Consultation with a Reflexologist in Moscow
Consultation with a reflexologist is necessary
if traditional medicine is not effective in treating diseases of the cardiovascular, nervous and digestive systems.
An appointment with a reflexologist begins with an initial examination, identifying the patient’s complaints and the reasons for their occurrence. Then the reflexologist establishes the diagnosis and the main problem areas, develops an individual treatment program, its duration and intensity of impact on bioactive points. To stimulate them and improve the patient's condition, the reflexologist uses various treatment methods. The main ones are: acupuncture, microtherapy, phonopuncture (micromassage combined with ultrasound), apitherapy and acupressure (mechanical action does not damage the integrity of the skin). A reflexologist not only treats diseases, he generally strengthens the immune defense, restores and increases vitality. The doctor uses more than 900 biologically active points on the body. It helps patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, neurological pathologies, vascular integrity disorders, nephritis and severe headaches.
When is a reflexologist indicated?
You can undergo a course of treatment with this specialist for any disease, as well as for the purpose of prevention:
- any pain;
- allergies;
- disorders of the reproductive system;
- acute and chronic inflammation;
- Cerebral palsy and developmental delays in children;
- immune system problems;
- threats of abortion and toxicosis;
- skin diseases;
- respiratory tract infections;
- anemia;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- insomnia, increased irritability, psychosis;
- liver and gallbladder diseases;
- after polio, rehabilitation of strokes, prevention of epilepsy attacks;
- drug, alcohol or other addictions.
Reflexology Clinics and Centers
We present the best Clinics and Reflexology centers in Moscow (65)
The reason to sign up for a consultation at the department of reflexology and neurology may be diseases of the musculoskeletal system and thyroid gland, speech delay and severe headaches.
A reflexotherapist diagnoses and treats various diseases of the nervous system, and participates in the rehabilitation of patients who have suffered severe injuries, heart attacks and cerebral hemorrhages. By influencing the reflex points of the body, the doctor is able to activate local blood circulation, increase the supply of oxygen to tissues, normalize hormonal levels and relieve a person from pain. For work, the specialist uses microneedles, plate and ball applicators, medical cups, liquid nitrogen, electrical equipment, pharmacological drugs and other means that irritate active points.
What does the doctor treat?
Patients suffering from:
- headaches;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system;
- pain in the spine, joints, arms and legs;
- severe PMS;
- vascular diseases;
- stress;
- heart disease;
- disruptions in the functioning of the respiratory system;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- loss of libido and impotence.
You should make an appointment with a doctor if you have persistent pain in the limbs, allergic reactions, chronic inflammatory diseases, delayed physical development in children, diseases associated with immunodeficiency; risks of spontaneous abortion, anemia, sleep disorders, emotional overload, drug or alcohol addiction.
When to see a reflexologist
Indications for consultation with a reflexologist are:
- pain of various localizations;
- digestive problems;
- the presence of chronic diseases of various organs;
- cluster headaches and migraines;
- presence of premenstrual syndrome;
- decreased immunity;
- muscle spasms;
- infertility, cystitis, prostatitis and other pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- chronic fatigue, psycho-emotional disorders, depressive and asthenic conditions;
- functional autonomic disorders.
Since a reflexologist treats not individual diseases, but the entire body, indications for consultation also include frequent infectious diseases and the rehabilitation period after various injuries and operations.
Diagnostics
There are no specific tests prescribed by a reflexologist. As a rule, the patient is referred for consultation to this specialist by therapists, neurologists and doctors of other specialties, who have drawn up their opinion on the patient’s condition. At the appointment, the doctor can conduct his own manual diagnosis of the body, using the reflexology method of examining internal organs and systems. Almost the entire area of the human body is subject to examination, including the palms, ears, feet and face. The doctor presses his fingers on the active points and analyzes the patient’s reaction, drawing conclusions about the condition of certain organs.
Where to find reflexologists in Moscow?
The website contains all the necessary information about practicing reflexologists in Moscow and the region, indicating the address of the center where the specialist receives treatment.
In customer reviews you can find information about how old the doctor is, his medical experience and his attitude towards patients. By calling the clinic number, you can find out more detailed information about the doctor’s work experience and clarify the appointment schedule by appointment. The price of an initial visit to a reflexologist in Moscow depends on the qualifications of the specialist and the level of the medical institution and varies from 750 to 5000 rubles. Reflexology is a science that deals with the development of methodological complexes consisting of various techniques aimed at treating many diseases through targeted impact on certain areas of the body.
Reflexology is often used in therapy, pediatrics, neuropathology, dentistry, obstetrics, gynecology, narcology, psychiatry and other branches of medicine.
Tips from a reflexologist
Some techniques can be performed independently at home in front of a mirror, but you need to have knowledge about acupuncture and have a mirror. Active points can also be massaged anywhere. If you follow these simple recommendations, you can stop the course of many chronic diseases and avoid relapses.
Almost any disease can be prevented if you follow simple tips:
- you need to get proper rest;
- nutrition should be rational and balanced;
- physical activity must correspond to the level of training;
- walks should be daily;
- you should not abandon treatment for any disease;
- Self-medication has consequences.
Read also…. Qigong gymnastics for the spine and joints
What is a reflexologist?
A reflexologist is a medical worker who has graduated from a higher medical institution and received the specialty “Reflexotherapist,” which was introduced by the Ministry of Health back in 1998.
The doctor prescribes and implements acupuncture procedures, acupuncture lifting, micro-acupuncture, acupressure and other methods of acupressure on reflexogenic areas of the body. This method of treatment is very common, as it does not involve taking medications and has a small number of contraindications, which means it can be used for any age group.
A reflexologist is able to save a patient from many diseases, since during a treatment session, blood circulation is activated locally, tissue nutrition is increased, and hormonal levels are normalized.
The specialist practices in clinics, rehabilitation centers, and is engaged in scientific activities in institutes and research centers.
A reflexologist deals with the prevention, detection, treatment of various diseases of the nervous system, helps patients with rehabilitation after injuries, strokes, etc.
Reflexologist: who is he, what does he treat and what organs does he affect, when to contact him
Reflexology is a science that develops all kinds of techniques that are used to treat many diseases through acupressure on the body. All types are mastered by a reflexologist. Reflexology is used in almost all branches of medicine.
Who is it What does it treat Methods used How is it treated
Reflexologist - who is he?
A reflexologist is a specialist who provides treatment by influencing active points on the body - acupuncture. The latter are associated with the work of internal organs and systems.
It is possible that some of the techniques that a reflexologist has are similar to chiropractic techniques.
But reflexology does not require additional medications, which means it has fewer contraindications, including age.
Reflexotherapists are doctors who have graduated from medical school and have received a specialty in reflexology.
A neurologist can become a specialist such as a reflexologist, and then work in a clinic or in a scientific or research institute.
His activities are related to the prevention and rehabilitation of various conditions of the nervous and mental systems. At the same time, reflexology techniques are often used in traumatology.
The range of diseases treated by a reflexologist
The range of diseases that a reflexologist treats is huge. It’s easier to say that this is a therapist who, using acupuncture, treats diseases.
These include: cardiovascular, digestive pathologies, diseases of the genitourinary and central nervous systems, and, of course, diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
But, an acupuncturist can correct sexual and psychological disorders.
You can effectively cope with the following pathologies using reflexology:
- enuresis, encopresis;
- neurological consequences of stroke;
- complications after childbirth;
- long-term diseases of the genitourinary system;
- obesity;
- various addictions;
- neuroses, insomnia, depression;
- radiculitis and neuralgia;
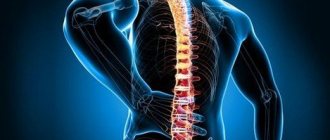
- pain in the spine and joints;
- migraine, hot flashes;
- psoriasis, neurodermatitis;
- erectile disfunction.
Read also…. Rheumatism: symptoms
Reflexology helps to avoid the use of medications and surgical interventions. It can be either an independent therapy or an additional method to the main one.
What organs does a reflexologist affect?
This question is difficult to answer, because a good reflexologist can work with any point on the body, which means that the whole body is involved in the process, and one organ cannot be singled out.
When should you see a reflexologist?
It is easy to contact a specialist such as a reflexologist with symptoms of any disease at all stages except severe ones. You can also simply use reflexology for preventive purposes.
A short list of what to see and what a reflexologist treats:
- any pain;
- symptoms of acute respiratory diseases;
- allergy symptoms;
- symptoms of infection;
- symptoms of damage to the musculoskeletal system;
- immunodeficiency states;
- pathology of the reproductive system;
- habitual miscarriage and toxicosis;
- developmental delay in the child and cerebral palsy;
- skin diseases;
- liver and gallbladder diseases;
- insomnia, irritability;
- consequences of strokes and epilepsy attacks;
- tobacco, alcohol and other addictions.
What tests should I take before visiting a reflexologist?
A visit to a specialist such as a reflexologist does not require any mandatory tests. But if you want to cure a specific disease, then it is better to take medical records and the results of studies conducted earlier. This will help the doctor get a complete picture of the disease and its course. And based on these data, decide on treatment tactics.
For example, if you are worried about the spine, take the latest x-rays, densitometry data, discharge notes after operations or visits to a neurologist or traumatologist. The more objective data you provide, the more effective the prescribed treatment will be.
Reflexology methods
Reflexologist - who found out and what he treats, but how? The answer is simple - by irritating areas on the patient's body using the following techniques.
- Acupuncture or acupuncture. With this technique, thin needles of varying lengths are inserted into points on the body. The depth of penetration and the length of the needle depend on the location of the specific point. Before the procedure, the skin is treated with an antiseptic; the needle can be inserted slowly, with scrolling, or even several needles can be placed at one point. Pain is also determined by the speed of insertion and the point itself, but more often the patient experiences a burning sensation at the site of acupuncture insertion.
- Acupressure or acupressure. Using fingers, the doctor acts on active points.
- Thermopuncture. Active points are affected by heat from special cones or cigars made of wormwood. At the same time, the patient feels some warmth.
- Phonopuncture. The effect is carried out using ultrasound. It is able to stimulate the central nervous system, so good reviews are found in the treatment of neurological diseases. The points are stimulated for several seconds for 10 minutes.
- Application reflexology. This technique uses thin plates and balls 2 mm in size, which are attached to the body for several days. Instead of plates, you can use onions, ginger and other warming herbs. This method is often used because it does not cause any pain.
- Magnetotherapy. In this case, active points are stimulated using a magnetic field.
- Electropuncture. A small electrical impulse is sent through a needle inserted into a biologically active point.
- Pharmacopuncture. Method of administering drugs under the skin of an active point.
Read also…. Treatment of a herniated disc or how to get rid of pain
In addition, the reflexologist can apply cupping massage over the point or use infrared radiation for influence. Any of these techniques can be combined with hirudotherapy. There are about 10 procedures per course.
Additionally, a reflexologist can use a computer program that will assess the patient’s condition before each visit and effectively and inexpensively monitor the progress of the procedure.
Reflexology techniques have many advantages - they can be used for any disease, any concomitant pathology. Reflexology is indicated for both children and the elderly.
What to expect at the reception?
The appointment of such a specialist as a reflexologist takes place in an equipped room. The office has a couch, storage space for sterile needles and various devices for phono- and electropuncture.
First, the doctor must find out what complaints the patient came with, assess the current condition, and identify biological active points that are responsible for the functioning of the organ involved in the pathological process.
After studying the data from medical records and any other studies, the specialist selects a technique that should be effective for the indicated pathology. If chronic diseases worsen during the course, then this should also be reported to the reflexologist.
The effectiveness of reflexology should only be assessed by a specialist, which can be obtained already at the first session.
Tips from a reflexologist
Some techniques can be performed independently at home in front of a mirror, but you need to have knowledge about acupuncture and have a mirror. Active points can also be massaged anywhere. If you follow these simple recommendations, you can stop the course of many chronic diseases and avoid relapses.
Almost any disease can be prevented if you follow simple tips:
- you need to get proper rest;
- nutrition should be rational and balanced;
- physical activity must correspond to the level of training;
- walks should be daily;
- you should not abandon treatment for any disease;
- Self-medication has consequences.
Book an appointment with a reflexologist
Reflexology techniques activate the body's reserves, improve blood circulation, and stimulate the immune system. Reflexology helps to avoid unnecessary influences and operations, and the use of medications. It has strong analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Therefore, if you have any pain or symptoms, you can make an appointment with a specialist. And if necessary, a reflexologist in Moscow can be called to your home to urgently relieve pain.
Reflexologist: who is he, what does he treat and what organs does he affect, when to contact him Link to main publication
Source: https://proinfospine.ru/refleksoterapevt-kto-eto-chto-lechit-i-na-kakie-organy-vliyaet-kogda-obraschatsya.html
What does a reflexologist do?
The specialist influences the reflex points of the body using multiple methods at his disposal. Through their implementation, they influence the central nervous system and irritate skin receptors, which ultimately has a positive effect on the functioning of organs and systems.
The basis of all methods is irritation of the natural reflex by influencing the nerve endings. The impact itself may be as follows:
- Acupuncture, which includes acupuncture, acupuncture, acupuncture and acupuncture. Proprio and exteroceptors are exposed, causing damage to the subcutaneous tissue, skin, muscles and periosteum.
Microneedling, when exteroreceptors are exposed. In this case, only the skin is damaged.
Polymicroacupuncture also affects exteroceptors, however, it is introduced not one at a time, but a bunch of microneedles.
Manopressopuncture, in which the effect on the receptors is carried out without damaging the skin. In this case, the reflexologist’s work tool is his fingers.
Applicopressopuncture, when the receptors are influenced using plates and balls.
Vacuum pressopuncture, when the receptors are influenced using medical cups.
Thermopuncture is possible with or without skin damage by heating with wormwood cigars, moxa, etc.
Thermoacupuncture involves inserting needles with a heated cone. The deep layers of skin and tissue are damaged.
Cryotherapy is a treatment using liquid nitrogen.
Electropuncture – treatment is carried out by applying electrodes of various shapes to the body.
Electroacupuncture, when electric current is supplied to the points of influence through special needles.
Pharmacoacupuncture, when medications are injected into points of influence using needles.
In addition, in the practice of a reflexologist there are such techniques as: phonopuncture (exposure to ultrasound), laser puncture (exposure to coherent laser beams), heliopuncture (exposure to ultraviolet, infrared and other radiation) and magnetopuncture (exposure using electronic fields).
Specifics of the work of a reflexologist and methods of treatment
Reflexologists have several methods of influencing human biological points:
- acupuncture;
- acupressure - mechanical effect on the skin without damaging it;
- phonopuncture, ultrasound and micromassage;
- apitherapy;
- microtherapy.
To date, more than 900 acupuncture points have been opened, corresponding to the organs and systems of the human body. By influencing these points, the doctor helps improve vital energy, which helps strengthen the body. Reflexology methods have found their application in the treatment of neurological diseases, arthritis, vascular disorders, eye diseases, migraines, nephritis and diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
This is exactly what a neurologist-reflexologist does. What cures besides this?
What tests do you need to take when visiting a reflexologist?
There are no mandatory tests that must be taken before visiting a specialist. However, if you have any disease, you should bring the existing examination results and specialist opinions. Based on them, it will be possible to create the most effective treatment plan.
neurologist. reflexologist.
Candidate of Medical Sciences, neurologist, doctor of the highest category, constantly publishes in scientific journals, is the author of methodological recommendations for doctors. Received additional education in the areas of “hirudotherapy”, “neurotraumatology”, “emergency cardiology in traumatology”. More than twenty years of medical activity have formed the idea of the need for a rational combination of pharmacological correction and non-drug forms of therapy, based on their individual and justified need for the patient. Education: internship in neurology; Novosibirsk State Medical University (1994). Specialization: Expert assessments in the healthcare system. Medical labor examination, NSMA, certificate (2001). Author of 10 publications and 1 methodological recommendation for doctors. Winner of the Presidential Grant and Laureate of Government Awards in the field of medicine. Candidate's dissertation Clinical and neuroimaging features of discirculatory encephalopathy among liquidators of the consequences of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident (2003). Medical experience – 17 years. Education .
“The doctor is a professional, I can’t say anything bad. There is a result of the treatment, but I was counting on a much smaller amount. The complaints are rather about the clinic and the fact that no one warned in advance about the cost of additional services, neither the doctor nor the clinic. So, already at the checkout, surprises awaited me in the form of additional charges. For example, a consultation of 10-15 minutes, when the doctor examines it, is 2500, his procedure (manual therapy) is another 2500, x-rays, of course, are also paid separately. Further, during the repeat procedure, they also calculated separately the electric massage - 2500 and the manual therapy itself - 2500. For 3 trips to the clinic, I left 15,000 + medications. It is necessary to warn clients immediately about all additional costs. »
District: Dynamo, Savelovskaya.
reflexology: 3500 rub. / conv.
neurology: 3500 rub.
A specialist who knows how to heal the body using biologically active points. One of these methods is acupuncture, which affects a system, a complex of organs, and not just any individual organ, so acupuncture treatment should only be carried out by a specially trained doctor - otherwise the procedure can be both ineffective and unfavorable.
It is advisable that the reflexologist have a specialization in neurology.
What diseases does a reflexologist treat?
Allergic diseases: - allergic rhinitis;
- allergies; - urticaria; - Quincke's edema; - hay fever. Pain syndromes - wandering pain; - pain in the thigh; - Pain in the eyes; - a sore throat; - chest pain; - stomach ache; - abdominal pain; - pain in the anus; - tooth pain; - pain in the hand; - pain in the collarbone; - pain in the sacrum and coccyx; - pain in the face; - pain in the shoulder blade; - pain in the pelvis; - pain in the mammary gland; - pain in the bladder; - pain in the external genitalia; - leg pain; - pain in the groin area; - pain in the liver; - pain in the esophagus; - pain in the spine; - pain in the penis; - lower back pain; - pain in the perineum; - pain during childbirth; - pain in the hand; - heartache; - backache; - joint pain; - pain in the pelvis; - pain in the jaw; - pain in the neck; - pain in the cheek; - pain in the urethra; - earache; - pain in the buttock; - pain in the tongue; - pain in the testicles; - phantom pain.
Gynecological pathology - adnexitis; - female infertility; - vaginitis; - vulvitis - dysmenorrhea; - hypermenorrhea; - vaginal itching; — menopausal syndrome; - prolapse of the uterus.
Infectious diseases - influenza; - acute respiratory infections; - mumps; - fever syndrome.
Diseases of children - cerebral palsy; - delayed speech development in children; — perinatal pathology of the nervous system; - rickets.
Emergency conditions - fainting; - heatstroke; - shock.
Pathology of pregnancy and childbirth - hypogalactia; - delayed passage of the placenta; - violation of cervical dilatation; - habitual abortion; - weakness of labor; - spastic conditions of the uterus; - toxicosis of pregnant women.
Pathology of the autonomic nervous system - Raynaud's disease (syndrome); — autonomic polyneuropathy; - vegetative-vascular dystonia; - ganglioneuralgia of the pterygopalatine ganglion; - ganglioneuralgia of the ciliary ganglion; - ganglioneuralgia of the ear node; - damage to the upper cervical node; - damage to the stellate ganglion; - hypothalamic syndrome; — meteopathic reactions; - sympathetic truncite; — solarite; - erythromelalgia.
Eye pathology
Blepharitis; - hemeralopia; - hypermetropia; - glaucoma; - dacryocystitis; - itching of the conjunctiva; - iridocyclitis; - cataract; - keratitis; - conjunctivitis; - squint; - optic neuropathy; - myopia; — retinal pigmentary degeneration; - retinopathy; - lacrimation; - choroiditis.
Pathology of teeth and oral cavity - pathology of the temporomandibular joint; - gingivitis; - glossodynia; - periodontal disease.
Pathology of the immune system - immunodeficiency states.
Skin pathology - acne (acne vulgaris); - alopecia areata; - total alopecia; - warts; - vitiligo; - dermatitis; - itching of the genitals; - itching of the perineum; - widespread itching; - carbuncle; - lichen planus; - red (rosacea) acne; - herpes zoster; - psoriasis; - eczema; - furunculosis.
Pathology of blood and hematopoiesis - anemia; - thrombocytopenia.
Pathology of male genital organs - azospermia; - aspermia; - male infertility; - orchitis; - pathological emissions; - prostatitis; - epididymitis.
Pathology of the musculoskeletal system - deforming arthrosis; - joint contractures; - osteocondritis of the spine; - periarthrosis; - gout; - polyarthropathy; — post-traumatic arthropathy; - heel spur; - scoliosis; - epicondylosis of the humerus.
Pathology of the respiratory system - bronchial asthma; - bronchitis; - cough; - pleurisy; - pneumonia; - tracheitis; - pulmonary emphysema.
Pathology of the peripheral nervous system - secondary contracture of facial muscles; - vertebrogenic lumbodynia; — vertebrogenic lumboischialgia; - intercostal neuralgia; - neuralgia of the occipital nerve; - trigeminal neuralgia; - neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve; - neuropathy of the femoral nerve; - neuropathy of the tibial nerve; - neuropathy of the oculomotor nerve; - neuropathy of the facial nerve; - radial nerve neuropathy; - neuropathy of the peroneal nerve; - neuropathy of the sciatic nerve; - brachial plexopathy; - lumbosacral plexopathy; - cervical plexopathy; - polyneuropathy; - polyradiculoneuropathy; — vertebrogenic thoracalgia; - vertebrogenic cervicalgia; — vertebrogenic cervicobrachialgia; — vertebrogenic cervicocranialgia.
Pathology of the digestive tract - diarrhea; - dyspepsia; - dysphagia; - hypersalivation; - hyposalivation; - constipation; - heartburn; - hiccups; - flatulence; - belching; - vomit; - nausea.
Diseases of the esophagus - esophageal dyskinesia; - spasm of the esophagus; - stenosis of the esophagus.
Stomach diseases - gastric atony; - gastroptosis; - hyperchlorhydria; - hypochlorhydria; - chronic gastritis; - chronic gastroenteritis; - stomach ulcer.
Diseases of the small intestine - duodenitis; - intestinal colic; - impaired intestinal motility; — paresis of the small intestine; - intestinal spasm; — chronic enteritis; — chronic enterocolitis; — chronic appendicitis; - duodenal ulcer.
Diseases of the large intestine - colitis; - diseases of the rectum; - rectal prolapse; - haemorrhoids; - itching of the anus; - anal fissures.
Liver diseases - hepatitis; - hepatic colic.
Diseases of the gallbladder - biliary dyskinesia; - cholelithiasis.
Diseases of the pancreas - chronic pancreatitis.
Pathology of the kidneys and urinary tract - nephritis; - pyelonephritis; - renal colic; - urethritis; - cystitis.
Mental pathology - psychogenic anorexia; — asthenic syndrome; - insomnia; - depression; - hysteria; - hypochondria; — logoneurosis; - manic state; - neurasthenia; - psychasthenia; - writer's cramp; — reactive states; - drowsiness; - anxiety; - neurotic tics; - emotional sweating; - excessive dreams; - phobias; - emotional instability; - enuresis.
Pathology of the sexual sphere - anorgasmia; - vaginismus; — involutional decrease in sexual function; - premature ejaculation; - priapism; — paracentral lobule syndrome; - decreased libido; - decreased erection; - frigidity.
Pathology of the cardiovascular system - functional arrhythmia; - arterial hypertension; - arterial hypotension; - vascular atherosclerosis; - cardiopsychoneurosis; — myocardial dystrophy; - paroxysmal tachycardia; - angina pectoris; - varicose veins of the lower extremities; - obliterating endarteritis; - phlebitis and thrombophlebitis.
Pathology of connective tissue - ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis); - rheumatoid arthritis.
Pathology of the ear, nose and throat - anosmia; - Meniere's disease (syndrome); - vestibulopathy; - sinusitis; - deaf-mute; - laryngitis; - laryngospasm; — neuropathy of the auditory nerve; - nose bleed; - ozena; - otitis media; - nasal polyps; - rhinitis; - rhinorrhea; - tympanitis; - tonsillitis; - pharyngitis; - frontal sinusitis; - nasal boil; - noise in ears.
Pathology of the central nervous system - amnesia; - aphasia; - blepharospasm; — hemiparesis/hemiplegia; - dysarthria; - trembling; - dizziness; — closed craniocerebral injury; - facial hemi- and paraspasm; - minor chorea; - meningism; - movement disorders of the leg; - motor disorders of the hand; - lower spastic paraparesis; - paresthesia; - parkinsonism; - polio; - consequences of cerebral stroke; — consequences of a spinal stroke; - multiple sclerosis; - spastic torticollis; - sensory disorders of the leg; - sensory disorders of the hand; - spinal cord injury; - cerebrovascular insufficiency; - epilepsy.
Pathology of the endocrine system - hyperthyroidism; - hypothyroidism; - goiter; - diabetes insipidus; - obesity; - diabetes.
Substance abuse - alcoholism; - drug addiction; - smoking.