What is euthyroidism?
Euthyroidism is pathological changes in the thyroid gland, which, with properly selected therapy, are reversible. With this disease, the functionality of the organ remains unimpaired.
It is important to distinguish the symptoms of euthyroidism from the symptoms of other thyroid pathologies, including:
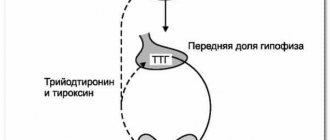
- Hypothyroidism. In this case, the patient develops persistent deficiency of the thyroid hormones T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine). There are few of them produced in the body, or they are quickly destroyed. While the level of pituitary hormone (TSH) remains elevated.
- Hyperthyroidism. With this disease, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland is observed. The patient will have increased levels of hormones such as T3 and T4.
An important distinguishing characteristic of euthyroidism is that with this disease the tissue of the thyroid gland grows, but the level of hormones remains within normal limits. However, a person with euthyroidism cannot be called absolutely healthy. A hormonal surge can occur at any moment. Moreover, it is unknown whether the level of thyroid hormones will decrease or, on the contrary, increase.
As a rule, euthyroidism does not last long. Serious disturbances occur in the patient’s body, primarily affecting the functioning of the thyroid gland. Therefore, it is so important to recognize the disease at an early stage of development.
The fact is that thyroid hormones are responsible for such important processes as:
- Growth and development of the organism as a whole.
- Control of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, heart and blood vessels, musculoskeletal system, reproductive function.
- Regulation of metabolic processes. Hormones are involved in the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Without them, it is impossible to maintain normal water-salt balance in the body.
- Development of the immune system.
- Stress resistance.
Causes
For any change in the body there are prerequisites.
Factors for the appearance of euthyroidism:
- reducing the amount of iodine that enters the body;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- manifestation of imbalance in pregnant women;
- heredity (thyroid disease in relatives);
- autoimmune pathologies in the body;
- recurring inflammation in the thyroid gland;
- emotional overload;
- long periods of stress in which a person lives;
- nervous shocks.
Euthyroidism during pregnancy should be considered as a likely cause of inflammation of the thyroid gland. Hormonal levels change, and the load on internal organs, including the thyroid gland, increases. In most cases, after childbirth the condition is restored, and the symptoms of euthyroidism disappear.
Doctor visit.
Drug-induced euthyroidism of the thyroid gland often develops as a result of taking a drug; with the correct selection of the drug, it is possible to restore the normal functioning of the organ and the level of hormones in the blood.
Euthyroidism - causes
There are several reasons that can lead to the development of euthyroidism, including:
- Iodine deficiency in the body. When there is little iodine, the thyroid gland begins to increase in size, which becomes the basis for the development of various serious diseases.
- Hereditary predisposition. If a person’s close relatives suffer from thyroid pathologies, then it is likely that he will also encounter a similar problem. To recognize the disease in time, you need to undergo a thorough examination.
- Prolonged stress.
- Infectious diseases. Diseases such as tonsillitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, and frontal sinusitis can provoke euthyroidism.
- Frequent and uncontrolled use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs.
- Inflammatory processes localized in the thyroid gland itself.
- Living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
During pregnancy
Euthyroidism can be found in pregnant women who previously suffered from hyperthyroidism. The level of hormones returns to normal, since the body urgently needs them during this period.
When a decrease in thyroid hormones does not occur, the doctor will recommend medications to correct hormonal levels. You should not ignore medical recommendations, since the course of pregnancy and the health of the child depend on this. Therefore, all women with hyperthyroidism need to achieve euthyroidism at least for the period of gestation.
Necessary treatment for euthyroidism
Quite often, endocrinologists make a diagnosis of euthyroidism of the thyroid gland. How to treat this condition, what determines the tactics of therapeutic correction?
When a pathology is identified, the doctor explains to the patient what euthyroidism of the thyroid gland is, and he prescribes treatment only after all the necessary studies have been carried out.
If a mild degree of euthyroidism is observed, the specialist is recommended to undergo periodic tests and ultrasound examinations. Drug therapy is not needed in this situation.
As the pathological condition progresses, iodine preparations may be prescribed.
If euthyroidism of the thyroid gland is detected, treatment with folk remedies involves, first of all, correction of the diet and the inclusion of iodine-containing products.
Based on them, you can prepare many healthy and tasty dishes - this will compensate for the lack of iodine in the body.
Nowadays, a diagnosis of “euthyroidism of the thyroid gland” can be made quite often. Symptoms and treatment with folk remedies should be known to everyone.
Nutrition for euthyroidism of the thyroid gland should include the following foods:
A proper diet for euthyroidism of the thyroid gland makes the prognosis of the condition more favorable.
In cases where euthyroidism of the thyroid gland is observed, nutrition should be correct - if it is not possible to consume iodine-rich foods, then taking iodine-containing medications will save the situation.
Euthyroidism is not an independent pathology; it can be observed in a number of conditions and diseases. It is important to undergo regular preventive examinations and consult a doctor at the first symptoms of illness.
Paying attention to your own health will prevent the development of pathologies of the endocrine system.
Symptoms of euthyroidism
Since during euthyroidism the thyroid gland continues to produce the same amount of hormones as before, the symptoms of the disease will be mild. People turn to the doctor after they notice an increase in the size of their neck. Moreover, they consider this a purely cosmetic problem. The first symptoms of euthyroidism appear in the nervous system.
Nervous system. The person becomes apathetic and may become depressed. Moreover, no obvious reason for this condition will be identified. Memory begins to deteriorate, and cognitive processes in general suffer. If hypothyroidism is congenital, the child develops cretinism.
Women notice their hearing impairment, their vision begins to deteriorate. Numbness of the limbs often occurs. Changes in the functioning of the nervous system lead to the appearance of symptoms in other organs.
Neck. A lump appears in my throat. This leads to difficulty swallowing food. From time to time, or on an ongoing basis, a person experiences a pressing feeling in the neck area. People compare this symptom to the feeling of a noose around the neck.
Heart. There is a disturbance in its rhythm. Moreover, failures can be either barely noticeable or pronounced. They occur either as extrasystoles (extraordinary heart beats) or as tachycardia (rapid heartbeat).
Weight. People with euthyroidism experience decreased body weight. At the same time, the person continues to eat as before, that is, he does not follow a special diet. He does not have any serious pathologies.
Clinical symptoms of the euthyroid state
There are cases when euthyroidism of the thyroid gland does not produce symptoms, and the condition is detected during ultrasound or tomography.
In other situations, the following clinical manifestations can be observed:
- exhaustion of mental reactions;
- emotional stress;
- fatigue;
- insomnia at night, drowsiness during the day;
- soreness in the throat and neck area;
- increase in the size of the thyroid gland;
- difficulty swallowing.
The most common disease in which euthyroidism is observed is nodular goiter. This pathology is accompanied by diffuse proliferation of the thyroid gland with the formation of single or multiple nodes.
As the disease progresses, disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system appear: tachycardia, extrasystole and others. Weight fluctuations are possible, most often weight loss.
Focal changes in the thyroid gland are sometimes observed. Euthyroidism is accompanied by the formation of small nodules (up to 1 cm). These nodules are not considered true.
With this condition, general malaise and deterioration in well-being are possible. The concentration of iodothyronines remains within normal values, but the structure of the organ undergoes noticeable changes.
Sometimes the question arises: if a diagnosis of “euthyroidism of the thyroid gland” is made, will they be accepted into the army? The response to it is determined by the severity of the condition and the provoking factor of the disease.
The final decision on the possibility of service should be made by an endocrinologist.
Forms and degrees of the disease
Depending on the severity of pathological symptoms, there are 3 degrees of euthyroidism:
- First degree. The thyroid gland increases in size, but not much. It will not be possible to detect the proliferation of its tissues by palpation. There are no external signs of a change in its size.
- Second degree. The thyroid gland increases in size, but this cannot be determined by palpation.
- Third degree. The thyroid gland enlarges significantly, this is noticeable upon examination and palpation.
With non-toxic goiter, the thyroid tissue increases in size, resulting in the formation of one or more nodes.
Types of nodular goiter with damage to the gland:
- Endemic. It is formed due to iodine deficiency in the body.
- Nodular goiter with euthyroidism. The gland increases in size, but there are no nodes in it.
- Nodular goiter of the 1st degree. In such a goiter, 1 node is formed.
- Nodular goiter 2 degrees. In this case, several nodes are formed in the thyroid gland at once.
- Nodular goiter with multiple nodes intertwined with each other.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the patient will have different symptoms of euthyroidism.
During palpation and examination of the thyroid gland, the doctor can detect both its diffuse structure and several nodes. There may be several or one. Sometimes they merge into a single entity. With euthyroidism, the formation of a mixed goiter is also possible. In this case, it will contain both diffuse and nodular tissues. This type of disease is most often diagnosed in older women.
Can there be nodular euthyroid goiter?
The patient may have a nodular euthyroid goiter, but it will not persist for a long time. With diagnosed nodular euthyroid goiter, experts talk about the functional autonomy of the thyroid gland. After a short period of time, such a goiter transforms into a thyrotoxic one.
Diffuse and hypertrophic changes in thyrocytes occur only at an early stage of the disease. Thyrocytes have different abilities to proliferate, so in some areas of the gland cells divide faster, and in others - more slowly. For this reason, the patient develops a multinodular euthyroid goiter. When these pathological changes are completed, the transformed gland will begin to produce triiodothyronine, regardless of the commands given by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus.
Signs of the disease
For a doctor, pathology has a clear clinical picture:
- enlarged thyroid gland;
- diffuse changes in organ tissues;
- formation of nodes in the thyroid gland.
The organs of the endocrine system are sensitive to various endogenous and exogenous influences. The level of thyroid hormones can change at any time, decreased or increased, this will inevitably lead to the development or progression of a disease such as autoimmune thyroiditis.
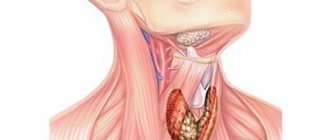
Location of the thyroid gland.
Ait euthyroidism is a chronic disease with severe damage to thyrocytes.
The specialist is able to establish the forms of pathology:
- focal;
- diffuse;
- peritumoral;
- juvenile
Autoimmune euthyroidism of the thyroid gland develops unnoticed in the patient. For a long time, a person is not bothered by the symptoms of the disease. Hypothyroidism is most often diagnosed in the euthyroid stage.
Manifestations of pathology
Symptoms are related to the underlying disease. The first sign is nervousness that appears in people.
Later joins:
- discomfort in the neck area;
- a characteristic symptom of thyroid pathology is a feeling of a lump in the throat;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- frequent headaches;
- drowsiness;
- rapid weight gain with a constant diet;
- change in voice timbre due to an increase in the size of the thyroid gland;
- dry cough possible.
Nodular goiter
The most common form of the disease is DEZ euthyroidism (diffuse euthyroid goiter). The gland is abnormal in size.
Doctors distinguish several types of nodular goiter:
- Endemic goiter . Develops due to the lack of the required concentration of iodine in the body (see Why is iodine deficiency dangerous?).
- Nodular goiter . Proliferation of gland tissue with the appearance of many nodules.
- Goiter with one node.
Goiter.
In the absence of treatment for nodular goiter, the overall picture is complemented by the following symptoms:
- discomfort in the chest area;
- tachycardia;
- arrhythmia.
Goiter is the common name for all cases of enlargement of the thyroid gland. In particular, it implies a change in the structure of the organ. Due to the peculiarities of the reaction of the nervous system and the dominance of regulatory centers, pathological processes develop in people only in one lobe of the thyroid gland.
What is the danger of euthyroidism?
Euthyroidism can be considered a safe condition, but only as long as a person maintains normal levels of hormones in the blood. If the disorder develops quickly, the patient will develop a nodular goiter. This pathology requires emergency treatment.
If the disease is ignored, serious complications may arise after some time. The likelihood of the formation of a malignant tumor or compression of the trachea increases. In such a situation, the thyroid gland has to be removed.
Other complications of euthyroidism include:
- Deterioration or loss of memory.
- Panic attacks.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
- Primary infertility.
- Depression.
- High blood cholesterol levels.
Video: surgeon, Doctor of Medical Sciences Viktor Nikolaevich Kosovan will talk about methods of treating nodular goiter with euthyroidism:
Definition
The thyroid gland is very small, hardly larger than the size of two V-shaped fingers. Very often, a patient experiences symptoms for a long time that do not directly indicate problems with the thyroid gland, since they are of a general nature.
With euthyroidism, all the test hormones in the blood (T3, T4 and TSH (see TSH hormone: what is it and its importance for human health)) will be normal, but when an ultrasound is performed, the picture will change dramatically. The doctor will notice on the monitor or image pathological processes that have affected the gland tissue: diffuse or nodular proliferation of tissue.
It is important to understand that the disease euthyroidism implies an increase in the size of the thyroid gland in the absence of any violations of normal values. It is dangerous to perceive clinical euthyroidism as the norm; it is a pathological condition that leads to serious diseases such as goiter and autoimmune thyroiditis.
Diagnosis of euthyroidism
Basic methods for diagnosing euthyroidism:
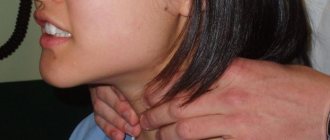
- Visual examination of the patient, palpation of the thyroid gland.
- Determination of TSH, T3 and T4 levels.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland. During the examination, it is possible to accurately determine the size of the organ, detect cysts, nodes, tumors, etc.
- Fine needle biopsy and scintigraphy. These methods are indicated for implementation if nodular changes are detected in the gland tissues.
- An immunogram during which antibodies to thyroglobulin are detected, as well as to the cells of the gland itself.
Based on the diagnostic data obtained, the doctor recommends treatment. Sometimes the patient simply continues to be monitored, and the person himself will need to take certain preventive measures. This management tactic is implemented in the case when the gland remains in a stable state, does not grow, and there are no pathological changes in it. The same applies to hormonal levels.
Diagnostics
The doctor begins to identify abnormalities in the thyroid gland by examining and palpating the patient.
Since clinical-hormonal euthyroidism most often takes the form of nodular goiter, in endocrinology there are 5 degrees of its development:
- the size of the organ is normal, so when palpating the iron is practically not palpable;
- the outlines of the thyroid gland are difficult to palpate;
- contours are distinguishable when swallowing;
- the goiter is visualized over a large area of the neck;
- The goiter protrudes strongly, swallowing movements are difficult for the patient and cause pain.
If violations are detected, a set of examinations is prescribed.
If violations are detected, a clinical and hormonal complex of examination of the patient is prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- scintigraphy - radioisotope analysis for thyroid hormones;
- biopsy and histological analysis of tissue (especially with a single node);
- contrast radiography of the retrosternal area (for large goiter).
Depending on the reasons, the following classification of pathology is accepted:
- Clinical or clinical-hormonal euthyroidism. Develops due to iodine deficiency, infections, autoimmune diseases, chemical intoxications.
- Endemic. A mass phenomenon in regions with iodine deficiency and unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Medication. Caused by drugs that suppress the gland.
- Euthyroidism during pregnancy.
- Sporadic. Occurs for an unknown reason.
Treatment of euthyroidism of the thyroid gland
Many patients diagnosed with euthyroidism are not given immediate treatment. A person is given recommendations regarding lifestyle. He will need to be regularly monitored by an endocrinologist to monitor the condition of the thyroid gland. It is necessary to donate blood to check hormone levels at least once every six months. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is performed once a year.
Drug therapy
If the patient does not feel well or develops any symptoms associated with thyroid pathology, he is prescribed therapy. Drugs that can be prescribed to patients with euthyroidism:
Microiodide. This medicine is available in tablets. Thanks to their intake, it is possible to regulate metabolic processes. The main active ingredients are molecular iodine and potassium iodide.
The drug is not prescribed to pregnant women, patients with neurosis, pulmonary tuberculosis, or if the body has an allergic reaction to its components.
The cost of the tablets is about 116 rubles.
Potassium iodide. The drug is available in tablet form. It contains crystalline iodine and potassium iodide. It is widely used to treat hyperthyroidism.
It is prohibited to prescribe tablets to people with intolerance to the main active ingredients, as well as pregnant women. Self-medication is unacceptable. The dose should be selected by a doctor. The cost of the medicine is 87.5 rubles.
Antistrumin. The drug is available in tablets. It should be taken by patients with iodine deficiency. It is prescribed for prophylactic purposes, as well as for the treatment of nodular goiter. The main active ingredient is potassium iodide. Pregnant women, patients with hyperthyroidism, tuberculosis and dermatitis should not take the drug.
The cost of the tablets is 210 rubles.
Yodamarin. Tablets are prescribed for the treatment and prevention of thyroid diseases. The active ingredient is potassium iodide. Yodamarin is not used to treat patients with hyperthyroidism and dermatitis, as well as allergies to the components included in its composition.
The cost of packaging the medicine is 200 rubles.
Levothyroxine. This drug is prescribed to patients with iodine deficiency. Taking it helps prevent the development of thyroid cancer and the formation of goiter. The main active ingredient is levothyroxine sodium. It is prohibited to prescribe tablets to persons with individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
You will need to pay 108 rubles for packaging.
Surgical intervention
Euthyroidism rarely becomes a reason for surgical intervention. It may be indicated for those patients whose thyroid tissues are characterized by accelerated growth rates (provided that they cannot be slowed down by taking medications). People whose thyroid cells have begun to degenerate into cancer cannot do without surgery.
The operation is carried out using the technique of small incisions. The doctor removes the overgrown tissue. The incisions heal quickly, and the scars left behind will be almost invisible. The main difficulty that faces the surgeon is determining the exact size of the tissue to be removed. If a mistake is made, the patient will develop hypothyroidism.
In this regard, only an experienced endocrinologist-surgeon can be allowed to perform the operation.
Access to altered tissues is carried out using endoscopic equipment. This allows you to avoid high trauma. The patient's recovery is rapid. As a rule, after 3 days he is discharged from the hospital. When the tissue has completely regenerated, a barely noticeable scar will remain on the neck.
Physiotherapeutic methods
To quickly cope with the disease, the doctor may recommend physiotherapeutic treatment methods to the patient.
Ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound therapy involves applying thermal and mechanical effects to the body. It is carried out using ultrasonic waves that emanate from a special apparatus at a certain frequency.
The effect is on the neck area, which improves tissue nutrition, increases blood flow, and normalizes metabolic processes. Inflammation can be stopped faster.
Laser therapy. Treatment is carried out using a laser. Thanks to its effect on the affected area, tissues are quickly restored, blood vessels dilate, and blood flows more strongly to the thyroid gland. If the thyroid tissue has been damaged by background radiation, then the DNA will restore its structure under the influence of the laser.
Another effect of laser treatment for euthyroidism is the acceleration of metabolic processes in the body.
Magnetic laser therapy. Magnetic laser therapy involves influencing the thyroid gland using electromagnetic fields. After a course of procedures, patients note that inflammation goes away and pain disappears. Metabolic processes in tissues are activated, due to which cells are restored much faster.
Singlet-oxygen cocktails. The steam-water mixture is activated using an apparatus, due to which oxygen passes into the singlet state. Drinking such water allows you to speed up metabolic processes in the body, remove harmful compounds from it, improve the condition of cells, and normalize blood circulation.
Cocktails are indicated for use by patients who have been diagnosed with goiter. However, their positive effect extends to all body systems.
Apipunkture is a treatment with bee venom. After entering the body in small doses, it has a beneficial effect on the patient’s nervous system, increases blood flow, normalizes sleep, and eliminates headaches.
It will not be possible to completely cope with euthyroidism thanks to bee stings, but it is quite possible to stop its symptoms. In terms of its effect, this procedure is not inferior to acupuncture.
Nodule in the thyroid gland. What is this?
A change in the structure of the tissue in the thyroid gland locally or with delimitation of a small area allows us to speak about the presence of a node. It may differ in tissue density, be homogeneous or heterogeneous. A nodule is a piece of tissue that has separated from the main mass of the gland in the process of changing its activity.
The formed nodule can be felt on the neck with your own hands or detected on an ultrasound if its size is still too small. The nodes are active and involved in the functioning of the thyroid gland; when depleted, it undergoes several stages of transformation into various forms.
| Name | Explanations | Reversibility of the process |
| Isoechoic | reversible | |
| Isoechoic | Heterogeneity of the tissue, changes are insignificant. | irreversible |
| Isoechoic | Heterogeneity of the tissue, changes are very pronounced. | irreversible |
| Isoechoic | Tissue heterogeneity, hypoechoic changes are present. | irreversible |
| Hypo- or anechoic | Cysts are detected (the cavity contains fluid and tissue debris). | irreversible |
| Scarring | irreversible | |
| Scar | irreversible |
Diet and other aspects of nutrition
If it has been established that the cause of euthyroidism is hidden in iodine deficiency, then you can try to cope with the problem with the help of diet.
The menu should include products such as:
- Sea fish: hake, pollock, haddock, capelin, cod.
- Shrimps.
- Squid.
- Feijoa.
- Sea kale.
- Persimmon.
- Liver.
- Spinach.
- Eggs.
Most iodine can be obtained from fish, algae and seafood.
When a person develops obesity against the background of euthyroidism, it is necessary to adjust the diet so that it contributes to weight loss.
The following foods and drinks are excluded from the menu:
- Flour dishes.
- Fatty food.
- Smoked meats.
- Fast food.
- Alcohol.
- Confectionery and other sweets.
A person should eat food that is a source of fiber. Salads should be prepared from fresh vegetables. Be sure to supplement the diet with bran, cereals, and nuts. Among the cereals, oatmeal and buckwheat are considered especially healthy.
Forecast
By paying close attention to your health, you can avoid worsening symptoms. The patient needs treatment only when the disease develops; in other cases, outpatient observation is sufficient.
It is possible to reduce the likelihood of developing adverse effects if you exclude the influence of harmful factors, change some dietary habits and regularly visit your doctor for examination.
Regular examination by a doctor.
The patient should avoid psycho-emotional stress and not take medications on their own unless they are prescribed by the attending physician. The price of irresponsibility is deterioration in health.
One should not assume that euthyroidism is the norm; the concentration of hormones can quickly change, which will cause a number of pathological changes in the body. The appearance of euthyroidism is rather a warning that the development of thyroid diseases is possible.
Who is at risk?
The risk of developing euthyroidism increases in the following individuals:
- People whose close relatives have been diagnosed with euthyroidism.
- People with inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland.
- People who spend a lot of time in the sun.
- People exposed to frequent stress.
- People with chronic nasopharyngeal diseases.
- People living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Pregnant women whose body needs minerals.
- Patients taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs.
What does this diagnosis mean?
Euthyroidism is a condition of the thyroid gland that is quite difficult to recognize on your own. With the disease, thyroid hormones are at normal levels, and nothing bothers the person, but an ultrasound examination reveals pathological changes.
Despite the fact that euthyroidism is considered a normal condition, this problem cannot be ignored. This condition must be monitored, because the thyroid gland is a rather complex organ, the disease of which shows virtually no symptoms, and euthyroidism gradually develops into a dangerous disease.
External signs of the disease may not appear for several years, so in most cases, thyroid diseases are treated too late, when the disease becomes chronic and a goiter or cancer forms.
Euthyroidism makes itself felt only when the size of the thyroid gland increases. The proliferation of thyroid tissue can be diffuse or form a multinodular euthyroid goiter. In most cases, enlargement of the gland is of the first or second degree.
Physiotherapeutic methods
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe the patient various physiotherapeutic procedures that help to get rid of euthyroidism more quickly.
- Ultrasound therapy. This method of physiotherapy is based on the influence of high-frequency environmental vibrations. The body is exposed to thermal and mechanical effects, which makes it possible to fight many diseases. Thanks to the effect on the front surface of the neck, blood circulation improves, metabolism is restored and the thyroid gland gradually decreases in size.
- Magnetic laser therapy. This procedure is a method of local exposure using electromagnetic radiation of the low-intensity optical spectrum. This method has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Patients recover faster, the process of restoration and normalization of metabolism begins.
- Laser therapy. Laser therapy is based on the use of radiation of a certain range, the source of which is a laser. The procedure has a vasodilating effect, stimulates the processes of regeneration and restoration of DNA after damage, which can also be caused by radiation. The metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates also improves, which helps speed up the healing process with euthyroidism.
- Apipunktura. Apipunkture involves applying bee venom to specific areas of the body. In small quantities, it has a beneficial effect on the human nervous system, stimulates blood circulation, eliminates insomnia and headaches. This method does not cure euthyroidism, but it can help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of this condition.
- Singlet-oxygen cocktails. Using a special device, the steam-water mixture is activated, after which oxygen is excited and it goes into the singlet state. Treated water helps activate internal processes, restore ionic permeability of cell membranes, remove toxins, and improve blood circulation. All these properties of cocktails help patients recover faster when goiter appears.
How to cure
Euthyroidism is characterized by various symptoms and treatment methods are chosen based on the manifestations of the disease. In the case when a patient experiences minor changes in the structure of an organ, treatment with medications is usually not prescribed. Periodic visits to the attending physician and an ultrasound scan are the only things required in this situation.
Medicines are prescribed only for advanced euthyroidism. The drugs are used to eliminate all symptoms and stop tissue growth. Both hormonal and iodine-containing medications may be suitable. If drug treatment does not give positive dynamics, direct surgery is performed, the purpose of which is to remove the nodes or a certain portion of the thyroid gland.
Traditional methods also have a beneficial effect on eliminating euthyroidism. With their help, the body is saturated with iodine, which normalizes the functioning of the thyroid gland. Applicable compositions:
- tinctures from walnut partitions;
- decoctions of chicory roots;
- chokeberry mixed with sugar;
- dried kelp.