Causes of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is transmitted by airborne droplets and contact. The incubation stage lasts from three to ten days. The infection mainly spreads in the autumn and spring, when the body is weakest. The main factors of infection include the following.
- Hypothermia.
- Violation of hygiene rules.
- Contact with sick people.
- Eye injury.
- Swimming in polluted waters.
- Weakened immune function.
Causes of the disease
In most clinical situations, the infection during the formation of adenoviral conjunctivitis enters the visual apparatus from other organs in which the infectious process is already developing (throat, nose, etc.). This suggests that this disease usually develops against the background of inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa.
Pathogenic viruses can enter the visual apparatus from the pharyngeal tonsils and other parts of the respiratory tract if there is inflammation in them. The main route of infection with adenoviruses is airborne. But a contact route of infection cannot be ruled out.
The main factors contributing to the progression of pathology:
- eye injury;
- regular contact with an infected person;
- surgical intervention in the visual apparatus;
- constant hypothermia.
Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis of the eyes
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is characterized by symptoms as follows.
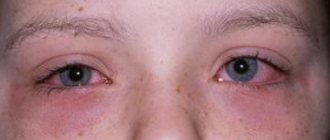
- Swelling and hyperemia of the conjunctiva.
- Burning sensation in the eyes.
- Increased tear production. In some situations, the discharge is purulent in nature.
- Manifestations of films of a specific nature on the mucous membrane. This symptom often occurs in children.
- Formations on the mucous membrane of the follicle of different sizes.
- Pain in the head.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
An important point is to contact a doctor in a timely manner when the first symptoms occur. Adenoviral conjunctivitis in children develops in autumn and winter. In medicine it is usually called keratoconjunctivitis. Infection mainly occurs in schools and preschool institutions, as well as in places where there are large crowds of people. Adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis affects the anterior part of the visual organ. Therefore, curing the disease is quite difficult, since no remedy has yet been invented that directly fights adenoviruses.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis in adults goes away within two weeks. But if you ask yourself how many days it takes for the disease to go away in children, then it all depends on timely treatment. In severe forms of the disease, complications may arise in the form of the development of bacterial or allergic type conjunctivitis with intoxication of the body, dry eye syndrome, keratitis, otitis and tonsillitis.
Treatment and prevention measures
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis must be carried out without fail. Treatment, as well as its duration, depends on the severity of the disease.
Doctors prescribe antiviral therapy:
- In the first week, instillation of deoxyribonuclease is prescribed up to 8 times a day.
- Interferon instillations are done several times a day during the second week of the disease.
- Antiviral ointments for eyelids. Tebrofenovaya, Florenalovaya, Bonaftonovaya or Adimalovaya ointment are suitable.
Antiallergic, anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs are prescribed in combination with antiviral drugs. In order to relieve pain and stinging sensation, antiseptic drops are prescribed.
Important! Doctors do not recommend treating adenoviral conjunctivitis with antibacterial agents.
After the main course of treatment, starting from the third week (and in the case of keratoconjunctivitis, from the 4th week), artificial tear preparations are prescribed, which help remove dryness and restore normal hydration of the mucous membrane. If conjunctivitis cannot be cured without complications, the rehabilitation period is quite long. Antiviral treatment is complemented by magnetophoresis. This is a physiotherapeutic procedure that affects the cornea and removes cloudiness. Without this procedure, several years after treatment, the disease may recur again.
Types of adenoviral conjunctivitis of the eyes
Adenoviral conjunctivitis has three main types. These include the following forms.
- Catarrhal form. It is characterized by local inflammatory processes, redness of the eyes, photophobia, lacrimation and the feeling of a foreign body in the eye. This type of disease goes away quite quickly and without consequences. Symptoms completely disappear after seven days.
- Follicular form. It is characterized by the appearance on the mucous membrane of a large number of bubbles that have different sizes. In appearance, they resemble a transparent capsule. Especially a lot of rashes can be noticed on the transitional fold. Also, the main symptoms are redness of the eyeball and eyelids and the appearance of purulent discharge. Follicular-type conjunctivitis in the first stages is similar to trachoma. But if the diagnosis is made by a doctor, then errors occur only in the rarest cases.
- Filmy form. The disease is diagnosed in twenty percent of all cases. The disease is characterized by the formation of grayish films that are located on the mucous membranes of the eyes. Often they are the thinnest plates that can be easily removed with a cotton swab. Only in certain situations can the films resemble dense deposits that are connected to the inflamed conjunctiva. They are much more difficult to remove, since the mucous membrane is damaged and begins to bleed. The main symptom is considered to be an increase in body temperature, which can last up to ten days. The main complication of this type is the formation of scars.
Diagnosis of the disease
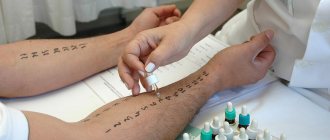
The first step is for the patient to seek help from a doctor. Based on complaints and examination, the doctor may prescribe tests. The most common diagnostic method is a smear from the conjunctiva of the eye and PCR scraping. Only after this is treatment prescribed.
Forms
Clinicians distinguish 3 forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis:
- catarrhal In this case, the inflammatory process is not acute. Symptoms of the pathology are expressed rather poorly. There is slight hyperemia, exudate is released in small quantities. The course is mild and without complications. The duration of disease progression is 7 days;
- follicular. It is characterized by the formation of vesicular eruptions on the surface of the mucosa. Their size may vary;
- filmy form. In this case, thin films form on the surface of the mucosa. They can be easily removed using a sterile cotton swab. With this form, a person’s well-being can greatly deteriorate. The body temperature rises, the head hurts, and weakness is felt throughout the body.
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in adults
Treatment of this disease is lengthy and very difficult. In such a situation, doctors resort to complex therapy. It consists in the use of antiviral drugs, the use of local agents in the form of antibacterial drops and ointments to prevent the addition of another infection. Antihistamines are also prescribed.
To treat adenoviral conjunctivitis, medications that are considered more effective are prescribed. These include the following drugs.
- Albucid. An excellent antimicrobial drug.
- Phloxal. Drops based on ofloxacin, which have an antimicrobial effect.
- Tobrex. An excellent product with antimicrobial properties. Can be prescribed to children from birth.
- Interferon. A drug with antiviral and immunostimulating effects. Available in powder form for preparing a suspension. Can be used in children from birth.
If all treatment rules are followed, the disease in adults goes away completely after two weeks.
Occurrence and course of the disease
The first symptoms of pathological progression appear approximately a week after infection with adenoviruses. The first signs are swelling and profuse lacrimation. At first, the inflammatory process affects only one eye, but after a few days it “moves” to the second eye. With adenoviral conjunctivitis, damage to the cornea can sometimes be observed.
The duration of adenoviral conjunctivitis is no more than one month. Most often, this disease develops in children and even infants, sometimes taking on the character of an epidemic. But adults can also become infected, especially if they do not follow the rules of hygiene and care for sick children (if there are any in the house).
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in children
Adenoviral conjunctivitis in childhood is much more severe than in adults. It is very important to notice the disease in time, because it can cause undesirable consequences. Treatment in children lasts up to four weeks depending on the form.
It is believed that the virus has the ability to camouflage itself in tissue cells. Therefore, in order to defeat it completely, you need to use drops that contain human interferon.
If adenoviral conjunctivitis is mild, then you can do without the use of eye drops. In such a situation, children are prescribed interferons, restorative drugs and immunostimulants. In addition to all this, it is recommended to strictly observe hygiene measures. This type of treatment will allow the child to quickly get back on his feet and recover.
In severe cases of the disease, adenoviral conjunctivitis must be treated with medications that have a wide range of antiviral effects. First, during the first seven, you need to apply eye drops at least eight times a day. After this, it will be enough to carry out up to three procedures per day.
If a complication occurs with strong discharge of pus, then treatment in this case consists of using drops with an antibacterial effect. This will help reduce the chance of infection. An excellent drug is an antihistamine that has vasoconstrictor properties. If the child feels dry eyes, then drops containing artificial tears can be used as a supplement.
Often, mild adenoviral conjunctivitis resolves quickly if all hygiene rules are followed, immunostimulating drugs are used, and antiseptic procedures are performed.
The duration of complex forms is three to four weeks. Often there is no relapse. But it is worth remembering that only a doctor should prescribe treatment, otherwise the child risks developing problems with visual function.
Who is susceptible to conjunctivitis?
The risk group includes children and adults from 20 to 40 years old.
Infection can occur not only through direct contact with a patient and through airborne droplets. Risk factors include hypothermia, visiting public places with large crowds of people, swimming pools, saunas, ARVI, eye injuries or surgery. Most people do not attach importance to viral conjunctivitis, believing that the disease does not cause harm to health. But one thing is known: if the disease is not treated, it will become chronic, which is characterized by the addition of a bacterial infection. In this case, serious complications arise, because not only the mucous membrane is affected, but also all tissues of the eye, and the cornea also becomes inflamed. Visual acuity also decreases.
The severity of complications and the appearance of acute or chronic forms of conjunctivitis depend on the immunity of the adult. The stronger it is, the lower the likelihood of a severe course of the disease.
Preventive measures to prevent adenoviral conjunctivitis of the eyes
To prevent the disease from making itself felt, you should follow several recommendations. This includes the following.
- Regularly wash your hands and face with soap before eating and after going outside.
- In the autumn and winter, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system not only for children, but also for adults. Immunostimulants that contain interferon will help with this. It is also worth taking vitamin complexes as a supplement.
- Take care of a balanced diet so that the body receives vitamins such as A, C, E and group B.
- Children need to walk as often as possible for at least two hours a day.
- During absence, you need to ventilate the room, and carry out quartz treatment in children's institutions.
- Cleaning must be done daily using disinfectants.
- When sick, the patient is advised to comply with bed rest and drink plenty of warm drinks.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis rarely causes complications, but only if the patient seeks help from a doctor in time.
Symptoms when infected with the disease
When affected by this type of conjunctivitis, patients experience severe swelling of the eyelids, tearing, redness and discharge from the conjunctival cavity.
Patients complain of a sensation of a foreign body in the eyelid area. In rare cases, they complain of photophobia, severe itching and burning.
In practice, ophthalmologists note that during an outbreak of such a disease, the patient experiences the following clinical symptoms:
- hyperemia of the eyelids and eyeball;
- formation of new capillaries;
- decreased sensitivity in the cornea;
- formation of erosion on the cornea;
- limited eyelid mobility.
In some patients, the parotid lymph nodes become enlarged and choroidal disease develops. A secondary infection develops in the absence of timely treatment of the disease.
Diagnostics
A diagnosis of an outbreak of infection can be made based on the characteristic clinical picture (acute onset, fever, typical damage to the mucous membrane of the eyeballs, pharyngitis, rhinitis). Isolated cases require laboratory confirmation.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist is required. Early diagnosis can be done using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which will detect viral DNA in material from the conjunctiva. An immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) and a complement fixation reaction (CFR) are suitable for this. Virological, serological, and cytological methods are used less frequently.
It is important to understand that with the adenoviral etiology of the process, a layer of bacterial flora often occurs, so it is necessary to perform a smear on the flora. In the typical film form, it is necessary to take a smear for the causative agent of diphtheria (BL smear) to protect yourself from possible complications due to incorrect diagnosis.