Danger of knots
The thyroid gland is responsible for energy metabolic processes. They support human physical activity. Brain and cardiac activity depends on the normal functioning of the organ. The thyroid gland plays an important role in other internal processes. Symptoms that signal the emergence of a problem that are associated with a lack of energy saturation in the body.
The knot is formed from a lack of iodine. This is the main, but not the only reason. Problems appear suddenly, the person does not feel any changes.
During examination, the doctor identifies nodes. In recent years, doctors have been talking about an increase in the incidence of the disease. The disease is becoming one of the most common. Nodes interfere with the normal functioning of the body. The node can have different sizes. Less than 1 cm of the node cannot be palpated; it can only be found using ultrasound. Treatment of small-sized formations is not required. The nodes are constantly examined, specialists monitor them, check the development or stability of the disease.
Thyroid nodules - what are they?
In most people, it is impossible to detect a node by palpation. The treating endocrinologist will need to use special equipment.
ATTENTION! The thyroid gland's job is to ensure metabolism. Without the hormone that this organ produces, the full functioning of the human body is impossible.
Characteristics of the disease
A nodular lesion in the thyroid gland is, in essence, a physiological process taking place in the endocrine system. There is a transformation of the tissue structure, compaction of individual lobes of the organ without visible enlargement of the entire gland.
If we study the latest statistics, we can conclude that almost half of women suffer from this disease over the age of 50 years. The older the woman is, the higher the percentage. Men can also be at risk of this disease, however, two to three times less often than women. If we take into account the global scale of the problem, then almost 30% of the population has nodular goiter.
It is precisely because these diseases are very difficult to recognize that not all sufferers seek help from medical institutions. The reason is ignorance of the fact that they are sick. It should be understood that the above statistics include only those individuals who consulted a doctor.
It very often happens that after the doctor informs the patient about the discovery of nodes, the patient panics and tries to get into expensive clinics, buys unnecessary medications, or resorts to traditional and alternative medicine. Consulting a specialist if dangerous symptoms appear is undoubtedly the right decision. He will explain that knots are not always life-threatening. They will determine whether the applicant requires treatment. You can accurately verify the presence of the disease only by taking certain tests and conducting an examination. One of the tests is blood testing for calcitonin.
Internet users can easily find articles describing recipes, medicines, tinctures or examples of alternative medicine that guarantee that the nodes and their formations will disperse. Under no circumstances should you start treating the disease yourself. All symptoms should be discussed with an endocrinologist; it is he who will decide what advice from the Internet and a healer can be used. Everything will depend on the type of pathology.
You need to understand that nodes are different in nature. A person can solve the problem with tumors up to 6 mm in size.
However, usually the patient does not even suspect the appearance of pathology or damage to the gland. Larger nodes will not disappear on their own and must be examined by specialists.
Scintigraphy and biopsy
Radioisotope scanning (scintigraphy), unlike other examination methods, allows you to absolutely clearly see the contours of the thyroid gland (regular x-rays do not show this, since the thyroid gland is very small in size and is almost no different in density from the tissues surrounding it). Also, using the method, you can determine the location of the thyroid gland in relation to other organs, as well as the nature of the suspicious node.
The method is based on the ability of the thyroid gland to capture iodine from the blood to produce hormones, while it is able to absorb both the element supplied with food and the radioactive isotope of iodine, which is distributed evenly or not (depending on how the organ functions) throughout the thyroid gland. After it accumulates in the body (usually about a day is allocated for this), the data is read using special sensors (gamma camera) and transmitted to a computer, allowing the doctor to determine the nature of the thyroid nodules:
- if the thyroid gland is in normal condition, it will absorb iodine isotopes evenly, so its color will be uniform;
- areas that absorb too much iodine become darker in color on the image and indicate increased hormone production and signal the development of diffuse toxic goiter (hot node). As a rule, hot thyroid nodules are not dangerous, unless an undetected cold nodule develops near it (the scanner is not able to detect areas whose area is less than one centimeter);
- a cold nodule is the most dangerous and often contains cancer cells. In the picture, it looks lighter compared to other areas of the thyroid gland, since iodine is not absorbed at all or does so in insignificant quantities, which leads to the fact that very little hormones are produced in this area or are not synthesized.
Despite the fact that scintigraphy makes it possible to determine the type of nodule, its results are not completely reliable, since it often happens that a cold nodule is disguised as a hot one, and the symptoms of its presence are mild at first.
It also often goes undetected if the malignant tumor is too small to be detected, or if it is covered by a hot node or healthy thyroid tissue. Therefore, in parallel with scintigraphy, a biopsy (tab of the thyroid nodules) is required. The essence of the method is that with the help of a very thin needle, cells are taken from the wall of the node, analyzing which they determine the danger and condition of the tumor. This method is more than ninety percent reliable, and contrary to popular belief, it is painless: according to reviews, the injection is no more painful than a regular muscle injection.
Reasons for the appearance of nodes
After discovering a disease, the patient wants to know the causes of its occurrence.
Experts identify the following number of causes of gland damage that cause dangerous symptoms:
- Accumulation of colloid in follicles. The source of the problem lies in improper blood circulation in one of the lobes of the organ.
- Various stress and depression. They lead to spasms. The vessels do not receive the necessary nutrition. Immunity decreases.
- Environmental problems. Carcinogenic substances become the impetus for the development of pathology. They interfere with the genetics of thyrocytes, causing them to rapidly divide.
- The presence of inflammatory processes, for example, tuberculosis. The infection affects the lobes of the gland. Nodes and tumors appear.
- High levels of radiation. These may be areas or hazardous production conditions. Radiation disrupts the functioning of body systems and leads to the formation of nodes.
- Heredity. Gland nodules are recognized by medical scientists as pathologies transmitted from generation to generation. The predisposition is quite high, the node is repeated.
- Iodine deficiency. Lack of the substance leads to enlargement of the gland and nodes.
Is a thyroid nodule dangerous?
Many patients who have been diagnosed with tumors in the thyroid gland want to know why the size and properties of the tumor are dangerous. Endocrinologists do not give a clear answer to this question. Every node needs research. The consequences of a malignant tumor can be tragic.
Most often, the appearance of benign tumors means minor and temporary disruptions in the functioning of the thyroid gland. The nature of the node matters. A colloid cannot develop into a malignant tumor.
Cancer forms in only 5% of cases. Even in the presence of metastases, the malignant tumor is treatable. If a pseudonodule is detected in a patient, then it is not the thyroid gland that needs treatment. It is necessary to eliminate the causes of inflammatory processes.
A slight increase in the neck should not cause panic. However, you should not try to get rid of the seal yourself. The patient does not know the true reasons why thyroid nodules arose. Symptoms and treatment are determined by a specialist.
Classification of the disease
Having studied the scientific literature, it is possible to give a classification and characteristics of nodes and organ lesions.
By number of seals:
- one node (single view);
- two or more numerous nodes.
According to the internal structure:
- Adenoma. This tumor has a round shape. It develops very slowly and has virtually no effect on other organs. Typically, the node and symptoms appear in women after 40 years of age.
- Thyroid cancer. Typically, this is a single node consisting of malignant cell compounds. It develops very quickly and has no clear boundaries. Cancer nodes do not have a membrane. Upon palpation, the tumor is quite dense to the touch.
- Cyst. This is a kind of density surrounded by a capsule with liquid contents inside. It can be detected by a doctor at any age. Thyroid nodules are distinguished by the fact that the formations, dense to the touch, grow rather slowly. When palpated, the fluid inside the gland nodes vibrates.
Symptoms of the disease
Treatment of thyroid pathology is based on studying the signs of the disease and a set of abnormalities.
Symptoms of health problems:
- Voice change. A large node compresses and pinches the larynx. The voice becomes hoarse.
- Swallowing problems. The patient begins to feel a “lump in the throat.”
- Breathing problems. As a result of pulmonary edema, the patient experiences shortness of breath.
- Indigestion. It manifests itself in frequent vomiting, nausea, constipation or diarrhea.
- Increased heart rate. In a calm state, the patient's pulse will be above 100 beats per minute. Such symptoms are called tachycardia.
- Muscle weakness and decreased function of the genital organs. In women, this leads to infertility, problems with menstruation, and in men, to potency or gynecomastia.
All symptoms may not appear in one patient. It could be 2-3. It is extremely rare that all symptoms are recorded during the examination of one woman.
Examination by a specialist
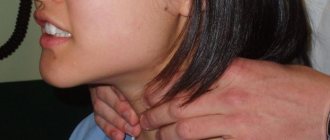
During the first examination, the doctor pays attention to the size of the thyroid nodules and the nature of the protrusion of the goiter in the front of the neck. The specialist palpates the density of the nodes, their number and volume.
The doctor takes special care:
- during examination of a patient under 14 years of age;
- over 70 years old;
- with noticeable voice problems;
- breathing problems;
- sharp pain when swallowing saliva.
The specialist begins treatment immediately if the size of the nodes is more than 1 centimeter.
If the node is more than 3 centimeters or grows very quickly, urgent surgery is recommended. Experts call this procedure a thyroidectomy.
How a knot is formed
The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck, slightly below the Adam's apple, in front of the larynx, which it covers in front and on the sides. Its dimensions are small: in its normal state, the thyroid gland weighs about twenty-five grams, and consists of two lobes that are connected to each other by an isthmus, shaped like a butterfly.
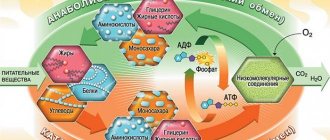
The thyroid gland is responsible for the production of biologically active substances - thyroid hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine) and calcitonin, which take an active part in metabolism and regulate many processes occurring in the body. In particular, they maintain metabolism at a normal level, are responsible for mental and physical activity, and ensure the normal functioning of the heart, brain and other internal organs.
Hormones are produced in follicles, small capsules whose walls are made of epithelial cells. On the outside they are enveloped in a network of nerve fibers and blood vessels, and on the inside they contain colloid, a substance from which hormones are produced.
The thyroid gland synthesizes thyroxine and triiodothyronine from iodine, which enters the body with water and food. Therefore, if this substance is not enough to be able to produce hormones, the thyroid gland has to increase its activity. At the same time, some areas of the thyroid gland are better at taking iodine from the blood and, accordingly, grow faster, while others do it more slowly.
Follicles that work more actively increase in size or number, which is why the areas where they are located become larger than the rest of the thyroid gland, forming one or more nodes (altered structure of part of the thyroid gland).
In addition to a lack of iodine, compaction in certain areas of the thyroid gland can be caused by poor ecology and hereditary predisposition. Radiation affects the appearance of nodules: it can cause mutations in thyroid cells, due to which they change their structure and begin to spontaneously divide.
However, not all thyroid nodules are malignant. A lack of iodine in the body usually provokes the appearance of non-tumor formations (for example, a colloid node), which are precisely formed due to the proliferation of cells in certain areas of the thyroid gland.
The detected tumors are mostly benign; cancer cells rarely form in them. They usually appear due to neck deformation, or if the thyroid gland produces too many hormones.
Malignant formations are detected in five percent of cases; cancer cells extend beyond the thyroid gland, grow in the surrounding tissues and are able to disperse throughout the body along with the blood (metastasize).
Such tumors are dangerous because they do not detect their appearance with special symptoms and become noticeable only when the situation requires drastic intervention.
Surgery
First, the patient is given general anesthesia, after which an incision is made in the neck. The thyroid gland is separated from the blood vessels and the damaged part is removed. The cyst is also removed along with the membrane. If cancer cells are suddenly discovered, the gland is completely removed. At the end of the operation, after blood circulation has been restored, the surgeon applies stitches. If there were no complications during the operations, then most likely the patient will be discharged after 3-4 days.
Treatment and methods of therapy
The most common method of drug complex. The drugs have different mechanisms of therapeutic action.
Thyroid hormones. Used to treat nodular goiter. The patient is put into thyrotoxicosis. The process of slow hormone production begins. The division of the cells that make up the node stops.
Thyrostatics. Treatment of adenoma and toxic nodular goiter. The drugs disrupt the process of combining iodine and hormones. The node does not change size, but the synthesis of hormones decreases.
Medicines containing iodine. Treatment of euthyroid goiter. The drugs create a favorable background for iodine saturation and stop the growth of nodes.
Treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist. Incorrect or self-treatment can activate the growth of pathological cells.
Methods for treating thyroid nodules
A benign colloid nodule does not require medical procedures. In all other cases, the method of getting rid of the tumor can be:
- Conservative . It is characterized by low efficiency and is rarely used in isolation. The essence of this method is the use of iodine-containing drugs and synthetic hormones.
- Minimally invasive . One of the varieties of this method is sclerotherapy with ethanol. A tumor can be treated by filling it with ethyl alcohol, which destroys the tumor tissue.
- Operational. It is used only in extreme cases in the presence of a deeply sprouted malignant tumor. Effective treatment is also carried out using the Surgitron , which has a lower level of trauma than a conventional scalpel.
ATTENTION! The patient must give up bad habits and follow the diet prescribed by the doctor. The thyroid gland, diseases of which are often associated with iodine deficiency, returns to stable functioning after a revision of the daily diet.
Traditional methods of treatment
There are people who do not accept modern medicine and are treated exclusively with folk remedies: various herbs and infusions.
The following formulations will help.
- Propolis solution. To create such a solution, you need to mix one teaspoon of propolis and 150 grams of refined oil. The resulting mixture must be heated and strained. The liquid is rubbed into the area of the gland once a day during the entire period of therapy. The result is improved blood circulation, a significant reduction in the number and size of nodes.
- Herbal infusion – white mistletoe. One teaspoon of medicinal plant is poured into 250 ml of cold water. Leave to infuse overnight. In the morning, the resulting infusion is filtered and drunk throughout the day. The medicinal composition prevents the growth of nodes.