causative agents of hepatitis are infectious viruses belonging to taxa A and E, B, C, delta infection D, which are characterized by inflammation of liver tissue, death of hepatocytes and disruption of the detoxification process.
The method of entry into the human body depends on the type of infection. Hepatitis caused by pathogens A and E is acute and is transmitted through nutrition or contact if hygiene rules are not observed (rarely washing hands or eating contaminated fruits and vegetables).
Infection with viruses B, C and D occurs through the blood and biological fluids of the patient. There are also known cases of the vertical route, when a baby is infected from a sick mother at the time of birth if the child has lesions on the skin. Often the pathology occurs chronically, without pronounced symptoms, so it is not possible to diagnose the disease immediately, and prolonged exposure to viruses on the liver leads to its destruction.
Liver syndromes are observed in severe acute forms of hepatitis and in its chronic course. The process of cell death can be stopped with antiviral drugs and restorative therapy.
The causative agents of hepatitis include cytomegalovirus, herpesvirus, rubella, TTV, SEN, and AIDS viruses.
Autoimmune disorders
In some cases, under the influence of a congenital disorder in the immune system, hepatocytes are destroyed. The situation is usually observed in infants; cytolysis syndrome in children develops with the progression of autoimmune diseases, or for unexplained reasons, their own antibodies affect organ cells. In this case, the gallbladder is without pathology, is not enlarged, and no changes are detected in the bile ducts.
The anomaly develops quickly; only a liver transplant can save the patient’s life; to improve the condition, therapy is carried out with immunosuppressants that inhibit the activity of the immune system.
Autoimmune disorders in an adult can be suspected if, when cytolysis is diagnosed, the patient does not drink alcohol, has not previously had a blood transfusion, there are no markers of viral damage, but biochemical changes in the composition of the blood and biopsy are detected.
Parasites
The liver is abundantly supplied with blood, the gland has a high content of glucose and glycogen, and the abundance of nutrients makes the organ attractive to parasites. Worms and protozoa not only damage tissues and clog bile ducts, but their waste products also have a toxic effect on the gland. The following types of parasites can cause liver problems:
- Echinococcus. Tapeworms parasitize in the tissues of the gland, forming cysts.
- Giardia. The simplest organisms, being in the gland, mechanically affect the tissue, release toxins and damage hepatocytes, causing inflammation.
- Amoebas. Parasites cause thrombosis, tissue necrosis and abscesses.
- Roundworms. Worms move from the intestines, clog the bile ducts, preventing the outflow of bile, producing cholestasis, causing cell death and tissue death.
Liver parasites reduce the immune defense of the organ, so helminthic invasion is often accompanied by viral or bacterial damage to the gland and inflammatory processes.
Lipids
Sometimes cytolysis progresses due to lipid metabolism disorders. Disorders usually occur after age 50. Changes develop due to excess weight, the formation of type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
Prevention of cytolysis
In order to prevent the development of such an unpleasant process as cytolytic syndrome, simple rules should be followed.
- Stick to a balanced diet. Spicy, fatty, fried foods provoke destruction of the organ membrane. And in order for the structure of the liver to remain unchanged, you should eat food that is delicately processed at temperatures, and also introduce a lot of vegetables, fruits and herbs into your diet.
- Detox treatment after taking aggressive drugs is a prerequisite for successful recovery of the body. This is necessary after using antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Refusal of alcohol. Ethyl alcohol and its derivatives have a detrimental effect on the condition of the liver. Of course, no one has ever suffered from a glass of good wine, but you should definitely avoid drinking beer every day, for example.
- Observe hygiene rules. It is very important to control the sterility of all devices used.
- Periodically carry out the prevention of helminthiasis. Folk recipes suggest taking pumpkin seeds, garlic and pine nuts for this.
Proper nutrition as disease prevention
Regardless of whether the development of cytolysis syndrome is caused by alcoholism or the “culprits” are viral lesions, autoimmune factors and diseases associated with improper lipid production, this condition harms the liver. And the following preventive measures will help protect this organ, making it much more resistant to various aggressive factors:
- establishing clear diet rules: excluding spicy, fatty and fried foods that destroy hepatocytes, eating foods that are minimally cooked, with plenty of greens, fruits and vegetables (except onions and garlic), as well as fatty sea fish and dairy products that accelerate regeneration liver cells;
- getting rid of alcohol addiction, if necessary, with the participation of specialists (narcologist and psychologist), since ethanol in alcoholic beverages not only destroys the membranes of liver cells, but also weakens the mechanisms of resistance of hepatocytes to external destructive influences;
- undergoing detoxification therapy after completing a course of taking hepatotoxic drugs (antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal contraceptives);
- compliance with personal hygiene requirements: do not drink contaminated water, do not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits, use a personal toothbrush, nail scissors, razors;
- ensuring the body’s protection from damage by parasites (in particular, helminths), for which it is not necessary to use medications - it is enough to periodically include pine nuts and pumpkin seeds in the diet, foods that are completely safe for liver cells.
Taking care of your own health should also include timely fight against diseases that could potentially affect the liver and provoke cytolysis syndrome of its cells. All measures taken together, including mandatory regular visits to the doctor, should lead to the fact that liver problems will be suppressed and will not develop further.
If a person diagnosed with liver cytolysis syndrome is very lucky, his condition will be reversible and not associated with potential complications leading to deterioration of the condition of this organ. Unfortunately, most often the onset of cytolysis becomes one of the symptoms of serious diseases, so defeating only it will be half the battle - you will have to fight the disease as a whole. And it’s easier to do this under one condition: control over your life and health, as well as strict compliance with the doctor’s instructions. And if the syndrome has not yet begun, think about your habits so as not to give it a chance to manifest itself.