Salpingoophoritis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. It does not occur on its own, but as a result of the influence of provoking factors.
How does this happen? What symptoms indicate the presence of this disease? How is diagnosis carried out? Can it be cured and what is needed for this? This and much more should now be discussed.
Pathogenesis
Before moving on to reviewing information about the symptoms and treatment of salpingoophoritis, it is necessary to discuss why it appears. There may be several reasons.
The first is infection by parasites. First, any pathogenic microorganism enters the female body - mycobacterium tuberculosis, gonococcus, E. coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus, etc. Then, if the woman ignored the symptoms and did not consider it appropriate to begin treatment, these parasites begin to develop and multiply. As a result, pathogenic microflora spreads throughout the body. Bacteria penetrate into organs and tissues. And they can, if the immune system and internal defenses are weakened, get into the fallopian tubes, and then into the ovaries.
Also, the appendages often become inflamed due to overwork, weakened immunity, and swimming in cold water.
Another pathology often occurs against the background of an infectious disease. The pathogen can enter the pelvic area even from the primary focus - purulent plugs in the tonsils or maxillary sinus.
A girl can catch the infection as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse. Especially if it occurred during menstruation, after an abortion or other intrauterine intervention.
By the way, the appendages can also become inflamed as a result of surgical termination of pregnancy. If it was done carelessly or during this period the patient’s immunity was weakened.
If we talk about provoking factors, these include stress, hypothermia, lack of a balanced diet and chronic fatigue.
Causes
Among the main reasons that cause bilateral salpingoophoritis are:
- hypothermia (caused, for example, by wearing thin tights in cold weather);
- casual sex. Sexual contact during menstruation can also lead to the development of pathology;
- various stresses.
As a rule, the pathogen penetrates the tissues of the genital organs through:
- lymph (together with lymph flow);
- blood (hematogenously);
- ascending route (from the vagina through the cervical canal, and then into the uterine cavity and tubes);
- in a descending manner (through the abdominal cavity from the sigmoid or cecum).
After pathogenic microorganisms enter the mucous membrane, inflammation begins there, which spreads to the muscle structures. After some time, the abdominal cavity, the surface of the ovaries and other nearby tissues are involved in the inflammatory process. After ovulation occurs, infectious bacteria enter the corpus luteum and continue to develop in the ovaries. As a result, the affected areas of the tubes and ovaries merge into one tissue.
Acute stage
First, it is worth briefly characterizing the clinical picture, and then moving on to a consideration of the principles of treatment of salpingoophoritis.
So, the acute stage occurs with characteristic symptoms:
- Intense pain in the lower abdomen that radiates to the sacrum and anus.
- Unpleasant, pronounced sensations on the side of inflammation.
- Discharge of a mucous or purulent nature.
- Fever.
- Fatigue, chills, weakness.
- Bloating and urinary disorders.
- Irritation of the peritoneum (symptoms of muscle protection), which are detected upon palpation.
- Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocytosis with a shift to the left side (detected by studying the blood taken for a test).
As a rule, bilateral salpingoophoritis is detected. Treatment cannot be delayed. In addition, this disease is usually combined with inflammation of the uterus.
The disease is often accompanied by algomenorrhea (painful menstruation) and menorrhagia (long and heavy periods).
It is also important to note that as inflammation increases, a purulent saccular tumor may form in the appendage area. This is called a tubo-ovarian abscess. With this disease, the fallopian tube and ovaries simply melt. As a result, one cavity is formed, filled with purulent contents.
Diagnosis of salpingoophoritis
Ultrasound is the most informative examination for salpingoophoritis
A doctor can diagnose salpingoophoritis only after:
- cytological analysis and bacterial culture will be carried out in order to isolate the pathogen
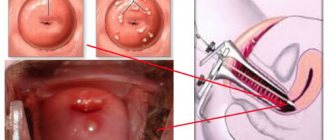
— previous medical history and possible past hormonal imbalances, missed pregnancies, abortion, and surgical interventions on the genitourinary system are taken into account. - an ultrasound vaginal examination was performed, which will reveal the stage of the disease, probable foci with pus, possible deposition of the disease on all appendages - laparoscopy was performed in acute stages of the disease and possible serious underlying diseases and partial infertility in chronic processes
Treatment of acute salpingoophoritis
If a woman is diagnosed with severe inflammation of the appendages, she will be immediately admitted to the hospital. In severe cases of inflammation of the appendages, treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting.
Doctors prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of intravenous or intramuscular injections. The woman is also given medications that are aimed at inhibiting the growth of anaerobes - parasites that receive energy in conditions where there is no oxygen.
It will also be necessary to relieve the symptoms of general intoxication. To do this, the patient is given intravenous drips, through which vitamins and solutions are introduced into the blood.
Taking immunomodulators is also required. If a woman is sick, then her body is weakened. And it is necessary to support the immune system through drugs that contain substances that can strengthen it.
As mentioned earlier, with this disease, the development of peritonitis or the formation of purulent sacs in the appendage area cannot be ruled out. This happens only in extreme, advanced cases, but if this happens, then surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Now they are doing laparoscopic operations. A 2-3 centimeter long incision is made on the woman's anterior abdominal wall, and then all the necessary manipulations are performed.
If we talk about first aid, then only applying cold to the suprapubic area will help. The use of a heating pad is contraindicated.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of chronic salpingoophoritis, as well as its other varieties, is carried out using several methods. This diagnosis is not a death sentence. As a rule, a woman who is diagnosed with acute or chronic salpingoophoritis will be sent to hospital.
The following methods are now used to treat the disease:
- non-drug treatment. It is carried out if the patient has chronic salpingoophoritis. In this case, UHF therapy, electrophoresis or magnetic therapy are used. Also, as physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, the doctor may prescribe diadynamic currents or treatment in a sanatorium to the patient;
- drug treatment. Prescribed for acute illness. The main group of drugs used to destroy the pathogen are antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs are used. There are several treatment regimens: the first involves the use of cefotaxime, ceftriaxone and other antibiotics. The second regimen involves taking lincosamides or fluoroquinolones. Quite often, to prevent the spread of chlamydial disease, the patient is also prescribed a macrolide or doxycycline;
- surgical intervention. Such treatment of salpingoophoritis is used if conservative therapy does not have the desired effect on the patient’s health. The laparoscopy method is used. In this case, the patient is injected into the peritoneal area with a solution of antibiotics.
Laparoscopy
Inpatient treatment usually takes from one week to 10 days. Afterwards, when the patient’s health improves and the inflammatory process is eliminated, the woman is discharged.
Among the folk remedies, the following are distinguished:
- taking potato juice on an empty stomach. To get potato juice, you need to grate several potatoes on a fine grater, squeeze, and mix the resulting liquid thoroughly before drinking (the starch contained there can settle to the bottom too quickly). To diversify the taste of this folk remedy, it is recommended to add carrot juice or any other juice. Taking this folk medicine helps eliminate the symptoms of the disease;
- Mix elecampane proportionally with meadowsweet and kermek. Add marin root to the resulting product, and then pink radiola. Infuse for a week in a 50-degree alcohol solution, and then drink the resulting tincture on an empty stomach in the morning and evening;
- meadow cornflower mixed with clematis grass, as well as tenacious. Pour the mixture with one liter of hot water and leave overnight, after boiling for 5 minutes. It is recommended to drink this folk remedy before meals 3 or 4 times a day, 100 grams each time.
It is worth remembering that folk remedies can only alleviate symptoms, and their use must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Otherwise, uncontrolled use of any prescriptions can lead to complications. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. It is necessary to contact a qualified specialist to carry out a diagnosis, identify the cause of the development of the pathology, and begin treating the disease.
Subacute stage
When discussing the symptoms and treatment of salpingoophoritis, one cannot help but touch upon this issue. The subacute stage is characterized by the development of inflammation only in the ovaries or in the fallopian tubes. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Heat.
- Bloating in the lower abdomen.
- General weakness.
- Chills and trembling.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by sexual intercourse.
- Colitis.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
- Discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- Burning and itching of the genitals. The sensations are similar to those a woman experiences with thrush.
The problem is that the subacute form resembles a female cold in many of its symptoms. And they pass quite quickly.
If a girl does not go to the doctor, but simply starts choosing her own medications, and even for a cold, then the disease will develop into chronic salpingo-oophoritis. And the treatment of this form is extremely difficult.
Causes of salpingoophoritis
The causes of salpingoophoritis can be different and it is important to identify them in time
You need to understand that the causes of salpingoophoritis can be different. Most often, these are various simple cocci that have reached the reproductive system from the genitals. They actively colonize and begin to trigger an immune response.
In addition, banal hypothermia, swimming in ponds, sitting on damp ground can also play a cruel joke and deprive a woman of the right to be a mother if there is a clinical picture of inflammation.
The causative agent of tuberculosis with blood also easily reaches the tubes, ovaries, and then, in addition to the lungs, the entire reproductive system becomes a target for tuberculosis. Unfortunately, it is difficult to avoid this even at the initial stage of the underlying disease. Well, what about without STDs? So in 80% of cases they become the first step to salpingo-oophoritis with a high risk of developing into sepsis or another more dangerous disease. Abortion and hormonal imbalances very often leave a mark on the tubes. They are considered more the cause of tubal adhesions and PCOS.
Stressful situations, frequent changes of sexual partners and failure to comply with the usual rules for women in terms of hygiene are again a danger of developing salpingoophoritis of varying degrees.
With a little delay, a woman can get a real bouquet of gynecological diseases, which increases its impact on her lifestyle and changes her plans for the future very seriously regarding healthy offspring.
Therapy for the subacute stage
If the doctor prescribes treatment in a timely manner (and this depends on the patient’s timely appointment for diagnosis), then it will be possible to prevent the formation of scar changes in the uterine appendages, which is fraught with persistent infertility.
The doctor prescribes certain medications for the treatment of salpingoophoritis. Their list is quite wide:
- Antiviral suppositories, injections and tablets. The most effective drugs are Clindacin, Acyclovir, Betadine and Terzhinan.
- Analgesics. They help relieve pain. The most common drugs are Neolgin, No-Shpa and Ibuprofen.
- Desensitizing agents. They relieve allergic reactions. Usually prescribed are Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Diprazin and Diazolin.
- Immunomodulators. The importance of taking them has already been discussed earlier. One of the best drugs in this category is Cycloferon.
- Antibiotics. Which one a woman needs depends on the pathogen that provoked the disease. They may prescribe Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone, or they may prescribe macrolides and Doxycycline.
- Probiotics. Necessary for normalizing the microflora of the vagina and intestines. Profibor, Bifiform and Linex are widely used.
- Hormonal drugs. Without them, it is difficult to normalize the menstrual cycle. There are many of them - “Regulon”, “Yarina”, “Lindinet”, “Jess”, “Klaira”, etc. The drug is prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist after examining the patient and studying her tests.
As you can see, the treatment of salpingoophoritis, in which the fallopian tubes are not yet affected, seems simpler, in contrast to the previous case.
Development mechanism
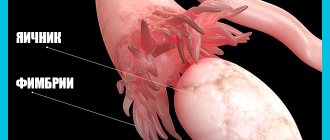
The uterine appendages are the fallopian tubes and the ovaries located in close proximity to them. The former are essentially oviducts: their function is to deliver the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity for further development of the embryo. The inner lining of the tubes is made of villous epithelium, which, by beating its cilia, directs the embryo in the desired direction. Additionally, its movement is facilitated by small worm-like contractions of the muscular lining of the tubes - their peristalsis.
MORE ABOUT: Fish oil mastopathy – Mastopathy
structure of female reproductive organs
Eggs mature in follicles (vesicles with liquid), which form in the ovarian tissue. One of them continuously increases in size during the cycle, and at the moment of ovulation it bursts and releases the female reproductive cell into the abdominal cavity. It ends up on the long outgrowths of the fallopian tube - the fimbria - and begins its journey to the uterus.
Normally, the environment of the uterus, fallopian tubes and abdominal cavity is sterile and reliably protected from the penetration of microorganisms. Any disturbance in the functioning of local or general immunity, invasive interventions, childbirth, abortion can lead to the penetration of pathogenic or opportunistic microflora, which inhabit the vagina and vulva.
The waste products of pathogenic microflora have a detrimental effect on the membranes of the uterine appendages. First, the inflammatory reaction affects the mucous layer, then spreads to the muscular and serous layers. The wall of the fallopian tube swells, its lumen narrows or it becomes completely obstructed.
In some cases, inflammatory exudate accumulates in the tube - hydrosalpinx or pus - pyosalpinx. Without treatment, the mass may rupture and become complicated by peritonitis. Another outcome is also possible: hydro- or pyosalpinx acquires a dense fibrous membrane and maintains the inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity for a long time.
inflammatory process in the uterine appendages - adnexitis (salpingoophoritis)
Together with inflammation in the fallopian tube, pathological changes occur in the ovarian tissue. Initially, the pathogen penetrates into its outer shell, and during ovulation it penetrates through it deep into the ovarian tissue. Inflammation of the ovary leads to disruption of its hormone-producing function and to the death of eggs. In its thickness, a cavity is often formed filled with pus (abscess) or inflammatory exudate (cyst).
Joint inflammation in the uterine appendages leads to disruption of the woman’s hormonal levels. Partial or complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes makes it impossible to conceive a child and the passage of the embryo into the uterine cavity - infertility or ectopic pregnancy develops.
Chronic illness
This form is diagnosed if a woman has been struggling with the disease for several months. And before we talk about the treatment of chronic salpingoophoritis, we need to understand how the disease enters this stage.
So, this is a polyetiological process of a pathological nature. First, the tissues of the internal organs are damaged, then inflammation occurs. And all this is due to the activity of parasites and other pathogenic microorganisms.
Depending on what exactly the pathogen is, exactly how it entered the body, and also by what mechanism the disease developed, nonspecific and specific infections are distinguished.
It should also be noted that the disease can become chronic due to improper or untimely treatment of bilateral salpingoophoritis.
If a woman suffers from this particular disease, she experiences remissions. Her condition improves, and the inflammatory reaction ceases to be pronounced. All signs may disappear altogether. But then an exacerbation of salpingoophoritis is possible. Treatment in this case is necessary immediately. Because frequent “outbreaks” of the disease lead to the following consequences:
- Development of endometritis. The inner mucous layer of the uterine wall becomes inflamed.
- The pelvic tissue becomes inflamed.
- Development of a purulent process.
- Formation of a limited cavity filled with pus (abscess).
- Phlegmon. This is the name for purulent acute diffuse inflammation that has no boundaries.
- Changes in hormonal levels.
- Formation of adhesions. If the disease lasts for a long time, the damaged cells of the ovaries or fallopian tubes are replaced. Because of them, the lumen narrows. This either leads to infertility or increases the risk of a future ectopic pregnancy.
In general, chronic salpingoophoritis, the treatment of which will now be discussed, is the most complex form of the disease in question, since it entails functional and hormonal changes in the female body.
Complications
Basically, the patient consults a doctor during an exacerbation of chronic salpingoophoritis, which is already an overdue action. Not every woman can feel symptoms at the very beginning of the disease, which is why this disease often has complications. The main ones:
- Endometritis. Inflammation from the fallopian tubes or ovaries can easily spread to the uterus itself. In this case, you have to treat two diseases at once.
- Abscess. An abscess is a cavity that fills with pus. This complication is very rare, but it still exists.
- Formation of adhesions. This complication is considered very serious. It involves replacing damaged cells with connective tissue. This causes the fallopian tubes to stick together. Very often leads to complete infertility and increases the risk of ectopic.
- Difficult pregnancy. Even if a woman was able to cure chronic salpingoophoritis, it will be much more difficult for her to bear a child than for an ordinary healthy woman. There may be threats of miscarriage or even spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
In order to avoid such serious complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor promptly at the first symptoms.
Fighting chronic inflammation
It is also necessary to talk about it, since we are talking about the symptoms and treatment of salpingoophoritis in women. Of course, in this case, as in all others, all recommendations and therapeutic measures are established by the attending physician.
Treatment of salpingoophoritis with antibiotics and drugs of other categories is not universal. All measures vary depending on how active the inflammatory process is.
The doctor also separately describes the treatment of relapse and the actions that must be performed during remission. All recommendations must be followed. This will help avoid aggravation, which brings many problems.
If we describe the recommendations in general, the treatment regimen looks something like this:
- A regimen that involves limiting physical activity is required.
- It is necessary to take drugs that are effective against the infectious agent.
- It is necessary to take anti-inflammatory drugs.
- It is mandatory to take antispasmodics, which will help reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the walls of the fallopian tubes.
- It is necessary to take antihistamines that reduce the severity of allergic reactions that are provoked by the infectious process.
- Carrying out detoxification.
After treatment of salpingoophoritis, the severity of the inflammatory reaction decreases significantly. This is what indicates remission.
At this stage, measures should be taken to destroy the infectious agent, if possible. Also, the woman will have to actively restore her immunity, and also, if the doctor recommends, undergo a course of any of the procedures listed below.
Treatment
Depending on the form and severity of the process, various treatment tactics for salpingoophoritis are chosen. Acute and subacute adnexitis, as well as exacerbations of the chronic form, require treatment in a hospital setting.
The first step is antibiotic therapy. Treatment of adnexitis of a specific type (tuberculosis, gonorrhea, diphtheria) is carried out according to generally accepted protocols for the treatment of these infections. To eliminate the symptoms of salpingoophoritis caused by nonspecific flora, antibiotics are selected taking into account the most likely pathogens.
To eliminate the symptoms of salpingoophoritis caused by nonspecific flora, antibiotics are selected taking into account the most likely pathogens.
The main combinations of drugs for the treatment of acute adnexitis:
- III generation cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime) Metronidazole.
- II generation cephalosporins (Cefuroxime) tetracyclines (Tetracycline, Doxycycline).
- Lincosamides (Clindamycin) Monobactams (Aztreonam).
- Fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin) Metronidazole.
Treatment of salpingoophoritis with antibiotics is a long process, taking at least 7-10 days. This therapy negatively affects the microflora of the intestines and vagina. To prevent dysbiosis, eubiotics (Bifidumbacterin, Bifikol, Acylact) are prescribed simultaneously with antibiotic treatment.
Symptoms of intoxication complicate adnexitis.
To eliminate them, detoxification treatment is required. Solutions of sodium chloride and glucose, protein and plasma replacement drugs are administered intravenously. At the same time, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Nurofen) are prescribed.
Treatment of chronic adnexitis beyond relapse is impossible without the use of physiotherapy. Magnetic therapy, ultrasound treatment, and laser irradiation are used on the appendage area. Carrying out procedures is also possible when the inflammatory process subsides in acute and subacute forms of salpingoophoritis.
To restore ovarian function, hormonal treatment of chronic adnexitis is prescribed. Combined estrogen-gestagen drugs are used contraceptively for at least 6 months.
Other treatments
They also need to be talked about. Treatment of salpingoophoritis can include a lot of different procedures aimed at eliminating the problem. In addition to the above, the following methods are practiced:
- Puncture of the vaginal vaults. It is used to introduce antibacterial drugs directly into the pelvic organs.
- Ultra-high frequency inductothermy. This involves influencing the appendages using a high-frequency electromagnetic field. In simple terms, the technique is based on thermal effects.
- Magnetotherapy. Method from the field of alternative medicine.
- Treatment of salpingoophoritis with electric shock. It has a neurostimulating, vasodilating and plastic effect.
- Treatment in a sanatorium.
- Plasmapheresis. A certain amount of blood is taken from the patient, cleared of infections, and then returned to the body.
- Gynecological massage of the uterus. It is aimed at restoring ovarian function, as well as eliminating defects in the appendages. It is carried out manually by a doctor.
In the vast majority of cases, it is possible to cope with the disease using any of the methods listed. But this is only if the patient did not ignore the ailment and went for diagnostics to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment in this case will be timely and effective.
However, in difficult, advanced situations one has to resort to extreme measures. Namely, to the removal of appendages.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out on the basis of a study of the woman’s medical history, as well as the disease itself. A specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis of “acute salpingoophoritis” if he finds in the medical history information about previous abortions, difficult births, and the use of an IUD to prevent pregnancy. It is also important to take into account the presence of symptoms characteristic of bilateral salpingoophoritis - pain in the lower abdomen, increased body temperature, etc.
Also, during the diagnosis, research is carried out in the laboratory. These include a blood test that can detect an increased number of white blood cells (this is an indicator of inflammation in the body). The doctor also takes a swab from the vagina and cervical canal. Such an analysis makes it possible to identify the pathogen, as well as determine which medications it is sensitive to.
During the diagnosis, hysterosalpingography is performed. This technique is very informative. A special contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity, after which an X-ray is taken.
Such a disease may require additional consultation of the patient with specialists other than the gynecologist (surgeon and urologist).
Traditional methods
If you believe the reviews, treating salpingoophoritis with self-prepared remedies is also effective. Doctors tend to be skeptical about this claim, but as a preventative measure, some “medicines” will be helpful. Here are some recipes:
- Mix dry linden and chamomile in equal proportions. Pour 50 grams of the resulting mixture into a saucepan and add 1 liter of water. Place the container on the fire and boil. Then remove, cool and strain. Use the resulting decoction for sitz baths or douching for 14 days.
- Mix in equal quantities the fruits of rowan, strawberry and hawthorn, string, nettle, mint, birch leaves and immortelle flowers. Pour boiling water (400 ml) over 20 grams of the mixture. Place in a cool, dark place to infuse. After 12 hours you can use it. You need to drink 70 ml three times a day for 10-14 days.
- You can try treating salpingoophoritis with folk remedies that have an antiseptic and desensitizing effect. It is necessary to mix alder fruits, licorice, elecampane, aralia rhizome, immortelle, horsetail, string and rose hips in equal parts. Grind everything. Pour 30 grams of the mixture with boiling water (0.5 l). Place in a dry and cool place for 8 hours. Then strain. Drink in 5 doses per day, always after meals. The course is at least ten days.
- The rhizomes of the swamp iris must be crushed. Pour boiling water (200 ml) over a few tablespoons of the plant. Leave in a dry place for 3 hours. Then strain. Either drink 3 spoons four times a day, or use for douching. The course is two weeks.
- Pour 15 grams of crushed echinacea with medical alcohol (500 ml). Close the container and let it brew in a cool, dark room. Let it brew for 14 days, shake periodically. Then add a little boiled water to dilute the strength. Take 5 drops 6 times a day for ten days.
Traditional treatment for salpingoophoritis is popular. There are dozens more recipes. But before you start taking any homemade medicine, you should consult your doctor. Otherwise, you can harm yourself.
Infusions and decoctions
In the morning before meals, squeeze the juice from two unpeeled potato tubers and drink. Carry out treatment every day until cure.
Mix St. John's wort, nettle and yarrow, a tablespoon each, and thyme, coltsfoot, marshmallow root, 2 tablespoons each. Pour 3 tbsp of boiling water over a liter. l. mixture and leave for a couple of hours. Morning, afternoon and evening, take 100 ml of infusion for 2 months.
2 tbsp. l. Grind and mix strawberry and birch leaves, corn silks, string and yarrow. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 1.5 liters of boiling water and leave to infuse for 5-6 days. Drink 100 ml 3 times a day for 30 days.
Take a couple of spoons from a mixture of equal parts of calendula, sweet clover and chamomile flowers, centaury and coltsfoot. Pour two glasses of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Drink 50 ml 5-6 times a day for 30 days. Avoid sexual activity for the duration of treatment. If nausea occurs, reduce the dose.
According to Art. l. mix thyme, St. John's wort, ginger, valerian roots, calamus, licorice. Add a couple of spoons of knotweed, birch leaves and oregano and three spoons of wormwood. 2 tbsp. l. Boil the mixture in 3 glasses of water for 20 minutes and leave for 2 hours. Drink 3-4 sips several times a day from 1 to 8 months, excluding menstruation.
Make a collection of rowan berries, mint, shepherd's purse, tansy and licorice root, a couple of spoons each. Add a mixture of 4 tablespoons of rosehip, 3 tablespoons of nettle and a spoonful of corn silk and calendula. Boil a couple of tablespoons of the mixture in 2 glasses of water for about 30 minutes, covering with a lid.
Pour a teaspoon of claspberry into a glass of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for 20 minutes. Drink a couple of large spoons 4-5 times a day, adding a little honey for taste. For the best effect, combine with baths of claspberry infusion.
Prevention
Let’s talk about this one last time. A girl will never encounter salpingoophoritis if she:
- Remember that even one unprotected sexual act can trigger the transmission of infection.
- Use contraception - condoms, suppositories and tablets for vaginal use. We must remember that the decency and fidelity of a single partner does not always exclude the presence of an STD.
- Regularly visit the doctor with your partner for examination. You can do this together even before the first intimacy occurs.
- Avoid anal-genital sexual intercourse without prior hygiene procedures.
- Maintain a balanced diet that includes all the microelements and vitamins necessary for the female body. A nutritionist can help in its preparation.
And most importantly, if you have 2-3 signs of the disease, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor. If you want to avoid the above consequences and expensive treatment that does not always go without complications, you must not ignore the symptoms.
Reasons for appearance
Modern medicine claims that salpingo-ophritis is caused solely by infection in the pelvic organs.
So, the following causes of adnexitis are distinguished:
- Sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, ureplasma, mycoplasma, gonorrhea, gonococci, streptococci. Infection with tuberculosis bacteria and various E. coli are also possible. In some cases, infection may also occur through household means, for example, in saunas, swimming pools, locker rooms, and other common areas, but such cases are rare. If infection occurs through sexual contact, treatment should be carried out simultaneously for both partners in order to prevent endless transmission of the infection to each other.
- Genital herpes. Causes the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the ovaries. The patient may not even realize that she is a carrier, since with strong immunity, genital herpes exists in the body in a latent form, does not manifest itself in any way and does not bother. However, as soon as the immune system fails, genital herpes begins to progress and, in addition to its direct symptoms (itching, blisters on the external genital organs), causes adnexitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
They contribute to inflammation of the uterus, which soon spreads to the ovaries and tubes. Such cases include diseases of the genitourinary system: inflammation of the bladder, cystitis, urethritis, etc. Adnexitis (salpingoophoritis), simultaneous inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes - Previous surgical interventions, including abortions. They increase the risk of inflammation in the peritoneum, as well as the development of adhesions.
- General decrease in immunity. Against the background of other diseases, it provokes the growth of pathogenic microflora, which could be in the body in a latent form and not cause any concern for a long time.
- Hypothermia, stress. Adnexitis caused by these factors is also associated with a decrease in the body's immune defense. Hypothermia in most cases is the root cause of exacerbation of the chronic course of the disease; the presence of external infection is not necessary for this.
- Uterine spiral. In itself, it is not the cause of acute salpingoophoritis, but it can provoke it at the time of installation or removal.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards. Promotes the entry of pathogenic organisms into the genital tract, causing inflammation. These are, as a rule, staphylococci and streptococci, which contribute to the development of unilateral adnexitis.