What it is
Candida fungi are one of the components of the natural human microflora. They live on the mucous membranes of the nose, vagina, mouth, intestines and pharynx. Some species are also found on the surface of the skin.
In ordinary life, these microorganisms do not cause a person any discomfort, but when local immunity is weakened, the balance of bacteria is disrupted and opportunistic fungi begin to actively multiply.
Candidiasis of the oral mucosa in adults and children develops frequently, but with timely diagnosis it can be easily treated.
Signs of chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
With this lesion, a very dense plaque appears, and the membranes of the oral cavity swell. Due to the abundance of plaques and nodules in the plaque, the patient is sometimes diagnosed with “lichen planus” or “leukoplakia” (of course, they are wrong).
The plaque affects a small area of the back of the tongue, the affected area resembles rhomboid glossitis.
With hyperplastic candidiasis, plaque appears on the back of the tongue
Palatal lesions occur as papillary hyperplasia. When the fungus is not treated, the mucous membrane becomes covered with difficult-to-remove yellow or grayish films.
Reasons for the development of candidiasis
A person can be a carrier of fungal microflora and not even know it; transmission occurs through physical contact, through household items, food, water, etc. Very often, candidiasis is diagnosed in newborns; children become infected with pathogenic microflora while passing through the birth canal if a woman has thrush in the vagina.
The main provoking factor that gives impetus to the active growth of fungi is considered to be a weakening of local immunity. Damage to the mucous membrane by opportunistic microflora occurs in people with severe hypothermia, hormonal imbalances, vitamin deficiency and human immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Among other causes of candidiasis, experts identify:
- long-term use of antibiotics, immunosuppressants or other drugs that disrupt the balance of natural microflora;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding (associated with changes in hormones);
- damage to the mucosa leads to the proliferation of fungal microflora. Very often, candidiasis occurs in people wearing artificial dentures and braces;
- frequent nervous tension;
- patients with oncology who are undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy;
- the presence of concomitant diseases (dysbacteriosis, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, etc.).
Oral thrush often occurs in people who abuse smoking and drinking alcohol. These products contain substances that disrupt the balance of normal microflora in the oral cavity.
The disease affects women taking oral contraceptives. Against their background, a change in hormone levels occurs, which leads to the activation of opportunistic microorganisms.
A photo of thrush in the mouth can be seen below.
How does the acute form of pseudomembrane candidiasis manifest?
The acute form of this fungal infection often occurs in many infants. This candidiasis is the most common.
For the most part, fungal infections of the mouth are signs of other diseases (this could be cancer, vitamin deficiency, metabolic problems).
Features of symptoms
The disease affects the back of the tongue, palate, cheeks and lips.
The tissue of the oral cavity is hyperemic and overdried. There is a coating in the mouth, the color and consistency of which resembles sour milk. At first it is easy to get rid of this plaque; it reveals a smooth and shiny, but swollen mucous membrane. If candidiasis is already in an advanced stage, the plaque cannot be cleaned off. It looks more like a crust, and the tissue is susceptible to erosion.
Important! Patients experience pain and burning sensations while eating. A clear provocateur of such discomfort is spicy or overheated food.
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of plaque in the mouth
Important! The most important thing is to notice the acute pseudomembrane form of glossitis in time and to distinguish it from desquamative glossitis that affects the back of the tongue.
Fungal stomatitis is often mistaken for leukoplakia or lichen planus. However, then the injured parts are not covered with plaque - hyperkeratosis nodules form on them. It is impossible to get rid of them by simple cleaning.
To differentiate candidiasis from other lesions, laboratory tests are performed.
To distinguish oral candidiasis from other pathologies, diagnosis is necessary
Types of thrush and main symptoms
There are many classifications of candidiasis, let's look at the most basic ones:
- Depending on the degree of manifestation of symptoms, acute and chronic stages are distinguished.
- According to the place of reproduction of the fungus, glossitis, stomatitis, gingivitis, tonsillitis and other types of candidiasis are distinguished.
According to the clinical picture of the course, the following types and symptoms of thrush are distinguished:
- pseudomembranous. It is one of the most common types of the disease and is most often diagnosed in childhood. Fungal microflora is localized on the lips, cheeks, tongue and palate. A characteristic feature is the presence of a white cheesy coating. At the initial stage, it is easy to remove, and as it progresses it acquires a hard consistency. This condition is worsened by the fact that after removing the plaque, erosions of various sizes form on its surface, they bleed and cause severe pain to the patient;
- atrophic. The initial stage is characterized by severe drying of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity, the mucous membrane acquires a red tint. Plaque does not form with this form;
- hypoplastic in the chronic stage. The fungus affects the entire tongue, palate and other mucous membranes in the mouth. The plaque has a very hard consistency and is difficult to separate. As a result, the patient develops capillary hyperplasia over time in the palate, a disease that is difficult to treat. Other symptoms include severe dry mouth, burning sensation and soreness.
If the acute stage of atrophic candidiasis is not treated in a timely manner, it develops into a chronic form. Most often, this pathology occurs in patients using removable orthodontic structures.
The main symptoms include dry mouth, burning, redness and swelling of the mucous membranes. The resulting white plaque is very difficult to remove; erosions or ulcers form under the dentures.
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself in various ways - it all depends on the condition of the patient’s body, the medications he took previously, the person’s age, the state of the immune system and many other factors.
Symptoms of thrush can vary
Important! Fungi can infect the mouth in different ways - they come in different forms that live separate lives or combine with each other and mutate.
Diagnostic methods
You can identify thrush yourself by noticing an unusual white cheesy coating. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor takes a smear from the affected area from the patient and sends it for further study in a bacteriological laboratory.
It is very important to carry out a differential diagnosis that will distinguish candidiasis from other similar diseases (eczema, herpes, seizures, lichen, etc.).
All about candidiasis in the oral cavity in adults
Oral candidiasis is medically called fungal stomatitis.
It occurs in acute and chronic forms, causing frequent relapses. Candida lives in the mucous membrane, in particular in the oral cavity - this is normal. Their concentration is observed in dental cavities affected by caries, pockets formed by periodontitis, and the recesses of the tonsils.
Their number can increase significantly if various pathological conditions arise in the body, leading to the development of candidal stomatitis.
This disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida . These yeast-like microorganisms are part of the normal human microflora. They live in the intestines, vagina, skin, and nasopharynx in 75% of people. And most of them show no signs of illness. Oral candidiasis primarily affects infants . Some children under one year old have had it several times. It is believed that children tolerate candidiasis better , and it is easier to get rid of it at this age.
However, the disease also occurs in adults. According to statistics, 10% of patients over 60 years of age suffer . It especially affects those who wear dentures. Since favorable conditions for their reproduction are created under them. In addition, candidiasis in the mouth appears as a result of a decrease in the body’s defenses; various diseases provoke this condition.
Oral candidiasis is more common in women . But men with bad habits are also susceptible to the disease . Today, candidiasis is much more common than before. This is due to the uncontrolled use of drugs, often unjustified, which leads to an imbalance of microflora and decreased immunity.
This is a single-celled fungus. It has 150 varieties, 20 of which cause human diseases. Candida in the mouth lives on different parts of the mucous membrane, settles on the tonsils, in the canals of damaged teeth, and carious cavities.
Candida belongs to the yeast-like fungi, but their difference from yeast is their lack of benefit to humans. Under favorable conditions, they begin to actively multiply, causing a disease - candidiasis.
Candida prefers an alkaline environment when the pH level is 7.8-8.5 units. It occurs in the oral cavity with excessive consumption of confectionery products and foods consisting of simple carbohydrates . The optimal temperature, which is favorable for their life, is 30-37 degrees.
Candida belongs to the imperfect fungi. The differences are as follows:
- they do not form mycelium, characteristic of mushrooms;
- their spores develop in special bags inside cells;
- under unfavorable conditions, the cell is saved in a dense protective shell - chlamydospore. They tolerate environmental influences well, so they can pass from person to person.
With a decrease in immunity, candida begins to change shape: the cells turn into oval rods and constantly divide. As a result of reproduction, long chains appear - pseudomycelium.
Candida strives to get inside the epithelium covering the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. They begin to develop in it, adversely affecting the tissue. As a result of their vital activity, candida secrete enzymes that break down fats, proteins and carbohydrates found in human cells. This way they destroy the oral mucosa, which causes unpleasant manifestations of candidiasis, such as pain, dryness and burning.
A completely healthy person can be a carrier of Candida, and such people constitute 50% of the population. The human body does not seem to notice fungi. But as soon as the chemical balance is disturbed and immunity decreases, the fungi become more active and begin to multiply intensively, forming colonies. This is how thrush develops.
There are many factors that provoke the development of oral candidiasis:
- weakened immune system, immunodeficiency, lack of immune cells;
- pregnancy - causes a decrease in the body's defenses, changes in hormonal balance, metabolism;
- tuberculosis, HIV, diseases of the digestive system and adrenal glands. Often, candidiasis in the mouth in adults becomes a sign of the development of diabetes mellitus;
- taking drugs that suppress the immune system, these include: corticosteroid drugs and cytostatics;
- long-term use of antibiotics. These medications affect the body's microflora, causing an imbalance of microorganisms. Fungi resistant to antibiotics begin to actively multiply as competitors are destroyed;
- dysbacteriosis and deficiency of vitamins synthesized by bacteria. These are group B, vitamins C and PP;
- bad habits lead to imbalance and reduce the body's defenses;
- radiation therapy - it is carried out if the patient suffers from a malignant tumor;
- oral contraceptives in some cases lead to hormonal imbalance, which causes the activation of fungi;
- trauma to the oral mucosa - microcracks appear as a result of malocclusion or dental damage;
- dentures - wearing them can injure the mucous membrane. Acrylic material often causes allergies, which helps fungi penetrate cells.
Oral candidiasis occurs due to infection from another person. It happens:
- during childbirth. Fungi living in the mother's vagina are passed on to the child;
- during kissing and sexual intercourse;
- when using shared utensils or brushing your teeth with someone else’s brush;
- when infected from animals. Children playing with kittens or puppies are at risk.
Thrush appears when the body is affected by several factors at once. Symptoms of the disease appear depending on the general condition of the body and the stage of development of the disease. Oral candidiasis most often occurs in children and the elderly. Their immune system often suffers from viral and chronic diseases. The disease occurs in two forms:
- acute include: pseudomembranous and atrophic candidiasis;
- to chronic: hyperplastic and atrophic.
These forms appear independently or follow from one another. First, candida invades cells, then begins to multiply in them and release toxins. They irritate the mucous membrane and disrupt the integrity of tissues. The vital activity of candida provokes swelling, redness, and a feeling of dryness . increased sensitivity and pain also appear .
Candida proliferation leads to the formation of pseudomycelium. Their clusters resemble a white cheesy coating that rises above the tissue of the mouth. The plaque contains:
At first, plaque looks like small white grains located on the reddened surface of the oral mucosa. Then the number of candida increases, and the plaque becomes similar to milky films or plaques . As the disease progresses, the affected areas merge with each other.
Plaques also form on the roof of the mouth, gums, tongue and tonsils. The skin of the lips may be affected and white flakes and flakes may also appear.
At an early stage of the disease, plaque is removed without effort . Inflamed skin is visible underneath, sometimes with ulcers. This is the result of the activity of fungi. Microorganisms release substances that destroy nearby cells. As the disease progresses, candida penetrates into the deep layers of the affected tissues .
Burning and itching in the mouth are caused by an allergic reaction and irritation of the membrane. The discomfort becomes stronger when swallowing saliva or eating food, especially sour, hot or spicy.
If candida prefers to settle in the throat, the swallowing process becomes difficult, the patient feels a “lump in the throat.”
The body reacts to the proliferation of fungi and the toxins they produce by raising the temperature .
Mycotic infection, which is caused by microorganisms, manifests itself as small
cracks and redness in the corners of the lips .
Sometimes they develop transparent scales or a white coating that can be easily removed. When the patient opens his mouth, he feels pain. Adults experience a jamming attack when their dentures do not fit properly. This is also confirmed by the drooping of the corners of the lips, which are always covered in saliva. As a result of the systemic influence of microorganisms on the patient, allergies, depletion of the immune system and poisoning of the body with the remnants of their vital activity occur.
Before prescribing oral treatment, the doctor makes a diagnosis. He listens to the patient’s complaints, performs a scraping from the mouth, and sends him for a blood test, which determines the blood sugar level. After studying the tests, the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen. To effectively eliminate oral candidiasis in adults, the doctor begins with the treatment of chronic diseases. The patient needs to get rid of the following diseases:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- leukemia;
- diabetes mellitus
Candidiasis in the mouth is treated by a dentist or periodontist. If the fungi have spread to other organs, treatment is carried out by a mycologist or infectious disease specialist. There are local and general treatment of oral candidiasis.
In general treatment, fungi are destroyed with medications that affect the entire body. They kill them in the mouth and other organs, removing the carrier state. Antimycotic drugs are classified into imidazoles and polyene antibiotics.
The latter include Levorin and Nystatin. They are used 4-6 times a day for two weeks. The tablets need to be dissolved in order for the effect of taking to be as high as possible. Improvement occurs after 5 days. The amount of plaque decreases, erosions are delayed. If these drugs do not have the desired effect, Amphotericin B is administered intravenously. Amphoglucamine tablets can also help. They are taken after meals twice a day for 2 weeks.
Imidazoles include drugs:
Take a course of 1-3 weeks, 50-100 mg per day. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the age of the patient and the severity of the disease.
Antimicrobial and antiparasitic drugs that stop the growth of fungi also help well:
- Fluconazole is effective against candida; it is prescribed 200-400 mg once a day;
- “Diflucan” (capsule form) is taken 50-100 mg once a day, the course of treatment is from 7 to 14 days;
- treatment is carried out with Nizoral tablets, taking 200 mg in a course of 2-3 weeks;
- Decamine caramel is dissolved one or two pieces at a time, the course of treatment lasts 10-14 days.
To strengthen the immune system, B vitamins are prescribed, as well as PP and ascorbic acid. It is also necessary to consume calcium gluconate for a month, which has a general strengthening effect and relieves signs of allergies. Antiallergic drugs also include Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen, and Suprastin.
At the same time, they take iron supplements, they restore its metabolism, disturbed by the activity of candida.
In order for the patient to recover faster, strengthen his immune system and at the same time prevent fungal infection, he is prescribed a vaccine. As an option, Pentoxyl and Methyluracil are used, which help the body resist fungi.
Local treatment is carried out with drugs that act on the mucous membrane, but do not enter the systemic circulation. They stop the proliferation of fungi, relieve symptoms, and restore damaged tissue:
- aniline dyes - brilliant green and methylene blue give the greatest effect;
- for applications - iodine preparations;
- for resorption - “Lizak” or “Lysozyme”;
- “Levorin ointment” or “Nystatin ointment” - for treating lips.
So, in order for the treatment of oral candidiasis to be effective, it is necessary to eliminate diseases that threaten the infection to become chronic. A positive result will appear if the doctor and the patient work together.
Based on materials from zub.guru
Oral candidiasis does not occur as an independent disease. The fungus indicates the development of pathological processes in the human body. The decline of the immune system sets in motion the growth and development of microflora. They increase their population and displace bacteria. Over time, oral candidiasis leads to the development of dysbiosis. Fungi easily digest fast carbohydrates. Therefore, therapy should include taking general and local medications, as well as following a diet.
Oral candidiasis is a disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Fungi represent a conditionally pathogenic microflora. Microorganisms normally do not pose a threat to human health. They begin their development under the influence of some favorable factor.
There are more than 150 species of fungi of the genus Candida. Only 20 of them pose a real health hazard. They settle on the tonsils, in the area between the teeth, gums, on the tongue and in carious tooth cavities. These microorganisms are not only found in the mouth. Fungi inhabit human skin, mucous membranes of the vagina, intestines and nasopharynx.
According to statistics, oral candidiasis most often affects infants . Children tolerate mouth fungus more easily, and the disease occurs with less damage to the body.
Fungi do not manifest themselves in the early stages of development. The disease begins to bother a person after the appearance of visible symptoms. The main route of transmission of microflora is contact.
Methods of infection by fungus:
- touching the carrier;
- through dishes;
- products;
- clothes;
- toys;
- mother's breastfeeding;
- towel;
- contact with dirty water in public baths and similar establishments.
Breasts become infected immediately after birth. Upon contact with the mother's breast, the oral cavity becomes colonized with a fungus. If the child was born with normal immunity, then there will be no problems.
Causes of oral candidiasis:
- Weakening of the immune system. This is the main factor that leads to the development of fungus. The body's defenses weaken under the influence of illness, hypothermia, hormonal imbalances and lack of vitamins. Oral candidiasis is a fairly common occurrence in people suffering from the immunodeficiency virus. With HIV, the immune system becomes defenseless against pathogenic microflora. Therefore, a white coating in the mouth is observed in many AIDS patients.
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics. Bacteria are part of the human microflora. They delay the development of fungi, preventing their population from increasing. Antibacterial drugs affect the state of microflora. Taking such medications should not exceed the prescribed course of treatment. Otherwise, an imbalance of microflora occurs, which contributes to the development of oral candidiasis.
- Dysbacteriosis. With a lack of vitamins B, C and PP, the bacterial population declines. Dysbacteriosis due to vitamin deficiency causes similar damage to the body that occurs with uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- Bad habits. Alcohol affects the general condition of a person. Under the regular influence of alcoholic beverages, a person’s health deteriorates significantly. Tobacco smoke directly affects the tissues of the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat and bronchus. It injures the mucous tissue, leaving behind microcracks. A favorable condition is created for the development of oral candidiasis.
- Mouth injuries. Burns of the mucous membrane or cuts leave behind wounds. These injuries create a local favorable environment for fungi.
- Pregnancy. The disease develops in women due to hormonal imbalances. In this situation, the fungus will develop not only in the mouth, but also on the skin or in the vagina. Fungal diseases of the vagina are called thrush. The problem must be corrected before delivery. Otherwise, the child risks getting a severe infection with candidiasis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Diabetes.
Oral candidiasis is divided into acute and chronic. Pathology has several types, on which the symptoms and treatment of the disease depend.
Types of oral candidiasis:
- Pseudomembrane. Occurs during the acute course of the disease. This is the most popular type of oral candidiasis. Occurs in infants and young children. It has a minimal effect on the body, but if left untreated it leads to a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition. Ulcers form in the oral cavity and become covered with a brown film. It separates poorly and leaves a bleeding wound behind. The child will refuse to eat. His temperature rises and his sleep gets worse. Babies who suck on a pacifier are at greater risk of developing oral thrush than other children.
- Atrophic. It occurs in an acute form. The mucous membrane becomes bright red. The tongue, cheeks and lips are affected. The taste buds of the tongue atrophy. The plaque is absent or weakly expressed.
- Chronic form of atrophic candidiasis. The affected areas become swollen. The person feels pain, itching or burning. Elderly people with dentures are susceptible to the disease. Ulcers and plaque appear on the gums under dentures. Seizures and glossitis are observed. The plaque is gray in color.
- Hyperplastic. A type of chronic candidiasis. There is a large layer of white coating on the tongue. The chronic form tends to remission and re-exacerbation. The patient will complain of burning, pain and dry mouth. The plaque is filled with fibrin, and the film is difficult to separate.
Symptoms of oral candidiasis in children are practically no different from the disease in adults. Due to anatomical features, the oral mucosa in babies is thinner. Therefore, candidiasis occurs more clearly and pronouncedly. The condition of patients worsens as the microflora develops.
Symptoms and signs of oral candidiasis:
- The mucous membrane of the mouth turns red. There is no plaque, but a burning sensation or pain appears.
- After a short period of time, small grains are detected. They occur on the tongue, palate, tonsils and pharyngeal mucosa.
- The grains increase in size and then merge, forming plaque. The candida film is difficult to separate. She leaves behind bleeding wounds. At this time, children stop eating, become capricious and sleep poorly. People develop a fever and the tissues of the throat and mouth become swollen.
- In severe cases, body temperature rises to 39-40 degrees. In adults, the fungus rarely leaves the oral cavity. But the lips of babies quite often become covered with plaque.
- Cracks in the corners of the mouth. The skin around the lips turns red.
- If candidiasis has spread to the pharynx, the person will have difficulty swallowing.
- There is a feeling of a lump in the throat that cannot be swallowed.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary first of all to differentiate oral candidiasis from leukoplakia, stomatitis, lichen ruber, glossitis, herpes and eczema of the lips. To do this, the doctor interviews the patient. An anamnesis is compiled, which includes collecting data about the person’s quality of life, symptoms, complaints, bad habits and the estimated nature of the course of the disease. After this, a preliminary diagnosis is made, which needs to be verified. To confirm the diagnosis, examinations are prescribed:
- serological;
- blood analysis;
- laboratory examination of washes and scrapings;
- cytological diagnostics;
- oral smear for bacteriological culture.
The doctor examines the mouth, skin and nails. In patients, foci of fungal infection are found not only in the mouth, but also in other parts of the body. If treatment is successful, a control test is prescribed. It is carried out using a microscope. Allows you to track trends in changes in the microflora of the mouth.
Treatment of oral candidiasis is divided into local and general therapy. Locally acting drugs are absorbed directly into the mucous membrane. A small part of the active substance reaches the bloodstream. Treatment of the affected area with such means allows you to act directly on the source of the disease.
Local preparations:
- Aniline dyes. To treat fungus in the mouth, use brilliant green, methylene blue and fucorcin solution.
- Applications with iodine.
- Lozenges Lizak and Lysozyme.
- Nystatin in the form of ointments.
- Levomekol.
Rinsing your mouth with solutions will quickly get rid of plaque on the mucous membranes. Disinfectants help heal ulcers and soothe itching and burning.
Mouth rinse solutions for candidiasis:
- sodium tetraborate 2%;
- sodium bicarbonate 2%;
- boric acid 2%;
- saline solution
For a positive effect, you need to rinse your mouth every 2-3 hours . The average course of treatment is 7-14 days.
General medications affect the entire body. The active substance of the drug penetrates the lesion along with the bloodstream. Such medicines are available in the form of tablets and capsules.
Preparations for the treatment of fungi:
- Diflucan. Available in capsules of 50-100 mg. Take 1 piece 1 time per day.
- Fluconazole. A strong antifungal drug. Prescribed 1 tablet per day.
- Decamine caramel. It has a local and general spectrum of action. Prescribed 1-2 pieces per day until the lollipop is completely absorbed.
- Nizoral. Available in tablet form. Use 1 to 2 pieces per day. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
- Nystatin and Levorin. The drugs belong to the group of polyene antibiotics. Doctors recommend dissolving 1 tablet 4-6 times a day.
- Amphotericin B. Available in the form of injection solutions. It is prescribed in severe situations when fungal infection becomes life-threatening.
Vitamins B2, B6, C, PP strengthen the immune system. They promote redox reactions, which makes it easier for the body to get rid of pathogenic microflora.
Diet for oral candidiasis is one of the key stages of therapy. The patient should exclude any foods containing sugar, flour and fatty foods. These nutrients are easily absorbed by fungi. Excluding fast carbohydrates from the diet will reduce the activity of pathogenic microflora.
List of prohibited and permitted foods for candidiasis:
Based on materials from pneumonija.com
Quick page navigation
A small amount of microscopic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida is always present on the mucous membrane of the human oral cavity.
However, a decrease in general or local immunity can provoke the proliferation of these opportunistic organisms, thereby causing an infectious disease - candidiasis (thrush) of the oral cavity (see photo).
Oral candidiasis is a disease most often found in young children (especially in infants) and the elderly (mainly in those who use dentures). The risk group also includes the category of people with severe immunodeficiency or an imbalance of the immune system.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease in an adult:
- Weakened immunity (immunodeficiency);
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the body and hormonal imbalance during pregnancy;
- The presence of serious diseases (for example, diabetes, HIV infection, tuberculosis);
- Functional diseases in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Vitamin deficiency (a consequence of malnutrition);
- The effects of various methods of radiation chemotherapy on the body;
- Alcohol abuse and smoking;
- Drug addiction;
- Injury to the oral cavity;
Provoking factors include long-term use of glucocorticosteroid drugs (drugs with anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, anti-shock and anti-toxic effects), cytostatics (anti-tumor drugs), antibiotics, as well as the use of oral contraceptives, since they can provoke hormonal imbalance.
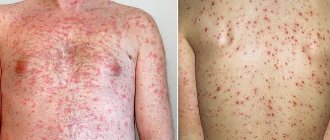
Oral candidiasis photo in adults
Infection in adults can be caused by direct contact with an infected person during kissing and sexual intercourse. The disease can also develop in a newborn baby due to passage through an infected birth canal.
candidiasis in the mouth photo symptoms
Signs of candidiasis of the oral mucosa in adults:
- The presence of redness, swelling, dryness and soreness in the mouth;
- White curd coating on the mucous membrane, which at the initial stage, in the form of small white grains, covers the surface of the cheeks from the inside;
- Milk films or plaques, which in severe forms of the disease even merge with each other, covering large areas of the oral cavity (tongue, tonsils, gums);
- Formation of white scales and flakes on the skin of the lips;
- When removing plaque, pronounced redness and ulcers are clearly visible in the oral cavity;
- Feeling of itching and burning in the mouth (as a manifestation of an allergy to a fungus);
- Feeling of a metallic taste in the mouth and decreased taste sensitivity;
- Multiple bleeding wounds in the mouth;
- Painful sensations when swallowing saliva, eating food;
- Feeling of a so-called “coma” in the throat;
- Increased body temperature;
- The formation of mycotic (yeast) seizures in the corners of the mouth, in which small scaly formations and white plaque are also visualized.
These are common symptoms of Candida fungus, they do not all have to be present at the same time!
Based on the presence of certain symptoms of oral candidiasis, the form of the disease can be determined. This can be acute candidiasis, which in turn is pseudomembranous and atrophic, or chronic candidiasis, which is also divided into two types: hyperplastic and atrophic.
candidiasis of the oral mucosa photo in a man (damage to the lips)
A symptom of pseudomembanosal oral candidiasis in children is the presence of small plaques in the mouth, which, if left untreated, can form erosive “pits.” Signs include extensive plaque and bleeding gums.
The disease is often accompanied by poor appetite or the child’s complete refusal to eat, sleep disturbances, increased body temperature, and the appearance of candidiasis.
Manifestations in adults, which, as a rule, indicate the development of hypovitaminosis, diabetes mellitus, blood diseases or malignant neoplasms:
- damage to the lips, cheeks, back of the tongue and palate;
- the presence of curd plaque in the mouth;
- pain when chewing food.
Signs of atrophic candidiasis in adults include a burning sensation and dryness in the mouth, redness of the mucous membrane and a change in the color of the tongue, which becomes bright crimson.
The main symptoms of chronic hyperplastic oral candidiasis in adults are the presence of dense plaque in the oral cavity and nodules and plaques on the tongue and palate.
The disease may also be accompanied by papillary hyperplasia (formation of shoots), the appearance of a hard-to-remove dense yellow film in the mouth and multiple bleeding erosive formations under the plaque. The patient experiences severe pain in the mouth.
Signs of chronic atrophic oral candidiasis in adults (which usually occurs in people wearing dentures):
- dryness and burning in the mouth;
- wearing a prosthesis is accompanied by pain;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- severe bleeding;
- erosion of the cavity under the prosthesis.
Often, with this form of candidiasis, a plaque that is difficult to remove is formed, which is poorly visualized, and therefore is rarely noticed by the patient.
If you independently detect symptoms of candidiasis in the oral cavity, you must consult a doctor who will diagnose you. The doctor must collect a detailed history, take scrapings from the oral mucosa and conduct a clinical blood test.
Treatment of oral candidiasis in adults should always be accompanied by additional measures to increase immunity and treatment of concomitant diseases (for example, diseased teeth). It is carried out by two methods: general and local.
General therapy consists of prescribing antifungal drugs, for example:
The duration of the course is usually 10 days. At this time, the doctor may prescribe regular resorption of Decamine caramels and the use of a solution of Potassium Iodide 2% to relieve dry mouth.
The local method of treating candidiasis is to use antiseptics that lubricate the oral cavity. This can be a solution of methylene blue or fucorcin, and rinsing is done with chlorhexidine or hexoral.
It is mandatory to take antifungal drugs, for example, Nystatin, Fluconazole, Terbinafine, Clotrimazole, Capofungin and others, which can be either tablets or in the form of a gel, ointment, solution and aerosol.
Systemic therapy method (carried out in cases where previous methods did not give the desired result) includes:
- The use of tablets and injections (since local therapy is ineffective);
- Introduction to the body of B vitamins, nicotinic and ascorbic acid, probiotics and immunomodulators;
- Taking Fluconazole.
Among a wide range of antibiotics with antifungal effects, doctors most often prescribe the drug “Fluconazole” for oral candidiasis of any form, which is associated with its good tolerability and long-term preservation in the blood plasma. This drug can inhibit (suppress) the spread of fungi and prevent the development of relapse of the disease.
There are a large number of traditional methods of treatment, but not all of them have a positive effect. The most effective methods are:
- rinsing with an aqueous solution with calendula or chamomile;
- lubricating the affected areas with juniper tincture;
- rinsing with cranberry, raspberry or carrot juice;
- applications using gauze swabs on which a decoction of oak bark is applied;
- lubricating the cavity with sea buckthorn or St. John's wort oil;
- inclusion of garlic, honey, yogurt or kombucha tincture in the diet.
To prevent relapse of the disease, it is important to adhere to a diet and the most balanced diet possible. To disinfect the oral cavity, you should consume honey and include foods such as fish, buckwheat and eggs in your diet. Carbohydrate-containing vegetables (for example, cabbage and cucumbers) will have a beneficial effect on the body.
Traditional methods of treatment should be agreed upon with the attending physician and used only as an addition to a course of medication!
Preventive measures to prevent the disease include:
- regular visits to the dentist;
- compliance with the rules of oral hygiene;
- stopping smoking and excessive drinking;
- including foods with plenty of protein in your diet;
- consumption of fermented milk products containing beneficial bifidobacteria;
- following the rules for caring for dentures.
In addition, to prevent the development of candidiasis, people with cancer and AIDS are required to be prescribed an antifungal drug (most often Fluconazole).
Why is it necessary to treat candidiasis?
Untreated candidiasis can cause complications, such as:
- bleeding;
- numerous pathogenic perforations (ulcers);
- sepsis;
- infertility;
- infection of a child;
- development of infections in other organs.
Treatment must be approached with particular scrupulousness due to the fact that in 2/3 of cases its advanced form can provoke exacerbations and complications. You should not resort to self-medication even with clinical manifestations. It is better to immediately consult a doctor who will select effective treatments for candidiasis.
Based on materials from zdrav-lab.com
Treatment
Based on the examination results, the doctor determines the form and stage of the disease and selects the appropriate treatment regimen. To treat patients with oral candidiasis, special antifungal drugs are used. The main active component of such drugs is fluconazole.
The patient is also prescribed immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, iron supplements, etc. To reduce the risk of developing an allergic reaction to fluconalzole, doctors prescribe concurrent use of antihistamines.
Other therapeutic measures include:
- regular rinsing of the mouth with solutions based on aniline dyes;
- lubricating the affected areas with iodine or Lugol's solution;
- lozenges that have a bactericidal effect.
In severe forms of candidiasis, treatment involves taking polyene antibiotics. This includes drugs such as Nystatin, Levorin, etc. The average course of therapy is 2 weeks, tablets are taken 3 to 4 times a day.
The important point is that they need to be absorbed in the oral cavity, thus their active effect on the affected areas of the mucous membrane is manifested.
A prerequisite for a positive treatment result is adherence to a strict diet. She excludes from her diet any sweets and products with a high yeast content. It is also not recommended to indulge in spicy or sour foods, which greatly irritate the inflamed mucous membrane.
ethnoscience
Patients often wonder how to cure candidiasis in the mouth without using medications.
There are several popular and effective recipes to combat this disease:
- Rinse with baking soda solution.
- Rinse with decoctions of St. John's wort or sea buckthorn.
- Freshly squeezed carrot juice. It contains a high level of beta-carotene, which suppresses the active proliferation of fungal microflora.
Treatment with folk remedies is advisable to carry out in combination with drug therapy. By itself, it will not bring the desired result, but will only increase the chances of unwanted complications.
Candidiasis in the mouth
This fungal disease is classified as a dysbiotic disorder. The spread of the disease is achieved by the rapid proliferation of Candida fungi, which are always present in the human body. An unfortunate combination of circumstances provokes a pathological effect of these fungi on the body: fungal infections of the mouth, skin, genitals, fungal sepsis and much more occur. Fungal infections in the mouth often occur in children (newborns, infants and young children), as well as in older people. Candida infections are typical for children from 3 to 10 years old or people over 60.
Important! Fungal stomatitis and glossitis are typical for infants or women during menopause.
This problem often occurs in infants
Prevention
The main preventive measures include:
- performing oral hygiene procedures;
- balanced diet;
- regular strengthening of the immune system;
- rejection of bad habits;
- taking probiotics during a course of antibiotic therapy;
- timely appointment with the doctor and completion of the necessary tests.
It is very important not to hesitate to contact a medical facility when the first symptoms appear, otherwise the chances of the disease progressing to the chronic stage increase, and this greatly complicates further treatment.
Conclusion
Oral candidiasis is common in adults and children. The disease is accompanied by the formation of a white cheesy coating in the mouth and other unpleasant symptoms.
For treatment, specific drugs from the antifungal group, regular rinsing, proper diet and lifestyle are used. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, you can get rid of the signs of candidiasis within 10-14 days. Delaying treatment increases the chances of developing complications.
Diagnostic measures
To make a diagnosis of oral candidiasis, you need to analyze the information given by the patient, the symptoms of the disease themselves, the results of laboratory tests - examine scrapings, do a quantitative analysis of fungal infection, and identify the sensitivity of fungi to drugs. During an examination of the oral cavity, the specialist discovers lesions characteristic of the fungus.
Important! If necessary, the patient is examined by a therapist (pediatrician for children), an infectious disease specialist, an allergist, an immunologist, and an endocrinologist.
To make a diagnosis, examination and careful diagnosis are necessary.
An intradermal allergy test is performed for Candida antigen and the presence of antibodies to the fungus. When candidiasis constantly recurs, diabetes must be excluded from the patient's history.
Intradermal allergy test
Diet
Proper nutrition is the basis for successful treatment. Candida fungi are known to thrive in high-carbohydrate environments. Sweet foods and baked goods must be excluded from the patient's diet. At the same time, you should limit your consumption of spicy and acidic foods, which irritate the mucous membranes and interfere with tissue healing.
The diet for oral candidiasis should include vegetables, greens; according to reviews from patients suffering from thrush, carrots have exceptionally beneficial properties.
Exclude from the diet:
- Products containing yeast;
- Confectionery;
- Mushrooms;
- Sauces;
- Carbonated drinks and alcohol.
Allowed to eat:
- cereals;
- vegetables, herbs (special attention should be paid to carrots and garlic);
- dairy products;
- lean fish and lean meats;
- liver;
- baked goods without yeast;
- herbal teas and natural juices;
- berries: cranberries, blueberries and lingonberries;
- nuts, seeds;
- flaxseed, coconut or olive oil;
- unsweetened fruits.
When the treatment is completed, do not rush to eat everything; it is better to gradually expand your diet by 1-2 foods per week. During the first 3-12 months after therapy, it is better to exclude foods high in sugar and vinegar, yeast baked goods, and mushrooms, so as not to provoke relapses.
The right diet will restore the functioning of the immune system and allow the body to quickly cope with the disease.